|
|

A circuit line is the physical line that carries data, voice, Frame Relay, or ATM traffic between an IGX or BPX node and customer premises equipment (CPE). Each piece of customer premises equipment is attached to a node through a circuit line. After a card has been "upped" with the upcd command, a circuit line on that card can be "upped" and configured.
This chapter:
The following table shows the permissible card combinations for CPE-to-IGX lines.
| Type | Country | Electrical Signal Format | Ones Density Enforcement | Multiplexing |
J1 | Japan | Coded Mark Inversion (CMI) |
| 31 channels @ 64kbps each |
E1 | Others | Alternate Mark Inversion (AMI) | High density bipolar 3 (HDB3) | 31 channels @ 64kbps each 1 E1 line on CDP/CVM, 8 E1 lines on UFM |
T1 | USA ASIA | Alternate Mark Inversion (AMI) | Bipolar Zero Substitution (B8ZS) | 24 channels @ 64kbps each 1 T1 line on CDP/CVM, 8 T1 lines on UFM |
E3 | Europe | Physical Layer Convergence Protocol per AT&T publication; ITU I-361 with HEC for E3 | HDB3 | ITU-T G.804, G.832 |
T3 | USA | Physical Layer Convergence Protocol per AT&T publication TA-TSY-00772 and 000773 for T3 | B3ZS+ | M13 mode |
| Service | Node Type | Front Card | Back Card |
|---|---|---|---|
ATM | IGX | UXM | BC-UAI BC-UAI-1T1 BC-UAI-1OC3 |
ATM | IGX | ALM/A | BC-UAI-1T3 |
Frame Relay | IGX | UFM-4C, UFM-8C | UFI-8T1-DB15, UFI-8E1-DB15, UFI-8E1-BNC |
Frame Relay | IGX | FRP-6, FRP-31/FRM-6, | FRI-T1, FRI-E1 |
Frame Relay | IGX | UFM-C | UFI-8T1-DB15 |
High Speed Data | IGX | SDP/HDM | SDI/RS-232 |
High Speed Data | IGX | SDP/HDM | SDI/RS-232 |
Voice | IGX | UVM | BC-UVI-2T1EC |
Voice | IGX | CDP/CVM | BC-T1 |
Frame relay, data, and voice connections require an active line. Use the commands in the following steps to establish a line. The card must be in either the active or standby state before you enter these commands.
Step 1 Use upln to activate a circuit line in a slot that contains the appropriate circuit line card set.
Step 2 Use cnfln to configure the circuit line.
The upln and cnfln commands establish the general parameters for the line but do not establish specific Frame Relay, data, or voice parameters. Refer to applicable chapters for details on a particular service. For example, "Data Connections" describes specific commands for data connections, and "Frame Relay Connections" describes specific commands for Frame Relay connections.
The following describes related commands.
Figure 5-1, Figure 5-2, Figure 5-3, Figure 5-4, and Figure 5-5 show the command sequence for setting up lines for voice, serial data, Frame Relay, ATM, and FastPADs, respectively. A yes/no decision branch for "Other Side?" and the vt command in the sequence indicates command sequences on local and far nodes. "Multiplex" refers to channelized streams.
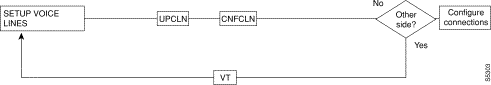
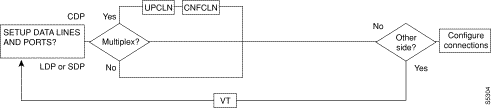
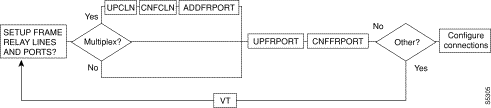
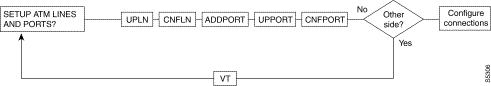
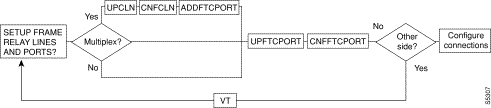
Table 5-3 shows the full command name and starting page for each line command description.
| Mnemonic | Description | Page |
|---|---|---|
cnfcassw | Configure CAS switching | |
cnfln | Configure line (same as cnfcln) | |
cnfrsrc | Configure resources | |
dnln | Down line (same as dncln) | |
dsplncnf | Display line configuration (same as dspclncnf) | |
dsplns | Display lines (same as dspclns) | |
dsptsmap | Display time slot map | |
prtlns | Print circuit lines (same as prtclns) | |
upln | Up line (same as upcln) |
Configures a UVM to convert channel associated signaling (CAS) and dual-tone multi-frequency (DTMF) tones to common channel signaling (CCS) call control messages. This conversion is necessary for voice networks in which a Voice Network Switch (VNS) uses SVCs to route calls from a CAS-based PBX through a WAN. Model B or later firmware on the UVM is necessary.
