|
|

The MGX 8220 shelf Release 3.0 allows the user to perform the following management functions:
To perform these user interface functions, the MGX 8220 shelf Release 3.0 offers a variety of physical access paths and a variety of protocols. Depending upon the function to be performed, there are four physical access methods that can be used as follows:
The protocols that can be employed are:
A matrix of permissible user interface combinations in Release 2 is shown in Table 3-1.
| UI Function | Physical Access Path | TCP/IP Protocols Used |
|---|---|---|
Enter Commands using CLI | ASC Maintenance Port ASC Control Port In-band BNM T3 Port LAN Port | None SLIP, TCP, Telnet IP, TCP, Telnet IP, TCP, Telnet |
Configure/Collect Statistics and Configuration Files | ASC Control Port In-band BNM T3 Port LAN Port | SLIP, TCP, TFTP IP, TCP TFTP IP, TCP, TFTP |
Enter Commands using SNMP | ASC Control Port In-band BNM T3 Port LAN Port | SLIP, UDP, SNMP IP, UDP, SNMP IP, UDP, SNMP |
Download Firmware | ASC Control Port In-band BNM T3 Port LAN Port | SLIP, TCP, TFTP IP, TCP, TFTP IP, TCP, TFTP |
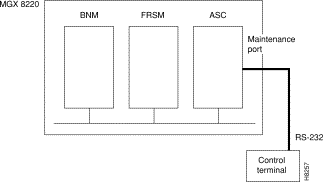
The maintenance port is the upper RS-232 connector on the ASC line module. The connector is DB-25 (female). With serial line access via the maintenance port, the user interface prompt appears once the dumb terminal is connected and the system is powered up. No special software is required and the connection is made through a standard (not null modem) cable. This arrangement is shown in Figure 3-1. Entering commands via a dumb (or emulated) terminal is the only use for the maintenance port. The maintenance port is configured for 8 data bits, no parity, one stop bit, and 9600 bps.
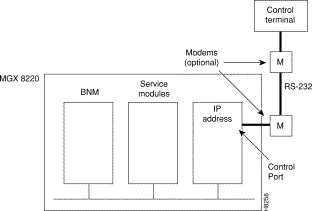
The control port is the middle RS-232 connector on the ASC line module. The connector is an RS-232 DB-25 (female). For this type of connectivity, the control terminal (PC or workstation) must support TCP/IP using a SLIP serial connection and the control port must have been previously configured with an IP address. The control terminal can be connected either locally or remotely using modems. When entering command line commands through the control port, the user interface prompt appears when user performs a Telnet login to the port's IP address.
The LAN Port on the ASC is an Ethernet AUI port.
The control and LAN Ports support Telnet (for CLI), TFTP and SNMP sessions as indicated in Table 3-1. Use of the control port is shown in Figure 3-2.
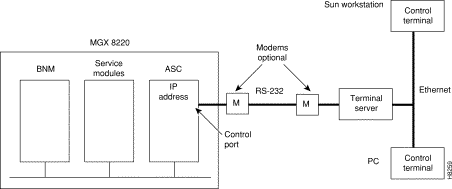
If you have multiple devices to configure, you might want to connect your workstation or PC to a terminal server, that can dial out to multiple devices. Figure 3-3 illustrates a possible scenario for terminal server control port access.
How the LAN port is connected is shown in Figure 3-4.

In-band access uses a portion of the bandwidth of the MGX 8220 shelf/BPX T3 connection by reserving a number of ATM virtual connections for network management functions. For this type of connectivity, the control terminal (PC or workstation) is connected through the BPX network and must support TCP/IP and the in-band port on the BNM must have been previously configured with an IP address. When using the in-band port to enter CLI commands, the user interface prompt appears when the user performs a Telnet login to the port's IP address. (See Figure 3-5.)

MGX 8220 systems have security features built-in to prevent unauthorized use of the system. The security features require that each user on the system have a valid account (specified by a userid), password, and privilege level.
The combination of account, password, and privilege level determine which commands the user can execute.
Before a user can be logged in, the user must have a previously assigned account, password, and privilege level. The account (userID) and privilege level are assigned using the adduser command. There is a default password which is used the first time a user logs in. When logged in, the user can change the password to a personal password with the cnfpwd configure password command.
Each user is assigned an account which is known by its userID which is specified as a parameter in the adduser command. The userID consists of up to 12 alphanumeric characters including letters, numbers, a hyphen, and an underscore. UserIDs are case sensitive.
When a user attempts to log in, the system prompts for a valid userID.
The MGX 8220 shelf permits one superuser account and 63 user accounts. The MGX 8220 shelf ships with a pre-configured superuser account (which can also be changed by Superuser).
