|
|

This chapter provides installation procedures for a Cisco 6260 without a POTS splitter configuration.
 |
Note The installation procedures in this chapter apply to a Cisco 6260 system shipped with the individual hardware components already installed. For information about installing or replacing hardware components in the Cisco 6260 chassis, see "Upgrading and Maintaining the Cisco 6260 System." |
 |
Warning Only trained and qualified personnel should be allowed to install, replace, or service this equipment. |
 |
Caution Before you begin the installation procedures, read the entire chapter for important information and safety warnings. |
 |
Note Before installing and cabling the equipment, be aware of standard safety practices and the
hazards involved in working with electrical circuitry to prevent accidents. See the
"Safety Requirements" section
for cautions and warnings that are necessary to ensure a safe and hazard-free installation. To see translations of the warnings that appear in this publication, refer to the Regulatory Compliance and Safety Information for the Cisco 6260 System document. |
 |
Tip See the "Cisco 6260 System Without a POTS Splitter Configuration" section for more information about Cisco 6260 without a POTS splitter configuration components. |
When you install a Cisco 6260 without a POTS splitter configuration, be sure that you follow the installation procedures in the proper sequence. Table 4-1 is a checklist of the installation steps in the order in which they should occur. Detailed installation instructions are located in the sections following Table 4-1.
 |
Caution Proper ESD protection is required whenever you handle Cisco equipment. Installation and maintenance personnel should be properly grounded using ground straps to eliminate the risk of ESD damage to the equipment. Cards are subject to ESD damage whenever they are removed from the chassis. |
| Check | Installation Procedure |
|---|---|
| 1. Measure the rack space. |
| 2. Attach Cisco 6260 ear brackets. |
| 3. Install the Cisco 6260 chassis in the rack. |
| 4. Install the blank faceplates in the open slots. |
| 5. Ground the Cisco 6260. |
| 6. Connect the Cisco 6260 chassis to the MDF1. |
| 7. Attach the Cisco 6260 power connections. |
| 8. Connect the alarm and BITS clock contacts. |
| 9. Apply power to the system. |
| 10. Verify that the fan trays are operational. |
| 11. Connect the Cisco 6260 system to the network. |
| 12. Install a subtended network configuration (optional). |
| 13. Connect the ethernet to the management network. |
| 14. Connect a console terminal. |
| 15. Connect the auxiliary port (optional). |
| 16. Complete the initial configuration. |
| 1MDF = main distribution frame |
The following sections detail the installation procedures for a Cisco 6260 without a POTS splitter configuration.
For the rack to remain stable, you must install your Cisco 6260 system from the bottom to the top of the rack.
Before you install any of the chassis, measure the total rack space required to install your system. The required rack space depends on the number of Cisco 6260 chassis that you plan to use. The number of chassis increases if you plan to install a subtended network.
 |
Note See "Preparing for Installation," to determine the total rack space you need for your configuration. |
 |
Warning To prevent bodily injury when mounting or servicing this unit in a rack, you must take special precautions to ensure that the system remains stable. The following guidelines are provided to ensure your safety: —This unit should be mounted at the bottom of the rack if it is the only unit in the rack. —When mounting this unit in a partially filled rack, load the rack from the bottom to the top with the heaviest component at the bottom of the rack. —If the rack is provided with stabilizing devices, install the stabilizers before mounting or servicing the unit in the rack. |
 |
Warning Never attempt to lift the chassis with the handles on the power supplies, fan trays, or the switching modules. These handles are not designed to support the weight of the chassis. Using them to lift or support the chassis can result in severe damage to the equipment and serious bodily injury. |
If you plan to expand your system to include more chassis in the future, allow space in the rack for additions, keeping in mind the weight distribution and stability of the rack.
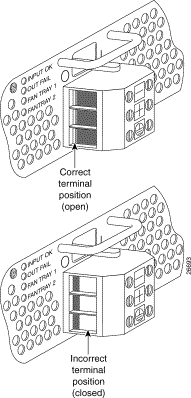
Verify that the ear brackets on the sides of the chassis are in the proper configuration to fit the rack, and if necessary, reinstall them. Ear brackets can be installed in two ways, as shown in Figure 4-1:

For Cisco 6260 installation in an ETSI 600-mm (23- inch) rack, attach the L-shaped ear brackets so that the short sides are against the chassis wall and the long sides protrude from the chassis.
