|
|

After you have configured the SwitchProbe device as discussed in "Initialization," you are ready to connect the device to the network. This chapter provides detailed instructions for connecting the interfaces on the SwitchProbe device to the network.
The following interfaces are discussed in this chapter:
Refer to "Specifications," for complete physical specifications of the small chassis and the front-access chassis.
Before connecting the SwitchProbe device to the network, note the following warnings and cautions:
 | Warning Before working on equipment that is connected to power lines, remove jewelry (including rings, necklaces, and watches). Metal objects heat up when connected to power and ground and can cause serious burns or weld the metal object to the terminals. |
The following interfaces are class 1 laser products:
Read the following warnings for interfaces with class 1 laser products:
 | Warning Because invisible laser radiation may be emitted from the aperture of the port when no cable is connected, avoid exposure to laser radiation and do not stare into open apertures. |
 | Caution To prevent possible damage to the SwitchProbe device, read "Site Requirements." |
 | Caution To prevent network interruptions, make sure all Token Ring or WAN interfaces are configured to the correct speed. |
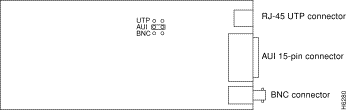
The Ethernet interface supports one of the following three cable types:
Cisco Systems sets the Ethernet interface to one of the three types during manufacture. A label in the lower right portion of the SwitchProbe device's front panel indicates the factory-configured setting.
Table 6-1 explains the labels and corresponding cables for the Ethernet interface.
| If the Label States... | Do the Following |
|---|---|
Configured for AUI (For AUI pin designations, see "Cable Pinouts.") | Connect a 10BASE5 Thicknet cable to the interface's thicknet connector. |
Configured for BNC | Connect a 10BASE2 Thinnet cable to the interface's Thinnet connector. |
Configured for UTP | Connect an category 5 UTP cable to the interface's RJ-45 UTP connector. |
The two LEDs on the Ethernet interface card are described in Table 6-2.
| LED Color | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
On | Link signal detected. | |
On | Heavy network traffic. |
To set the Ethernet connection, you must change an internal jumper on the Ethernet interface card.
To change the Ethernet connection type, see Figure 6-1 and follow these steps:
 | Warning Do not work on the system or connect or disconnect cables during periods of lightning activity. |
 | Warning Before working on a system that has an on/off switch, turn OFF the power and unplug the power cord. |
Step 1 Remove the screws and open the unit.
Step 2 Hold the cover in place and gently slip it off.
Step 3 Remove the network interface card.
The jumper is located on the board behind the connectors.
Step 4 Place the jumper on the selected option: UTP, AUI, or BNC.
For the Multiport 10BaseT Ethernet interface, connect a category 5 UTP cable into the interface's RJ-45 port.
For the Fast Ethernet half-duplex 100Base TX interface, connect a category 5 UTP cable into the interface's RJ-45 port.
For the Fast Ethernet half-duplex 100Base FX interface, connect a SC-to-SC 62.5/125 micron multimode fiber-optic cable into the interface's SC modular port.
For the Fast Ethernet full-duplex 100Base interface, see the following sections:
The Fast Ethernet Full-Duplex 100Base TX SwitchProbe device includes a Fast Ethernet FDX tap to monitor full-duplex network links.
The Fast Ethernet FDX tap front panel shown in Figure 6-2 provides Data Terminal Equipment (DTE) and Data Circuit-terminating Equipment (DCE) connectors for connection to the network. These connectors are RJ-45 jacks.
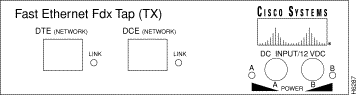
Two LEDs on the front panel indicate link status.
 | Caution Use only the adapter supplied with the Fast Ethernet FDX tap. If you use an adapter other than the one supplied, the tap can become permanently damaged. |
The rear panel shown in Figure 6-3 provides DTE and DCE connectors for connection to the SwitchProbe device. These connectors are RJ-45 jacks.
