|
|

The system reports communicate the operating and call processing status of the system to the host. These reports fall into three categories—configuration control, system status, and resource control.
The system reports consist of a string of bytes immediately following the Network Header. Refer to "Message Structure Overview." Although the format of the reports varies, they all begin with a Function Identifier. Table 5-1 shows the report type and Function ID for each system report.
| Function ID | Report Name | Report Type |
|---|---|---|
$80 | Resource Allocation | System Status |
$81 | Hardware Allocation | System Status |
$82 | Card Status | System Status |
$83 | Port Status | System Status |
$D0 | MF Digit | Resource Control |
$D1 (Standard) | DTMF Digit | Resource Control |
$D1 (Enhanced) | DTMF Digit | Resource Control |
$D2 | Permanent Signal Condition | Resource Control |
$D3 | Port Status | System Status |
$D4 | Spoken Digit | Resource Control |
$D6 | Resource Limitation | System Status |
$D9 | Card Status | System Status |
$DA | Outgoing Port Change of State | Resource Control |
$DB | Incoming Port Change of State | Resource Control |
$DC | Active/Standby Mode | Configuration Control |
$DD | Inpulse Rule Complete | Resource Control |
$DE | Voice Port Status | Resource Control |
$EA | ISDN Port Change of State | Resource Control |
$ED | ISDN Inpulse Rule Complete | Resource Control |
$F0 | Alarm Condition | System Status |
This chapter is divided into sections—one for each report—and arranged according to each report's Function ID.
The description for each report contains the following information:
Each byte in a report is a hexadecimal (base 16) number. Most reports require you to convert this hexadecimal number into binary (base 2) or decimal (base 10) numbers to interpret the byte. A Decimal-Hexadecimal-Binary conversion table is provided in Appendix B.
Byte offset values under the Format heading are counted from the initial byte of the Network Header (byte offset 0 to 3). Interpret these values according to the following list.
| Byte Offset | Meaning |
|---|---|
a | A single byte. |
a and b | Two consecutive bytes. |
a to c | All consecutive bytes between a and c. |
a/b | The second nibble of byte a and all of byte b. |
a to n | A variable number of consecutive bytes between a and n, inclusive. |
n + 1 | A byte that follows a variable. |
 |
Note Unless otherwise stated, all MF processing described in this chapter applies to both MF and MFCR2 processing. |
System Status
Same as Source VCA of command requesting this report.
The Resource Allocation ($80) report returns a bit map containing the status of each port within a given range and specified resource group. This report takes the same form as the Request Resource Allocation ($80) command, with the port information attached. The $80 report shows if a port is of the specified resource group and whether it is on line or off line. Ports in the maintenance busy state are reported as being off line. This report does not specify if the port is idle or busy. Each status byte contains information on four adjacent ports.
The $80 report is generated in response to an $80 command. If the resource group for which the report is requested is empty, the report is returned with the $01 network status byte—message processing was successful—but without any $80 report status bytes attached.
Figure 5-1 shows byte formatting for this report.

Function ID (byte offset 4)—Byte immediately following the Network Header; uniquely identifies the report from the system.
Address Range and Resource Group (byte offset 5)—Specifies the range of port addresses and resource group shown in this report; convert byte from hexadecimal to binary and interpret the bits as follows.
RRGGGGGG
Status Bytes (byte offsets 6 to 133)—Each report contains 128 Status Bytes; each Status Byte contains information for four adjacent ports. Ports are counted from lowest address to highest address within the requested range. Convert the byte from hexadecimal to binary and interpret the bits in pairs as described below.
The report below is in response to an $80 command.
04 05 06 07 08 09...nn
80 15 00 00 FF C1...55
Function ID = 80 (Resource Allocation)
Address Range and Resource Group = 00010101
Status Byte 1 = 00000000
Status Byte 2 = 00000000
Status Byte 3 = 11111111
Status Byte 4 = 11000001
Status Byte 128 = 01010101
The report below is in response to a Request Resource Allocation command for a resource group that is not defined in the database.
04 05
80 60
Function ID = 80 (Resource Allocation)
Address Range and Resource Group = 11000000
System Status
Same as source VCA of command requesting this report.
