|
|

This chapter provides general information for troubleshooting hardware faults during installation of the Cisco 6400 carrier-class broadband aggregator. For information about troubleshooting the software, refer to the Cisco 6400 Software Setup Guide.
This chapter includes the following sections:
If you encounter a problem after you have installed the Cisco 6400, you should perform a few basic troubleshooting procedures on your equipment before contacting customer service. These simple checks involve answering the following questions:
 |
Note Check the release notes for more information on how to solve problems. Release notes can be found on Cisco.com. See the "Obtaining Documentation" section. |
Refer to the following materials:
To perform general maintenance and troubleshooting tasks on the Cisco 6400, you should have the following:
Figure 4-1 is a flowchart to help you determine which component of your Cisco 6400 has malfunctioned. The decimal numbers in the following figure refer to the sections in this chapter where the various system elements are discussed.
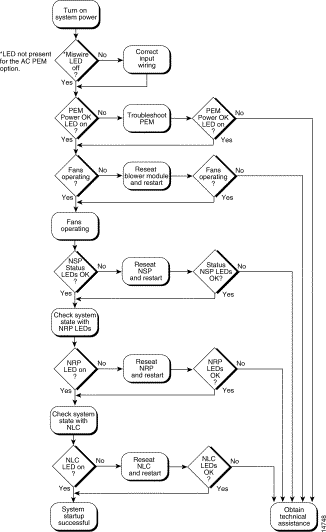
If an error is detected during a system powerup or hardware reset, the red NSP STATUS LED lights. The watchdog timer or software warm-start functions may run minimum diagnostics.
If any failures occur during the power-on sequence, forward a copy of the output to the Cisco technical assistance center (TAC) for diagnosis. To contact TAC, refer to the "Obtaining Technical Assistance" section
Use the show hardware command to display the hardware components installed. These components can include:
The following example shows output from the show hardware command (this is only a sample; your output will not match exactly):
Switch# show hardware
6400 named santa-2a-16, Date: 23:29:23 UTC Tue Jan 4 2000
Feature Card's FPGA Download Version: 0
Slot Ctrlr-Type Part No. Rev Ser No Mfg Date RMA No. Hw Vrs Tst EEP
8/0 155SM NLC 73-2890-02 02 09691183 Jul 20 98 00-00-00 1.0 0 2
1/1 155SM NLC 73-2892-02 02 09591457 Jul 20 98 00-00-00 1.0 0 2
0/0 CPU card 73-2996-02 02 09165973 Jul 20 98 00-00-00 2.0 0 2
0/1 FC-PFQ 73-2281-04 A0 08783319 Apr 25 98 00-00-00 4.1 0 2
DS1201 Backplane EEPROM:
Model Ver. Serial MAC-Address MAC-Size RMA RMA-Number MFG-Date
------- ---- -------- ------------ -------- --- ---------- -----------
C6400 2 100001 00107BA9C600 128 0 0 Jul 20 1998
Use the show version and show environment commands to display the following Cisco 6400 information:
Example
The following example shows output of the show version command (this is only a sample; your output will not match exactly):
Switch# show version
Cisco Internetwork Operating System Software
IOS (tm) 6400 Software (c6400r-g4p5-mz), Version 12.0(5)DC.......
Copyright (c) 1986-1999 by cisco Systems, Inc.
Compiled Tue 07-Oct-99 04:53 by jdoe
Image text-base: 0x60010910, data-base: 0x604E6000
ROM: System Bootstrap, Version XX.X(X.X.WAX.0) [integ 1.4.WAX.0], RELEASE SOFTWARE
Switch uptime is 2 weeks, 2 days, 39 minutes
System restarted by power-on
System image file is "bootflash:6400-wp-mz.112-8.0.1.FWA4.0.16", booted via bootflash
cisco NSP (R4700) processor with 65536K bytes of memory.
R4700 processor, Implementation 33, Revision 1.0
Last reset from power-on
1 Ethernet/IEEE 802.3 interface(s)
20 ATM network interface(s)
123K bytes of non-volatile configuration memory.
8192K bytes of Flash internal SIMM (Sector size 256K).