Before you can execute cnfcassw, note the following:
configure CAS switching
cnfcassw <line> <mode> <CCS type> <CAS type> <conn type> <country code>
<interdigit timeout> <tone level> <DTMF duration> <idle pattern> <parameters 6-18>
dspln, dsplncnf
| Privilege | Jobs | Log | Node | Lock |
1-2 | No | Yes | IGX | Yes |
cnfcassw 5.1
Description
Configure port 1 of the UVM in slot 5 to support CAS switching.
sw175 TN SuperUser IGX 8420 9.2 Sep. 17 1998 06:11 PST
Line 5.1 CAS Switching Parameters
=> CASSW mode [OFF] Parm 11 [00] (H)
CCS Type [ 1] (D) Parm 12 [00] (H)
CAS Type [ 1] (D) Parm 13 [00] (H)
Conn Type [a32 ] Parm 14 [00] (H)
Country code [00] (H) Parm 15 [00] (H)
Interdigit TO [05] (H) Parm 16 [00] (H)
Tone level [00] (H) Parm 17 [00] (H)
DTMF duration [0C] (H) Parm 18 [00] (H)
Idle pattern [54] (H)
Parm 6 [00] (H)
Parm 7 [00] (H)
Parm 8 [00] (H)
Parm 9 [00] (H)
Parm 10 [00] (H)
This Command: cnfcassw 5.1
Enter mode: Pbx/Server/Off (o):
| Parameter | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|
line | Specifies the line in the format slot.port. The line must be up before you can execute cnfcassw. | |
mode | Possible entries are "p" for PBX-end, "s" for server-end, or "o" for off. The applications are as follows:
| off |
CCS type | The range of entries 1-4. A 1 selects Q.SIG. | 1 |
CAS type | The range is 1-32. A 1 specifies AB signaling for 2-wire E&M line. | 1 |
connection type | Specifies the type of voice connection. Valid entries are a32 and a24. | a32 |
country code | The range is 0-0xFF. A 0, for example is the U.S. | 0 |
interdigit timeout | The range is 0-0xFF, where each hexadecimal value you enter is a multiplier of 50 millisecond increments. | 05, which results in 250 ms. |
tone level | Specifies the dB level of the DTMF below 0 dBm. The range is 0-0xFF. | 00 for 0 dB |
DTMF duration | Specifies the DTMF on/off duration. The range is 0-0xFF, and the value you enter is multiplied by 5 millisecond increments. | 0C, which results in 60 ms on then 60 ms off. |
idle pattern | Specifies the data pattern for the data channel. The range is 0-0xFF. | 7F for T1, |
parms 6-19 | Parameters 6-18 are reserved for future use. | 00 |
Configures a line to be compatible with the device to which it connects. The cnfln command applies to voice, data, Frame Relay, and ATM lines. See Table 5-1 for a list of the front and matching back cards. Because of the variety of line types and characteristics, the parameters section of this description has three tables to describe the parameters. The system automatically presents the correct options on the command line for each line type. If a parameter is not applicable to a card type, the system displays the parameter in half-tone or the value field of that parameter with dashed lines. Table 5-4 describes the parameters for voice, data, and Frame Relay parameters. Table 5-5 describes the parameters for the ATM Line Module (ALM/A). Table 5-6 describes the parameters for the ASI line card (BPX node). Table 5-7 describes the ATM parameters for the UXM card (IGX node).
For an ALM/A, the cnfln command lets you configure the receive rate and header type and enable payload scrambling. For more details on the features and configurable parameters of the ALM/A, refer to the Cisco IGX 8400 Series Reference and the Cisco IGX 8400 Series Installation manuals. Note that, although the cnfln display shows the transmit rate, you cannot configure it because the ALM/A transmit rate is always the maximum line rate.
Configure line
cnfln <line> <parameters>
dspln, dsplncnf, dsptsmap
| Privilege | Jobs | Log | Node | Lock |
1-2 | Yes | Yes | IPX, IGX, BPX | Yes |
cnfln 14
Configure voice line 14.
alpha TRM YourID:1 IGX 8420 9.2 Aug. 23 1998 09:55 PST
CLN 14 Configuration T1/24 CDP slot: 13
Loop clock: --
Line framing: --
coding: --
CRC: --
recv impedance: --
E1 signalling: --
encoding: --
T1 signalling: --
cable type: --
length: --
56KBS Bit Pos: --
pct fast modem: --
Last Command: cnfcln 14
Next Command:
cnfcln 7 n 2
Configure a Frame Relay T1 line for the following options: no loop clock and a receive impedance of 75 ohms.
alpha TRM YourID:1 IPX 16 9.2 Aug. 23 1997 09:55 PST
CLN 14 Configuration T1/24 FRPslot: 13
Loop clock: --
Line framing: ESF
coding: ZCS
CRC: --
recv impedance: --
E1 signalling: --
encoding: --
T1 signalling: --
cable type: ABAM
length: 0-133 ft.
