|
|

This chapter describes the system maintenance and monitoring capabilities available in the element management system (EMS), and includes the following sections:
EMS provides the following information about your NE, its plugin cards, and EMS:
To view the version of EMS software currently running on a workstation, select Help > Version from either Cisco 6700 NetView or Cisco 6700 NodeView. EMS displays the date and release number of the software in use.
Step 2 Double-click the node nameplate to launch the NE provision window. (See Figure 16-1.)
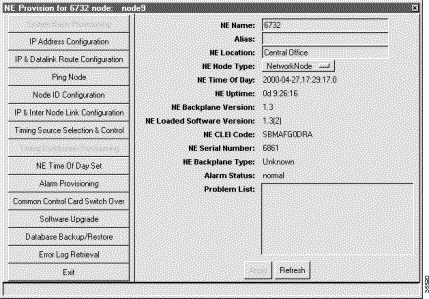
Information provided includes:

Step 2 In the drop-down Card ID menu, select a card to display that card's information, which includes:
The Cisco 6732 metallic test access card (MTAC) offers an EIA/TIA-232 interface (the older but more widely recognized term "RS-232" is used in this chapter) for local access through an EMS workstation. See the application note RS-232 Connection for the workstation provisioning procedure.
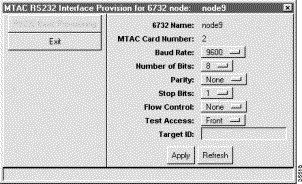
Step 2 Set the following parameters:
Step 3 Click Apply to provision the MTAC RS-232interface.
 |
Note You cannot provision an MTAC RS-232 port on a Cisco 6705 or Cisco IAD1101. |
The Ethernet port on the Cisco IAD1101 and on the Cisco 6705 main control card (MCC) can be shut down to secure the NE and prevent unauthorized system access.
 |
Caution Placing the Ethernet port out of service should only be performed after all provisioning is complete. You cannot communicate with the NE if this port is disabled, and a solid inter node data link (INDL) has not been established between the NE in question and a remote NE. |
Before disabling the Ethernet port, Cisco Systems recommends backing up the NE database so you can retrieve and use the information if any system difficulties occur. (See "Backing Up the System Database".)