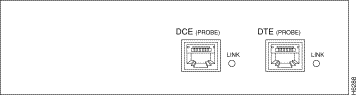
Two LEDs on the rear panel indicate link status.
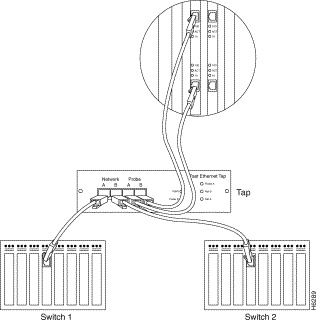
To connect the full-duplex 100Base TX interfaces to two switches, see Figure 6-4, and follow these steps:
Step 1 Connect a category 5 UTP or FTP crossover cable (included with the SwitchProbe device) into the interface's RJ-45 port labeled DTE.
Step 2 Connect the other end of this cable into the DTE (Probe) port of the Fast Ethernet FDX tap (TX).
Step 3 Connect a category 5 UTP or FTP crossover cable (included with the SwitchProbe device) into the interface's RJ-45 port labeled DCE.
Step 4 Connect the other end of this cable into the DCE (Probe) port of the Fast Ethernet FDX tap (TX).
Step 5 Connect a category 5 UTP or FTP cable into the DTE (Network) port of the Fast Ethernet FDX tap (TX).
Step 6 Connect the other end of this cable into Switch 1.
Step 7 Connect a category 5 UTP or FTP cable into the DCE (Network) port of the Fast Ethernet FDX tap (TX).
Step 8 Connect the other end of this cable into Switch 2.
Connecting the full-duplex 100Base FX interfaces of a Fast Ethernet SwitchProbe device to a network segment is a two-step process:
Step 1 Connect a fiber-optic splitter tap to the SwitchProbe device's 100Base FX interfaces.
Step 2 Connect the fiber-optic splitter tap to the network segment.
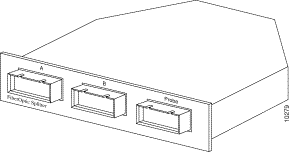
The Fast Ethernet FX SwitchProbe device requires a fiber-optic splitter tap, shipped with the device, to monitor the network. The splitter tap is passive—link integrity is maintained whether the device is on or off.
The fiber-optic splitter tap shown in Figure 6-5 contains three female SC duplex connection ports, labeled A, B, and Probe.
For instructions on installing the fiber-optic splitter tap, see "Attaching the Fiber-Optic Splitter Rack Panel (Optional)" and "Installing a Fiber-Optic Splitter in a Rack Panel" in "Installation."
The fiber-optic splitter tap kit shipped with the SwitchProbe device includes (among other cables) a four-foot SC-duplex-to-dual-SC-duplex multimode fiber cable.
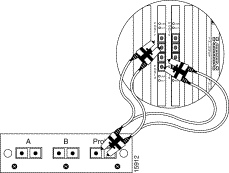
To connect the SwitchProbe device to the tap, see Figure 6-6 and follow these steps:
Step 1 Insert the end of the fiber cable labeled DTE into the SwitchProbe device's full-duplex 100Base FX interface labeled DTE.
Step 2 Insert the end of the fiber cable labeled DCE into the SwitchProbe device's full-duplex 100Base FX interface labeled DCE.
Step 3 Insert the other end of the fiber cable (the cable with only one connector) into the interface labeled "Probe" on the fiber-optic splitter tap.
After you connect the SwitchProbe device to the tap, you can connect the tap to the network segment.
Depending upon the type of cable you used between each switch and the tap, there are three possible configurations to connect the two switches to the fiber-optic splitter tap:
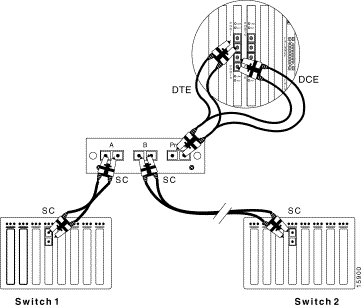
To connect a 100Base FX network with SC connectors to a fiber-optic splitter tap, see Figure 6-7 and follow these steps:
Step 1 Use the SC-to-SC cable included with the SwitchProbe device to connect Switch 1 to interface A on the fiber-optic splitter tap.
