|
|

Read this chapter before using the Catalyst 2600 in your network. This chapter contains information and instructions that are useful in preparation for using the Catalyst 2600 in your network. This chapter provides the following information:
This section discusses topics you should consider prior to implementing the Catalyst 2600 in your network.
The maximum frame length supported by the Catalyst 2600 is 4540 bytes (including the Frame Control [FC] and the Frame Check Sequence [FCS] characters). Be sure to configure all network software, interconnecting products, workstations, and user applications to send frames no larger than 4540 bytes.
In cut-through mode, the Catalyst 2600 truncates frames larger than 4540 bytes and adds an abort sequence at the end. Typically, if frames larger than 4540 bytes are sent, a network manager will detect the abort sequences from the Catalyst 2600.
In store-and-forward mode, switch ports will drop larger frames and generate a soft error on that port's LAN segment. The Catalyst 2600 provides statistics regarding frames that are too long. For more information, refer to "Viewing Statistics for a Specific Port" in "Managing Your Catalyst 2600."
With source-route switching, your network can contain duplicate MAC addresses. If there are duplicate MAC addresses in your network, they must be separated from the Catalyst 2600 by a source-route bridge. Otherwise, the Catalyst 2600 will learn the MAC address on more than one port and will not be able to accurately forward frames for that address.
If you are using the Catalyst 2600 in an SNMP-managed network, you must configure an initial IP address and the SNMP parameters from the console panels. You can then use either the console panels or an SNMP managing entity to view or change all parameters and management information, except the spanning tree parameters. You can view, but not change, the spanning-tree parameters from an SNMP manager.
The Catalyst 2600 provides five MIBs for use with SNMP-based management systems. There are four standard MIBs, which are defined by RFCs and are included with most SNMP management applications. The fifth is a proprietary MIB created specifically for the Catalyst 2600. The standard MIBs used are:
Each Catalyst 2600 kit has a disk containing these MIBs. If your network is SNMP managed, give this disk to the network management operator so that it can be compiled into the SNMP-based network manager. If you are not currently using an SNMP manager, store the disk for future use.
The Catalyst 2600 contains two Universal Feature Card slots that will accommodate optional, field-installable, Universal Feature Cards (UFCs), which provide additional connections. If you are installing a UFC with your Catalyst 2600, configure the UFC per the instructions shipped with it before you customize your Catalyst 2600.
Prepare a Configuration Parameters worksheet for each Catalyst 2600 you plan to install. The items on the worksheet follow the same order as the fields that appear on the console panels.
Step 1 Make a copy of the Configuration Parameters Worksheet (from the "Worksheets" appendix) for each Catalyst 2600 you will install.
Step 2 Configure the Catalyst 2600 and fill in the worksheet as you read, or fill in the worksheet now and configure the switch later. In either case, it is important to have a completed worksheet on file because it represents the only backup of the Catalyst 2600 configuration data.
The front of the Catalyst 2600 contains an EIA 232 port. This port allows you to establish a serial link connection with the Catalyst 2600. Using this connection, you can access the Catalyst 2600 console panels, which you can use to configure, monitor, and manage the Catalyst 2600.
You can establish either a local or remote connection to the Catalyst 2600. For a local connection, you directly connect a PC, or other DTE, to the EIA 232 port on the Catalyst 2600. For a remote connection, connect a modem to the EIA 232 port then dial in from your remote workstation.
To connect a local terminal to the Catalyst 2600, perform the following steps:
Step 1 Begin running your terminal emulation software on the PC or other DTE to which you will connect the Catalyst 2600.
Step 2 Set the terminal using the parameters listed in Table 4-1.
| Baud rate | 1200, 2400, 4800, 9600, 19,200, 38,400, or 57,600 (9600 is the default) |
| Parity | None |
| Data bits | 8 |
| Stop bits | 1 |
| Handshaking | None |
| Terminal emulation | VT100 |
| Duplex | Full |
| Software flow control (XON/XOFF) | Off |
| Hardware flow control (RTS/CTS) | Off |
| Line wrap | Off |
| Screen scroll | On |
| CR translation | CR |
| Backspace (BS) translation | Destructive |
| Break length (milliseconds) | 350 |
| Enquiry (ENQ) | Off |
| EGA/VGA true underline | Off |
| Terminal width | 890 |
| ANSI 7- or 8-bit commands | 7 |
If you are using the Microsoft Windows terminal emulation, disable the "Use Function, Arrow, and Ctrl Keys for Windows" option, located in the Terminal Preferences menu under Settings.
Step 3 Connect the EIA 232 port on the Catalyst 2600 to your PC or DTE device using a null-modem cable or straight-through cable and null-modem adapter. The Catalyst 2600 has a 9-pin male connector. For pin-out and cable information, refer to the appendix "Cable and Pin Information".