Configuration register is 0x2101
Switch#
Example
The following example shows output of the show environment command (this is only a sample; your output will not match exactly):
Switch# show environment
Temperature normal:chassis inlet measured at 27C/80F
Temperature normal:chassis core measured at 33C/91F
Fan: OK
Power Entry Module 0 status: OK
Switch#
Configuration problems generally develop when the system is first installed, when the system configuration is changed, or when new equipment is added to the network and is not configured properly.
You should carefully review the port configuration information contained in your site log records, and verify that the physical equipment configuration matches the internal software configuration. By reviewing the port configuration information, you can determine whether any changes are needed to equipment and cabling in the central office or outside plant facilities.
Electrical problems are divided into two categories:
Site electrical problems can include:
Cisco 6400 electrical problems can include:
The Cisco 6400 powers down when the temperature exceeds a specified threshold. If that happens, you should identify and correct the cause of the overheating before repowering the system.
If the blower module is unplugged for two minutes, the Cisco 6400 powers down automatically.
Signal input and output problems can occur at any point in the network and can be caused by mechanical defects in the cables, poor connections, or lack of signal caused by other equipment failures.
Refer to your site log and other facility records to check signal connections for your facility.
You can use the ping command to confirm network connections between the switch and another node on the network. The ping command sends Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) echo request packets out, and receives a confirmation if the connection is good. The ping command format is:
ping host [packet_size] [packet_count]
An optical signal I/O problem can be caused by:
The power budget (PB) is the maximum possible amount of power transmitted. The following equation shows the calculation of the power budget:
PB = PTmin - PRmin
Where:
PTmin = Minimum transmitter power
PRmin = Minimum receiver sensitivity
Insufficient power budget occurs when the power margin (PM) is less than 0. PM is equal to the power budget minus the link loss (LL).
PM = PB - LL
Three factors contribute to link loss:
 |
Note These are typical values; refer to the manufacturer's documentation for the actual values. |
Receiver overload can occur when (PRmax - (PTmax - LL)) is less than 0, where PRmax is maximum receiver power and PTmax is maximum transmitter power. To prevent overloading the receiver, you can use an attenuator on the link between any single-mode SONET transmitter and the receiver. Doing so should increase the value of LL.
 |
Note Refer to "System Specifications" for fiber-optic power levels for the OC-3/STM-1 and the OC-12/STM-4 NLCs. |
If an Ethernet connection on your Cisco 6400 fails to work properly, and the corresponding LNK (Link) LED is not lit (steady green), check for the following problems:
If the LNK LED is lit (steady green), but the Ethernet port does not seem to be working properly, make sure that the port in question is configured properly and is not administratively shut down. If you have a working console connection, complete the following steps:
Switch> configure terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
Switch(config-if)# int eth0/0/0
Switch(config-if)# no shut
Switch(config-if)# exit
Switch(config)# exit
Switch#
Step 2 Check that the Ethernet port in question has a valid IP address assigned to it.
For more information about configuring Ethernet ports, refer to the Cisco 6400 Software Setup Guide.
If the cable, connections, power, and configuration all check out, and you still cannot connect to the Ethernet port on the module, replace the module in question. If the problem persists, contact Cisco TAC for further assistance. See the "Obtaining Technical Assistance" section.
If the console screen connected to a Cisco 6400 console port appears frozen or fails to work properly, check for the following problems:
Information about the Cisco 6400 field-replaceable units (FRUs) is given in the following sections:
All Cisco 6400 FRUs are hot swappable. Procedures for removing and replacing the FRUs can be found in the Cisco 6400 Installation and Replacement of Field-Replaceable Units.
Table 4-1 lists general FRU fault symptoms and recommendations.
