|
|

The MGX 8260 Media Gateway notifies maintenance or operations personnel of equipment alarms using the following features and components:
This chapter explains how to monitor alarms from the command line interface, and set up email and trap notifications.
To monitor alarms, you perform the following tasks:
For more information on front panel indicators, see the "Front Panel Controls and Indicators" section.
Shelf alarms provide information on environmental, clock, and software operation. When checking alarms, start with commands that list summary information. Then use commands that provide details about the event or condition interest.
Step 1 To view shelf alarms, enter the lsalms command.
Step 2 Interpret the listing as follows:
=========================================================================
Shelf Alarms (lsalms)
=========================================================================
Shelf Card Error : false
Shelf Software Error : false
Shelf Integrated Alarm : major
Slot 1 : Clear
Slot 2 : Major
Slot 3 : Clear
Slot 4 : Clear
Slot 5 : Clear
Slot 6 : Major
Slot 7 : Clear
Slot 8 : Clear
Slot 9 : Clear
Slot 10 : Clear
Slot 11 : Major
Slot 12 : Clear
Slot 13 : Clear
Slot 14 : Clear
Slot 15 : Clear
Slot 16 : Clear
Card : Major
Chassis Temperature : Clear
Voltage : Clear
Fan : Clear
Shelf Alarm History : major
| Displayed Information | Description |
|---|---|
Shelf Card Error | Shelf card error indication:
|
Shelf Software Error | Shelf software error indication:
|
Shelf Integrated Alarm | The shelf integrated alarm indicates the combined alarm condition for all shelf, card, line, and EMM alarms. Valid states:
|
Shelf Slot Alarm (Slot 1-16) | The slot integrated alarm indicates the combined alarm condition for the specified card and its associated lines and EMM alarms. Valid states:
|
Card | The card alarm indication:
|
Chassis Temperature | The chassis temperature alarm indication:
|
Voltage | The chassis voltage alarm indication:
|
Fan | The fan speed alarm indication:
|
Shelf Alarm History | The chassis alarm history indication:
|
Step 3 Clear active alarms as described in the "Clearing Alarms" section.
Card alarms provide information on card operation and events.
To view card alarms, follow these steps:
Step 1 List information for a card using the lscd command, and specifying the slot location of the card.
The system displays the card information.
=======================================================================
Physical Card Entry (lscd)
=======================================================================
Physical Card Number : 11
Logical Card Number : 11
Front Card Type : bsc
Back Card Type : dmcBsc6T3
Daughter Card 1 Type : bim4T3E3
Daughter Card 2 Type : *
Card State : active
Card Service : 0
Hardware Revision : 1
Firmware Revision : BSC_B_r01.01.b1
Software Revision : BSC_r01.01.b1
Front Card Serial # : bsc-093
Back Card Serial # : t3e3-141
Fab Version :
Failure Reason : failResonNone
Reset Reason : watchDogReset
Mismatch Reason : noMismatch
Integrated line alarm state : Clear
Line performance alarm state : Clear
EMM temperature alarm state : Clear
EMM voltage alarm state : Clear
SW error alarm state : Clear
Component failure alarm state : Clear
ATM Queue Profile # : 1
RAM Backup : disabled
Interface Mode : bkcd led
Interface Mode : bkcd
Step 2 Check the alarm fields for alarm indications. The alarm types vary somewhat by card type.
Step 3 Clear any active alarms as described in the "Clearing Alarms" section.
This section describes viewing DS1 alarm and line status, and setting and viewing alarm thresholds.
To view DS1/E1 alarms, follow these steps:
Step 1 List alarm information using the lsds1ln command, specifying the slot and line number, delimited by a period, of the line.
The system displays the following DS1 information:
=======================================================================
DS1 Line Entry (lsds1ln)
=======================================================================
DS1 Line : 16.1
E1/T1 Line Type : t1
Related DS3 Line (BSC only) : 501
Line Type : dsx1ESF
Line Coding : dsx1B8ZS
Send Code : dsx1SendNoCode
Line Signal Mode : none
Line Signal Bits : 1
Time Elapsed in Interval : 439
Line Valid Intervals : 0
Line Idle Code : 127
Line Loopback Config : dsx1NoLoop
Transmit Clock Source : localTiming
Circuit Identifier : PM4388 TOCTL Rev.0x1
IPDC Echo Cancel : na
Alarm : Major
Far end LOF (Yellow Alarm) : No
Near end sending LOF Indication : Yes
Far end sending AIS : No
Near end sending AIS : No
Near end LOF (Red Alarm) : Yes
Near end Loss Of Signal : No
Near end is looped : No
E1 TS16 AIS : No
Far End Sending TS16 LOMF : No
Near End Sending TS16 LOMF : No
Near End detects a test code : No
Far End sending Remote Multiframe Alarm Indication : No
Near End Sending Remote Multiframe Alarm Indication : No
Far End sending Loss of CRC Multiframe : No
Other Failure : No
LED Status : Solid RED
Line Status : UP
Step 2 Check the alarm fields for alarm indications. The alarm types vary somewhat by card and line type.
Step 3 Clear any active alarms as described in the "Clearing Alarms" section.