Step 2 Set the Admin Status of the Ethernet port to OutOfService.
Step 3 Click Apply to put the Ethernet port out of service. EMS displays a warning message. (See Figure 16-5.)
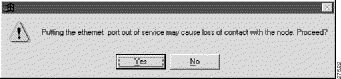
Step 4 Click Yes to disable the Ethernet port.
 |
Caution The Ethernet port remains inoperable until you send a remote instruction from an EMS workstation using an INDL to place the port back in service. |
Performance monitoring is the action of collecting data on the signal over a period of time to detect degradations in the section, line, or path. The parameters that are collected are based on signal integrity, number of protection switches, and number of failures.
All Cisco 6700 Series line interface modules are synchronized to Greenwich Mean Time (GMT), rather than the "Time of Day" setting on the EMS workstation. One-day performance monitoring (PM) tests use GMT, not the EMS time of day, to determine the start and end times of the 24-hour monitoring window.
Table 16-1 through Table 16-6 show the codes for monitoring degradations on sections, lines and paths.
| PM Code | Definition | Description |
|---|---|---|
CV-L | Coding violation - line | The count of BPVs and EXZs occurring over the accumulation period. An EXZ increments the CV-L by one, regardless of the length of the zero string. For a B8ZS-coded signal, BPVs that are part of the zero substitution code are excluded from the count. |
ES-L | Errored second - line | The count of seconds during which one or more of the following has occurred: BPVs, EXZs and LOSs. For a B8ZS-coded signal, BPVs that are part of the zero substitution code are excluded. |
SES-L | Severely errored second - line | The count of seconds during which 1,544 or more BPVs or EXZs, or one or more LOS defects, have occurred. |
CV-P | Coding violation - path | For DS1-ESF paths, this parameter is a count of detected CRC-6 defects. For DS1-SF Paths, this parameter is a count of defected FEs. |
CSS-P | Controlled slip second - path | Only applies to DS1 extensions and Multiple Interface Group Features. This parameter is a count of seconds during which a CS has occurred. Counts of CSs can be accurately made only in the NE of the DS1 signal where the CS took place. |
ES-P | Errored second - path | For DS1-ESF, this parameter is a count of one-second intervals containing one or more CRC-6 errors or one or more CS events, or one or more SEF or AIS defects. In the case of DS1 SF, this parameter is a count of one second intervals containing one or more FE events, or one or more CS events, or one or more SEF or AIS defects. |
FC-P | Failure count - path | The number of LOS/LOF/AIS-L (near-end) or RDI-L (far-end) failures. Count is incremented only when the failure goes from off to on. |
PSC-P | Protection switch count - path | The number of switches between working and protect fibers when in 1+1 linear mode. |
PSD-P | Protection switch duration - path | The number of seconds that the facility has been on the protection fiber. Only applicable if revertive line switching is used. |
SAS-P | Severely errored frame/alarm indication signal - path | The number of seconds containing one or more SEFs, or one or more AIS defects. |
SES-P | Severely errored second - path | For DS1-ESF paths, this parameter is a count of seconds during which at least one of the following has occurred: 320 or more CRC-6 errors, or one or more SEF or AIS defects. For DS1-SF paths, an SES is a second containing the occurrence of eight FEs (if both Ft and Fs bits are considered), four FEs (if only Ft bits are considered), or one or more SEF or AIS defects. |
SEFS-P | Severely errored frame second - path | A count of seconds containing one or more SEFs, or one or more AIS defects. |
UAS-P | Unavailable second - path | A count of one-second intervals during which the DS1 path is unavailable. A DS1 path is said to be unavailable at the onset of 10 contiguous SESs. The 10 SESs are included in unavailable time. Once unavailable, the DS1 path becomes available at the onset of 10 consecutive seconds with no SESs. The 10 seconds with no SESs are excluded from unavailable time. |
| PM Code | Definition | Description |
|---|---|---|
CV-S | Coding violation - section | Coding Violation - Count of B1 BIP-8 violations. |
ES-S | Errored second - section | Number of seconds that at any time during the second either at least one BIP error occurred, or an SEF/LOS was present. |
SES-S | Severely errored second - section | Number of seconds during which 155 or more BIP errors occurred or an SEF/LOS was present. |
SEFS-S | Severely errored frame second - section | Number of seconds during which an OOF/LOS occurred. |
| PM Code | Definition | Description |
|---|---|---|
CV-L | Coding violation - line | Count of B2 BIP-8 violations. |
ES-L | Errored second - line | Number of seconds that at any time during the second either at least one BIP error occurred, or an SEF/LOS/AIS-L was present. |
SES-L | Severely errored second - line | Number of seconds during which 154 or more BIP errors occurred or an SEF/LOS/AIS-L was present. |
UAS-L | Unavailable second - line | Number of seconds that a line is unavailable. A line is unavailable when 10 consecutive SESs have been detected, and begins at the beginning of the SES sequence (back in time). It is cleared at the beginning of 10 nonSESs. |
FC-L | Failure count - line | Number of LOS/LOF/AIS-L failures. Count is incremented only when the failure goes from off to on. |
PSC | Protection switch count - line | Number of switches between working and protect fibers when in 1+1 linear mode. |
PSD | Protection switch duration - line | Number of seconds that the facility has been on the protection fiber. Only applicable if revertive line switching is used. |
| PM Code | Definition | Description |
|---|---|---|
CV-L | Coding violation - | Count of B2 BIP-8 violations at the far-end. This is carried in the Remote Error Indicator (REI) overhead byte. |
ES-L | Errored second - | Number of seconds that at any time during the second either at least one REI error occurred or an RDI-L was present. |
SES-L | Severely errored second - far-end line | Number of seconds during which 154 or more REI errors occurred or an RDI-L was present. |
UAS-L | Unavailable second - far-end line | Same as the near-end, except it is based on SES-FE. |
FC-L | Failure count - | Same as the near-end, but counts RDI-L failures. |
| PM Code | Definition | Description |
|---|---|---|
CV-P | Coding violation - path | Count of B3 BIP-8 violations. |
ES-P | Errored second - path | Number of seconds that at any time during the second either at least one BIP error occurred, or an SEF/LOS/AIS-L/AIS-P/LOP was present. |
SES-P | Severely errored second - path | Number of seconds during which 2400 or more BIP errors occurred, or an SEF/LOS/AIS-L/AIS-P/LOP was present. |
UAS-P | Unavailable second - path | Number of seconds that a line is unavailable. A line is unavailable when 10 SESs have been detected, and begins at the beginning of the SESs (back in time). It is cleared at the beginning of 10 nonSESs. |
FC-P | Failure count - path | Number of LOS/LOF/AIS-L/AIS-P/LOP failures. Count is incremented only when the failure goes from off to on. |
| PM Code | Definition | Description |
|---|---|---|
CV-P | Coding violation - far-end path | Count of B3 BIP-8 violations at the far-end. This is carried in the remote error indicator (REI) overhead byte. |
ES-P | Errored second - | Number of seconds that at any time during the second either at least one REI error occurred, or an RDI-P was present. |
SES-P | Severely errored second - far-end path | Number of seconds during which 2400 or more REI errors occurred, or an RDI-P was present. |
UAS-P | Unavailable second - far-end path | Same as the near-end except it is based on SES-FE. |
FC-P | Failure count - far-end path | Same as the near-end, but counts RDI-P failures. |
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Posted: Mon Feb 5 13:08:10 PST 2001
All contents are Copyright © 1992--2001 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Important Notices and Privacy Statement.