| Symptom | Recommended Action |
|---|---|
System fails to come up. | 1. Check the STATUS LEDs on all modules and cards, and the power LEDs on the PEMs. If none are on, see Table 4-14 (DC PEM) and Table 4-16 (AC PEM). 2. If the system has power, check the FAIL LED on the NSP. If the FAIL LED is steady yellow, see Table 4-3. 3. Check the blower module and ensure that it is fully inserted. 4. Ensure that all FRUs are properly inserted. |
System experiences a critical alarm. (Critical LED on NSP lights yellow.) | Enter the show facility-alarm status command at the console. |
System experiences a major alarm. (Major LED on NSP lights yellow.) | Enter the show facility-alarm status command at the console. |
System experiences a minor alarm. (Minor LED on NSP lights yellow.) | Enter the show facility-alarm status command at the console. |
You cannot establish a console or Telnet connection to the system. | For information about troubleshooting Ethernet connections, refer to the "Ethernet Connections" section. For information about troubleshooting the console port serial connections, refer to the "Console Port Serial Connections" section. |
System overheats. | Troubleshoot the blower module (Table 4-12). |
System experiences a power problem. | Troubleshoot the PEM(s), referring to the PEM section of this table and to Table 4-14 (DC PEM) and Table 4-16 (AC PEM). |
Figure 4-2 shows the NSP indicators and connectors on the faceplate.
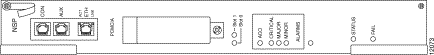
Table 4-2 describes the LEDs on the NSP faceplate.
| LED | Status | Condition |
|---|---|---|
STATUS | Steady yellow | Cisco IOS is not running. |
FAIL | Yellow | NSP has failed. |
| ETH | ||
ACT (Activity) | Green | Packets are being transmitted and received. |
LNK (Link) | Steady green | Port is operational. |
PCMCIA Slot 0 PCMCIA Slot 1 | Steady green Steady green | Slot is active. Slot is active. |
| ALARMS | ||
CRITICAL | Yellow | Alarm is active. |
MAJOR | Yellow | Alarm is active. |
MINOR | Yellow | Alarm is active. |
Table 4-3 lists the NSP fault indications and recommended actions.
| Symptom | Recommended Action |
STATUS LED is not lit. | 1. Check LEDs on other modules and cards. If none are lit, refer to Table 4-13 and Table 4-15. 2. If LEDs on other modules and cards are lit, remove the card from its slot and check for bent or broken pins on the backplane. Return the card to its slot and screw it firmly into place. 3. Replace the card. Note You can store a node's software and configuration files in NVRAM and on a PCMCIA Flash card. If the files are stored on a PCMCIA card, you can move the PCMCIA card from the faulty NSP to the replacement NSP before you install the replacement NSP. This enables the new NSP to initialize itself without resetting other cards. If the new NSP must read the chassis configuration from NVRAM, it resets all the cards in the chassis. Refer to Cisco 6400 Installation and Replacement of Field-Replaceable Units for complete instructions on replacing NSPs and other cards. 4. If the problem persists, contact Cisco TAC. |
FAIL LED is yellow, indicating that the NSP failed. | Reinsert the NSP. If the problem persists, contact Cisco TAC. Refer to the "Obtaining Technical Assistance" section. |
The NSP comes up, but you cannot establish a console or Telnet connection to the system. | 1. Ensure that the terminal settings are properly set. For information about terminal settings, refer to the "Connecting a Terminal to the Console Port" section. 2. If you still cannot connect, check the console cable. Is it firmly connected? Is it the right kind of cable with proper connectors? Refer to "Hardware Description" to check pinouts. 3. If the cable checks out and you cannot connect to the NSP, reinsert the module. If the problem persists, replace the NSP. 4. If you achieve a console connection, enter: Switch> configure terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line.
End with CNTL/Z.
Switch(config-if)# int eth0/0/0
Switch(config-if)# no shut
Switch(config-if)# exit
Switch(config)# exit
Switch#
5. Enter show log to review console messages recorded in the system log. |
Card cannot be fully inserted into its slot. | Ensure that you are using slot 0A or 0B for the NSP module. |
Figure 4-3 shows the NRP-1 indicators and connectors on the faceplate.