Step 2 Connect Switch 2 to interface B on the fiber-optic splitter tap. Use the cable which was originally plugged into Switch 1.
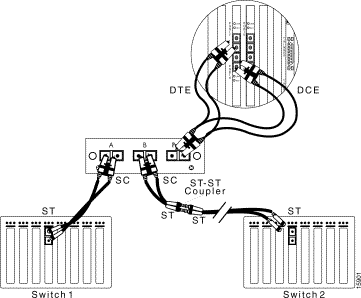
To connect a 100Base FX network with ST connectors to a fiber-optic splitter tap, see Figure 6-8 and follow these steps:
Step 2 Use the other SC-to-ST cable included with the SwitchProbe device to connect the ST-to-ST coupler to interface B on the fiber-optic splitter tap. (Plug the ST connector into the ST-to-ST coupler and plug the SC connector into the tap.)
Step 3 Connect Switch 2 to the ST-to-ST coupler. Use the cable which was originally plugged into Switch 1.
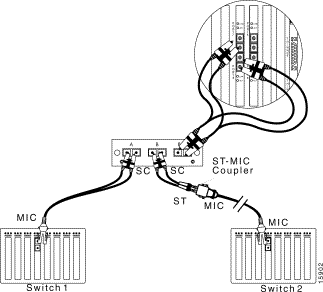
To connect a 100Base FX network with MIC connectors to a fiber-optic splitter tap, see Figure 6-9 and follow these steps:
Step 2 Use the SC-to-ST cable included with the SwitchProbe device to connect the ST-to-MIC coupler to interface B on the fiber-optic splitter tap (Plug the ST connector into the ST-to-MIC coupler and plug the SC connector into the tap.)
Step 3 Connect Switch 2 to the ST-to-MIC coupler. Use the cable which was originally plugged into Switch 1.
The 100Base FX interface adapter card has two LEDs (described in Table 6-3). The 100Base TX interface adapter card has four LEDs.
| LED Color | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
Green | On Off | Link signal detected. |
Amber | On Blinking Off |
Moderate traffic on the network. No traffic on the network. |
Depending on the mode configuration of the Fast Ethernet interfaces, you can make the following physical connections:
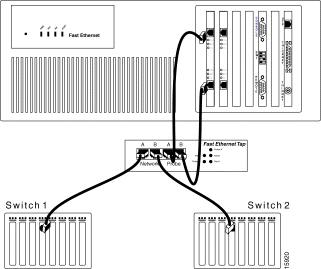
To connect the full-duplex 100Base TX ports of the Fast Ethernet four-port model to two switches, see Figure 6-10 and follow these steps:
Step 1 Connect a category 5 UTP or FTP straight-through cable (included with the SwitchProbe device) into one of the two RJ-45 100Base TX ports on the device's Fast Ethernet interface.
Step 2 Connect the other end of this cable into the "Probe A" port of the Fast Ethernet tap.
Step 4 Connect the other end of this cable into the "Probe B" port of the Fast Ethernet tap.
Step 5 Connect a category 5 UTP or FTP straight-through cable into the "Network A" port of the Fast Ethernet tap.
Step 6 Connect the other end of this cable into Switch 1.
Step 7 Connect a category 5 UTP or FTP straight-through cable into the "Network B" port of the Fast Ethernet tap.
Step 8 Connect the other end of this cable into Switch 2.
Connecting the full-duplex 100Base FX ports of the Multiport Fast Ethernet and Fast EtherChannel to two switches is a two-step process:
Step 1 Connect a fiber-optic splitter tap to the full-duplex 100Base FX ports.
Step 2 Connect the fiber-optic splitter tap to the two switches.
The fiber-optic splitter tap kit shipped with the SwitchProbe device includes (among other cables) a four-foot SC-duplex-to-dual-SC-duplex multimode fiber cable.