To view DS1 alarm thresholds, enter the lsds1alm command, specifying the slot and line number, delimited by a period, of the line. The system displays the alarm threshold list:
=======================================================================
DS1 Line Alarm Thresholds (lsds1alm)
=======================================================================
DS1 Line : 16.1
Red Severity : major
RAI Severity : minor
Perf Alarm Severity : minor
LCV 15 Min Threshold: 14
LCV 24 Hr Threshold: 134
LES 15 Min Threshold: 12
LES 24 Hr Threshold: 121
LSES 15 Min Threshold: 10
LSES 24 Hr Threshold: 100
PCV 15 Min Threshold: 35
PCV 24 Hr Threshold: 50
PES 15 Min Threshold: 35
PES 24 Hr Threshold: 50
PSES 15 Min Threshold: 35
PSES 24 Hr Threshold: 50
SEFS 15 Min Threshold: 2
SEFS 24 Hr Threshold: 17
PSAS 15 Min Threshold: 2
PSAS 24 Hr Threshold: 17
UAS 15 Min Threshold: 10
UAS 24 Hr Threshold: 10
BES 15 Min Threshold: 35
BES 24 Hr Threshold: 50
PCSS 15 Min Threshold: 35
PCSS 24 Hr Threshold: 50
| Displayed Information | Description |
|---|---|
DS1 Line | The slot and line number of the DS1 line |
Red Severity | Severity of near end Loss Of Frame |
RAI Severity | Severity of Remote Alarm Indication |
Performance Alarm Severity | Severity of any performance alarms |
Threshold counters (Table 6-1) | The thresholds for line errors that invoke a performance alarm. |
Refer to the following table for a list of threshold counters and default values:
| Threshold | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|
LCV 15 | 15 minute line code violations | 14 |
LCV 24 | 24 hour line code violations | 134 |
LES 15 | 15 minute line errored seconds | 12 |
LES 24 | 24 hour line errored seconds | 121 |
LSES 15 | 15 minute severely errored seconds | 10 |
LSES 24 | 24 hour severely errored seconds | 100 |
PCV 15 | 15 minute path coding violations | 35 |
PCV 24 | 24 hour path coding violations | 50 |
PES 15 | 15 minute path errored seconds | 35 |
PES 24 | 24 minute path errored seconds | 50 |
PSES 15 | 15 minute path severely errored seconds | 35 |
PSES 24 | 24 hour path severely errored seconds | 50 |
SEFS 15 | 15 minute severely errored framing seconds | 2 |
SEFS 24 | 24 hour severely errored framing seconds | 17 |
PSAS 15 | 15 minute alarm indication signal seconds | 2 |
PSAS 24 | 24 hour alarm indication signal seconds | 17 |
UAS 15 | 15 minute unavailable seconds | 10 |
UAS 24 | 24 hour unavailable seconds | 10 |
BES 15 | 15 minute bursty errored seconds | 35 |
BES 24 | 24 hour bursty errored seconds | 50 |
PCSS 15 | 15 minute path controlled slip seconds | 35 |
PCSS 24 | 24 hour path controlled slip seconds | 50 |
This command changes the configuration settings for alarm severity, integration period, and thresholds for various error conditions, such as LCV, LES, and LSES. The performance alarm is set if the line errors exceed any of the threshold counts set by this command.
To change alarm threshold values, enter the chds1alm command as described in the "chds1alm" section.
This section describes the procedures for viewing E1 alarm and line status, and setting and viewing alarm thresholds.
To view E1 alarms, follow these steps:
Step 1 List alarm information using the lse1alrm command, specifying the slot and line number, delimited by a period, of the line.
The system displays the following line information:
=======================================================================
E1 Line Alarms (lse1alrm)
=======================================================================
E1 Line : 3.1
Receving RAI : No
Transmitting RAI : No
Receiving AIS : No
Transmitting AIS : No
Receiving OOF : No
Receiving OOMF : No
Receiving LOS : No
Near End Local Loopback : No
Near End Remote Loopback : No
Near End Remote Payload Loopback : No
BERT in effect : No
Far End Remote Loopback : No
Detected Near End Remote Loopback: No
Receiving RMAI : No
Transmitting RMAI : No
Receiving TS16 Alarm Indication : No
Step 2 Clear any alarms using the procedures in the "Clearing Alarms" section.
To view individual E1 performance alarms, follow these steps:
Step 1 List 15-minute alarm information using the lse1perf15 command, specifying the slot and line number, delimited by a period, of the line.
The system displays the following line information:
=======================================================================
E1 15 min Performance Alarms (lse1perf15)
=======================================================================
E1 Line : 3.1
LCV 15 minutes threshold exceeded: No
LES 15 minutes threshold exceeded: No
PCV 15 minutes threshold exceeded: No
ES 15 minutes threshold exceeded: No
SES 15 minutes threshold exceeded: No
CSS 15 minutes threshold exceeded: No
BES 15 minutes threshold exceeded: No
UAS 15 minutes threshold exceeded: No
ESR 15 minutes threshold exceeded: No
SESR 15 minutes threshold exceeded: No
FEESR 15 minutes threshold exceeded: No
FESESR 15 minutes threshold exceeded: No
FEBEESR 15 minutes threshold exceeded: No
FEBESESR 15 minutes threshold exceeded: No
CRCESR 15 minutes threshold exceeded: No
CRCSESR 15 minutes threshold exceeded: No
Step 2 Check the alarm fields for alarm indications.
Step 3 Clear any alarms using the procedure in the "Clearing Alarms" section.
Step 4 List the 24-hour alarm information using the lse1perf24 command, specifying the slot and line number, delimited by a period, of the line.
The system displays the following line information:
=======================================================================
E1 24 hour Performance Alarms (lse1perf24)
=======================================================================
E1 Line : 3.1
LCV 24 Hour threshold exceeded: No
LES 24 Hour threshold exceeded: No
PCV 24 Hour threshold exceeded: No
ES 24 Hour threshold exceeded: No
SES 24 Hour threshold exceeded: No
CSS 24 Hour threshold exceeded: No
BES 24 Hour threshold exceeded: No
UAS 24 Hour threshold exceeded: No
ESR 24 Hour threshold exceeded: No
SESR 24 Hour threshold exceeded: No
FEESR 24 Hour threshold exceeded: No
FESESR 24 Hour threshold exceeded: No
FEBEESR 24 Hour threshold exceeded: No
FEBESESR 24 Hour threshold exceeded: No
CRCESR 24 Hour threshold exceeded: No
CRCSESR 24 Hour threshold exceeded: No
Step 5 Check the alarm fields for alarm indications.
Step 6 Clear any alarms using the procedure in the "Clearing Alarms" section.