For Cisco 6260 installation in a 19-inch rack, attach the ear brackets so that the long side of each L is against the chassis wall and the short side protrudes from the chassis.
 |
Note The ear brackets are installed in the factory for a 19-inch rack configuration. |
Complete the following steps to install the Cisco 6260 chassis.
 |
Warning Two people are required to lift the chassis. Grasp the chassis underneath the lower edge and lift with both hands. To prevent injury, keep your back straight and lift with your legs, not your back. |
Step 1 Connect a grounding strap to the ESD grounding jack that is located on the top right of the front of the Cisco 6260 chassis.
Step 2 Using a Phillips-head screwdriver, attach the two mounting aids to the rack. Use two screws for each mounting aid, as shown in Figure 4-2. The lower edge of the mounting aid lines up with the bottom of the chassis.
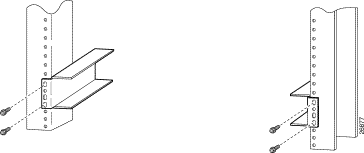
Step 3 Carefully lift the chassis from underneath and rest it on the mounting aids, as shown in Figure 4-3.
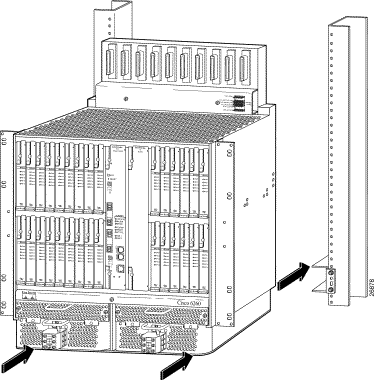
Step 4 Push the chassis back into the rack.
Step 5 Using a Phillips-head screwdriver, screw the ear brackets on the chassis to the rack. Use two screws at the top of each ear bracket and two at the bottom (four screws per bracket). For stability, make sure you use at least one round hole at each end of each bracket (the ear brackets have both round and oval holes).
Step 6 Repeat Step 1 through Step 5 for each Cisco 6260 chassis that you are installing.
Blank faceplates should occupy any empty slots in the Cisco 6260 chassis. Blank faceplate installation is similar to line card installation.
Complete the following steps to install blank faceplates in the Cisco 6260:
Step 1 Connect a grounding strap to the ESD grounding jack that is located on the top right of the front of the Cisco 6260 chassis.
Step 2 Vertically align the blank faceplate edge with the guides at the top and bottom of the slot.
Step 3 Lift up on the ejector tab and gently apply pressure to the bottom of the faceplate while pushing the blank faceplate into the slot.
Step 4 Push on the faceplate to fully seat the blank faceplate.
Step 5 Press down on the ejector tab to secure the faceplate.
Complete the following steps to connect the grounding lug on the Cisco 6260.
 |
Warning When you are installing the unit, the ground connection must always be made first and disconnected last. |
 |
Warning Before connecting or disconnecting ground or power wires to the chassis, ensure that power is removed from the DC circuit. To ensure that all power is OFF, locate the circuit breaker on the panel board that services the DC circuit, switch the circuit breaker to the OFF position, and tape the switch handle of the circuit breaker in the OFF position. Use a voltmeter to test for 0 (zero) voltage at the power terminals on the chassis. |
Step 1 Ensure that power in the direct current (DC) circuit is off.
Step 2 Remove all paint or oxidation from the rack at the point of the grounding connection.
Step 3 Measure enough wire to connect the Cisco 6260 to the rack. Use 10 American Wire Gauge (AWG) green or green with yellow stripes wire to ground the Cisco 6260 chassis.
 |
Note Use only as much wire as is necessary to make the connection. |
Step 4 Use a wire stripping tool to remove the covering from the end of the grounding wire. The manufacturer of the grounding lug might have a specific recommendation about the length of wire to be stripped.
Step 5 Insert the stripped end of the grounding wire into the open end of the grounding lug. Be careful not to leave any wire strands outside the lug.
Step 6 Use the crimping tool to compress the lug onto the wire.
Step 7 To verify the quality of the crimp, inspect it and tug gently on the wire.
Step 8 Locate the three grounding holes on the Cisco 6260 side panel. (See Figure 4-4.)
Step 9 Match the holes in the grounding lug to the appropriately spaced pair of grounding holes on the side of the chassis. Use the top two holes for a 5/8-inch lug, as shown in Figure 4-4. Use the bottom two holes for a 3/4-inch lug.
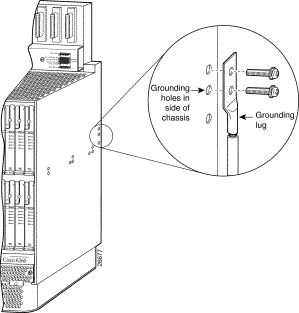
Step 10 Insert the screws through the holes in the lug and the chassis. Use the Phillips-head screwdriver to tighten the screws and secure the grounding lug firmly to the chassis.