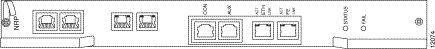
Table 4-4 describes the LEDs on the NRP-1 faceplate.
| LED | Status | Condition |
|---|---|---|
STATUS | Steady green | NRP-1 is active (primary). |
FAIL | Steady yellow | NRP-1 has failed. |
| ETH | ||
ACT (Activity) | Blinking green | Packets are being transmitted and received. |
LNK (Link) | Steady green | Port is operational. |
| FE | ||
ACT (Activity) | Blinking green | Packets are being transmitted and received. |
LNK (Link) | Steady green | Port is operational. |
Table 4-5 lists the NRP-1 module fault indications and recommended actions.
| Symptom | Recommended Action |
STATUS LED is not lit. | 1. Check LEDs on other modules. If none are lit, see Table 4-13 (DC PEM) and Table 4-15 (AC PEM). 2. If power LEDs on other modules and cards are lit, reinsert the NRP. 3. If the problem persists, replace the module or contact Cisco TAC. |
FAIL LED is yellow, indicating that the NRP failed. | Reinsert the NRP. If the problem persists, contact |
Module cannot be fully inserted into its slot. | Inspect connectors on both the card and the backplane, looking for bent pins or other damage. Use slots 1 to 8 (slots 0A and 0B are reserved for NSP modules). |
Module experiences problems in one slot but operates normally in another. | Contact Cisco TAC. |
Figure 4-4 shows the NRP-2SV indicators and connectors on the faceplate.

 |
Warning Class 1 laser product. To see translations of this warning, refer to the Regulatory Compliance and Safety Information document that accompanied this device. |
 |
Warning Invisible laser radiation present. To see translations of this warning, refer to the Regulatory Compliance and Safety Information document that accompanied this device. |
 |
Warning Because invisible radiation may be emitted from the aperture of the port when no fiber cable is connected, avoid exposure to radiation and do not stare into open apertures. To see translations of this warning, refer to the Regulatory Compliance and Safety Information document that accompanied this device. |
| |
Varning! | Osynlig laserstrålning när denna del är öppen och förregleringen är urkopplad. Rikta inte blicken in mot strålen. |
| |
Varoitus | Alleviates ja suojalukitus ohitettaessa olet alttiina näkymättömälle lasersäteilylle. Äjä katso säteeseen. |
The LEDs on the NRP-2SV indicate port and module status (Table 4-6).
| LED | Status | Condition |
|---|---|---|
STATUS | Steady green | NRP-2SV is active. |
FAIL | Steady yellow | NRP-2SV has failed. |
| GBIC | ||
TX | Blinking green | Packets are being transmitted. |
RX | Blinking green | Packets are being received. |
LNK | Steady green | Port is operational. |
The NRP-2SV faceplate also has a four-digit alphanumeric display that indicates status information and error codes.
Figure 4-5 shows the OC3/STM-1 single-mode NLC indicators and connectors on the faceplate.
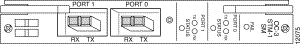
Figure 4-6 shows the OC3/STM-1 multimode NLC indicators and connectors on the faceplate.
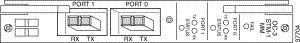
 |
Warning Class 1 laser product. To see translations of this warning, refer to the Regulatory Compliance and Safety Information document that accompanied this device. |
 |
Warning Invisible laser radiation present. To see translations of this warning, refer to the Regulatory Compliance and Safety Information document that accompanied this device. |
 |
Warning Because invisible radiation may be emitted from the aperture of the port when no fiber cable is connected, avoid exposure to radiation and do not stare into open apertures. To see translations of this warning, refer to the Regulatory Compliance and Safety Information document that accompanied this device. |
| |
Varning! | Osynlig laserstrålning när denna del är öppen och förregleringen är urkopplad. Rikta inte blicken in mot strålen. |
| |
Varoitus | Alleviates ja suojalukitus ohitettaessa olet alttiina näkymättömälle lasersäteilylle. Äjä katso säteeseen. |
Figure 4-7 shows the DS3 NLC indicators and connectors on the faceplate.

Table 4-7 describes the LEDs on the OC-3/STM-1 and DS3 NLC faceplates.