To view E1 performance alarm thresholds, enter the lse1alm command, specifying the slot and line number, delimited by a period, of the line. The system displays the alarm thresholds:
E1 Line Alarm Thresholds (lse1alm)
=======================================================================
E1 Line : 3.1
Red Severity : major
RAI Severity : minor
RMAI Severity : minor
T16 Severity : minor
Perf Alarm Severity : minor
LCV 15 Min Threshold : 14
LCV 24 Hr Threshold : 134
LES 15 Min Threshold : 12
LES 24 Hr Threshold : 121
UAS 15 Min Threshold : 10
UAS 24 Hr Threshold : 10
FE ESR 15 Min Threshold : 800
FE ESR 24 Hr Threshold : 800
FE SESR 15 Min Threshold : 20
FE SESR 24 Hr Threshold : 20
FEBE ESR 15 Min Threshold : 800
FEBE ESR 24 Hr Threshold : 800
FEBE SESR 15 Min Threshold: 20
FEBE SESR 24 Hr Threshold : 20
CRC ESR 15 Min Threshold : 800
CRC ESR 24 Hr Threshold : 800
CRC SESR 15 Min Threshold : 20
CRC SESR 24 Hr Threshold : 20
ES ESR 15 Min Threshold : 800
ES ESR 24 Hr Threshold : 800
SES ESR 15 Min Threshold : 20
SES ESR 24 Hr Threshold : 20
ES 15 Min Threshold : 35
ES 24 Hr Threshold : 50
SES 15 Min Threshold : 35
SES 24 Hr Threshold : 50
BE 15 Min Threshold : 35
BE 24 Hr Threshold : 50
PCV 15 Min Threshold : 35
PCV 24 Hr Threshold : 50
CSS 15 Min Threshold : 35
CSS 24 Hr Threshold : 50
| Displayed Information | Description |
|---|---|
DS1 Line | The slot and line number of the DS1 line |
Red Severity | Severity of near end Loss Of Frame |
RAI Severity | Severity of Remote Alarm Indication |
RMAI Severity | Severity of RMAI |
Performance Alarm Severity | Severity of any performance alarms |
Threshold counters (Table 6-2) | The thresholds for line errors that invoke a performance alarm. |
Refer to the following table for a list of threshold counters:
| Threshold | Description | Default1 |
|---|---|---|
LCV 15 | 15 minute line code violations | 14 |
LCV 24 | 24 hour line code violations | 134 |
LES 15 | 15 minute line errored seconds | 12 |
LES 24 | 24 hour line errored seconds | 121 |
UAS 15 | 15 minute unavailable seconds | 10 |
UAS 24 | 24 hour unavailable seconds | 10 |
FE ESR 15 | 15 minute errored second ratio caused by frame errors | 800 |
FE ESR 24 | 24 hour errored second ratio caused by frame errors | 800 |
FE SESR 15 | 15 minute severely errored second ratio caused by frame errors | 20 |
FE SESR 24 | 24 hour severely errored second ratio caused by frame errors | 20 |
FEBE ESR 15 | 15 minute far end block error resulting from ESR | 800 |
FEBE ESR 24 | 24 hour far end block error resulting from ESR | 800 |
FEBE SESR 15 | 15 minute far end block error resulting from SESR | 20 |
FEBE SESR 24 | 24 hour far end block error resulting from SESR | 20 |
CRC ESR 15 | 15 minute errored second ratio caused by CRC errors | 800 |
CRC ESR 24 | 24 hour errored second ratio caused by CRC errors | 800 |
CRC SESR 15 | 15 minute severely errored second ratio caused by CRC errors | 20 |
CRC SESR 24 | 24 hour severely errored second ratio caused by CRC errors | 20 |
ESR 15 | 15 minute errored second ratio caused by errored seconds | 800 |
ESR 24 | 24 hour errored second ratio caused by errored seconds | 800 |
SESR 15 | 15 minute severely errored second ratio caused by severely errored seconds | 20 |
SESR 24 | 24 hour severely errored second ratio caused by severely errored seconds | 20 |
ES 15 | 15 minute errored seconds | 35 |
ES 24 | 24 hour errored seconds | 50 |
SES 15 | 15 minute severely errored seconds | 35 |
SES 24 | 24 hour severely errored seconds | 50 |
BE 15 | 15 minute burst errors | 35 |
BE 24 | 24 hour burst errors | 50 |
PCV 15 | 15 minute path coding violations | 35 |
PCV 24 | 24 hour path coding violations | 50 |
CSS 15 | 15 minute controlled slip seconds | 35 |
CSS 24 | 24 hour controlled slip seconds | 50 |
| 1For ESR thresholds, the value shown equals 1000 time the actual ratio. |
These commands changes the thresholds for various error conditions, such as LCV, LES, and LSES. The performance alarm is set if the line errors exceed any of the threshold counts set by this command.
To change performance alarm threshold values, enter the che1alm15 or che1alm24 command.
To change alarm severity threshold values, enter the che1almsev command.
This section describes viewing DS3 alarm and line status, and setting and viewing alarm thresholds.
To view DS3 alarms, follow these steps:
Step 1 List alarm information using the lsds3ln command, specifying the slot and line number, delimited by a period, of the DS3 line.
The system displays the following DS3 information:
=======================================================================
DS3 Line Entry (lsds3ln)
=======================================================================
DS3 Line : 11.501
Line Type : dsx3M23
Line Coding : dsx3B3ZS
Send Code : dsx3SendNoCode
Line Status : 464
Time Elapsed : 559
Valid Intervals : 0
Cable Length : 1
Transmit Clock Source : localTiming
Circuit Identifier : 0
Alarm : Yes
Rcv RAI Failure : No
Xmit RAI Failure : Yes
Rcv AIS : No
Transmit AIS : No
Loss of Frame : Yes
Loss of Signal : Yes
Loopback State : No
Rcv Test Code : No
Other Failure : No
LED Status : Solid RED
Step 2 Check the alarm fields for alarm indications. The alarm types vary somewhat by card type.
Step 3 Clear any active alarms as described in the "Clearing Alarms" section.
To view DS3 alarm thresholds, enter the lsds3alm command, specifying the The slot and line number, delimited by a period, of the DS3 line.
