|
|

The management functions available on the FastPADmp/mpr units are:
The user can access most of these functions, known as "called functions". Only the alarm transmission function is a "calling" function, since it transmits alarm messages to the user.
Access to the "called" functions can be obtained by using the following syntax:
The access code must be typed without spaces between the various identifiers (e.g. 19200099D19TT00).
Only one subscriber can access a function at a given time (except for the traffic generator function).
DNIC : | Identification of the whole private network or a sub-network. | |
ZO : | Identification of the zone in the network, corresponding to the equipment. | |
AB : | Management function subscriber number. | |
| The management functions are treated as an internal subscriber of the FastPADmp. The subscriber number are: | |
| 99: | standalone equipment, |
| 90: | module 0 of equipment, |
| 91: | module 1 of equipment, |
| 92: | module 2 of equipment. |
D : | Data separator. |
|
IS No : | Internal service number characterizing the text of the messages distributed by the FastPADmp may be written in: | |
| · binary code, for processing by a management center, | |
| · ASCII | for use by a |
| · clear language | terminal |
(CR) : | Carriage return key
|
|
The examples of messages given on the pages that follow are in ASCII or clear language only.
The assignment of the IS Nos. is as follows:
| Function | Internal Service |
| ||
| Binary | ASCII | Clear Language | Default Password | |
Traffic generator Outstanding events Exchange observation File transfer Statistics Alarms Telemaintenance Configuration MMI (Man-Machine Interface) Billing Dynamic line management (DLM) Management Access Point (MAP) Extended statistics | - 01 03 09 05 - 11 - - 07 - 32 - | 00 02 04 - 06 - 12 - - 08 - - - | - 15 or 16 - - 14 - - 10 17 - - 18 20 | GG EE OO TT SS
MM CC RR TX
PP SC |
PASSWORD: | The password that has to be entered to access the management functions. This password consisting of from 1 to 6 alphanumeric characters, is defined at the time of configuration and may be different for each function. To allow calling from a terminal, the parity bit is ignored when the password is checked. Except for screening by the password, there is no restriction on the address of the calling party. |
ACO No: | This is the suffix; it is a special addition to some internal services. It is defined in the paragraphs dealing with each of these services. |
Calling the traffic generator function (in ASCII) of equipment with address 192000185 in the TRANSPAC network.
The access code to the internal service is:
 Traffic Generator Access Code
Traffic Generator Access Code
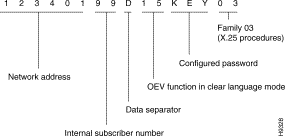
Calling the outstanding events (OEV) function (password KEY, ACO No. = 03) in the clear-language mode, of node 01 of network 1234.
The access code of the internal service is:
When an erroneous access code is typed, access to the management function selected is rejected and an error code is displayed on the screen. The meanings of the codes are given in Chapter 15 (Network Trouble Management).
Cause | Message |
· password incorrect: | Clear DTE 182 |
· internal service number: | |
· internal service number busy: | Clear DTE 181 |
· line number of the "Observation" function incorrect | Clear DTE 183 |
· line number of the OEV family function incorrect: | Clear DTE 184 |
All messages delivered by a management function have the same heading.
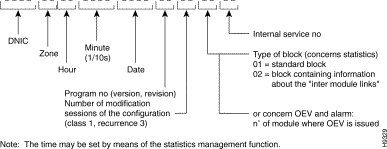
EQUIP No : ------
DATE : --/--/-- TIME --/--/--
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Posted: Thu Jan 25 13:46:25 PST 2001
All contents are Copyright © 1992--2001 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Important Notices and Privacy Statement.