56KBS Bit Pos: --
pct fast modem: --
Last Command: cnfcln 7 n 2
Next Command:
cnfln 4.2 7F 0 N
Configure ASI port 4.2 with an idle code 7F and without payload scrambling.
ca19 VT SuperUser BPX 8620 9.2 Aug. 23 1998 19:11 GMT
LN 4.2 Configuration T3 [96000 cps] ASI-T3 slot:4
Loop clock: -- Idle code: 7F hex
Line framing: --
coding: --
CRC: --
recv impedance: --
E1 signalling: --
encoding: -- cable type:
T1 signalling: -- length: 0-450 ft.
HCS Masking: Yes
Payload Scramble: No
56KBS Bit Pos: --
pct fast modem: --
Last Command: cnfln 4.2 7F 0 N
Next Command:
cnfln 12
Configure the ALM/A in slot 12.
reach TN SuperUser IGX 8420 9.2 July 22 1998 12:39 PDT
LN 12 Config T3/3 [452 cps] ALM slot: 12
Transmit Line Rate: 96000 cps
Receive Line Rate: 452 cps
Header Type: VCC
Payload Scramble Yes
Last Command: cnfln 12 452 vcc y
Next Command:
cnfln 10.1 N D4 ZCS AB 4 20 _
Configure line 1 on the UVM in slot 10 with no loop clock, D4 framing, Zero Code Suppression coding, AB T1 signalling, and 20% expected channel utilization by a high speed modem.
sw176 TN SuperUser IGX 8420 9.2 Sep. 15 1998 13:37 PST
LN 10.1 Config T1/24 UVM slot: 10
Loop clock: No
Line framing: D4 cnfg: External
coding: ZCS slot.line: --
CRC: -- CAS-switching: PBX-end
recv impedance: -- SVC-Caching : On
E1/J1 signalling: --
encoding: u-law
T1 signalling: AB
cable type: ABAM
length: 0-133 ft.
56KBS Bit Pos: msb
pct fast modem: 20
This Command: cnfln 10.1 N D4 ZCS AB 4 20 _
Turn on SVC-Caching (Y):
This release has added a prompt to configure a UVM line for SVC Caching. It is also supported on CVM lines on the IPX. The SVC Caching feature speeds up call setup for most VNS controlled calls by avoiding some of the call setup/tear-down operations when a call originates or terminates.
Refer to the VNS Installation and Configuration Manual for more information on SVC Caching.
| Parameter | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|
slot or slot.line | Specifies the line. If the back card has one line connector and cable, enter the slot number. If the card has more than one physical line, include a line number. If the card is a UVM, however, enter just the slot number. | |
loop clock | Enables the transmit and receive control leads to use the same clock. Format for the parameter is Y or N | N |
line framing | Configures T1 line framing to be D4 or ESF. Note that UFM-C series is ESF only. | D4 (ESF |
line coding | Configures T1 and E1 coding: |
|
| T1: ZCS B8ZS AMI | ZCS |
| E1:HDB3 ZCS | HDB3 |
line CRC on | Enables CRC-4 detection for E1 lines. Use either Y or N | N |
E1 recv impedance | Parameter Impedance Description 1 75 ohm unbalanced 2 75 ohm balanced 3 20 ohm balanced 4 0-133 ft ABAM cable 5 133-266 ft ABAM cable 6 266-399 ft ABAM cable 7 399-533 ft ABAM cable | 1 |
signaling | E1: Common channel signaling (CCS) or | CAS |
| T1: ABCD or ABAB (with ESF line framing) or AB | AB |
encoding | A-law | depends on the back card |
cable type/length | Parameter Voice Circuits Frame Relay Circuits 1 0-220 ft. MAT cable CSU Network Interface 2 220-440 ft MAT cable 0-133 ft ABAM cable 3 440-655 ft MAT cable 133-266 ft ABAM cable 4 0-133 ft ABAM cable 266-399 ft ABAM cable 5 133-266 ft ABAM cable 399-533 ft ABAM cable 6 266-399 ft ABAM cable 533-655 ft ABAM cable 7 399-533 ft not used 8 533-655 ft not used | 4 |
56kbs bit stuffing | most significant byte (msb) | msb |
pct fast modem | Expected ADPCM fast connections (range 0-100). High speed modems preclude the use of ADPCM. Consequently, channel load requirements increase over that required for a voice channel. The pct fast modem parameters specify the expected channel utilization (%) by a high speed modem. | 20 |
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
line | Identifies the line. The line is the slot number of the ALM/A. |