The system displays the alarm threshold list:
=======================================================================
DS3 Line Alarm Thresholds (lsds3alm)
=======================================================================
DS3 Line : 11.501
Red Severity : major
RAI Severity : minor
Perf Alarm Severity : minor
NE Alarm UpCount : 6
NE Alarm DownCount : 1
NE Alarm Threshold : 14
LCV 15 Min Threshold: 14
LCV 24 Hr Threshold : 134
LES 15 Min Threshold: 12
LES 24 Hr Threshold : 121
PCV 15 Min Threshold : 10
PCV 24 Hr Threshold : 10
PES 15 Min Threshold : 10
PES 24 Hr Threshold : 10
PSES 15 Min Threshold: 10
PSES 24 Hr Threshold : 10
SEFS 15 Min Threshold: 2
SEFS 24 Hr Threshold : 17
AIS 15 Min Threshold : 10
AIS 24 Hr Threshold : 10
UAS 15 Min Threshold: 10
UAS 24 Hr Threshold : 10
CCV 15 Min Threshold: 10
CCV 24 Hr Threshold : 10
CES 15 Min Threshold: 10
CES 24 Hr Threshold : 10
CSES 15 Min Threshold: 10
CSES 24 Hr Threshold : 10
| Displayed Information | Description |
|---|---|
DS3 Line | The slot and line number of the DS3 line. |
Red Severity | The near end Loss Of Frame indication severity. |
RAI Severity | The Remote Alarm Indication severity. |
Performance Alarm Severity | The performance alarm severity. |
Performance Alarm Threshold | The performance alarm indication. The performance alarm is set if any of the thresholds is exceeded (see Table 6-3). |
NE Alarm UpCount | The up counter value for NE alarms. |
NE Alarm Down Count | The down counter value for NE alarms. |
NE Alarm Threshold | The threshold for NE alarm indication. |
| Threshold | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|
LCV 15 | 15 minute line code violations | 14 |
LCV 24 | 24 hour line code violations | 134 |
LES 15 | 15 minute line errored seconds | 12 |
LES 24 | 24 hour line errored seconds | 121 |
PVC 15 | 15 minute P-bit coding violations | 10 |
PVC 24 | 24 hour P-bit coding violations | 10 |
PES 15 | 15 minute P-bit errored seconds | 10 |
PES 24 | 24 hour P-bit errored seconds | 10 |
PSES 15 | 15 minute P-bit severely errored seconds | 10 |
PSES 24 | 24 hour P-bit severely errored seconds | 10 |
SEFS 15 | 15 minute severely errored framing seconds | 2 |
SEFS 24 | 24 hour severely errored framing seconds | 17 |
AISS 15 | 15 minute alarm indication signal seconds | 10 |
AISS 24 | 24 hour alarm indication signal seconds | 10 |
UAS 15 | 15 minute unavailable seconds | 10 |
UAS 24 | 24 hour unavailable seconds | 10 |
CCV 15 | 15 minute C-bit coding violations | 10 |
CCV 24 | 24 hour C-bit coding violations | 10 |
CES 15 | 15 minute C-bit errored seconds | 10 |
CES 24 | 24 hour C-bit errored seconds | 10 |
CSES 15 | 15 minute C-bit severely errored seconds | 10 |
CSES 24 | 24 hour C-bit severely errored seconds | 10 |
The chds3alm command changes the configuration settings for alarm severity, integration period, and thresholds for various error conditions, such as LCV, LES, and LSES. The performance alarm is set if the DS3 errors exceed any of the threshold counts set by this command. To change alarm threshold values, enter the chds3alm command as described in the "chds3alm" section.
Fast Ethernet lines raise an alarm when an active line goes down, and invoke informational events for line configuration changes.
To view the information for configured Fast Ethernet lines, enter the lsethlns command. The system lists summary information for all Fast Ethernet lines:
=======================================================================
Ether Lines (lsethlns)
=======================================================================
Line IP Address Subnet Mask Status Gateway Addr
====== =============== =============== ================ ===============
9.1 12.18.6.12 255.255.255.0 active 12.18.6.1
9.2 12.18.7.11 255.255.255.0 inactive 12.18.7.1
| Displayed Information | Description |
|---|---|
Line | The slot and line number for the Fast Ethernet line |
IP Address | The IP address for the Fast Ethernet line |
Subnet Mask | The IP address mask for the Fast Ethernet line |
Status | The operational status for the line, as follows:
|
Gateway Addr | The primary IP gateway for this line |
This section describes viewing OC-3 alarm and line status, and setting and viewing alarm thresholds.
To view OC-3 alarm severity, follow these steps:
Step 1 List alarm information using the lssonetalms command.
The system displays the following alarm information:
=======================================================================
List alarm Severity for all SONET lines (lssonetalms)
=======================================================================
Slot.Line Red Severity Yellow Severity Perf Alarm Severity
========= ================ ================ =================
9.1 major minor minor
9.2 major minor minor
Step 2 Clear any active alarms as described in the "Clearing Alarms" section.
To view OC-3 alarms, follow these steps:
Step 1 List alarm information using the lssonetln command.
The system lists information for the OC-3 line:
=======================================================================
Sonet Line Entry (lssonetln)
=======================================================================
Sonet Line : 9.1
Medium Type : sonet
Time Elapsed in Interval : 69174
Line Valid Intervals : 76
Line Coding : sonetMediumNRZ
Line Type : sonetMultiMode
Circuit Identifier : PMC-PM5351-S/UNI-TETRA ver.0x02
Admin Status : up
Line Status(1) : 5402a
Line Status(2) : 10
Interface Type : oc3
Frame Type : sts3c
Loopback State : sonetNoLoop
HCS masking : disable
Payload Scrambling : enable
Frame Scrambling : enable
Transmit Clock Source : localTiming
Support Path ERDI : disable
Step 2 Interpret the Line Status as a bitmap with the following indicators:
Step 3 Check the alarm fields for alarm indications. The alarm types vary somewhat by card type.
To view OC-3 alarm thresholds, enter the lssonetalm command, specifying the slot and line number, delimited by a period, of the OC-3 line.