Step 11 Prepare the other end of the grounding wire and connect it to an appropriate grounding point in your site.
Step 12 Repeat Step 1 through Step 11 for each Cisco 6260 chassis, as necessary.
Use ten RJ-21 (Champ) cables to connect the Cisco 6260 to the MDF. This connection is for xDSL data flow between the Cisco 6260 and the MDF.
See "Port Mapping Specifications" for port mapping information.
Ensure that all champ connectors are securely screwed in to the connector panel at the top of the Cisco 6260 chassis.
 |
Note If unshielded cable is used for FCC Class A or EN55022 Class A compliance, the cables must be looped through ferrites. |
External power is supplied to the system as -48 VDC from the central office (CO) power source or rectifier to the fuse and alarm panel. Power is fed from the fuse and alarm panel to receptacles in terminal blocks located on the power entry modules (PEMs) installed in the Cisco 6260 chassis.
Connect the power connections on each PEM to separate power sources to achieve full power redundancy. If you do not require power redundancy, use the terminals on a single PEM, or connect both PEMs to a single power source.
Complete these instructions to connect the Cisco 6260 system to a -48 VDC power source. Ground the chassis before you attempt this procedure, as described in the "Ground the Cisco 6260" section.
 |
Note See "Preparing for Installation," for the calculation tables that you need to determine the minimum power requirements for your system. |
 |
Caution To prevent the system from powering up, do not install the fuses at this time. If the fuses are already installed in the fuse and alarm panel, remove them. You can replace the fuses after the system is installed and connected. |
Follow these instructions to attach the power connections to the Cisco 6260 PEM:
Step 1 Verify that power in the DC circuit is off.
 |
Warning Before connecting or disconnecting ground or power wires to the chassis, ensure that power is removed from the DC circuit. To ensure that all power is OFF, locate the circuit breaker on the panel board that services the DC circuit, switch the circuit breaker to the OFF (0) position, and tape the switch handle of the circuit breaker in the OFF (0) position. Use a voltmeter to test for 0 (zero) voltage at the power terminals on the chassis. |
Step 2 Connect a grounding strap to the ESD grounding jack that is located on the top right of the front of the Cisco 6260 chassis.
Step 3 Prepare the wire for the Cisco 6260 power and grounding connections, as follows:
a. Measure enough wire (6 to 10 AWG multistranded copper wire) to connect each of the PEM power connections to the fuse and alarm panel, as well as enough to connect the grounding receptacle on the PEM terminal block to the grounding connection at the DC power source.
b. Cut the ends of the power and ground wires so that the ends are straight, not slanted.
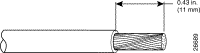
c. Measure 0.43 inch (11 mm) up from the end of each power and ground wire and place a mark at that point. These are the wire ends that will be connected to the Cisco 6260.
d. Use the wire stripping tool to remove 0.43 inch (11 mm) of the covering from both ends of each wire. Trim the ends of the covering so that they are straight, as shown in Figure 4-5, not slanted.
 |
Warning Remove the covering from exactly the specified length of each power wire. If you strip too much of the covering, exposed wire protruding from the terminal block will create an electrical hazard. If you strip too little of the covering, the wire may not make a good contact with the terminal, or it may not be held securely in place in the terminal block. |
Step 4 Use a flat-head screwdriver to turn all three screws on the terminal block counterclockwise to open the terminal connectors: + (positive), - (negative), and ground. This step ensures that the correct opening is presented for the wires, as shown in Figure 4-6.
Step 5 Insert the end of the grounding wire into the grounding receptacle, which is the bottom receptacle in the terminal block on the PEM (see Figure 4-7). The stripped part of the wire must be fully inserted into the terminal block so that no bare wire is exposed.
Step 6 Ensure that no wire strands are left outside the connector.
Step 7 Using the screwdriver and a clockwise motion, tighten the ground screw in the terminal block. Gently tug on the wire to ensure that it is firmly in place.

Step 8 Make sure that the other end of the grounding wire is connected to ground at the DC power source.
Step 9 If you are connecting two power sources to the Cisco 6260 system, repeat Step 2 through Step 8 for the second PEM.
 |
Warning Only a DC power source that is isolated from the AC main power source with reinforced insulation, and that complies with the other safety extra-low voltage (SELV) requirements in UL1950, CSA 950 3rd Edition, EN 60950, and IEC950, can be connected to a Cisco 6260 system. This requirement ensures that in a catastrophic power source fault condition, hazardous voltages are not present on power terminals and connectors. |
Step 10 After connecting the battery return wire to the external power source, insert the other end into the receptacle labeled + (positive) on the terminal block of the first PEM, as shown in Figure 4-8. The stripped part of the wire must be fully inserted so that no bare wire is exposed. Using the screwdriver and a clockwise motion, tighten the terminal screw. Gently tug on the wire to ensure that it is firmly in place.