Table 4-8 lists the OC-3/STM-1 and DS3 NLC fault indications and recommended actions.
| Symptom | Recommended Action |
|---|---|
STATUS LED is not lit. | 1. Check LEDs on other cards. If none are lit, see Table 4-14. 2. If LEDs on other cards are lit, remove the card from its slot and check for bent or broken pins on both the card and the backplane. Return the card to its slot and screw it firmly into place. 3. Replace the card. 4. If the problem persists with a new card, contact |
FAIL LED is lit. | 1. Check STATUS LED on the NSP, if it is not lit, refer to the "NSP Module Faults" section. 2. Reinsert the NLC. If the FAIL LED lights up, replace the NLC. 3. If the problem persists, contact Cisco TAC. |
Interface fails to come up. | 1. Enter the command show int atm slot/sub-slot/port. The results tell you about the interface status. If the trunk is administratively down, use the no shut config command to bring it up. 2. Use the loopback command to run an OC-3/DS3 loopback test. If the card fails the loopback test, reinsert the card. Refer to Cisco 6400 Command Reference for more information about the loopback command. 3. If your cable is too long or if your optical signal passes through too many connectors, signal attenuation will cause signal quality problems. Check cable length and number of connectors. 4. Check that the transmit (TX) and receive (RX) connectors are not reversed on the NLC. 5. Check optical connectors for damage or for scratches on the optical surface. Replace connectors if necessary. 6. Check optical connectors for dirt on the optical surface. If a connector is dirty, clean it by blowing compressed air from a distance of 3 inches (8 cm). You can also clean the connectors on most cables with an alcohol-moistened, lint-free wipe. Check the cable manufacturer cleaning instructions first.
7. For more information about fiber optic connections, refer to the "Fiber-Optic Connections" section. |
Card cannot be fully inserted into its slot. | 1. Visually inspect connectors on both the card and the backplane, looking for bent pins or other damage. 2. Ensure the full-height NLC carrier is properly inserted and fastened. |
Figure 4-8 shows the OC-12/STM-4 NLC indicators and connectors on the faceplate.

 |
Warning Class 1 laser product. To see translations of this warning, refer to the Regulatory Compliance and Safety Information document that accompanied this device. |
 |
Warning Invisible laser radiation present. To see translations of this warning, refer to the Regulatory Compliance and Safety Information document that accompanied this device. |
 |
Warning Because invisible radiation may be emitted from the aperture of the port when no fiber cable is connected, avoid exposure to radiation and do not stare into open apertures. To see translations of this warning, refer to the Regulatory Compliance and Safety Information document that accompanied this device. |
| |
Varoitus | Alleviates ja suojalukitus ohitettaessa olet alttiina näkymättömälle lasersäteilylle. Äjä katso säteeseen. |
| |
Varning! | Osynlig laserstrålning när denna del är öppen och förregleringen är urkopplad. Rikta inte blicken in mot strålen. |
Table 4-9 describes the LEDs on the OC-12/STM-4 NLC faceplate.
| LED | Status | Condition |
|---|---|---|
FAIL | Steady yellow | OC-12/STM-4 NLC failed |
TX (transmit) | Green | Transmit activity |
RX (receive) | Green | Receive activity |
STATUS | Green | Active (primary) |
Table 4-10 lists the OC-12/STM-4 NLC fault indications and recommended actions.
| Symptom | Recommended Action |
|---|---|
STATUS LED is not lit. | 1. Check LEDs on other cards. If none are lit, see Table 4-14 (DC PEM) and Table 4-15 (AC PEM). 2. If LEDs on other cards are lit, remove the card from its slot and check for bent or broken pins on both the card and the backplane. Return the card to its slot and screw it firmly into place. 3. Replace the card. 4. If the problem persists with a new card, contact |
FAIL LED is lit. | 1. Check STATUS LED on the NSP, if it is not lit, refer to 2. Reinsert the NLC. If the FAIL LED is lit, replace the NLC. 3. If the problem persists, contact Cisco TAC. |
Interface fails to come up. | 1. Enter the command show int atm slot/sub-slot/port. The port will always be 0. The results tell you about the interface status. If the trunk is administratively down, use the no shut config command to bring it up. 2. Use the loopback command to run an OC-12 loopback test. If the card fails the loopback test, reinsert the card. Refer to Cisco 6400 Command Reference for more information about the loopback command. 3. If your cable is too long or if your optical signal passes through too many connectors, signal attenuation will cause signal quality problems. Check cable length and number of connectors. 4. Check that the transmit (TX) and receive (RX) connectors are not reversed on the NLC. 5. Check optical connectors for damage or for scratches on the optical surface. Replace connectors if necessary. 6. Check optical connectors for dirt on the optical surface. If a connector is dirty, clean it by blowing compressed air from a distance of 3 inches (8 cm). You can also clean the connectors on most cables with an alcohol-moistened, lint-free wipe. Check the cable manufacturer cleaning instructions first.
