|
|

TrueView Catalyst 1600 Manager enables you to manage Catalyst 1600 ports and source routing information, monitor traffic on the Catalyst 1600, download code to the Catalyst 1600 and create and edit virtual LANs. For information about virtual LANs, see Appendix B, "Controlling Broadcast Frames with Virtual LANs."
When you select a Catalyst 1600, Catalyst 1600 Manager polls the device for information and updates the dialog boxes at regular intervals.
To view a graphical representation of a Catalyst 1600, either double-click on the icon representing the device or on the entry in the Catalyst 1600 Manager Table. See Figure 3-1.
For information about viewing a table of devices, refer to TrueView Applications Installation and User Guide.
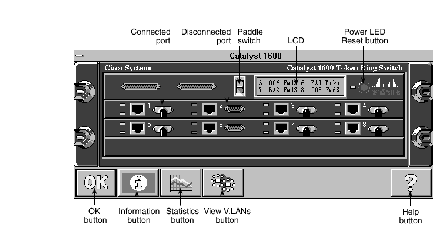
The Catalyst 1600 dialog box represents the port LEDs and LCD display as they appear on the actual device, but does not indicate whether STP or UTP cable is connected to a port. If a device is connected to a port, it always appears to be connected to the DB9 (STP) connector.
You can view and configure information about a Catalyst 1600 in the Information dialog box. You can also gain access to information about source routing, port attributes and version numbers of the hardware and software.
To view and edit information about the Catalyst 1600:
Step 1 Start Catalyst 1600 Manager.
The Catalyst 1600 dialog box is displayed (see the section "Viewing the Catalyst 1600" earlier in this chapter).
Step 2 Click on the Information button.
The Information dialog box is displayed.
The fields in the dialog box are described in Table 3-1.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | The descriptive name that you assign to the Catalyst 1600. Make sure the name is less than 16 characters long. |
| Location | The description that you enter to record the location of the Catalyst 1600. Make sure the location is less than 20 characters long. |
| Comments | The descriptive comment that you enter to record information about the Catalyst 1600. Make sure the comment is less than 40 characters long. |
| Password | The password that you enter to manage the Catalyst 1600. Make sure the password is 6 through 8 characters long. |
| Source routing | The source routing status of the Catalyst 1600. |
| Up time | The length of time the Catalyst 1600 has been running since the last reset. |
| Switch status | The current status of the Catalyst 1600 (see the section "Understanding the Status of the Catalyst 1600" later in this chapter). |
| IP address | The IP address of the Catalyst 1600. If you do not set an IP address, the field contains the value 0.0.0.0. |
| Subnet mask | The IP subnet mask of the Catalyst 1600. If you do not set an IP subnet mask, the field contains the value 0.0.0.0.
If the Automatic subnet mask check box is enabled, the class of the IP address determines the subnet mask. |
If the password for the Catalyst 1600 is incorrect, enter the password to write information to the device (see the section "Using the Password" in Chapter 2, "Getting Started").
The messages that describe the status of the Catalyst 1600 in the Information dialog box are described in Table 3-2.
| Message | Description |
|---|---|
| Catalyst 1600 status is normal | The Catalyst 1600 is operating normally. |
| Catalyst 1600 has not been found on the network | Catalyst 1600 Manager cannot find the Catalyst 1600 on the network. The condition occurs when you add a device that cannot be found, or when you start Catalyst 1600 Manager and a Catalyst 1600 in the database cannot be found. |
| Catalyst 1600 has been lost from the network | Catalyst 1600 Manager cannot find a Catalyst 1600 that was previously found on the network. |
| Incorrect password for Catalyst 1600 | Your password for the Catalyst 1600 is incorrect. The condition may indicate that another management station has changed the password for the Catalyst 1600. |
| Catalyst 1600 requires new code | The Catalyst 1600 microcode is corrupted, or a user has pressed the Reset button on the Catalyst 1600 to start the loader program. |
| Downloading to Catalyst 1600 | Catalyst 1600 Manager is downloading to the Catalyst 1600. |
| There is a warning condition on one of the ports | The Catalyst 1600 has detected a warning condition on one or more ports. For example, a beaconing condition or single station error may have occurred. |
| There is an error condition on one of the ports | One or more ports have unexpectedly closed. |
| Catalyst 1600 status is unknown | Catalyst 1600 Manager cannot determine the status of the Catalyst 1600. |
You can scroll through the LCD messages on the Catalyst 1600 using the paddle switch in the Catalyst 1600 dialog box. If you have entered a valid password, changing the LCD display also changes the display on the actual Catalyst 1600.