The system displays the alarm thresholds:
=======================================================================
Sonet Line Alarm Thresholds (lssonetalm)
=======================================================================
Sonet Line : 9.1
Red Severity : major
Yellow(RAI) Severity : minor
Perf Alarm Severity : minor
Section CV 15 Min Threshold : 15
Section CV 24 Hr Threshold : 134
Section ES 15 Min Threshold : 12
Section ES 24 Hr Threshold : 120
Section SES 15 Min Threshold : 10
Section SES 24 Hr Threshold : 100
Section SEFS 15 Min Threshold : 5
Section SEFS 24 Hr Threshold : 20
Line CV 15 Min Threshold : 15
Line CV 24 Hr Threshold : 134
Line ES 15 Min Threshold : 12
Line ES 24 Hr Threshold : 120
Line SES 15 Min Threshold : 10
Line SES 24 Hr Threshold : 100
Line UAS 15 Min Threshold : 12
Line UAS 24 Hr Threshold : 20
Path CV 15 Min Threshold : 15
Path CV 24 Hr Threshold : 134
Path ES 15 Min Threshold : 12
Path ES 24 Hr Threshold : 120
Path SES 15 Min Threshold : 10
Path SES 24 Hr Threshold : 100
Path UAS 15 Min Threshold : 12
Path UAS 24 Hr Threshold : 20
| Displayed Information | Description |
|---|---|
Sonet Line | The slot and line number of the line. |
Red Severity | The red alarm severity. |
Yellow (RAI) Severity | The yellow alarm severity. |
| Threshold | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|
Section CV 15 Min Threshold | Section code violation threshold for 15 minutes. | 15 |
Section CV 24 Hr Threshold | Section code violation threshold for 24 hours. | 134 |
Section ES 15 Min Threshold | Section errored seconds threshold for 15 minutes. | 12 |
Section ES 24 Hr Threshold | Section errored seconds threshold for 24 hours. | 120 |
Section SES 15 Min Threshold | Section severely errored seconds threshold for 15 minutes. | 10 |
Section SES 24 Hr Threshold | Section severely errored seconds threshold for 24 hours. | 100 |
Section SEFS 15 Min Threshold | Section severely errored frame seconds threshold for 15 minutes. | 5 |
Section SEFS 24 Hr Threshold | Section severely errored frame seconds threshold for 24 hours. | 20 |
Line CV 15 Min Threshold | Line code violation threshold for 15 minutes. | 15 |
Line CV 24 Hr Threshold | Line code violation threshold for 24 hours. | 134 |
Line ES 15 Min Threshold | Line errored seconds threshold for 15 minutes. | 12 |
Line ES 24 Hr Threshold | Line errored seconds threshold for 24 hours. | 120 |
Line SES 15 Min Threshold | Line severely errored seconds threshold for 15 minutes. | 10 |
Line SES 24 Hr Threshold | Line severely errored seconds threshold for 24 hours. | 100 |
Line UAS 15 Min Threshold | Line unavailable seconds threshold for 15 minutes. | 12 |
Line UAS 24 Hr Threshold | Line unavailable seconds threshold for 24 hours. | 20 |
Path CV 15 Min Threshold | Path code violation threshold for 15 minutes. | 15 |
Path CV 24 Hr Threshold | Path code violation threshold for 24 hours. | 134 |
Path ES 15 Min Threshold | Path errored seconds threshold for 15 minutes. | 12 |
Path ES 24 Hr Threshold | Path errored seconds threshold for 24 hours. | 120 |
Path SES 15 Min Threshold | Path severely errored seconds threshold for 15 minutes. | 10 |
Path SES 24 Hr Threshold | Path severely errored seconds threshold for 24 hours. | 100 |
Path UAS 15 Min Threshold | Path unavailable seconds threshold for 15 minutes. | 12 |
Path UAS 24 Hr Threshold | Path unavailable seconds threshold for 24 hours. | 20 |
The chsonetalm command changes the configuration settings for alarm severity, integration period, and thresholds for various error counters. The performance alarm is set if the errors exceed any of the threshold counts set by this command. To change alarm threshold values, enter the chsonetalm command as described in the "chsonetalm" section.
The MGX 8260 Media Gateway monitors three key environmental conditions:
Sensor readings translate to alarm conditions according to four fixed threshold levels (see Figure 6-1).
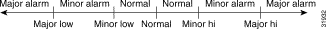
In most cases, the MGX 8260 Media Gateway monitors environmental conditions with multiple sensors located at different physical locations. When listing environmental conditions, specify the sensor ID that corresponds to the sensor you want to view. The following tables list sensors by type and id.
| SId | emmSensorType = temp(1) | emmSensorType = voltage(2) |
|---|---|---|
1 | Main board bottom | 5 V |
2 | Main board top | 3.3 V |
3 | Main board front | 2.5 V |
4 | CSM board |
|
5 | BIM board bottom |
|
6 | BIM board top |
|
7 | Main board middle |
|
| SId | emmSensorType = temp(1) | emmSensorType = voltage(2) |
|---|---|---|
1 | Main board top | 5 V |
2 | Main board bottom | 3.3 V |
| SId | emmSensorType = temp(1) | emmSensorType = voltage(2) |
|---|---|---|
1 | Main board top | 5 V |
2 | Main board bottom | 3.3 V |
3 | Main board middle | 2.5 V |
4 | MSM1 board bottom | 1.8 V |
5 | MSM1 board top |
|
6 | MSM2 board bottom |
|
7 | MSM2 board top |
|
8 | Main board front |
|
| SId | emmSensorType = temp(1) | emmSensorType = voltage(2) |
|---|---|---|
1 | Main board bottom | 5 V |
2 | Main board top | 3.3 V |
3 | Main board front | 2.5 V |
4 | BIM board top |
|
5 | BIM board bottom |
|
6 | BIM board middle |
|
7 | Main board middle |
|
| SId | emmSensorType = voltage(1) | emmSensorType = fan(2) |
|---|---|---|
1 | 1.5 Volts Bus A | Fan number 1 |
2 | 1.5 Volts Bus B | Fan number 2 |
3 | -48 Volts Bus A | Fan number 3 |
4 | -48 Volts Bus B | Fan number 4 |
5 |
| Fan number 5 |
6 |
| Fan number 6 |
Use this section to view sensor details, such as the sensor reading and thresholds, for a single unit. To monitor a single sensor, enter the lsemm command, specifying the unit type, sensor type, and sensor id, as described in the "lsemm" section. The system displays the sensor information. The following sections show sample listings for different sensors.
To view the voltage sensor 1 information for slot 11, enter the following command:
lsemm slot11 2 1
The system displays the following information:
=======================================================================
Environment Monitoring Module Reading (lsemm)
=======================================================================
EMM UnitId : slot11
EMM SensorType : voltage-mvolt
EMM SensorID : 1
EMM Alarm Status : clear
EMM Sensor Reading : 4970 voltage-mvolt
Maj Alarm Hi Threshold : 5500
Maj Alarm Lo Threshold : 4500
Min Alarm Hi Threshold : 5300
Min Alarm Lo Threshold : 4700
| Displayed Information | Description |
|---|---|
EMM UnitId | The slot or chassis with the sensor |
EMM SensorType | The type of environmental sensor |
EMM SensorID | The number of a sensor on a unit |
EMM Alarm Status | The status of the environmental alarm:
|
EMM Sensor Reading | The sensor reading:
|
Maj Alarm Hi Threshold | The threshold value separating a major alarm from a minor alarm for high readings |
Maj Alarm Lo Threshold | The threshold value separating a minor alarm for a high reading from normal operation |
Min Alarm Hi Threshold | The threshold value separating a major alarm from a minor alarm for a low reading |
Min Alarm Lo Threshold | The threshold value separating a minor alarm for a low reading from normal operation |
To view the temperature sensor 1 information for slot 11, enter the following command:
lsemm slot11 1 1
The system displays the following information:
=======================================================================
Environment Monitoring Module Reading (lsemm)
=======================================================================
EMM UnitId : slot11
EMM SensorType : temp-celsius
EMM SensorID : 1
EMM Alarm Status : clear
EMM Sensor Reading : 30 temp-celsius
Maj Alarm Hi Threshold : 75
Maj Alarm Lo Threshold : -5
Min Alarm Hi Threshold : 70
Min Alarm Lo Threshold : 0
See the Voltage Sensor Listing for a description of the table.