receive rate | Specifies the receive rate for the line. The range for a T3 line is 150 cells per second (cps) through 96000 cps. For an E3 line, the range is 150 cps-96000 cps. |
header type | The header type is either VCC or VPC. The default is VCC. Refer to the IGX-related documentation for an explanation of the header type on the ALM/A. |
payload scramble | Enables or disables payload scramble. The default is No. |
| Parameter | Description | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
line number | Specifies the ASI line to configure | |||
line options | Specifies the ATM line options: | |||
| Parameter | Description | Options | Default |
| Loop clock | Enable loop clocking | Yes/No | No |
| Idle Code | Hex data placed in unused payload of cells. | 0 - FF | 7F |
| Cable | Length and type of cable used for trunk. | 1 = 0 - 225 | 1 |
| HCS Masking | Masking of cell header checksum to disable error checking. | Yes | No | Yes |
| Payload Scramble | Whether or not to scramble (randomize) the cell payload data. Note: for E3, this must always be set to Yes. | Yes | No | No |
| Parameter | Description | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
slot.line | Specifies which line on which slot to configure | |||
line options | Specifies the ATM line options: | |||
| Parameter | Description | Options | Default |
| Loop clock | Enable loop clocking | Yes/No | No |
| Idle Code | Hex data placed in unused payload of cells. | 0 - FF | 7F |
| HCS Masking | Masking of cell header checksum to disable error checking. | Yes | No | Yes |
| Payload Scramble | Whether or not to scramble (randomize) the cell payload data. Note: for E3, this must always be set to Yes. | Yes | No | Yes |
| Frame Scramble | Whether or not to scramble (randomize) the frame data. Note: for E3, this must always be set to Yes. | Yes | No | No |
| Cell Framing | Choose the cell framing format. Select either STS-3C (SONET) or STM-1 (SDH). | STS-3C | STM-1 | STS-3C for OC-3 |
Use the cnfrsrc command to partition resources (ports and trunks) for Automatic Routing Management PVCs, VSI-MPLS (Multiprotocol Label Switching), or PNNI SVCs. To configure SVCs, an Extended Services Processor shelf must be configured in the BPX node. (If you want to configure resources for a VSI-MPLS controller or PNNI SVCs, refer to cnfrsrc in the "VSI Commands" chapter for more information specific to configuring VSI options.)
You can configure a virtual trunk to be dedicated to VSI or to Automatic Routing Management. You cannot configure a virtual trunk for both VSI and Automatic Routing Management.
This command was introduced in Release 9.1 to support physical trunks. It has been extended to support virtual trunks. After VSI has been enabled, the virtual trunk becomes a "dedicated" VSI virtual trunk. Note that if the trunk has already been added or if the VPI value has not been configured, you will not be able to configure the VPI value. (Switch software will block you from doing so.)
Configurable resources (using cnfrsrc) are:
The resources that you can currently configure are the number of connection IDs (conids) and the trunk bandwidth. You use the cnfrsrc command to configure the cell rate and number of connections on a BXM card only. (You cannot use the cnfrsrc command on the IGX.)
You configure all port and trunk attributes with cnftrk, cnftrkparm, or cnfrsrc. Note that when you change a physical port attribute, you will be notified that all the logical (physical and virtual) trunks on the port are affected.
Configure resource
cnfrsrc <slot>.<port> <maxpvclcns> <maxpvcbw> <partition> <e/d> <minvsilcns> <maxvsilcns> <vsistartvpi> <vsiendvpi><vsiminbw> <vsimaxbw>
dsprsrc
| Privilege | Jobs | Log | Node | Lock |
1-6 | No | No | BPX (BXM cards only | No |
cnfrsrc 11.2 256 96000 y 1 e 0 0 1 1 0 0
Configure resource partitions on card slot 11, port 2, to use Automatic Routing Management PVCs.