For more information about the LCD messages, refer to the Catalyst 1600 Installation Guide.
To scroll through the LCD messages:
Step 1 Start Catalyst 1600 Manager.
Step 2 The Catalyst 1600 dialog box is displayed (see the section "Viewing the Catalyst 1600" earlier in this chapter).
Step 3 Click on the paddle switch to the left of the LCD panel to move forwards or backwards through the messages.
You can view the ring number, node address, ring speed, and status of a Catalyst 1600 port in the Port Information dialog box.
To view information about a port:
Step 1 Start Catalyst 1600 Manager.
The Catalyst 1600 dialog box is displayed (see the section "Viewing the Catalyst 1600" earlier in this chapter).
Step 2 Move the mouse pointer over a port.
The pointer changes to indicate that information is available.
Step 3 Click on the port.
The Port Information dialog box is displayed. For information about the port status messages, see the section "Understanding the Status of a Port" later in this chapter.
The port status messages that are shown in the Port Information dialog box are described in Table 3-3.
| Message | Description |
|---|---|
| Port status is normal | The Catalyst 1600 port is enabled.
If the port is configured for Node mode, it is only reported as normal if a device is inserted. If the port is configured for Concentrator mode, it is reported as normal whether a device is inserted or not. |
| Port is disabled | The port interface is disabled. |
| Adapter has closed | The port has been removed from the ring. |
| Port is only station on ring | The Catalyst 1600 port is the only node on the ring. This message does not represent an error condition, unless you expect more nodes to appear on the ring. |
| Ring is beaconing | The ring to which the port is connected is beaconing. Check your network connections. |
| Source routing is disabled | The port does not forward source-routed frames. |
| Bridge test failed: ports are on the same ring | Two or more Catalyst 1600 ports are connected to the same token ring. |
| Bridge test failed: duplicate | A device with the same bridge number as the |
| bridge on network | Catalyst 1600 exists between two of the rings that are attached to the Catalyst 1600. |
You can view the ring number, node address, ring speed, and port interface mode of all the Catalyst 1600 ports in the Port Attributes dialog box.
To view information about all the ports:
Step 1 Start Catalyst 1600 Manager.
The Catalyst 1600 dialog box is displayed (see the section "Viewing the Catalyst 1600" earlier in this chapter).
Step 2 Click on the Information button.
The Information dialog box is displayed.
Step 3 Click on the Port Attributes button.
The Port Attributes dialog box is displayed.
The settings in the Port Attributes dialog box are described in Table 3-4.
You can set a Locally Administered Address (LAA) for each Catalyst 1600 port, or reset the address to the hard-wired address, in the Addresses dialog box.
To change the address of a port:
Step 1 Start Catalyst 1600 Manager.
The Catalyst 1600 dialog box is displayed (see the section "Viewing the Catalyst 1600" earlier in this chapter).
Step 2 Click on the Information button.
The Information dialog box is displayed.
Step 3 Click on the Port Attributes button.
The Port Attributes dialog box is displayed.
Step 4 Click on the Addresses button.
The Addresses dialog box displays the current and hard-wired addresses for each port on the Catalyst 1600.
Step 5 Click on the Reset button to restore the hard-wired address, or edit the address using the keyboard.
A Locally Administered Address (LAA) must begin with the digit 4, 5, 6 or 7.
Step 6 Click on the OK button.
The port address is changed.
You can view and configure information about source-routing for the Catalyst 1600, and for each of the ports on the Catalyst 1600, in the Source Routing dialog box. You can also view source-routing statistics, and configure spanning tree parameters for each port.
To view source-routing information for a Catalyst 1600:
Step 1 Start Catalyst 1600 Manager.
The Catalyst 1600 dialog box is displayed (see the section "Viewing the Catalyst 1600" earlier in this chapter).
Step 2 Click on the Information button.
The Information dialog box is displayed.
Step 3 Click on the Source Routing button.
The Source Routing dialog box is displayed.