To view the fan sensor 1 information, enter the following command:
lsemm chassis 1 1
The system displays the following information:
=======================================================================
Environment Monitoring Module Reading (lsemm)
=======================================================================
EMM UnitId : chassis
EMM SensorType : fan-rpm
EMM SensorID : 1
EMM Alarm Status : clear
EMM Sensor Reading : 3308 fan-rpm
Maj Alarm Hi Threshold : 9999999
Maj Alarm Lo Threshold : 2900
Min Alarm Hi Threshold : 9999999
Min Alarm Lo Threshold : 3100
See the Voltage Sensor Listing for a description of the table.
To view a summary of environmental information, enter the lsemms command.
The system displays the environmental status and readings:
=======================================================================
Environment Monitoring Module Readings (lsemms)
=======================================================================
UnitId SensorType SensorId AlmStatus SensorReading
====== ================== ======== ========= =============
slot6 temp-celsius 1 clear 28
slot6 temp-celsius 2 clear 37
slot6 temp-celsius 3 clear 30
slot6 temp-celsius 4 clear 31
slot6 temp-celsius 5 clear 35
slot6 temp-celsius 6 clear 0
slot6 temp-celsius 7 clear 0
slot6 temp-celsius 8 clear 33
slot6 voltage-mvolt 1 clear 4944
slot6 voltage-mvolt 2 clear 3271
slot6 voltage-mvolt 3 clear 2494
slot10 temp-celsius 1 clear 32
slot10 temp-celsius 2 clear 38
slot10 temp-celsius 3 clear 23
slot10 temp-celsius 4 clear 24
slot10 temp-celsius 5 clear 31
slot10 temp-celsius 6 clear 40
slot10 temp-celsius 7 clear 31
slot10 voltage-mvolt 1 clear 4970
slot10 voltage-mvolt 2 clear 3288
slot10 voltage-mvolt 3 clear 2468
slot11 temp-celsius 1 clear 30
slot11 temp-celsius 2 clear 36
slot11 temp-celsius 3 clear 31
slot11 temp-celsius 4 clear 27
slot11 temp-celsius 5 clear 36
slot11 temp-celsius 6 clear 32
slot11 temp-celsius 7 clear 39
slot11 voltage-mvolt 1 clear 4970
slot11 voltage-mvolt 2 clear 3271
slot11 voltage-mvolt 3 clear 2455
chassis voltage-mvolt 2 clear 1510
chassis voltage-mvolt 4 clear 47320
chassis fan-rpm 1 clear 3292
chassis fan-rpm 2 clear 3308
chassis fan-rpm 3 clear 3409
chassis fan-rpm 4 clear 3461
chassis fan-rpm 5 clear 3341
chassis fan-rpm 6 clear 3443
For a description of the output, see Viewing Environmental Information.
To configure alarm notifications, you perform the following tasks:
The email facility works in conjunction with SNMP traps to notify registered users of alarms or significant events in the MGX 8260 Media Gateway. A system administrator can register up to ten users for email notifications and up to twenty trap events for each user. Upon occurrence of an event, the system sends an email to all registered users that contains alarm or event details and related system information.
To use email alerts, follow these steps:
Step 1 Register the domain name and IP address of your existing email server.
Step 2 Register the trap events you want users to receive. For more information, see"Working With Traps" section.
To configure the email server and source email address, follow these steps:
Step 1 Enter the email server command, chem, as described in the "chem" section.
For example, Cisco Systems could set the email server as follows:
chem cisco.com 10.1.1.1 admin@cisco.com
Step 2 Confirm your settings using the lsem command.
The system lists the email server information.
To register email traps, follow these steps:
Step 1 Identify an unused index number using the lseregs command.
Step 2 Add a user and trap registrations using the addereg command as specified in the "addereg" section.
For more information, refer to the section in this chapter pertaining to the alarm you want to add.
The following example registers user 1 for major shelf and EMM alarms:
addereg 1 user@domain.com 1000 1800
Step 3 Check the entry, using the lsereg command.
The system displays registration details.
This section explains how to change existing email registrations. To change optional parameters, follow the command line convention described in Chapter 1. For example, to leave a value unchanged type the # symbol as a placeholder.
To change an email trap registration, follow these steps:
Step 1 Identify the index number of the registration you want to change using the lseregs command.
Step 2 Get a complete list of the traps for the index you want to change using the lsereg command, specifying the index.
Step 3 Apply the desired changes using the chereg command. For trap values you don't want to change, enter the # symbol as a placeholder.
The following example adds major card alarms to trap 3 of the email alerts for user 1.
chereg 1 user@domain.com # # 1105
Step 4 Verify the entry using the lsereg command.
The system displays registration details.
To delete an email trap registration, follow these steps.
Step 1 Identify the index number of the user to delete using the lseregs command.
Step 2 Delete the desired entry using the delereg command, specifying an index.
The system deletes the registration at the specified index.
The following example deletes all email alerts for user 1:
delereg 1
To list the email server information, enter the lsem command.
The following list is displayed:
=======================================================================
Email Alert Server & Source Configuration (lsem)
=======================================================================
Server Domain Name: cisco.com
Server IP Address: 10.1.1.1
Source Email Address: support@cisco.com
| Displayed Information | Description |
|---|---|
Server Domain Name | The domain name of the email server |
Server IP Address | The IP address of the email server. The IP address 0.0.0.0 disables the email feature |
Source Email Address | The 'from' email address for messages from the MGX 8260 Media Gateway |
To list the details of one email alert registration, enter the lsereg command, specifying a number 1-10 to identify the user.