The multimode duplex SC connectors only contain receive (Rx) connections. To connect the fiber-optic splitter tap to full-duplex 100Base FX ports, see Figure 6-11 and follow these steps:
Step 1 Insert the end of the fiber cable labeled DCE into the top port of a full-duplex 100Base FX interface (the top port is the interface's DCE port).
Step 2 Insert the end of the fiber cable labeled DTE into the bottom port of the same full-duplex 100Base FX interface (the bottom port is the interface's DTE port).
Step 3 Insert the other end of the fiber cable (the cable with only one connector) into the port labeled "Probe" on the fiber-optic splitter tap.
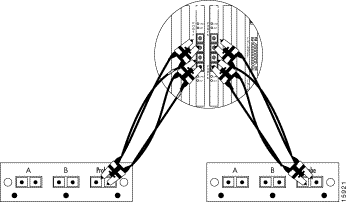
After you connect the SwitchProbe device to the tap, connect the tap to the network segment.
Depending on the type of cable you used between each switch and the tap, there are three possible configurations to connect two switches to the fiber-optic splitter tap:
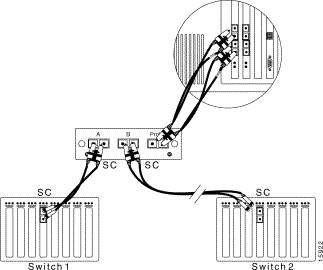
To connect a 100BASE FX network with SC connectors to a fiber-optic splitter tap, see Figure 6-12 and follow these steps:
Step 1 Use the SC-to-SC cable included with the SwitchProbe device to connect Switch 1 to interface A of the fiber-optic splitter tap.
Step 2 Connect the end of the cable, which was originally plugged into Switch 1, to interface B of the fiber-optic splitter tap.
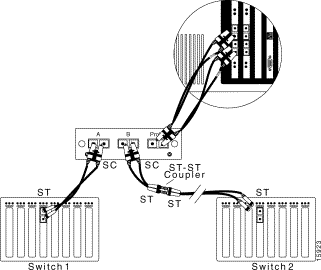
To connect a 100Base FX network with ST connectors to a fiber-optic splitter tap, see Figure 6-13 and follow these steps:
Step 1 Use the SC-to-ST cable included with the SwitchProbe device to connect Switch 1 to interface A of the fiber-optic splitter tap. (Plug the ST connector into Switch 1 and plug the SC connector into the tap.)
Step 2 Use the other SC-to-ST cable included with the SwitchProbe device to connect the ST-to-ST coupler to interface B of the fiber-optic splitter tap. (Plug the ST connector into the ST-to-ST coupler and plug the SC connector into the tap.)
Step 3 Connect the end of the cable, which was originally plugged into Switch 1, to the ST-to-ST coupler.
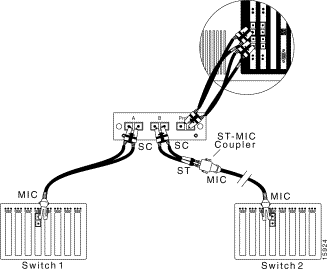
To connect a 100Base FX network with MIC to a fiber-optic splitter tap, see Figure 6-14, and follow these steps:
Step 1 Use the SC-to-MIC cable included with the SwitchProbe device to connect Switch 1 to interface A of the fiber-optic splitter tap. (Plug the MIC connector into Switch 1 and plug the SC connector into the tap.)
Step 2 Use the SC-to-ST cable included with the SwitchProbe device to connect the ST-to-MIC coupler to interface B of the fiber-optic splitter tap. (Plug the ST connector into the ST-to-MIC coupler and plug the SC connector into the tap.)
Step 3 Connect the end of the cable, which was formerly plugged into Switch 1, to the ST-to-MIC coupler.
Each Multiport Fast Ethernet interface contains LEDs.