The fields that define source routing are defined in the following table.
| Field | Description | |
|---|---|---|
| Source routing | Whether source routing by the Catalyst 1600 is enabled. | |
| Bridge number | The bridge number that identifies the Catalyst 1600. The bridge number is a hexadecimal number in the range 0 through F. | |
| Ring number | The number of the ring that is connected to the port. The ring number is a three-digit hexadecimal number in the range 001 through FFF. | |
| Source routing | Whether source routing is enabled for the port. | |
| Hop count | The total number of hops a broadcast frame is allowed to make. The Catalyst 1600 does not forward frames that have exceeded the hop count limit. The hop count is a decimal number in the range 1 through 7. | |
| Max frame size | The maximum frame size that the Catalyst 1600 forwards. The maximum size that the Catalyst 1600 supports is 4472 bytes. | |
Station type | The types of station that are attached to the ring that is connected to the Catalyst 1600 port. | |
| Anything | Workstations and servers are attached to the ring that is connected to the Catalyst 1600 port. | |
| Workstations | Only workstations are attached to the ring that is connected to the Catalyst 1600 port. | |
The information ensures that the Catalyst 1600 does not forward broadcast frames originating on workstation-only rings to other workstation-only rings. The Catalyst 1600 performs port-to-port blocking on all IPX and NetBIOS source-routed broadcast frames, except for NetBIOS ADD_NAME_QUERY and ADD_GROUP_NAME_QUERY frames. For more information, refer to Appendix C, "Glossary of Terms." | ||
You can view and configure the spanning tree parameters that define how the Catalyst 1600 and bridges on the network establish the best route to forward single route broadcasts on the Catalyst 1600.
The spanning tree parameters in the Spanning Tree dialog box apply when you enable source routing in the Source Routing dialog box.
To view Spanning Tree parameters for a Catalyst 1600:
Step 1 Start Catalyst 1600 Manager.
The Catalyst 1600 dialog box is displayed (see the section "Viewing the Catalyst 1600" earlier in this chapter).
Step 2 Click on the Information button.
The Information dialog box is displayed.
Step 3 Click on the Source Routing button.
The Source Routing dialog box is displayed.
Step 4 Click on the Spanning Tree button.
The Spanning Tree dialog box is displayed.
The Spanning Tree parameters are described in Table 3-6.
You can view information about the frames that the Catalyst 1600 receives and transmits for all frames, non-broadcast frames, All Routes Explorer frames and Spanning Tree Explorer frames. You can also view the number of frames that the Catalyst 1600 discards.
To view source-routing statistics:
Step 1 Start Catalyst 1600 Manager.
The Catalyst 1600 dialog box is displayed (see the section "Viewing the Catalyst 1600" earlier in this chapter).
Step 2 Click on the Statistics button.
The Source Routing Statistics dialog box is displayed.
Step 3 Click on the More button to view detailed statistics for an individual port.
The Source Routing Statistics dialog box for the port is displayed.
When you have entered a valid password (see the section "Using the Password" in Chapter 2, "Getting Started"), you can download boot or run-time microcode to a Catalyst 1600.
When you request to download a file containing microcode:
Step 1 The Catalyst 1600 restarts.
Step 2 The file is downloaded.
Step 3 Existing microcode held in flash ROM is erased.
Step 4 The Catalyst 1600 restarts with the new code.
Before downloading a microcode file to the Catalyst 1600, check the version that is running on the device (see the section "Viewing Version Information" later in this chapter). To distinguish between files containing boot and run-time microcode, examine the first four letters in the filename as shown in Table 3-7.
| Description | Format | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Run-time code | SRSW<version number>.BIN | SRSW102R.BIN |
| Boot code | SRSB <version number>.BIN | SRSB102R.BIN |
To download microcode to a Catalyst 1600:
Step 1 Start Catalyst 1600 Manager.
The Catalyst 1600 dialog box is displayed (see the section "Viewing the Catalyst 1600" earlier in this chapter).
Step 2 Click on the Reset button.
A warning is displayed.
Step 3 To proceed, click on the OK button.
The Open dialog box is displayed.
Step 4 Select the file that you want to download to the Catalyst 1600.
Step 5 Click on the OK button.
While you download microcode, the Catalyst 1600 is inoperative and users cannot access network resources such as file servers. Downloading microcode may take several minutes to complete.
You can view information about the version number of Catalyst 1600 hardware and software, and find out the name of the microcode file that is running on the Catalyst 1600.
To view version information:
Step 1 Start Catalyst 1600 Manager.
The Catalyst 1600 dialog box is displayed (see the section "Viewing the Catalyst 1600" earlier in this chapter).
Step 2 Click on the Information button.
The Information dialog box is displayed.
Step 3 Click on the Version Info button.
The Version Information dialog box is displayed.
TrueView Catalyst 1600 Manager enables you to configure virtual LANs that include one or more Catalyst 1600 devices, or view a list of the virtual LANs to which a Catalyst 1600 belongs. For information about virtual LANs, see Appendix B, "Controlling Broadcast Frames with Virtual LANs."
