|
|

This chapter describes how to establish global resource monitoring options for the ISM environment. Appropriate procedures are included in the following sections:
 |
Note If you are configuring ISM for the first time, follow the procedures in Chapter 5, "Configuring ISM," in the CiscoWorks Blue Internetwork Status Monitor Installation Guide. |
To enable ISM resource management and interface monitoring, complete the following steps:

The ISM Administration menu panel (Figure 3-2) is displayed.
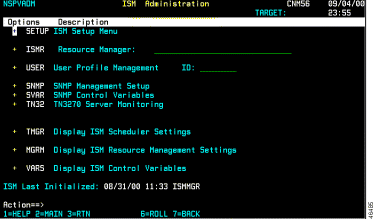
Step 2 Select Setup and press Enter. The ISM Resource Management Setup—First Panel (Figure 3-3) is displayed.
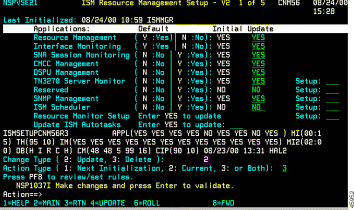
The ISM Resource Management Setup—First Panel contains the following fields:
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
Last Initialized | Indicates the date and time the ISM Resource Manager was last initialized. |
Resource Management | Indicates that resource management is enabled in the ISM interface. This field is always set to Y. |
Interface Monitoring | Indicates whether interface monitoring is enabled. The display columns show the default, initial, and current values. The default setting is Y. |
SNA Session Monitoring | Indicates whether SNA Session Monitoring is enabled in the ISM interface. The display columns show the default, initial, and current values. The default setting is N (not enabled). To fully enable SNA Session Monitoring, you must create SNA Resource Management definitions. |
CMCC Management | Indicates whether CMCC Management is enabled in the ISM interface. The display columns show the default, initial, and current values. The default setting is N (not enabled). See "Monitoring CMCCs," for more details. |
DSPU Management | Indicates whether DSPU Monitoring is enabled in the ISM interface. The display columns show the default, initial, and current values. The default setting is N (not enabled). To fully enable DSPU Session Monitoring, you must create DSPU Resource Management definitions. |
TN3270 Server Monitor | Indicates whether the TN3270 Server Monitor is enabled in the ISM interface. The display columns show the default, initial, and current values. The default setting is N (not enabled). To enable global TN3270 server monitoring, enter YES in the Setup field. See "Monitoring TN3270 Servers," for more details. |
Reserved |
|
SNMP Management | Indicates whether SNMP Management is enabled in the ISM interface. The display columns show the default, initial, and current values associated with SNMP Session options. The default setting is N (not enabled). To enable global SNMP management, enter YES in the Setup field. See "Enabling SNMP Management" section for more details. |
ISM Scheduler | Indicates whether the ISM Scheduler is enabled in the ISM interface. The display columns show the default, initial, and current values associated with scheduling options. The default setting is N (not enabled). To enable global scheduling, enter YES in the Setup field. See "Enabling Resource Monitor Scheduling" section for more details. |
Step 3 Press PF8 to display the ISM Resource Management Setup—Second Panel (Figure 3-4).
 |
Note Press PF4 to save your changes, exit this procedure, and return to the ISM Administration menu panel. |
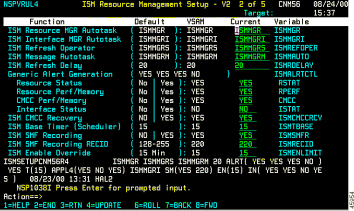
The ISM Resource Management Setup—Second Panel contains the following fields:
| Field | Default Value |
ISM Autotasks | |
ISM Resource MGR Autotask | Defines the default autotask, ISMMGR for the ISM Resource manager. Do not change this value. |
ISM Interface MGR Autotask | ISMMGRI |
ISM Refresh Operator | ISMMGRS |
ISM Message Autotask | ISMMGRM |
ISM Refresh Delay | 20 |
Generic Alert Generation To send generic alerts to NetView's NPDA hardware monitor, enable the alert generation rule for resource status. | |
Resource Status | No |
Resource Perf/Memory | No |
CMCC Perf/Memory | No |
Interface Status | No |
ISM Functions | |
ISM CMCC Recovery | No |
ISM Base Timer (Scheduler) | 15 |
ISM SMF Recording | No If you change the ISM Recording setting to Yes, the ISM SMF Recording RECID field automatically defaults to 220. |
ISM SMF Recording RECID | 220 |
ISM Enable Override | 15 ISM Enable Override setting limits the amount of time (in minutes) that an operator remains in enable mode. If the operator enters enable mode for a router, ISM cannot monitor the router. If the operator remains in enable mode for two monitoring periods, ISM Enable Override removes the operator from enable mode. |
Step 4 Press PF8 to display the ISM Resource Management Setup—Third Panel (Figure 3-5).