The following list is displayed:
=======================================================================
Email Alert Registration Entry (lsereg)
=======================================================================
EmailRegIndex :1
EmailAddress :user@domain.com
TrapNum1 : 1000 TrapNum2 : 1800 TrapNum3 : 0
TrapNum4 : 0 TrapNum5 : 0 TrapNum6 : 0
TrapNum7 : 0 TrapNum8 : 0 TrapNum9 : 0
TrapNum10: 0 TrapNum11: 0 TrapNum12: 0
TrapNum13: 0 TrapNum14: 0 TrapNum15: 0
TrapNum16: 0 TrapNum17: 0 TrapNum18: 0
TrapNum19: 0 TrapNum20: 0
| Displayed Information | Description |
|---|---|
EmailRegIndex | The unique index number to the user account |
Email Address | The email address where the alarm notifications are sent |
TrapNum1 to TrapNum20 | The number of the registered trap condition. To map the trap number to an alarm or event, see the "Working With Traps" section. |
To list a summary of the email alert registration entries, enter the lseregs command. The following list is displayed:
=======================================================================
Email Alert Registration Entries (lseregs)
=======================================================================
Index Trap1 Trap2 Trap3 Trap4 EmailAddress
===== ======= ======= ======= ======= ===============================
1 1000 1800 0 0 user@domain.com
2 1001 3001 0 0 user2@domain.com
You can register SNMP managers to receive SNMP trap messages on alarms or significant events in the MGX 8260 Media Gateway.
To register an SNMP trap manager, enter the addtmgr command as described in the "addtmgr" section. The bitmap parameter is a bitwise specification of trap categories to subscribe. Each bit represents a category of traps. For more information on trap numbers, see Understanding Trap Numbers.
| Bit | Trap | Description |
|---|---|---|
0 | Severity | Major (trap severity selection) |
1 | Severity | Minor (trap severity selection) |
2 | Severity | Information (trap severity selection) |
3 | 1000-1099 | Shelf |
4 | 1100-1199 | Card |
5 | 1200-1299 | SNMP |
6 | 1300-1399 | Dsx1 Line |
7 | 1400-1499 | Dsx3 Line |
8 | 1500-1599 | Sonet Line |
9 | 1600-1699 | Ether Line |
10 | 1700-1799 | Voice Port |
11 | N/A | Ether Channel |
12 | N/A | Voice Channel |
13 | 1800-1899 | EMM |
14 | 1900-1999 | Clock |
15 | 2000-2099 | DSP |
16 | 2100-2199 | DMCMAP |
17 | 2200-2299 | ISDN |
18 | 2300-2399 | MGCP |
19 | 2400-2499 | Backhaul Session |
The system sends the specified trap messages to registered managers as trap events occur. For more information on traps, see "Working With Traps".
The following example subscribes the manager at address 10.1.1.10 and udp port 162 to receive trap messages for minor and informational events for cards and DS1 lines.
addtmgr 10.1.1.10 162 2 public 86
You build a trap subscription argument for the addtmgr command. For example, to register for minor alarms, informational messages, card alarms, and DS1 line alarms, build the following trap subscription bitmap:
| Trap: | dsx1Line | SNMP | Card | Shelf | Information | Minor | Major |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bit Value | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| Bit Position | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
To use this bitmap, convert it to a decimal value and specify it as the last argument. Binary 1010110 is 86 decimal. The second argument (2) sets the in-band interface as the default interface for sending traps when the routing table has no trap manager.
To change a SNMP trap registration, enter the chtmgr command as described in "chtmgr" section. The following example changes the manager at address 10.1.1.10 and udp port 162 to receive events for the traps specified by bitmap 1100110.
chtmgr 10.1.1.10 162 2 public 102
To delete a SNMP trap registration, enter the deltmgr command, specifying the address of the SNMP manager who wants to discontinue notification of trap events. The system discontinues trap messages to the specified IP address.
The following example deletes the trap manager at 10.1.1.10.
deltmgr 10.1.1.10
To view one SNMP trap registration, enter the lstmgr command. The system displays the trap registration information.
=======================================================================
Trap Manager Registration Entry (lstmgr)
=======================================================================
Trap Manager IP Address (Index) : 10.15.38.22
UDP Port to Trap Manager : 162
Network Interface for Trap Delivery : scc-eth-if
Trap Community String : public
Traps Subscription Bitmap : 56
Manager-specific Trap Sequence Number : 0
| Displayed Information | Description |
|---|---|
Trap Manager IP Address | The IP address of the registered manager. |
UDP Port to Trap Manager | The UDP port of the registered manager. |
Network Interface for Trap Delivery | The MGX 8260 interface for delivering trap messages. Fixed at scc-eth-if. |
Trap Community String | The name of the community string. |
Trap Subscription Bitmap | A bitmap of traps to send to the manager (See Table 6-10). |
Manager-specific Trap Sequence Number | The manager-specific trap sequence number. |
To view all SNMP trap registrations, enter the lstmgrs command. The system displays the current trap managers.
=======================================================================
Trap Manager Registration Entries (lstmgrs)
=======================================================================
Mgr IP Address UDP Port Interface Community String
================ ========== =========== ====================
10.15.38.22 162 scc-eth-if public
The MGX 8260 Media Gateway generates trap messages when significant changes occur in the chassis. These changes range from major alarms to informational events. While most alarms report chassis events, a few report summary information about current line state. The MGX 8260 Media Gateway sends these trap messages to SNMP managers and users registered to receive email notification. You can also view trap information from the command line interface.
To view traps, use the lstraps command.
The system displays the information such as the following:
08/15/2000 18:28:21 02 02 MAJOR TRAP Line 7 is in line major alarm 0x00000040
08/15/2000 18:28:19 02 02 INFO* TRAP Line 7 is modified
08/15/2000 18:28:19 02 02 INFO* TRAP Line 7 is added
| Column | Description |
|---|---|
Date | The event date |
Time | The event time |
Physical Slot | The physical slot number |
Logical Slot | The logical slot number |
Severity | The event severity |
Type | The type of event |
Description | A text description of the trap |
Traps are identified by a unique number, starting with 1000. This section lists traps by function.