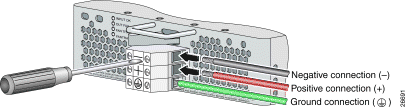
Step 11 After connecting the power lead to the external -48V power source, insert the other end of the wire into the receptacle labeled - (negative) on the terminal block of the first PEM, as shown in Figure 4-8. The stripped part of the wire must be fully inserted so that no bare wire is exposed. Using the screwdriver and a clockwise motion, tighten the terminal screw. Gently tug on the wire to ensure that it is firmly in place.
Step 12 If you are connecting a second power source, repeat Step 10 and Step 11 to wire it to the second PEM.
 |
Note Be sure that the chassis is connected to earth ground as described in the "Ground the Cisco 6260" section on page 4-7. The Cisco 6260 requires two or three ground connections, one to the side of the chassis and one to each PEM. |
Step 13 Repeat Step 2 through Step 12 for each Cisco 6260 chassis, as necessary.
 |
Warning Do not yet power up the system. |
 |
Note Connecting the alarm and BITS clock contacts are optional procedures. |
Complete the following steps to connect the external alarm and BITS clock contacts:
Step 1 Connect the external alarm device and BITS clock to the wire-wrap pins on the I/O module at the top of the chassis.
a. Measure one strand of twisted-pair wire (24 AWG industry standard T1/E1 cable) long enough to connect to the appropriate pin.
b. Use a wire stripper to remove the casing from both ends of the wire.
c. Use a wire-wrapping tool to attach the wire to the appropriate pin.
d. Use a wire-wrapping tool to attach the other end of the wire that is used in Step 1c to either the BITS clock source or alarm relay contact.
e. Repeat this step to wire-wrap all the necessary pins.
 |
Note The BITS pins on Cisco 6260 I/O cards are slot specific. BITS_A pins are assigned to chassis slot 11 and BITS_B pins are assigned to chassis slot 10. Each BITS clock input is independent and terminated at 100 ohms. |
Step 2 Reboot the system to reassociate the system MAC address.
Step 3 Repeat Step 1 and Step 2 for each Cisco 6260 chassis, as necessary.
Complete the following steps to apply power to the Cisco 6260 system:
Step 1 Apply power to the system with one of the following methods:
 |
Caution If the power connections are improperly made and power is applied while the cards are installed, the cards and chassis could be damaged. |
Step 2 Verify that the power connections are made correctly, as described in the "Attach Cisco 6260 Power Connections" section.
Step 3 Check the polarity of the -48 VDC connections to each chassis by attaching a voltmeter with the minus lead on -48RTN and the plus lead on -48V_A or -48V_B. Ensure that the meter reads between -40.5 VDC and -75 VDC. If your voltmeter shows a positive voltage, check to ensure that the meter leads are not reversed. If the voltmeter shows a negative voltage that is out of the -40.5 VDC to -75 VDC range, check the power supply for failure or check for a blown fuse in the fuse and alarm panel.
Step 4 Turn on power to the DC circuit.
Step 5 Use a voltmeter to check the voltage at the terminal block. Connect the voltmeter positive contact to the positive (+) terminal on the Cisco 6260 terminal block. Connect the voltmeter negative contact to the negative (-) terminal on the Cisco 6260 terminal block. If the power is wired correctly, you will see a reading of -48V on the voltmeter.
Step 6 At the front of the chassis, switch the circuit breakers on both PEMs to the ON (1) position.
Step 7 Repeat Step 1 through Step 6 for each Cisco 6260 chassis, as necessary.
Verify that the fan trays are operational by checking the fan tray LEDs, located on the PEMs that are installed beneath the fan trays. If the LED is
 |
Caution The fans in both fan trays must run continuously. The system might suffer thermal damage if the fans in either tray stop for more than 5 minutes. |
The following sections provide instructions for making E3, E1, and OC-3c network connections from the Cisco 6260 system.
The E3 network connection is made from E3 I/O module. Complete the following steps to connect the E3 I/O module to the network.
 |
Tip We recommend that you label each data cable at both ends to identify its destination. |
Step 1 Verify that you have both a DS3/2DS3 NI-2 card and an E3 I/O module installed in the Cisco 6260 chassis.