Each account is assigned a privilege level when the account is established with the adduser command. Only an established user can execute the adduser command to open a new account and then can only specify a privilege level of the new account at the same or lower level than his or her own privilege level.
All commands have an assigned privilege level. A command can only be executed by a user whose privilege level is equal to or above the privilege level of the command. There is one superuser privilege level and 6 user levels designated 1 through 6 (with 1 being the highest).
A default password is used the first time a user logs in (see the release notes for details of the default password). Once a user is logged on, the user can change his or her own password using the cnfpwd command
The password must consist of 6 to 15 characters. Only letters, numbers, a hyphen, an underscore, and spaces are allowed. The password is case-sensitive. For security, the password is not displayed as it is entered.
When a user attempts to log in, the system prompts for a valid password after the userID prompt has been entered. The user must respond with the account's valid password.
The following paragraphs describe how to setup the various user interface access paths. Initiating commands to the shelf involves providing the correct user password.
To login to the system, follow these steps:
Step 1 At the login: prompt, type in your userID and hit ENTER.
The password: prompt appears.
Step 2 Type in the appropriate password and hit ENTER
The card number: prompt appears.
Step 3 Enter the slot number of the card to receive the commands, and hit ENTER. The normal command prompt appears. You can enter commands for the specified card/slot.
To issue commands to another module, the user must issue the cc slotnumber command and hit ENTER.
1. After setting up and powering up the MGX 8220 shelf, a CLI login: prompt appears on the terminal connected to the maintenance port. (See Chapter 5, "Service Configuration".)
2. Login as described above. Upon successful login, the standard CLI prompt showing the node name assigned to the shelf, the shelf number, logged in slot number, logged in card type, and status is displayed.
3. At the nodeName.shelf#.slot#.cardType.cardStatus> prompt, CLI commands can be entered.
Before you can access the MGX 8220 shelf using the control port, LAN port or in-band virtual connection, you must configure IP addresses for each of these destinations on the ASC card. To configure IP addresses, proceed as follows:
1. Establish a CLI connection to the shelf (either over the maintenance port or a port which has previously been configured with an IP address
2. At the login: prompt, enter your userid.
3. At the password: prompt, enter your password.
4. At the card number: prompt, enter the slot number (3 or 4)of the ASC card, for example:
5. Enter a cnfifip command to configure the control port, LAN port or in-band port IP address.
For the control port and Ethernet port the MGX 8220 shelf is now configured for you to access the unit via the specified port. The "Connecting via the Control Port" and "Connecting via the LAN Port" sections in this chapter provide details. For in-band access, you need a connection across the network. See the "Connecting via an In-band Connection" section in this chapter for details.
There are two methods of connecting to the control port. They are:
The procedures are described below:
1. Setup the control port on the MGX 8220 shelf using cnfifip with and interface type of 28 as described in the previous section.
2. Make sure the PC has TCP/IP installed and is configured for SLIP communication.
3. Configure the PC COM port to match that of control port (data rate, parity, and so forth).
4. Using the control port IP address, ping the MGX 8220 shelf to check connectivity.
5. Start the Telnet application for entering CLI commands, the SNMP manager application for managing the MGX 8220 shelf through SNMP commands, or start the TFTP application to configure or collect statistics.
If the workstation used for entering commands is to be connected over a terminal server:
1. Setup the control port on the MGX 8220 shelf using cnfifip with an interface type of 28 as described in "Setting Up IP Addresses for Control Port, LAN Port or In-band Access" above.
2. Make sure the terminal server has TCP/IP installed and is configured for SLIP communication.
3. Configure the terminal server RS-232 port to match that of control port (data rate, parity, etc.).
4. Setup the IP address of the control port of the terminal server (RS-232) to the MGX 8220 control port ID address.
5. Using the control port IP address, ping from the X-Term workstation to the MGX 8220 shelf to check connectivity.
6. Using the control port IP address of the MGX 8220 shelf as the destination address, start the Telnet application for entering CLI commands, the SNMP manager application for managing the MGX 8220 shelf through SNMP commands, or start the TFTP application to configure or collect statistics.
Before you can access the MGX 8220 shelf using the in-band method, you must set up or add a connection across the network. To configure a connection to the MGX 8220 shelf that will terminate on the in-band port of the ASC card, proceed as follows:
1. Configure the MGX 8220 In-band IP address using cnfifip with an interface type 37 as described in Setting Up IP Addresses for Control Port, LAN Port or In-band Access in the previous section.
2. Management connection end-points are already configured on the MGX 8220 shelf. The reserved end-points for management purposes in Release 2 are VPI = 3, and VCI = 8 to 15.
3. Add a connection from the BNI connected to the management terminal (directly or indirectly) to the BNI in the BPX switch connected to the MGX 8220 shelf using a destination address of
VPI = 3, and VCI = 8 to 15.