sw98 TN SuperUser BPX 8600 9.2.0r Apr. 4 1998 16:40 PST
Port/Trunk : 11.2
Maximum PVC LCNS: 256 Maximum PVC Bandwidth:96000
Min Lcn(1) : 0 Min Lcn(2) : 0
Partition 1
Partition State : Enabled
Minimum VSI LCNS: 0
Maximum VSI LCNS: 0
Start VSI VPI: 1
End VSI VPI : 1
Minimum VSI Bandwidth : 0 Maximum VSI Bandwidth : 0
Last Command: cnfrsrc 4.1 256 26000 1 e 512 7048 2 15 26000 100000
Next Command:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
slot.port | Specifies the BXM card slot and port number. |
Maximum PVC LCNs | The maximum number of LCNs allocated for Automatic Routing Management PVCs for this port. The range is 1 to 256. 256 is the default. For trunks, there are additional LCNs allocated for Automatic Routing Management that are not configurable. You can use the dspcd <slot> command to display the maximum number of LCNs you can configure using the cnfrsrc command for the given port. For trunks, "configurable LCNs" represent the LCNs remaining after the BCC has subtracted the "networking LCNs" needed. A trunk has 270 networking LCNs, or channels. For a port card, a larger number is shown, as compared with a trunk card. This is because a trunk uses 270 networking LCNs, as compared with a port card, which uses no networking LCNs. Setting this field to "0" would disable Automatic Routing Management PVCs on the specified port. Note that you must specify a value greater than 0 for the Maximum PVC LCNs, Maximum PVC Bandwidth, and Maximum VSI LCNs parameters. Otherwise, you will not be able to create any Automatic Routing Management PVC connections on a BXM card. Also, if these parameters do not have values greater than 0, you will be unable to change the connection channel amount when you configure the BXM trunk using cnftrk. |
Maximum PVC Bandwidth | Specifies the maximum bandwidth of the port allocated for Automatic Routing Management use. The range is 0 to 352207. 0 is the default. You can configure the Maximum PVC Bandwidth value for ports, but not for trunks. Note that you must specify a value greater than 0 for the Maximum PVC LCNs, Maximum PVC Bandwidth, and Maximum VSI LCNs parameters. Otherwise, you will not be able to create any Automatic Routing Management PVCs on the BXM card. |
Configure Partition | Answer yes or no to begin configuring resources for the partition. If you enter "n" for No, you will not be prompted to configure any VSI options. If you are configuring Automatic Routing Management PVCs, enter "n" for No. |
Partition ID | Specifies the ID number of the partition. 1 is the default. Always use 1 in Release 9.1. In this release, you can use 2. (The range of 0 to 255.) |
Enable Partition | Answer yes or no to enable your configured partition. |
Minimum VSI LCNs | The minimum number of LCNs guaranteed for this partition. The range is 1 to 256. 0 is the default. The VSI controller guarantees at least this many connection endpoints in the partition, provided there are sufficient free LCNs in the common pool to satisfy the request at the time the partition is added. When a new partition is added or the value is increased, it may be that existing connections have depleted the common pool so that there are not enough free LCNs to satisfy the request. The BXM gives priority to the request when LCNs are freed. The net effect is that the partition may not receive all the guaranteed LCNs (min LCNs) until other LCNs are returned to the common pool. You can increase this value dynamically when there are enough unallocated LCNs in the port group to satisfy the increase. You may not decrease the value dynamically. All partitions in the same port group must be deleted first and reconfigured in order to reduce this value. To avoid this deficit condition, which could occur with maximum LCN usage by a partition or partitions, it is recommended that all partitions be configured ahead of time before adding connections. Also, it is recommended that all partitions be configured before adding a VSI controller using the addshelf command. |
Maximum VSI LCNs | The total number of LCNs the partition is allowed for setting up connections. The min LCNs is included in this calculation. If max LCNs equals min LCNs, then the max LCNs are guaranteed for this partition. Otherwise, (max - min) LCNs are allocated from the common pool on a FIFO basis. If the common pool is exhausted, new connection setup requests will be rejected for the partition, even though the maximum LCNs has not been reached. You may increase this value dynamically when there are enough unallocated LCNs in the port group to satisfy the increase. You may not decrease the value dynamically. All partitions in the same port group must be deleted first and reconfigured in order to reduce this value. Different types of BXM cards support different maximum values. If you enter a value greater than the allowed maximum, a message is displayed with the allowable maximum value. Note that you must specify a value greater than 0 for the Maximum VSI LCNs, Maximum PVC Channels, and Maximum PVC Bandwidth parameters. Otherwise, you will not be able to add any connections on a BXM card. |
Start VSI VPI | By default the TSC (for example, the 7200 or 7500 series router) will use either a starting VSI VPI of 1 or 2 for tag switching, whichever is available. If both are available, a starting VSI VPI of 1 is used. The VPI range should be 2-15 on a BPX 8620 VSI. The VSI range for tag switching on the BPX 8620 is configured as a VSI partition, usually VSI partition number 1. VSI VPI 1 is reserved for Automatic Routing Management PVCs. (This restriction applies only to trunks, not to ports. For a port, you can use any VPI value.) For a port UNI, the VPI range is 1 to 255. For a port NNI, the range is 1 to 4095. For trunks that do not have Automatic Routing Management configured, the VPI ranges are the same as for ports. The VSI partition for tag switching should start at VPI 2. If VPI 2 is not to be used, you can use the tag switching VPI interface configuration on the TSC to override the defaults. For trunks with Automatic Routing Management configured, the range is 2 to 4095. Always set to 2 for trunks. |
End VSI VPI | Two VPIs are sufficient for Release 9.1, although it may be advisable to reserve a larger range of VPIs for later expansion, for example, VPIs 2-15. The range is the <Start VSI VPI > value to 4095. |
Minimum VSI Bandwidth | The minimum port bandwidth that can be used by this partition in cells/second. The range is 0 to <Maximum Line Rate>. For example, the OC-3 line rate is 352207. 0 is the default. |
Maximum VSI Bandwidth | The maximum port bandwidth that can be used by this partition. This value is used for VSI Qbin bandwidth scaling. The range is 0 to <Maximum Line Rate>. For example, the OC-3 line rate is 352207. 0 is the default. |
Deactivates ("downs") a line. After dnln executes, the line no longer generates framing, and no statistics are gathered. Before you deactivate a line, use delcon to remove all connections on the line and use dnport to deactivate the port associated with the line.