Table 6-4 and Table 6-5 describe the Fast Ethernet interface LEDs.
| LED | Color | Status | Meaning |
|---|---|---|---|
100 | Green | On | Port is active and monitoring a 100 mbps Fast Ethernet network. No link signal detected or no cable is attached. |
ACT (2 LEDs) | Amber | Off (always) | |
10 | Green | On | Port is active and monitoring a 10 mbps Ethernet network. No link signal detected or no cable is attached. |
| LED | Color | Status | Meaning |
|---|---|---|---|
LINK | Green | On | Port is active and monitoring a 100 mbps Fast Ethernet network. No link signal detected or no cable is attached. |
ACT | Amber | Off (always) | No transmit activity. |
The Token Ring interface supports both Type 1 foil twisted-pair (FTP) and Type 2 unshielded twisted-pair (UTP) cables. The connectors for each topology is as follows:
For the RJ-45 UTP connector pin designations, see "Cable Pinouts."
The default configuration for the Token Ring interface is through the FTP connector. You can attach the network to the UTP port by inserting the appropriate UTP cable into the UTP connector. The device automatically detects and configures to the UTP connection.
Two SC connectors enable you to connect the SwitchProbe device to the ring—either a SC-to-MIC or a SC-to-SC 62.5/125 micron multimode fiber-optic cable.
You can either connect the SwitchProbe device directly to the ring as a DAS, or use a concentrator to connect it in a "dual homing" configuration. In either case, the SwitchProbe device sees the same network traffic.
If you connect the FDDI DAS SwitchProbe device directly to the ring as a DAS, you should use an optical bypass switch to maintain the integrity of the dual ring in the event of a failure. You can use an optical bypass switch with a modular RJ-12 station connector. For the pin designations of an RJ-12 connector, see "Cable Pinouts,"
 | Caution To prevent possible damage to the SwitchProbe unit, do not insert telecommunications cabling into the optical bypass switch connector. |
To connect the FDDI DAS SwitchProbe device in a dual-homing configuration, use the two free M-ports on the concentrator, and follow these steps:
Step 1 Connect the B port of the SwitchProbe device to one of the M ports on the concentrator.
Step 2 Connect the A port of the SwitchProbe device to an M port on the same or a different concentrator.
Connecting to a different concentrator results in better fault tolerance if one of the concentrators fail.
| LED B | LED A | Description |
|---|---|---|
Alternately green and amber | Normal mode of operation, indicating the B-M link is active and the A-M link is in standby mode. | |
Solid green | The B-M link has failed and the A-M link has taken over. The SwitchProbe device is still attached to the ring. | |
Blinking green | Blinking green | Both the B-M and A-M links have failed. The SwitchProbe device is off the ring. Verify connectivity. |
Blinking amber | ||
Solid amber |
| |
Off | Off | If off after the SwitchProbe unit boots, and if the Error LED on the front panel is blinking, indicates a SwitchProbe device failure. |
| 1Link Confidence Test. |
The WAN interfaces support connections to V.35, X.21, EIA/TIA-449, and EIA-530. Only a V.35 cable is shipped with the SwitchProbe device. To purchase other cables, contact your Cisco Systems' sales representative.
Each WAN interface is a single port with a 26-pin, D-type connector. Use an appropriate adapter cable and WAN tap for each supported connection. The WAN interface operates in monitor mode only (tracking network traffic).
Before connecting the SwitchProbe device to the network, note the following warnings:
 | Warning This equipment is to be installed and maintained by service personnel only as defined by AS/NZS 3260 Clause 1.2.14.3 Service Personnel. |
 | Warning The telecommunications lines must be disconnected 1) before unplugging the main power connector and/or 2) while the housing is open. |
 | Warning Do not work on the system or connect or disconnect cables during periods of lightning activity. |
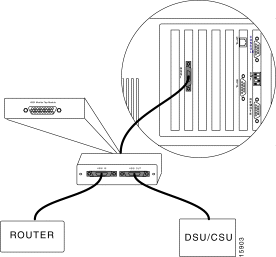
You use a WAN tap kit to connect the WAN interface to a network segment.
The WAN tap monitors the DTE and DCE circuits of a link between a router and a channel service unit/data service unit (CSU/DSU). You can connect and disconnect the SwitchProbe device without disrupting the link between the router and the CSU/DSU.