The E3 I/O module connections marked P1 attach to the ATM switch. Two 75-ohm Bayonet-Neill-Concelman (BNC) connectors for E3 transmit (TX) and receive (RX) are provided. See Figure 4-10 for the location of the P1 BNC connectors.
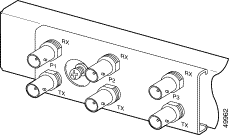
Step 2 Attach one end of a coaxial cable (type 734A or equivalent) to the P1 TX BNC connector on the E3 I/O module.
 |
Note See Table 2-4 for cable requirements. |
Step 3 Attach the other end of the cable to the ATM switch.
Step 4 Attach one end of a coaxial cable (type 734A or equivalent) to the P1 RX BNC connector on the E3 I/O module.
Step 5 Attach the other end of the cable to the ATM switch.
Step 6 Repeat Step 1 through Step 5 for each Cisco 6260 chassis, as necessary.
The E1 network connection is made from E1 I/O module. Complete the following steps to connect the E1 I/O module to the network:
Step 1 Verify that you have both a DS3+T1/E1 IMA NI-2 card and an E1 I/O module installed in the Cisco 6260 chassis.
The E1 I/O module connections attach to the ATM switch. Cisco provides four sets of two vertically paired E1 RJ-48c (120-ohm) connectors that can be used as network trunk connections, individual E1 subtend links, connections to IMA subtending groups, or connections to IMA group trunk interfaces. See Figure 4-11 for the location of the E1 RJ-48 receptacle connectors.
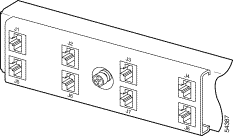
Step 2 Connect one end of an RJ-45 cable to one of the RJ-48 receptacle connectors on the E1 I/O module. If you have a subtended network configuration installed, this connection must be made to the E1 I/O module in the subtending host chassis.
 |
Note If unshielded cable is used for FCC Class B or EN55022 Class B compliance, the cables must
be looped through ferrites. See Table 2-4 for cable requirements. |
Step 3 Connect the other end of the cable used in Step 2 to the ATM switch.
 |
Note Verify that the pinouts of the RJ-45 cable connect transmit to receive and receive to transmit. |
Step 4 Repeat Step 1 through Step 3 for each Cisco 6260 chassis, as necessary.
 |
Note Use the procedures in this section to make IMA network connections. See the "IMA Configuration" section for more information on IMA network connections. |
OC-3c network connections are made from the OC-3c/OC-3c NI-2 card. Complete the following steps to connect the OC-3c/OC-3c NI-2 card to the network.
 |
Warning Do not stare into the beam or view it directly with optical instruments. |
Step 1 Verify that an OC-3c/OC-3c NI-2 card is in slot 10 of the Cisco 6260 chassis (or slot 11, if you are installing a secondary card for NI-2 redundancy).
Step 2 Attach the RX cable from the ATM switch to the trunk 1 (TRNK 1) TX connector in the inset on the NI-2 card faceplate. The TX connector is the one closer to the top of the faceplate. The connector IDs are silkscreened inside the inset. See Figure 1-18 for the location of OC-3c network interface connectors.
Step 3 Attach the TX cable from the ATM switch to the TRNK 1 RX connector in the inset on the NI-2 card faceplate. The RX connector is closer to the bottom of the faceplate. See Figure 1-18 for the location of OC-3c network interface connectors.
Step 4 Repeat Step 1 through Step 3 for each Cisco 6260 chassis, as necessary.
If you are installing a subtended network configuration, complete the steps in the following sections, which provide installation procedures for E3, E1, and OC-3c subtended network configurations.
If you are not installing a subtended network, proceed to the "Connect the Ethernet to the Management Network" section.
 |
Note For overview information on a subtended network configuration, see the "Subtended Network Configuration" section on. |
Coaxial connections for E3 subtending cabling are located on the I/O module. The P1 TX and RX BNC connectors are reserved for network trunk cabling, or for upstream cabling from a subtended node chassis to the host. The P2 or P3 TX and RX BNC connectors on the subtending host chassis I/O module are connected to the P1 TX and RX BNC connectors on the subtended node chassis I/O module.
Figure 4-12 shows the three sets of BNC connectors and their location on the E3 I/O module.

Complete the following steps to cable the E3 I/O module for subtending:
Step 1 On the subtending host chassis I/O module, attach one end of a BNC cable to the P2 (or P3) TX BNC connector.
Step 2 On the first subtended node chassis I/O module, attach the other end of the cable to the P1 RX BNC connector.
Step 3 On the subtending host chassis I/O module, attach one end of a BNC cable to the P2 or (P3) RX BNC connector.