 |
Note Press PF4 to save your changes, exit this procedure, and return to the ISM Administration menu panel. |
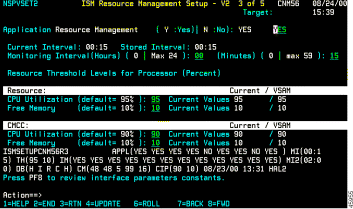
The ISM Resource Management Setup—Third Panel contains the following fields:
| Field | Default Value | ||
Resource Management | Indicates that resource management is enabled in the ISM interface. This field is always set to Y. | ||
Monitoring Intervals | |||
Current Interval | Current resource monitoring interval in hours and minutes. | ||
Stored Interval | Stored resource monitoring interval in hours and minutes. | ||
Monitoring Interval (Hours) and (Minutes) | Specify a new resource monitoring interval in hours and minutes.
| ||
Resource Thresholds | |||
CPU Utilization | Specify a new CPU utilization threshold for a resource, as a two-digit percentage. For example, enter 80 to enter a new threshold of 80%. Enter 00 to suspend CPU utilization threshold monitoring for a resource. | ||
Free Memory | Specify a new free memory threshold for a resource, as a two-digit percentage. For example, enter 20 to enter a new threshold of 20%. Enter 00 to suspend free memory monitoring for a resource. | ||
CMCC Thresholds | |||
CPU Utilization | Specify a new CPU utilization threshold for a CMCC resource, as a two-digit percentage. For example, enter 80 to enter a new threshold of 80%. Enter 00 to suspend CPU utilization threshold monitoring for a CMCC resource. | ||
Free Memory | Specify a new free memory threshold for a CMCC resource, as a two-digit percentage. For example, enter 20 to enter a new threshold of 20%. Enter 00 to suspend free memory threshold monitoring for a CMCC resource. | ||
Step 5 Press PF8 to display the ISM Resource Management Setup—Fourth Panel (Figure 3-6).
 |
Note Press PF4 to save your changes, exit this procedure, and return to the ISM Administration menu panel. |
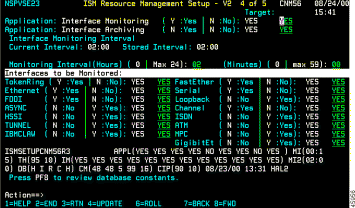
The ISM Resource Management Setup—Fourth Panel contains the following fields:
| Field | Default Value | ||
Interface Monitoring | Enables or disables interface monitoring for all resources. | ||
Interface Archiving | Enables or disables interface archiving for all resources. | ||
Monitoring Intervals | |||
Current Interval | Current interface monitoring interval in hours and minutes. | ||
Stored Interval | Stored interface monitoring interval in hours and minutes. | ||
Monitoring Interval (Hours) and (Minutes) | Specify a new interface monitoring interval in hours and minutes.
| ||
Interfaces | |||
TokenRing | Indicates whether Token Ring interfaces are to be monitored. The default setting is YES (monitor Token Ring interfaces). | ||
Ethernet | Indicates whether Ethernet interfaces are to be monitored. The default setting is YES (monitor Ethernet interfaces). | ||
FDDI | Indicates whether FDDI interfaces are to be monitored. The default setting is YES (monitor FDDI interfaces). | ||
ASYNC | Indicates whether Asynchronous interfaces are to be monitored. The default setting is NO (do not monitor Asynchronous interfaces). | ||
HSSI | Indicates whether HSSI interfaces are to be monitored. The default setting is NO (do not monitor HSSI interfaces). | ||
Tunnel | Indicates whether Tunnel interfaces are to be monitored. The default setting is NO (do not monitor Tunnel interfaces). | ||
IBMCLAW | Indicates whether IBM CLAW interfaces are to be monitored. The default setting is NO (do not monitor IBM CLAW interfaces). | ||
FastEther | Indicates whether FastEthernet interfaces are to be monitored. The default setting is YES (monitor FastEthernet interfaces). | ||
Serial | Indicates whether Serial interfaces are to be monitored. The default setting is YES (monitor Serial interfaces). | ||
Loopback | Indicates whether Loopback interfaces are to be monitored. The default setting is NO (do not monitor Loopback interfaces). | ||
Channel | Indicates whether Channel interfaces are to be monitored. The default setting is YES (monitor Channel interfaces). | ||
ISDN | Indicates whether ISDN interfaces are to be monitored. The default setting is NO (do not monitor ISDN interfaces). | ||
ATM | Indicates whether ATM interfaces are to be monitored. The default setting is NO (do not monitor ATM interfaces). | ||
MPC | Indicates whether Multiprotocol (MPC) Point-to-Point interfaces are to be monitored. The default setting is NO (do not monitor MPC interfaces). | ||
GibabitEt | Indicates whether GigabitEthernet interfaces are to be monitored. The default setting is NO (do not monitor GigabitEthernet interfaces). | ||
Step 6 Press PF8 to display the Resource Management Constants Setup panel (Figure 3-7).