Down line
dnln <line number>
upcln, dsplns, dsptsmap
| Privilege | Jobs | Log | Node | Lock |
1-2 | Yes | Yes | IPX, IGX, BPX | Yes |
dnln 12
Deactivate line 12.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
line number | Specifies the line. If the back card has one line, enter the slot number. If the card has more than one line, include a line number. |
dnln 3.12
Deactivate line 12 on slot 3.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
slot.line number | Specifies the slot and line to down on the UXM. |
Displays the configuration of a line. Table 5-11 shows all possible parameters in the display. The fields that actually contain data depend on the type of line.
| Screen Item | Description | Options |
|---|---|---|
LN configuration | Line type and the number of channels. | T1 |
Loop clock | Specifies whether the receive clock is | Y |
Line framing | Identifies the type of line framing | DS4 for T1 |
Line coding | Identifies the line coding used by | E1: HDB3, AMI |
CRC | Specifies the CRC checking on E1 lines | Y |
recv impedance | Nominal impedance for the receive line. | 75 ohms balanced or unbalanced 120 ohms balanced |
E1 signaling | Identifies the signaling type used for E1. | CCS or ABCD with CAS |
encoding | Specifies the voice encoding scheme | µlaw |
T1 signaling | Identifies the signaling type used for T1 | ABCD or ABAB (with ESF line framing) or AB (with D4 line framing); CCS is available in timeslot 24 if applicable PBXs need it. |
56 kbps Bit Pos: | Position in word for bit stuffing on 56 kbs data channels. | MSB or LSB |
Pct fast modem |
|
|
Cable type | Specifies the T1 or E1 cable type (used | MAT |
Cable length | Specifies the T1 or E1 cable length in | 0-220 220-440 440-655 0-133 133-262 262-393 393-524 524-655 T3/E3 = 0-255 ft.|greater than 255 ft. |
Cnfg | Applies to the UVM: cnfg shows the mode of an individual UVM port. The slot.line identifies the line. | External, Passing, Blocked, or Inserting See the UVM documentation in the Cisco IGX 8400 Series Reference for a description of these modes. |
Transmit Line Rate | Applies to ATM line cards: the display | The value is always the maximum for the line and is in cells per second (cps): 96000 cps for T3, 80000 cps for E3, or 353208 cps for OC-3. |
Receive Line Rate | Applies to ATM line cards: the display | The value is in cells per second (cps). The range is 150-9600 cps for T3, 150-80000 cps for E3, or 353208 cps for OC-3. |
Header Type | Applies to ATM cards: the display | The header type is VCC or VPC. |
Payload Scramble | Applies to ATM cards: the display | The display shows "Yes" or "No." |
Display line configuration
dsplncnf <line number>
cnfln (obsolete name: cnfcln)
| Privilege | Jobs | Log | Node | Lock |
1-6 | No | No | IPX, IGX, BPX | o |
dsplncnf 5.1
Displays configuration for line 1 of the UVM in slot 5. The "cnfg" field shows "External," so all DS0s terminate on line 1. Also, CAS switching is off, and SVC caching is on.
sw175 TN SuperUser IGX 8420 9.2 Sep. 17 1998 23:28 PST
LN 5.1 Config E1/30 UVM slot: 5
Loop clock: No
Line framing: On cnfg: External
coding: HDB3 slot.line: --
CRC: No CAS-Switching: Off
recv impedance: 75 ohm + gnd SVC-Caching : On
E1/J1 signalling: CAS
encoding: A-LAW
T1 signalling: --
cable type: --
length: --
56KBS Bit Pos: msb
pct fast modem: 20
Last Command: dspclncnf 5.1
Next Command:
dsplncnf 13
Display the configuration of the line card in slot 13. The card in slot 13 is an ALM/A.