Step 4 Plug in the Catalyst 2600 if you have not already done so, or press the Reset button. The Catalyst 2600 does not have a power switch; the Catalyst 2600 is powered on when you plug in the power cord. The Catalyst 2600 will then perform a series of self-test diagnostics, which last about 4 minutes. (For more information about these diagnostic tests, refer to the section "Resetting the Catalyst 2600 and Running Diagnostic Tests.")
Step 5 When diagnostics are complete, continue with the steps under "Using the Console Panels."
You can monitor the Catalyst 2600 remotely by using a connection established through any Hayes-compatible modem. To connect a modem to the Catalyst 2600, perform the following steps:
Step 1 Set up your modem according to its instructions.
Step 2 Connect the cable from the EIA 232 port on the modem to the EIA 232 port on the Catalyst 2600.
Step 3 Set the modem as follows:
| Echo | Off |
| Result codes | Off |
| Wait for connection | 45 seconds |
| Pause between calls | 6 seconds |
| Drop DTR between calls | Yes |
| Send CR between calls | Yes |
| Auto baud detect | On |
| Send init if CD high | Yes |
| Maximum dial attempts | 999 |
 | Caution Some modems use slightly different names for the options. It is important that your modem be configured correctly. The settings shown in bold are particularly important. If your modem is not configured correctly, the connection may cause the Catalyst 2600 to reset. |
Step 4 Begin running your terminal emulation software on the PC or other DTE to which you will be connecting the Catalyst 2600.
Step 5 Set the terminal using the emulation parameters listed in Table 4-1.
Step 6 Dial in to the Catalyst 2600 modem from your remote site.
Step 7 Continue with "Using the Console Panels."
There are three types of communications problems that you might encounter: no communication, corrupted communication, and dropped characters. This section suggests steps to resolve such problems. In some cases, you are instructed to alter the configuration of the connection at the terminal or at the Catalyst 2600. For information about altering the configuration of your terminal emulator, refer to the documentation that accompanied your emulation program. For information about altering the configuration of the connection at the Catalyst 2600, refer to the section "Customizing the Console Session."
If no communication is established:
Step 1 Check the cables and physical connections. Ensure that you are using the proper cable and adapter.
Step 2 Check the handshaking configuration at the terminal and the Catalyst 2600. Handshaking at the Catalyst 2600 is controlled by the Hardware Flow Control field on the Serial Link Configuration panel. Refer to the section "Customizing the Serial Link" for more information.
 | Caution Hardware handshaking must be turned on at the Catalyst 2600 and at the terminal. You must also be using a 7-wire or 9-wire cable to the terminal. If hardware handshaking is off and you are using a 3-wire cable, a catastrophic failure of the Catalyst 2600 can occur. |
Step 3 If the Catalyst 2600 has just been installed and is not yet in use, reset the Catalyst 2600. Resetting the Catalyst 2600 while it is in use will disrupt your network.
Step 4 If the problem continues, contact the Cisco Technical Assistance Center (TAC).
If communication is established but the data displayed is corrupted:
Step 1 Ensure that the baud rate set at the Catalyst 2600 and at the terminal match.
Step 2 Verify the configuration of the terminal emulation, specifically:
Step 3 If the Catalyst 2600 has just been installed and is not yet in use, reset the Catalyst 2600.
 | Caution Resetting the Catalyst 2600 while it is in use will disrupt your network. |
Step 4 If the problem continues, contact the Cisco Technical Assistance Center (TAC).
If communication is established but some of the characters appear to be dropped or lost:
Step 1 Reduce the baud rate configured at the Catalyst 2600. We suggest using a baud rate of 9600.
Step 2 Enable the software handshaking feature. Handshaking at the Catalyst 2600 is controlled by the Software Flow Control field on the Serial Link Configuration panel. Refer to the section "Customizing the Serial Link" for more information.
 | Caution Hardware handshaking must be turned on at the Catalyst 2600 and at the terminal. You must also be using a 7-wire or 9-wire cable to the terminal. If hardware handshaking is off and you are using a 3-wire cable, a catastrophic failure of the Catalyst 2600 can occur. |
Step 3 If the problem continues, contact the Cisco Technical Assistance Center (TAC).
As an alternative to a serial link connection, you can use a Telnet session to access the Catalyst 2600 console panels. Using a Telnet session to configure, monitor, and manage the Catalyst 2600 can be more convenient. There are some limitations, however, that you might encounter if using a Telnet session to access the console panels. These limitations are also discussed in this section.