4. Using the in-band IP address of the MGX 8220 shelf as the destination address, start the TELNET application for entering CLI commands, the SNMP manager application for managing the
MGX 8220 shelf through SNMP commands, or start the TFTP application to configure or collect statistics.
The LAN port allows the shelf to be connected to an Ethernet network through using an appropriate transceiver. Thus a workstation connected to the Ethernet network can communicate directly with the MGX 8220 shelf. The port should be given an IP address to allow TCP/IP protocols to be used.
1. Setup the LAN on the MGX 8220 shelf using cnfifip with an interface type of 26 as described above.
2. Make sure the Ethernet workstation has TCP/IP installed and is configured for TCP/IP communication.
3. Start the Telnet application for entering CLI commands, the SNMP manager application for managing the MGX 8220 shelf through SNMP commands, or start the TFTP application to configure or collect statistics.
The Command Line Interface (CLI) uses a simple alphanumeric terminal and employs the concept of a system prompt to which the user types in commands.
The CLI also employs the concept of a user being logged into a particular module (slot) in the
MGX 8220 shelf and all commands entered are assumed to apply to that module (slot). In this way the CLI can be used for managing both the core cards and the service modules.
For security, logging in involves entering a correct preassigned password which allows the user access only to commands of a specified privilege level or below.
For information on performing some of the management functions using the StrataView Plus Connection Manager and Equipment Manager, see the Cisco StrataView Plus User Guide.
One command that must be entered using the CLI is the Configure Interface IP address (cnfifip). Since a control station, including StrataView Plus, uses an IP address to communicate with the shelf, the various ports on the shelf must first be assigned IP addresses using the cnfifip command.
Each CLI command and its syntax and privilege level is provided in the Cisco MGX 8220 Command Reference.
This step must be performed on the BPX switch at BOTH ends of the connection ("A" and "B"). This connection is established only once per shelf.
On the BPX switch:
1. Perform an uptrk command to enable the T3 line to the MGX 8220 shelf.
2. Perform a cnftrk command.
3. Perform an addshelf command to enable the port to the MGX 8220 shelf.
The MGX 8220 shelf provides the ability to manage the shelf through Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) commands. These commands are issued from an SNMP Manager which accesses the MGX 8220 shelf either through the Ethernet port, the control port, or in-band connection.
Each ASC and service module in the shelf contains an SNMP agent and a Management Information Base (MIB) for that module. The SNMP agent responds to GET, GET NEXT and SET commands from the SNMP Manager, thereby providing the user with the ability to interrogate and update the MIB.
The MIB resides with an object ID of axis under the strataCom branch of the SNMP tree structure (1.3.6.1.4.1.351.110) as shown in Figure 3-6. The MIB consists of five major sections:
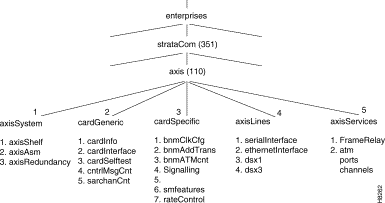
The axisSystem section consists of three sub-sections:
The cardGeneric section contains objects that are common to all card types. This section contains five subsections.
This section contains objects that are specific to a particular type of card. The cardSpecific section contains seven sub-sections:
The axisLines section consists of four subsections:
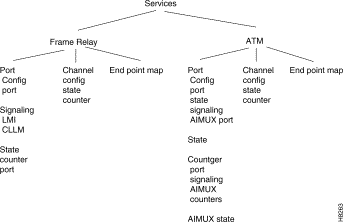
The axisServices sections consists of the AXIS service. This section contains information about frame relay channel configurations, configurable parameters, and LMI signalling. This section also contains similar MIB objects for ATM services.
The services for frame relay are further organized as shown in Figure 3-7.
The MIB is distributed as a text file (ASN.1) on a diskette from which it can be printed and used to compile the MIB into an SNMP Manager. The MIB (and hence the MGX 8220 shelf) can also be managed from StrataView Plus (Release 8.1). For complete details of managing the shelf from StrataView Plus, refer to the Cisco StrataView Plus Guide.
The MGX 8220 shelf Release 3 supports the transfer of data files between the shelf and a workstation using Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP). The functions provided by these file transfers are the configuring and collection of statistics and the downloading of MGX 8220 firmware.
In order to perform a file transfer the workstation must establish connectivity with the shelf either through the control port (using SLIP) or through the In-band port. In both cases TCP/IP protocol is employed and the shelf must be assigned an IP address. For details of how to establish connectivity, refer to the section,"Setting Up Management Connectivity to the MGX 8220 Shelf".
The MGX 8220 shelves are shipped with the latest version of the firmware already pre-loaded.