Step 4 On the first subtended node chassis I/O module, attach the other end of the cable to the P1 TX BNC connector.
Step 5 Repeat Step 1 through Step 4 to connect the subtending host chassis to each subtended node chassis.
See Figure 1-3 for an illustration of an E3 subtending network configuration.
Connections for E1 subtending cabling are located on the I/O module. The RJ-48 E1 connectors on the subtending host chassis I/O module are connected to the RJ-48 E1 connectors on the subtended node chassis I/O module.
Figure 4-13 shows the eight RJ-48 E1 connectors and their location on the E1 I/O module.

Complete the following steps to cable the I/O module for E1 subtending:
Step 1 Connect one end of an RJ-45 crossover cable to one of the RJ-48 receptacle connectors on the subtending host chassis E1 I/O module.
Step 2 Connect the other end of the cable to one of the RJ-48 receptacle connectors on the subtended node chassis E1 I/O module.
Step 3 Repeat Step 1 and Step 2 to connect the subtending host chassis to each subtended node chassis.
 |
Note If you are using an E1 trunk to the network, the trunk connection originates at one of the RJ-48 receptacle connectors on the E1 I/O module. Therefore, you can have only seven subtended node chassis. |
See Figure 1-4 for an illustration of an E1 subtending network configuration.
Connections for OC-3c subtending are made from the faceplate of the OC-3c/OC-3c NI-2 card installed in the subtending host chassis to the faceplate of the OC-3c/OC-3c NI-2 card installed in the subtended node chassis. See Figure 1-18 for the location of theOC-3c subtending connectors on the faceplate of the NI-2 card.
To cable the Cisco 6260 system for OC-3c subtending, complete the following steps:
Step 1 Locate the TRNK 1 network interface connectors (TX and RX) and the subtend (SBTD) 2 interface connectors (TX and RX) on the front of each OC-3c/OC-3c NI-2 card.
Step 2 Attach an OC-3c fiber-optic cable to the SBTD 2 TX interface connector on the NI-2 card installed in the subtending host chassis.
Step 3 Attach the other end of the cable to the TRNK 1 RX interface connector on the NI-2 card installed in the subtended node chassis.
Step 4 Attach an OC-3c fiber-optic cable to the SBTD 2 RX interface connector on the NI-2 card installed in the subtending host chassis.
Step 5 Attach the other end of the cable to the TRNK 1 TX interface connector on the NI-2 card installed in the subtended node chassis.
Step 6 To cable your system for APS link redundancy, repeat Step 1 through Step 5 for the secondary NI-2 cards installed in slot 11 of each host and subtending chassis.
See Figure 1-5 for an illustration of an OC-3c subtending network configuration.
 |
Warning The ports labeled "ENET," "CNSL," and "AUX" are safety extra-low voltage (SELV) circuits. SELV circuits should be connected only to other SELV circuits. Because the DSL circuits are treated like telephone-network voltage, avoid connecting the SELV circuit to the telephone network voltage (TNV) circuits. |
 |
TimeSaver We recommend that you label each data cable at both ends to identify its destination. |
Complete the following steps to connect the Ethernet to the management network:
Step 1 Connect the Ethernet cable to the NI-2 card ENET receptacle (see Figure 1-18 for the location of the ENET receptacle on the faceplate of the NI-2 card).
 |
Note See Table 2-4 for cable and ferrite requirements. |
Step 2 Run the cable through the ferrite one time, loop the cable back through the ferrite, and clamp the ferrite shut.
Step 3 Connect the other end of the cable to the management network (for example, a LAN).
Connect a VT100-compatible terminal to the NI-2 card CNSL receptacle (see Figure 1-18 for the location of the CNSL receptacle on the faceplate of the NI-2 card). Connect the terminal to a power source and set it up using the values shown in Table 4-2.
 |
Warning The ports labeled "ENET," "CNSL," and "AUX" are SELV circuits. SELV circuits should be connected only to other SELV circuits. Because the DSL circuits are treated like telephone-network voltage, avoid connecting the SELV circuit to the TNV circuits. |
Baud rate | 9600 to 38,400 bps (transmit and receive) |
Character size | 8 bits |
Parity | None |
Stop bits | 1 |
Flow control | None |
Connect a terminal, a modem, or another serial device to the NI-2 card RJ-45 AUX receptacle (see Figure 1-18 for the location of the AUX receptacle on the faceplate of the NI-2 card).
 |
Note This action is optional. |
 |
Warning The ports labeled "ENET," "CNSL," and "AUX" are SELV circuits. SELV circuits should be connected only to other SELV circuits. Because the DSL circuits are treated like telephone-network voltage, avoid connecting the SELV circuit to the TNV circuits. |
 |
TimeSaver We recommend that you label each data cable at both ends to identify its destination. |
When you turn on the Cisco 6260 for the first time, an interactive dialog called the System Configuration Dialog appears in a window on the console screen. The System Configuration Dialog guides you through the initial configuration process. (You can run the dialog at any time by entering the setup command in privileged EXEC mode.)