To establish a Telnet session to the Catalyst 2600:
Step 1 On the IP Configuration panel, the IP State must be set to "BootP When Needed" or "BootP Always."
Step 2 Configure your Telnet client to use a VT100/VT220 compatible setup.
Step 3 Telnet to the Catalyst 2600 using its assigned IP address. For information about assigning an IP address to the Catalyst 2600, see "Configuring IP Information" in "Configuring the Catalyst 2600."
Step 4 Continue the Telnet session with "Using the Console Panels."
To terminate the Telnet session, press Ctrl-B, or use the method provided by the Telnet application.
If you experience difficulty opening a Telnet session with the Catalyst 2600, verify the settings for your Telnet client. Ensure that the terminal type is set to VT100, VT102, or VT220.
If you choose to use a Telnet session to access the console panels of the Catalyst 2600, you should be aware of the following limitations:
If you attempt to access a console panel that is already accessed by another telnet or serial link session, "Console is currently in use" is displayed.
If you are using Telnet to access the console panels, be aware that:
A Telnet session can be terminated involuntarily from the console or as a result of certain configuration changes.
When the console is idle and Telnet is active, a user at the console can terminate the Telnet session without warning (refer to the section "Customizing and Managing the Telnet Sessions"). When the Telnet sessions ends, the Telnet session panel displays the message: "Your session has been terminated due to system maintenance work."
The Telnet session also ends if a user changes any of the following:
After you have established a connection to the Catalyst 2600 via either a serial link or a Telnet session, the Copyright Panel (Figure 4-1) is displayed.
To access the console panels:
Step 1 Type the password, if one has been configured. The default is that no password is set.
Step 2 Press ENTER to advance to the Main Menu (Figure 4-2).
Step 3 Use your cursor to move to the item of your choice and press ENTER.
From this menu you can:
As you move through the console panels, follow these guidelines:
The panels associated with each Main Menu selection are described in the following chapters:
To customize your console session, select Configuration>Console Configuration. The Console Configuration panel (Figure 4-3) is displayed.
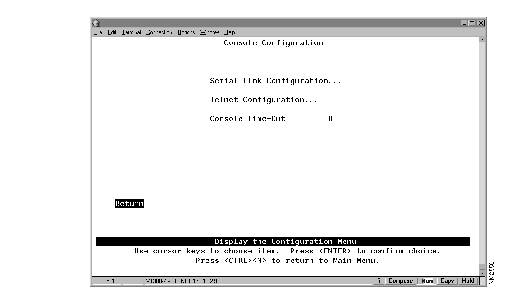
The following information is displayed on this panel:
| To | Select | Then |
|---|---|---|
| Change the console time-out | Console Time-Out | Specify the new value. |
| Specify parameters for a console session via a serial link | Serial Link Configuration | Refer to "Customizing the Serial Link." |
| Specify parameters for a console session via Telnet | Telnet Configuration | Refer to "Customizing and Managing the Telnet Sessions." |
| Save your changes | Return |
To view and change the parameters for a serial link console session, select Serial link Configuration on the Console Configuration panel. The Serial Link Configuration panel is displayed.
The following information is displayed on this panel:
| To | Select | Then |
|---|---|---|
| Change the current settings... | The appropriate parameter... | Specify the new value. |
| Save your changes... | Return |
To view and change the parameters for a Telnet console session, select Telnet Configuration on the Console Configuration panel. The Telnet Configuration panel (Figure 4-4) is displayed.
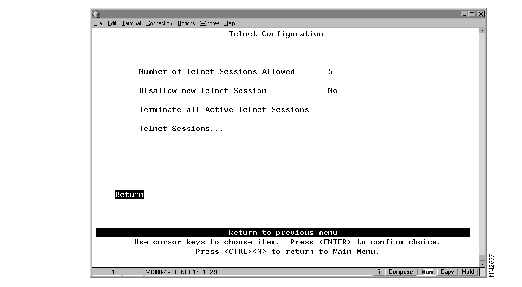
The following information is displayed on this panel:
| To | Select | Then |
|---|---|---|
| Change the current settings... | The appropriate parameter... | Specify the new value. |
| Stop all active Telnet sessions... | Terminate All Active Telnet Sessions | |
| Display information about a specific Telnet session... | Telnet Sessions | Refer to "Managing Individual Telnet Sessions." |
| Save your changes... | Return |
To display information about or close any active Telnet session, select Telnet Sessions from the Telnet Configuration panel. The Telnet Sessions panel (Figure 4-5) is displayed.
The following information is displayed on this panel:
| To | Select | Then |
|---|---|---|
| Stop a specific Telnet session... | Close_Session | Specify the index number of the session to close |
| Save your changes... | Return |
|
|