sw142 TN SuperUser IGX 16 9.1 July 31 1997 12:01 PDT
LN 13 Config T3/1 [150 cps] ALM slot: 13
Transmit Line Rate: 96000 cps
Receive Line Rate: 150 cps
Header Type: VCC
Payload Scramble: No
Last Command: dsplncnf 13
Next Command:
dsplncnf 12.1
Display the line configuration for 12.1. The card is slot 12 is an ASI in a BPX node.
ca20 LAN SuperUser BPX 8620 9.2 Aug. 23 1998 10:35 PST
LN 12.1 Configuration T3 [96000 cps] ASI-T3 slot:12
Loop clock: -- Idle code: 7F hex
Line framing: --
coding: --
CRC: --
recv impedance: --
E1 signalling: --
encoding: -- cable type:
T1 signalling: -- length: 0-450 ft.
HCS Masking: Yes
Payload Scramble: No
56KBS Bit Pos: --
pct fast modem: --
Last Command: dsplncnf 12.1
Next Command:
dsplncnf 7.1
Displays configuration for line 1 of the UXM OC-3 card set in slot 7.
sw224 TN SuperUser IGX 16 9.0.n2 Aug. 27 1997 16:09 GMT
LN 7.1 Config OC-3 UXM slot: 7
Loop clock: No
Idle code: 7F hex
HCS Masking: Yes
Payload Scramble: Yes
Frame Scramble: Yes
Cell Framing: STS-3C
Last Command: dsplncnf 7.1
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
line number | Identifies the line in the format slot or slot.line. If the back card has one line connector and cable, enter the slot number. If the card has more than one physical line, such as a UXM, enter a slot and line number. In the case of a UVM, however, enter just the slot number. |
Displays basic configuration and status information for all the lines on the node. The information includes the line number, the type of line, and the line alarm status. The line type shows whether the line is J1, T3, E3, T1, E1, or OC-3 and shows the number of configured DS0s. Line alarm status categories include:
♦ Clear—Line OK | Alarm Information Signal |
♦ Loss of Signal | Remote Out of Frame |
♦ Out of Frame | Remote Out of Packet Frame |
♦ Minor—Bad clock source | Loss of Multiframe |
display lines
dspclns
dncln, dsptrks, upcln
| Privilege | Jobs | Log | Node | Lock |
1-6 | No | No | IPX, IGX, BPX | No |
dsplns
Display circuit lines on the node.
sw109 VT SuperUser IGX 8420 9.2 Aug. 20 1998 18:40 PST
Line Type Current Line Alarm Status
3 T1/24 Clear - OK
5.1 E1/30 Clear - OK
5.2 E1/30 Clear - OK
5.3 E1/30 Clear - OK
5.7 E1/30 Clear - OK
5.8 E1/30 Clear - OK
7.1 T1/24 Clear - OK
11 E1/30 Clear - OK
Last Command: dsplns
Next Command:
Use the dsptsmap command to display the channel to time slot mapping usage information on a UVM card on an IGX node or a CDP/CVM card on an IPX node. The dsptsmap command is for use with the SVC caching feature which speeds up call setup for most VNS controlled calls. The SVC caching feature avoids some of the call setup/tear-down operations associated with addcon and delcon as a call originates or terminates. The SVC caching feature reduces the connect time for many switch calls over a busy network.
To use the dsptsmap command, the line must have SVC caching enabled on it. You can find out if a channel is disabled by using the dsptsmap command.
The cnfln command is used to configure the SVC caching parameter setting.
The dspcons command is used to view disabled connections provided the SVC has not been deleted.
The dsplncnf command will show the value (On/Off) of the SVC caching mode feature.
Refer to the VNS Installation and Configuration Manual for more information on SVC caching.
Display the channel to time slot mapping usage for a UVM on an IGX node.
dsptsmap <line_number>[update_interval]
cnfuiparm, cnfln, cnfupcln, dncln, dsptrks, dspln, dsplncnf
| Privilege | Jobs | Log | Node | Lock |
1-6 | No | No | IPX, IGX | No |
dsptsmap 7.2
Display channel to time slot mapping for a specified line.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
line_number | slot.line for UVM or line for CVM/CDP |
interval_number | Interval in seconds between screen updates. The default value is controlled by "Screen Update Time" in the cnfuiparm command. |
dsptsmap 9 1
Enabled channels are shown on the screen underlined and in reverse video. Disabled (cached) channels are shown with the channel number underlined and in reverse video, while the time slot is shown in normal video. Channels that have no connection are shown in normal video for both channel number and time slot.