When you complete the dialog, the system displays the configuration command script that you have created. It then offers you three options:
[0] Go to the IOS command prompt without saving this config.
[1] Return back to the setup without saving this config.
[2] Save this configuration to nvram and exit.
If you enter 2, the configuration is saved and used. If you answer 0 or 1, the configuration you created is not saved. Enter 1 if you wish to discard the configuration and restart the System Configuration Dialog.
Complete these steps before you run the System Configuration Dialog:
Step 1 Determine the IP address for the Ethernet interface.
Step 2 If you plan to configure in-band management, determine the IP address for the ATM interface that will be used for in-band management (ATM0/1 or ATM0/2).
Step 3 Find out what the password strategy is for your environment. The System Configuration Dialog window prompts you for three passwords, plus an SNMP community string. The three required password types are enable secret, enable, and virtual terminal.
Step 4 Choose a name for the Cisco 6260. (This step is optional.)
The System Configuration Dialog offers two configuration options: basic management setup and extended setup.
An example of each type of setup follows the "Interface Numbering" section.
The System Configuration Dialog window and the CLI use the following interface numbering scheme:
This is the basic management setup example:
--- System Configuration Dialog ---
Would you like to enter the initial configuration dialog? [yes/no]: y
At any point you may enter a question mark '?' for help.
Use ctrl-c to abort configuration dialog at any prompt.
Default settings are in square brackets '[]'.
Basic management setup configures only enough connectivity
for management of the system, extended setup will ask you
to configure each interface on the system
Would you like to enter basic management setup? [yes/no]: y
Configuring global parameters:
Enter host name [DSLAM]:
The enable secret is a password used to protect access to
privileged EXEC and configuration modes. This password, after
entered, becomes encrypted in the configuration.
Enter enable secret: beansoup
The enable password is used when you do not specify an
enable secret password, with some older software versions, and
some boot images.
Enter enable password: beansoup
% Please choose a password that is different from the enable secret
Enter enable password: lab1
The virtual terminal password is used to protect
access to the router over a network interface.
Enter virtual terminal password:
% No defaulting allowed
Enter virtual terminal password: lab
Configure SNMP Network Management? [yes]: y
Community string [public]:
Current interface summary
Any interface listed with OK? value "NO" does not have a valid configuration
Interface IP-Address OK? Method Status Protocol
ATM0/0 unassigned NO unset up up
Ethernet0/0 unassigned NO unset up up
ATM0/1 unassigned NO unset down down
ATM0/2 unassigned NO unset down down
Enter interface name used to connect to the
management network from the above interface summary: Ethernet0/0
Configuring interface Ethernet0/0:
Configure IP on this interface? [yes]: y
IP address for this interface: 172.27.144.141
Subnet mask for this interface [255.255.0.0] :
Class B network is 172.27.0.0, 16 subnet bits; mask is /16
The following configuration command script was created:
hostname DSLAM
enable secret 5 $1$pR/1$0zH7ohDaUKNML3SC2.RF5.
enable password lab1
line vty 0 4
password lab
snmp-server community public
!
no ip routing
!
interface ATM0/0
no ip address
!
interface Ethernet0/0
no shutdown
ip address 172.27.144.141 255.255.0.0
!
interface ATM0/1
shutdown
no ip address
!
interface ATM0/2
shutdown
no ip address
!
end
[0] Go to the IOS command prompt without saving this config.
[1] Return back to the setup without saving this config.
[2] Save this configuration to nvram and exit.
Enter your selection [2]: 2
% Shutdown not allowed for ATM0/0.
Building configuration...
Use the enabled mode 'configure' command to modify this configuration.
Press RETURN to get started!
This is the extended setup example:
--- System Configuration Dialog ---
Continue with configuration dialog? [yes/no]: yes
At any point you may enter a question mark '?' for help.
Use ctrl-c to abort configuration dialog at any prompt.
Default settings are in square brackets '[]'.