Catalyst 1600 Manager maintains a master record of the virtual LANs that you define in an RSVLAN.INI file in the same directory as the Catalyst 1600 Manager program files. RSVLAN.INI contains information about the Catalyst 1600 devices and rings that belong to each virtual LAN. Whenever you create or edit virtual LANs, the information is automatically downloaded to Catalyst 1600 devices.
Because the local record of virtual LANs must match the configuration that you have downloaded to each Catalyst 1600, Catalyst 1600 Manager always verifies that each Catalyst 1600 exists on the network, and that the password is correct, before downloading a new configuration to a series of Catalyst 1600 devices.
To create a new virtual LAN, you must be able to identify the Catalyst 1600 devices that will belong to the virtual LAN, the rings that will be included in the virtual LAN, and whether the virtual LAN will be impermeable or permeable (see Appendix B, "Controlling Broadcast Frames with Virtual LANs"). You can also include new ring numbers to provide for expansion of the virtual LAN.
To create a new virtual LAN:
Step 1 Display the Catalyst 1600 Manager Table using the instructions in TrueView Applications Installation and User Guide.
Step 2 Click on the Catalyst 1600 devices that you want to include in the virtual LAN.
The table rows corresponding to the Catalyst 1600 devices are highlighted.
Step 3 Click on the New VLAN button.
The Edit Virtual LAN dialog box displays a list of included devices, and the rings you can add to the virtual LAN in a list of unused rings.
Step 4 Enter a name (1 through 16 characters) for the virtual LAN in the name field.
Step 5 To create a permeable virtual LAN, enable the Permeable check box.
Step 6 Click on the rings that you want to add, and click on the Add button.
The rings that you selected are removed from the list of unused rings and shown in the list of included rings.
Step 7 To add new rings that will be used in the future, click on the New Ring button and specify a three-digit hexadecimal number for the ring.
The new ring is shown in the list of included rings, with two exclamation marks to indicate that the ring is not found on the Catalyst 1600 devices that belong to the virtual LAN.
Step 8 Click on the OK button to create the virtual LAN.
When you create a virtual LAN, Catalyst 1600 Manager verifies that the appropriate passwords are correct before downloading the new configuration to the Catalyst 1600 devices in the virtual LAN. If passwords are required, you are prompted to enter the passwords before proceeding.
 | Warning Downloading the virtual LAN to an incomplete set of Catalyst 1600 devices results in inconsistent definitions of virtual LANs, and may result in undesirable forwarding or blocking of broadcast frames. |
You can edit and update the virtual LANs that have been configured on managed Catalyst 1600 devices.
When you edit the virtual LAN configuration, Catalyst 1600 Manager downloads information stored in the RSVLAN.INI file to each Catalyst 1600 device that belongs to the virtual LAN.
To edit virtual LANs:
The All Virtual LANs dialog box displays a list of defined virtual LANs.
The name of the virtual LAN is highlighted.
The Edit Virtual LAN dialog box displays the Catalyst 1600 devices and rings that belong to the virtual LAN, and whether the type of virtual LAN is impermeable or permeable.
The new configuration is downloaded to all included Catalyst 1600 devices.
You can view a list of the virtual LANs that are configured on a particular Catalyst 1600, and view the configuration of the virtual LANs.
To view virtual LANs on a Catalyst 1600:
The Catalyst 1600 dialog box is displayed (see the section "Viewing the Catalyst 1600" earlier in this chapter).
The View Virtual LANs dialog box is displayed.
The name of the virtual LAN is highlighted.
The View Virtual LAN dialog box displays the configuration of the virtual LAN. Any rings that are not connected directly to the Catalyst 1600 are indicated by two exclamation marks.
You can delete virtual LANs from each Catalyst 1600 that belongs to the virtual LAN.
To delete virtual LANs:
The All Virtual LANs dialog box displays a list of defined virtual LANs.
The name of the virtual LAN is highlighted.
The virtual LAN is deleted.
If you experience problems with the current configuration and want to create new virtual LANs, you can delete the virtual LANs from an individual Catalyst 1600.
 | Warning Deleting virtual LANs from individual Catalyst 1600 devices results in inconsistent definitions of virtual LANs, and may result in undesirable forwarding or blocking of broadcast frames. |
To delete virtual LANs from a device:
The Catalyst 1600 dialog box is displayed (see the section "Viewing the Catalyst 1600" earlier in this chapter).
The View Virtual LANs dialog box is displayed.
The name of the virtual LAN is highlighted.
A warning is displayed, asking you to confirm the operation.
If the password for the device is correct, the virtual LAN is deleted from the selected Catalyst 1600.
|
|