 |
Note Press PF4 to save your changes, exit this procedure, and return to the ISM Administration menu panel. |
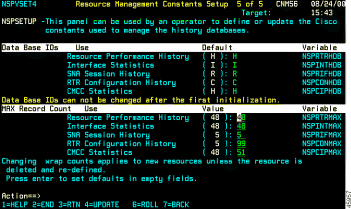
The Resource Management Constants Setup panel contains the following fields:
| Field | Default Value | ||
Data Base IDs
| |||
Resource Performance History | VSAM database ID used by ISM for global resource performance history data. | ||
Interface Statistics | VSAM database ID used by ISM for global interface statistics. | ||
SNA Session History | VSAM database ID used by ISM for global SNA session history data. | ||
AIX Configuration History | VSAM database ID used by ISM for global AIX Configuration history data. | ||
CMCC Statistics | VSAM database ID used by ISM for global CMCC statistics data. | ||
MAX Record Count
| |||
Resource Performance History | Maximum number of records the database can contain before overwriting router performance history data. | ||
Interface Statistics | Maximum number of records the database can contain before overwriting interface statistics. | ||
SNA Session History | Maximum number of records the database can contain before overwriting SNA session history data. | ||
RTR Configuration History | Maximum number of records the database can contain before overwriting router configuration history data. | ||
CMCC Statistics | Maximum number of records the database can contain before overwriting CMCC statistics. | ||
Step 7 Press PF4 to save your changes, exit this procedure, and return to the ISM Administration menu panel.
To enable SNMP Management, use one of the following procedures:

The SNMP Management Setup for ISM panel contains the following fields:
| Function | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
SNMP Monitoring Operator | SNMPMGR | Main SNMP autotask. It initializes and monitors SNMP. |
SNMP Message autotask | SNMPOPER | Monitors SNMP related messages, processes SNMP traps, and performs recovery for the SNMP interface. |
SNMP TRAP Monitoring | YES | Not Required. |
SNMP PING Monitoring | NO | Not Required. |
Generic Alert Generation | NO | Not Required. |
Community Name | public | Default community name used by the SNMP manager when adding a new resource to ISM. |
Default Mask | 255.255.255.0 | Default mask used by the SNMP manager when adding a new resource to ISM. |
PING Monitoring Interval | 00:00 | Reserved. |
Recovery Interval | 00:00 | Reserved. |
TCP/IP OS/390 Task Name |
| Enter the TCP/IP task name with which to interface with NetView. This name is used to verify that TCP/IP is running. |
Local IP Address |
| Enter the IP address of the TCP/IP with which to interface with NetView. The SNMP manager autotask uses this IP address to verify a working SNMP connection between TCP/IP and NetView. |
To enable the ISM Scheduler, complete the following steps:

Step 2 On the ISM Schedule Setup panel, under the Group ID column, type the name of a resource group.
Step 3 A monitoring interval is the time that an assigned autotask waits before collecting resource and interface statistics for a selected resource group.
To specify monitoring intervals, enter the number of 15-minute increments in the Resource Mon. and Interface Mon. fields. For example, to specify an interval of 60 minutes, enter 4.
Step 4 To assign an autotask to a resource group in the AUTOTASK field, enter the name of the ISM autotask member that you want to use to manage the corresponding group of resources.
To remove an autotask monitoring schedule, enter D in the Delete field beside the resource group ID.
Step 5 Press PF4 to save your changes.
To view a list of all the users defined to ISM, issue the ismusers command. The ISM Authorized Users panel is displayed (Figure 3-11). To modify a users profile, change the profile options and press PF4 to update.
For more information on defining ISM user profiles, see Chapter 5, "Configuring ISM," in the CiscoWorks Blue Internetwork Status Monitor Installation Guide.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Posted: Sat Oct 7 16:36:57 PDT 2000
Copyright 1989-2000©Cisco Systems Inc.