Basic management setup configures only enough connectivity
for management of the system, extended setup will ask you
to configure each interface on the system
Would you like to enter basic management setup? [yes/no]: no
First, would you like to see the current interface summary? [yes]: yes
Interface IP-Address OK? Method Status Protocol
ATM0/0 70.0.0.2 YES NVRAM up up
Ethernet0/0 172.27.32.156 YES NVRAM up up
ATM0/1 unassigned YES unset down down
ATM0/2 unassigned YES unset administratively down down
ATM18/0 unassigned YES unset initializing down
ATM18/1 unassigned YES unset initializing down
ATM18/2 unassigned YES unset initializing down
ATM18/3 unassigned YES unset initializing down
ATM21/0 unassigned YES unset administratively down down
ATM21/1 unassigned YES unset administratively down down
ATM21/2 unassigned YES unset administratively down down
ATM21/3 unassigned YES unset administratively down down
ATM26/0 unassigned YES unset down down
ATM26/1 unassigned YES unset down down
ATM26/2 unassigned YES unset down down
ATM26/3 unassigned YES unset down down
Configuring global parameters:
Enter host name [DSLAM]: sw-ni2-2
The enable secret is a password used to protect access to
privileged EXEC and configuration modes. This password, after
entered, becomes encrypted in the configuration.
Enter enable secret: lqb
The enable password is used when you do not specify an
enable secret password, with some older software versions, and
some boot images.
Enter enable password [lab]: lab
The virtual terminal password is used to protect
access to the router over a network interface.
Enter virtual terminal password [lab]:
Configure SNMP Network Management? [no]:
Configure IP? [yes]:
Configure IGRP routing? [yes]: no
Configuring interface parameters:
Do you want to configure ATM0/0 interface? [yes]:
Configure IP on this interface? [yes]:
IP address for this interface [70.0.0.2]:
Subnet mask for this interface [255.0.0.0] :
Class A network is 70.0.0.0, 8 subnet bits; mask is /8
Do you want to configure Ethernet0/0 interface? [yes]:
Configure IP on this interface? [yes]:
IP address for this interface [172.27.32.156]:
Subnet mask for this interface [255.255.0.0] :
Class B network is 172.27.0.0, 16 subnet bits; mask is /16
Do you want to configure ATM0/1 interface? [yes]:
Configure IP on this interface? [no]:
Do you want to configure ATM0/2 interface? [no]:
Do you want to configure ATM18/0 interface? [yes]:
Configure IP on this interface? [no]:
Do you want to configure ATM18/1 interface? [yes]:
Configure IP on this interface? [no]:
Do you want to configure ATM18/2 interface? [yes]:
Configure IP on this interface? [no]:
Do you want to configure ATM18/3 interface? [yes]:
Configure IP on this interface? [no]:
Do you want to configure ATM21/0 interface? [no]:
Do you want to configure ATM21/1 interface? [no]:
Do you want to configure ATM21/2 interface? [no]:
Do you want to configure ATM21/3 interface? [no]:
Do you want to configure ATM26/0 interface? [yes]:
Configure IP on this interface? [no]:
Do you want to configure ATM26/1 interface? [yes]:
Configure IP on this interface? [no]:
Do you want to configure ATM26/2 interface? [yes]:
Configure IP on this interface? [no]:
Do you want to configure ATM26/3 interface? [yes]:
Configure IP on this interface? [no]:
The following configuration command script was created:
hostname sw-ni2-2
enable secret 5 $1$12Lo$vGKa1wlRcNyw06j1bgGQd0
enable password lab
line vty 0 4
password lab
no snmp-server
!
ip routing
!
interface ATM0/0
ip address 70.0.0.2 255.0.0.0
!
interface Ethernet0/0
ip address 172.27.32.156 255.255.0.0
!
interface ATM0/1
no ip address
!
interface ATM0/2
shutdown
no ip address
!
interface ATM18/0
no ip address
!
interface ATM18/1
no ip address
!
interface ATM18/2
no ip address
!
interface ATM18/3
no ip address
!
interface ATM21/0
shutdown
no ip address
!
interface ATM21/1
shutdown
no ip address
!
interface ATM21/2
shutdown
no ip address
!
interface ATM21/3
shutdown
no ip address
!
interface ATM26/0
no ip address
!
interface ATM26/1
no ip address
!
interface ATM26/2
no ip address
!
interface ATM26/3
no ip address
!
end
[0] Go to the IOS command prompt without saving this config.
[1] Return back to the setup without saving this config.
[2] Save this configuration to nvram and exit.
Enter your selection [2]:2
Building configuration...
Use the enabled mode 'configure' command to modify this configuration.
Press RETURN to get started!
 |
Note To configure your system, refer to the appropriate software or network management configuration guides. |
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Posted: Mon Dec 9 08:37:43 PST 2002
All contents are Copyright © 1992--2002 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Important Notices and Privacy Statement.