7. For more information about fiber optic connections, refer to the "Fiber-Optic Connections" section. |
Card cannot be fully inserted into its slot. | 1. Visually inspect connectors on both the card and the backplane, looking for bent pins or other damage. 2. Ensure the full-height NLC carrier is properly inserted and fastened. |
 |
Note Because the OC-12 has a single port, a second OC-12 module is required for an exernal loopback test. Contact Cisco TAC for more information. |
Figure 4-9 shows the blower module front panel and its indicators.
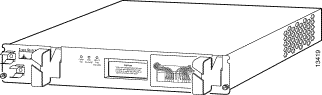
Table 4-11 describes the blower module LEDs located on the front center panel.
| LED | Status | Condition |
|---|---|---|
Steady green | Fans are operational. | |
SINGLE FAN FAILURE | Steady yellow | Failure has occurred and alarms are triggered. |
MULTI-FAN FAILURE | Steady yellow | Redundant fan has failed and the system will shut down. |
Table 4-12 lists the blower module fault indications and recommended action.
| Symptom | Recommended Action |
Green LED on blower module fails to go on. | 1. Make sure the blower module is fully inserted into the chassis. 2. Check input power connections. If connections are loose or reversed, the chassis does not receive power and fans do not run. 3. Replace the blower module. |
1. Make sure that all intake and exhaust vents on the front and rear of the chassis are free of blockages. 2. Make sure that the ambient temperature and other environmental factors in the system area are within the ranges specified in "System Specifications." 3. Make sure all cards and blank faceplates are in place. The cooling system cannot operate effectively unless the chassis is fully enclosed. 4. Check the air filter, and if necessary clean or replace it. 5. Reduce the ambient temperature. |
Figure 4-10 shows the DC PEM and its indicators.
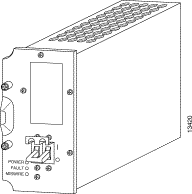
Table 4-13 describes the DC PEM LEDs located on the bottom front panel.
| LED | Status | Condition |
|---|---|---|
POWER | Steady green | Power is available. |
FAULT | Steady yellow | The PEM has failed or is turned off. |
MISWIRE | Steady yellow | Cables are wired incorrectly and should be reversed. |
Table 4-14 lists the DC PEM fault indications and recommended actions.
| Symptom | Recommended Action |
Green LED on PEM fails to go on. | 1. Make sure the circuit breaker on the PEM is turned on. 2. Make sure the PEM is properly seated and screwed in place. 3. Make sure power leads are properly connected to power connectors on the backplane. If connections are loose or their polarity is reversed, chassis does not receive power. 4. Check the power source. 5. Move the PEM to the other PEM slot. If the PEM still fails, replace it. |
PEM experiences problems in one slot but operates normally in the other. | 1. Ensure that the input power to both slots is correct. 2. If the problem persists, contact Cisco TAC. |
Figure 4-11 shows the AC PEM and its indicators.
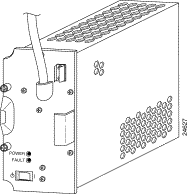
Table 4-15 describes the AC PEM LEDs located on the bottom front panel.
| LED | Status | Condition |
|---|---|---|
POWER | Steady green | Power is available. |
FAULT | Steady yellow | The PEM has failed or is turned off. |
Table 4-16 lists the AC PEM fault indications and recommended actions.
| Symptom | Recommended Action |
Green LED on PEM fails to go on. | 1. Make sure the power enable switch to the PEM is turned on. 2. Make sure the PEM is properly seated and screwed in place. 3. Make sure the power cable is plugged in properly. 4. Check the power source. 5. Move the PEM to the other PEM slot. If the PEM still fails, replace it. |
PEM experiences problems with one cable but operates normally with the other. | 1. Ensure that the input power on the cable is correct. 2. If the problem persists, contact Cisco TAC. Refer to the "Obtaining Technical Assistance" section. |
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Posted: Fri Jul 5 10:57:47 PDT 2002
All contents are Copyright © 1992--2002 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Important Notices and Privacy Statement.