The WAN tap kit consists of the following items:
To install the WAN tap kit, see Figure 6-15 and follow these steps:
Step 1 Insert the one-foot section of the Y-shaped cable between the router and the CSU/DSU.
This section of the Y-shaped tap cable has identical connectors on each end. (Connector styles include V.35, X.21, EIA/TIA-232, EIA/TIA-449, and EIA-530.)
 | Caution Never use force to connect the cables. Forcing connectors can permanently damage the connector's pins. |
Step 2 Insert the six-inch section of the Y-shaped cable into the tap unit.
The section of the Y-shaped tap cable contains a DB-26 connector.
Step 3 Insert one end of the 15-foot, straight tap cable into the tap unit.
Step 4 Insert the other end into the WAN port on the SwitchProbe device.
This cable has two DB-26 connectors (one at each end).
Step 5 Power on the device.
The POWER LED on the tap unit lights up and remains on while the tap unit receives power.

You can connect a management device to the Multiport T1/E1 WAN SwitchProbe device in one of two ways:
The Multiport T1/E1 WAN SwitchProbe device supports out-of-band management through the serial port labeled Remote using SLIP, or through the Ethernet or Token Ring interface.
Use the SLIP connection as a secondary connection to access all network statistics. The SLIP link is normally used as a backup link when the network is not operational, or when the agent is not accessible.
To perform out-of-band management through the active Ethernet interface, follow these steps:
Step 1 Connect an Ethernet cable to the Ethernet interface.
Step 2 Configure the interface mode to manage.
Set the speed of the Token Ring interface to match the speed of the network before you connect the SwitchProbe device, or it might interfere with network operations.
To perform out-of-band management through the active Token Ring interface, follow these steps:
Step 1 Connect a Token Ring cable to the Token Ring interface.
Step 2 Configure the interface mode to manage.
The Multiport T1/E1 WAN SwitchProbe device supports side-band management (manage and monitor mode on the same interface) through the active Ethernet interface, or through the active Token Ring interface.
To make a side-band connection, follow these steps:
Step 1 Connect an Ethernet cable to the active Ethernet interface, or connect a Token Ring cable to the active Token Ring interface.
Step 2 Configure the interface mode to manage and monitor.
HSSI SwitchProbe devices use a HSSI tap to connect into the DTE and DCE circuits of the WAN link.
The HSSI tap measures 1.5 inches high, by 4 inches wide, by 4 inches deep, and can be set on a tabletop. The front panel of the tap includes a single DB-26 connector to connect the tap module to the WAN port of the SwitchProbe device.
The rear panel includes two SCSI II connectors:
The HSSI SwitchProbe device taps the DTE and DCE circuits of the HSSI link through an active tap interface. Connecting the HSSI SwitchProbe device to the network segment is a two-step process:
Step 1 Connect the HSSI tap between the router and CSU/DSU.
Step 2 Connect the HSSI interface of the SwitchProbe device to the tap.
Before connecting the HSSI SwitchProbe device to the network segment, you must follow these prerequisite steps:
Step 1 Set the WAN interface speed if the speed of the network to which you are connecting is not 1250 kbps. See "Changing the Token Ring and WAN Interface Speed," in "Initialization."
Step 2 Set the encapsulation protocol, if the encapsulation protocol used on the network to which you are connecting is not Cisco HDLC. See "Changing the Encapsulation Protocol (WAN Only)" in "Initialization."
To connect the HSSI SwitchProbe device to the network using the HSSI tap, see Figure 6-16, and follow these steps:
Step 1 Use the cable that connects the router to the DSU/CSU to connect the router to the HSSI IN port on the HSSI tap.
Step 2 Use the HSSI cable (included with the SwitchProbe device) to connect the DSU/CSU to the HSSI OUT port on the HSSI tap.
Step 3 Use the tap cable (included with the SwitchProbe device) to connect the single DB-26 port on the back of the HSSI tap to the HSSI WAN interface on the SwitchProbe device.
The ATM SwitchProbe device requires a fiber-optic splitter, shipped with the device, to monitor the network. The splitter is passive—link integrity is maintained whether the device is on or off.