The MGX 8220 firmware upgrades can be downloaded over the network. Firmware and firmware upgrades for the MGX 8220 shelf are also distributed as a Firmware Media Kit on diskettes. The contents of the kit are:
TFTP, either through the control port or in-band ATM, is used for downloading firmware from a workstation into the MGX 8220 modules.
The host uses the following command sequence to download the firmware as follows.
1. tftp <dest_IP_add>,
2. tftp> bin
3. tftp> put <source_file_name> <dest_file_name>,
If the download process is disrupted for a timeout or other such errors, restart the TFTP download process without resetting the MGX 8220 shelf.
If there is a hardware or system failure that requires resetting the card being downloaded, the firmware must be downloaded using the backup boot procedure. This is a two step procedure.
Step 1 Download the boot firmware.
Step 2 Download the on-line firmware.
If a backup boot procedure becomes necessary, contact technical support for assistance.
After the firmware file has been transferred completely and successfully, the module should be reset for the downloaded firmware to take effect.
To configure statistics, you must create a file referring to the shelf containing the counters you wish to collect. Transfer that file to the shelf using TCP/IP TFTP.
Collecting statistics causes the statistics to be transferred as a data file to the workstation. The workstation first requests the statistics and the MGX 8220 shelf responds by uploading the statistic file to the workstation. A list of statistics counters for each card type is provided in Appendix B, "Specification".
The method of collecting statistics in the MGX 8220 shelf conforms to the standards employed in IPX switches and BPX nodes. StrataView Plus (Release 7.2 and later) supports the standard TFTP method of configuring and collecting statistics and can be used as the workstation which is attached to the MGX 8220 shelf for this purpose. StrataView Plus provides a convenient and easy-to-use graphical user interface (GUI) for both configuring the statistics to be collected and actually collecting those statistics from the MGX 8220 shelf. Using StrataView Plus relieves the user of knowing and constructing the file formats required for correctly transferring the statistics files.
Each type of statistic collected in WAN switching networks is categorized under a major grouping known by an object type name and an object type number and minor grouping known as a sub-type. Within the sub-type, the statistic has a statistic type number. For example, the statistic "ATM Cell Header HEC Errors" has an object type name of IPX-ATM, an object type of 2, a sub-type of 1 and a statistic type of 45. This combination of groups and type number uniquely identify a particular type of statistic.
Each MGX 8220 shelf statistic can be configured individually for collection. To configure statistics, the workstation transfers a file (filename = enable.stats) using TFTP to the MGX 8220 shelf which specifies those statistic types to be collected. The specified statistics are grouped by Object Type, then Object Sub-type. Multiple Object types each containing multiple Object Sub-types each containing multiple Statistic types can be specified in one file.
To collect statistics from the MGX 8220 shelf, the workstation uses TFTP to issue a request in the form:
Get Nodename.mmddyyhhmm, where
Upon receipt of this message, the shelf responds with a file containing the collected statistics.
| Field Description | Field Size |
|---|---|
Fixed Header Section | |
Domain number of MGX 8220 shelf | 1 byte |
Node number of MGX 8220 shelf | 1 byte |
Release number (example, 725a for release 7.2.5.A) | 4 bytes |
Status byte | 1 byte |
Peak Flag | 1 byte |
File collection interval | 1 byte |
Bucket interval | 1 byte |
Number of Object Types | 1 byte |
Data Dependent Section | |
Object Type identifier | 1 byte |
Number of Object Sub-types | 2 bytes |
Object Sub-type identifier | 1 byte |
Key information | variable length |
Number of Stat types | 1 byte |
Stat type | 1 byte |
Stat value | 4 bytes |
Peak value | 4 bytes |
REPEAT Stat type, Stat value and Peak value for each bucket until number of stat types is satisfied | n bytes |
REPEAT Object Sub-type section | n bytes |
REPEAT Object type section | n bytes |
The MGX 8220 shelf provides Save and Restore functions which are performed using the TFTP facility.
The Save function allows a user to copy a service module's current configuration file (which is saved on a disk on the ASC) to a network file system. The Restore function allows a user to copy a service module's configuration file from the network file system to the ASC disk. Using these functions, the configuration files for the MGX 8220 service modules can be backed up to an independent network system and later restored if the configuration files in the MGX 8220 shelf become lost or corrupted or if the configuration is to be restored to a previous version.
The TFTP Get command is used to save a configuration as follows:
where configuration filename is:
For example:
will save the configuration file for the service module in slot 5.
The TFTP Put command is used to save a configuration as follows:
where configuration filename is:
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Posted: Tue Dec 17 19:39:02 PST 2002
All contents are Copyright © 1992--2002 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Important Notices and Privacy Statement.