For example:
Specify the line_number parameter in slot.line format for UVM, and line format for CDP/CVM.
Use the optional update_interval parameter to control how often the screen gets updated. If you do not enter any value through the CLI, the value of the "Screen Update Time" parameter set using in the cnfuiparm command is used.
sw176 TRM StrataCom IGX 16 9.1.0 Sep. 5 1997 11:00 PST
Line 7.2 Channel to Timeslot Map
Chan TS Chan TS Chan TS Chan TS
-------- -------- -------- --------
1 1 9 14 17 17
2 2 10 12 18 5
3 22 11 18 19 19
4 5 12 10 20 20
5 11 13 13 21 21
6 6 14 9 22 3
7 7 15 15 23 23
8 8 16 9 24 24
This Command: dsptsmap 7.2
Hit DEL key to quit:
Prints the current line configuration and line alarm status for a node. This command uses the same syntax, and prints the same information as is displayed using the dsplns command. See the dspclns command for syntax and output information.
print line configuration
prtlns
dsplns
| Privilege | Jobs | Log | Node | Lock |
1-6 | Yes | No | IGX, BPX | Yes |
prtlns
This command uses the same syntax and prints the same information as is displayed using the dsplns command. See the dsplns command for syntax and output information.
Activates (ups) a line. Use the upln command to make the line available for configuring and to start statistics gathering.
You must activate ports at both ends of the line by executing the upport command before running upln. You must execute upln at both ends of the line. Executing upln at only one end of the line eventually causes an alarm. Once both ends of the line are active, you can add connections with the addcon command or optionally configure the line's signal characteristics for the data you intend for the line. See cnfln for information on defining the line characteristics.
A line consists of a cable for transmitting data and the interface circuitry for the line. The cable can be a coaxial wire, fiber optic, or a twisted pair. See Table 5-1 for information on card combinations.
The Ports and Trunks feature lets you configure multiple trunk lines and circuit line cards on a single BXM or UXM card simultaneously. In previous releases, when a single port is upped as a trunk (by using the uptrk command), all the remaining ports on that card are treated as a trunk. Similarly, when you upped a single port as a circuit line (by using the upln command), all the remaining ports on the card are treated as circuit line ports.
The Ports and Trunks feature lets you configure multiple trunk lines and circuit lines on a single BXM or UXM card simultaneously. In previous releases, when a single port is upped as a trunk (by using the uptrk command), all the remaining ports on that card are treated as a trunk. Similarly, when you up a single port as a circuit line (by using the upln command), all the remaining ports on the card are treated as circuit line ports. This feature allows the BXM and UXM trunks to be trunk line cards as well as circuit line cards, and to allow trunks and circuit lines to coexist on these cards.
For example, assuming that a four-port BXM card is plugged into slot 11, you could do the following:
1. uptrk 11.1
2. upln 11.2
3. upln 11.3
4. uptrk 11.4
That is, you could up a trunk at port 1 on slot 11, up a line at port 2 of slot 11, up a line at port 3 of card slot 11, and also up a trunk at port 4 of card slot 11.
In Release 9.2, the BXM or UXM card can be a trunk card and a line (port) card at the same time. For example, a BXM slot can up port 1 as a trunk interface while upping port 2 as a line interface.
To support the Multi-Level Channels Statistics feature, you will be prompted when you attempt to up the line with upln or up the trunk with uptrk, warning you that you must initialize the channel statistics level before the card will be activated. This warning applies only when upping the first trunk or first line on the card.
Channel Statistic Level must be initialized prior to card activation
Up line
upln <line number>
cnfcln, dsplns, dspln, dncln
| Privilege | Jobs | Log | Node | Lock |
1-2 | Yes | Yes | IPX, IGX, BPX | Yes |
upln 4.2
Activate line 4.2. After this command executes, the system displays the status of the line using the same information as dsplns displays.
ca19 VT SuperUser BPX 8620 9.2 Aug. 23 1998 19:08 GMT
Line Type Current Line Alarm Status
4.1 T3 Clear - OK
4.2 T3 Clear - OK
Last Command: upln 4.2
Next Command:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
line number | Identifies the line number in the form slot for a single-line card or slot.port for a card with more than one line. |
upln 3.2
Activate line 2 on slot 3. After this command executes, the system displays the status of the line using the same information as dsplns displays.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
slot.line number | Specifies the slot and line to up on the UXM. There can be no more than sixty four (64) lines per node. The upln command will be rejected if all sixty four lines have already been upped. |
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Posted: Fri Nov 8 07:08:09 PST 2002
All contents are Copyright © 1992--2002 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Important Notices and Privacy Statement.