Shelf alarms create trap conditions that you can use for email alerts. The following table summarizes the alarm conditions and corresponding trap numbers for shelf and environmental alarms:
| Event | Severity | Trap Number |
|---|---|---|
Shelf major alarm | Major | 1000 |
Shelf minor alarm | Minor | 1001 |
Shelf alarm clear | Info | 1002 |
Shelf security alert | Minor | 1003 |
Shelf cold start | Major | 1004 |
Shelf alarm history change | Info | 1005 |
Shelf DS1 type change | Major | 1006 |
Shelf configuration cleared | Info | 1007 |
EMM major alarm | Major | 1800 |
EMM minor alarm | Minor | 1801 |
EMM alarm clear | Info | 1802 |
Clock major alarm | Major | 1900 |
Clock minor alarm | Minor | 1901 |
Clock alarm cleared | Info | 1902 |
Clock switched | Info | 1903 |
The following table summarizes the alarm conditions and corresponding trap numbers for card alarms:
| Event | Severity | Trap Number |
|---|---|---|
Card inserted | Info | 1100 |
Card removed | Info | 1101 |
Card failed | Major | 1102 |
Core card switchover | Major | 1103 |
Service card switchover | Minor | 1104 |
Card major alarm | Major | 1105 |
Card minor alarm | Minor | 1106 |
Card alarm cleared | Info | 1107 |
Card active | Info | 1108 |
Core redundancy failed | Major | 1109 |
Service module redundancy failed | Major | 1110 |
Multiservice Media module major alarm | Major | 1111 |
Physical card mismatched | Minor | 1112 |
Physical card configuration cleared | Info | 1113 |
Card in standby | Info | 1114 |
Physical back card inserted | Info | 1115 |
Physical back card removed | Info | 1116 |
DMC map added | Info | 2000 |
DMC map deleted | Info | 2001 |
DMC map modified | Info | 2002 |
DSP minor alarm (1 DSP down) | Major | 2101 |
DSP major alarm (all DSPs down) | Major | 2102 |
The following table summarizes the alarm conditions and corresponding trap numbers for DS1 alarms:
| Event | Severity | Trap Number |
|---|---|---|
DS1 line added | Info | 1300 |
DS1 line deleted | Info | 1301 |
DS1 line modified | Info | 1302 |
DS1 line major alarm | Major | 1303 |
DS1 line minor alarm | Minor | 1304 |
DS1 line alarm cleared | Info | 1305 |
DS1 line performance major alarm | Major | 1306 |
DS1 line performance minor alarm | Minor | 1307 |
DS1 line performance alarm clear | Info | 1308 |
DS1 line update threshold | Info | 1309 |
DS1 line payload loopback up | Info | 1310 |
DS1 line - line loopback up | Info | 1311 |
DS1 line other loopback up | Info | 1312 |
DS1 line loopback down | Info | 1313 |
DS1 line BERT on | Info | 1314 |
DS1 line BERT off | Info | 1315 |
E1 line performance major alarm | Major | 1316 |
E1 line performance minor alarm | Minor | 1317 |
E1 line performance alarm cleared | Info | 1318 |
E1 line threshold updated | Major | 1319 |
DS1 trap update sent1 | Info | 1320 |
| 1Trap sends information for all lines, not a single event. |
The following table summarizes the alarm conditions and corresponding trap numbers for DS3 alarms:
| Event | Severity | Trap Number |
|---|---|---|
DS3 line added | Info | 1400 |
DS3 line deleted | Info | 1401 |
DS3 line modified | Info | 1402 |
DS3 line major alarm | Major | 1403 |
DS3 line minor alarm | Minor | 1404 |
DS3 line alarm cleared | Info | 1405 |
DS3 line performance major alarm | Major | 1406 |
DS3 line performance minor alarm | Minor | 1407 |
DS3 line performance alarm clear | Info | 1408 |
DS3 line threshold update | Info | 1409 |
DS3 line payload loopback up | Info | 1410 |
DS3 line - line loopback up | Info | 1411 |
DS3 line other loopback up | Info | 1412 |
DS3 line loopback down | Info | 1413 |
| Event | Severity | Trap Number |
|---|---|---|
SONET line added | Info | 1500 |
SONET line deleted | Info | 1501 |
SONET line modified | Info | 1502 |
SONET line major alarm | Major | 1503 |
SONET line minor alarm | Minor | 1504 |
SONET line alarm cleared | Info | 1505 |
SONET line performance major alarm | Major | 1506 |
SONET line performance minor alarm | Minor | 1507 |
SONET line performance alarm clear | Info | 1508 |
SONET line threshold update | Info | 1509 |
SONET line - line loopback up | Info | 1510 |
SONET line serial loopback up | Info | 1511 |
SONET line parallel loopback up | Info | 1512 |
SONET line loopback down | Info | 1513 |
The following table summarizes the alarm conditions and corresponding trap numbers for Fast Ethernet alarms and events:
| Event | Severity | Trap Number |
|---|---|---|
Ether line active or added | Info | 1600 |
Ether line delete | Info | 1601 |
Ether line config change | Info | 1602 |
Ether line alarm while in active state | Major | 1603 |
Ether line alarm while inactive | Info | 1604 |
Ether line alarm clear | Info | 1605 |
Ether line non-recoverable failure | Major | 1606 |
Voice ports generate informational events for configuration changes. The only way to access these events is by using SNMP traps or email alerts. The following table summarizes the events and corresponding trap numbers for the voice ports:
| Event | Severity | Trap |
|---|---|---|
Voice port added | Info | 1700 |
Voice port deleted | Info | 1701 |
Voice port modified | Info | 1702 |
The following table summarizes the ISDN conditions and corresponding trap numbers for ISDN alarms and events:
| Event | Severity | Trap |
|---|---|---|
D-Channel added to DS1 or E1 | Info | 2200 |
D-Channel deleted | Info | 2201 |
DLSAP profile added | Info | 2202 |
DLSAP profile deleted | Info | 2203 |
MACSAP profile added | Info | 2204 |
MACSAP profile deleted | Info | 2205 |
D-Channel connected | Info | 2206 |
D-Channel disconnected | Info | 2207 |
D-Channel information about a card | Info | 2208 |
The following table summarizes the MGCP conditions and corresponding trap numbers for MGCP alarms and events:
| Event | Severity | Trap |
|---|---|---|
MGCP core parameter changed | Info | 2300 |
MGCP IP address, port, or domain changed | Info | 2301 |
The following table summarizes the Backhaul conditions and corresponding trap numbers for Backhaul alarms and events:
| Event | Severity | Trap |
|---|---|---|
Backhaul set added | Info | 2400 |
Backhaul set deleted | Info | 2401 |
Backhaul group added | Info | 2402 |
Backhaul group deleted | Info | 2403 |
Backhaul session added | Info | 2404 |
Backhaul session deleted | Info | 2405 |
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Posted: Sat Sep 28 14:14:28 PDT 2002
All contents are Copyright © 1992--2002 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Important Notices and Privacy Statement.