The fiber-optic splitter shown in Figure 6-17 contains three female SC-duplex connection ports labeled A, B, and Probe.
For instructions on installing the fiber-optic splitter, see "Attaching the Fiber-Optic Splitter Rack Panel (Optional)" and "Installing a Fiber-Optic Splitter in a Rack Panel" in "Installation."

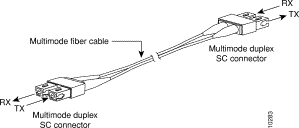
Two 24-foot SC-duplex-to-SC-duplex multimode fiber cables (Figure 6-18) are shipped with the ATM SwitchProbe device.
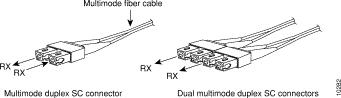
One four-foot SC-duplex-to-dual-SC-duplex multimode fiber cable (Figure 6-19) is also shipped with the ATM SwitchProbe device.
Connecting an ATM SwitchProbe device to a network segment is a two-step process:
Step 1 Connect the fiber-optic splitter to a network segment.
Step 2 Connect the fiber-optic splitter to an ATM SwitchProbe device.
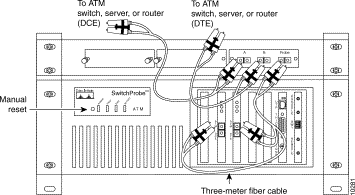
To connect the fiber-optic splitter to the network, see Figure 6-20, and follow these steps:
Step 1 Remove all dust caps from the fiber-optic splitter connector ports.
Step 2 Remove all dust caps from connectors at the ends of the cables you will be using.
Keep these caps for future use.
Step 3 Connect a multimode fiber cable with SC male connectors to an ATM switch, server, or router.
Step 4 Connect the other end of the multimode fiber cable with SC male connectors to the splitter's female SC duplex connector labeled "A."
Step 5 Connect one end of the 24-foot fiber cable (with male SC connectors) to a second ATM switch, server, or router.
Step 6 Connect the other end of the 24-foot, fiber cable to the splitter's female SC duplex connector labeled "B."
You should now have one cable extending from your DCE device to the splitter's "A" connector, and another cable from your DTE device to the splitter's "B" connector.
To connect the fiber-optic splitter to the ATM SwitchProbe device, see Figure 6-20, and follow these steps:
Step 1 Connect the single-duplex end of the four-foot SC duplex multimode fiber cable to the fiber-optic splitter's female SC duplex connector labeled Probe.
The other end of the four-foot SC duplex multimode fiber cable splits into two separate ends. The SC connectors only contain receive (Rx) connections.
Step 2 Connect each end of the cable into the ATM interface cards of the ATM SwitchProbe device as follows:
You can connect a management device to the ATM SwitchProbe device in one of two ways:
The ATM SwitchProbe device supports out-of-band management through the serial port labeled Remote using SLIP or through the Ethernet interface.
You can use the SLIP connection as a secondary connection through which you access all network statistics. The SLIP link is normally used as a backup link when the network is not operational, or when the agent is not accessible.
To perform out-of-band management through the active Ethernet interface, follow these steps:
Step 1 Connect an Ethernet cable to the active Ethernet interface.
Step 2 Configure the interface mode to manage.
The ATM SwitchProbe device supports side-band management (manage and monitor mode on the same interface) through the device's active Ethernet interface.
To make a side-band connection, follow these steps:
Step 1 Connect an Ethernet cable to the active Ethernet interface on the front panel.
Step 2 Configure the interface mode to manage and monitor.
Each ATM interface card contains three LEDs shown in Table 6-7.
| LED | Color | Status | Meaning |
|---|---|---|---|
Top LED | Amber | On | Heavy network traffic. |
Middle LED | Amber | Off (always) | No transmit activity. |
Lower LED | Green | On | A link signal has been detected. |
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Posted: Wed Oct 2 08:43:25 PDT 2002
All contents are Copyright © 1992--2002 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Important Notices and Privacy Statement.