The Hardware Allocation ($81) report returns a bit map of ports within a given range. The report contains 66 bytes. The first two bytes contain the Function ID and Address Range information. The next 64 bytes contain hardware address information, with each byte representing 8 port addresses.
The $81 report is generated in response to a Request Hardware Allocation ($81) command.
Figure 5-2 shows the byte formatting for this report.
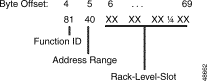
Function ID (byte offset 4)—Byte immediately following the Network Header; uniquely identifies the report from the system.
Address Range (byte offset 5)—Specifies the port address range for which the report was generated. Interpret the byte according to the following list.
Rack-Level-Slot (byte offset 6 to 68)—Each report contains 64 rack, level, slot (R-L-S) bytes; each byte contains 8 port addresses worth of information. Interpret the bytes according to Table 5-2.
| Hexadecimal Values | R-L-S Range |
|---|---|
$01 to $14 | 1-1-2 to 1-1-21 |
$15 to $29 | 1-2-1 to 1-2-21 |
$2A to $3E | 1-3-1 to 1-3-21 |
$3F to $53 | 2-0-1 to 2-0-21 |
$54 to $68 | 2-1-1 to 2-1-21 |
$69 to $7D | 2-2-1 to 2-2-21 |
$7E to $92 | 2-3-1 to 2-3-21 |
The report below gives the R-L-S locations for ports in the address range $200 to $3FF. Port addresses $220 to $237 correspond to a card in R-L-S location 1-2-2, and port addresses $2E0 to $2F8 correspond to a card in R-L-S location 1-3-9. All other port addresses in this range are not allocated. Because they are T1 cards, they have 24 port addresses assigned to them.
81 40 00 00 00 00 16 16 16 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
32 32 32 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
00 00 00 00 00 00
No status bytes attached.
System Status
Same as Source VCA of command requesting this report.
The Card Status ($82) report informs the host of the status of a card. The card location is represented both by the port address and the physical rack, level, and slot (R-L-S) address. The report includes the status of the card and the type of the card.
One $82 report is generated for each card specified in a Card Status ($82) command. In the case of a multispan card, an $82 report is generated for each span in the slot.
The $82 report takes the form of a command returned with a $01 network status byte.
The system's response to the $82 command is a separate $82 report for each card specified in the $82 command from the host. In the case of a multispan card, a separate $82 report is generated for each interface.
Figure 5-3 shows the byte formatting for this report.
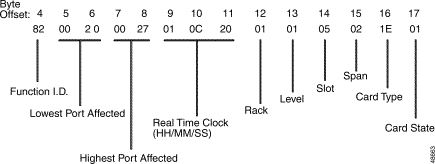
Function ID (byte offset 4)—Byte immediately following the network header; uniquely identifies the report from the system.
Lowest Port Affected (byte offsets 5 and 6)—Hexadecimal representation of the first port address on the card for which the report is sent. This is also useful in identifying the span for which the report is sent in the case of a multispan card. This field is set to $00 if the card is not found in the database.
Highest Port Affected (byte offsets 7 and 8)—Hexadecimal representation of the last port address on the card for which the report is sent. This is also useful in identifying the span for which the report is sent in the case of a multispan card. This field is set to $00 if the card is not found in the database.
Real Time Clock (byte offset 9 to 11)—Time represented in the format Hours:Minutes:Seconds; hours, minutes, and seconds are represented separately in hexadecimal.
Rack-Level-Slot Code (byte offsets 12 to 14)—Specifies the rack, level, and slot in which the card is located. Valid values are:
Convert the decimal value of the slot into hexadecimal for encoding. For multispan cards (4xE1/T1), if the query has a zero as the span specifier, (representing all four interfaces), there will be four responses, one for each interface. In this case, the $82 reports contain the same R-L-S for all the spans, but the lowest and highest ports affected are differentiated. The span specifier indicates the span for which the report is generated.
Span Code (byte offset 15)—Represents the interface (span) number for a multi-span card, for which the report is generated. The value is 1 for a single-span card status report.
Card Type (byte offset 16)—Type of the card for which the report is generated. This field is set to $00 if the card is not found in the database. The possible values of the field, if the card is present in the database, are as follows:
Card State (byte offset 17)—Card states are defined as follows:
The following $82 command requests the status of the cards 1, 1, 6 and 1, 1, 7.
04 050607 08 091011 12
82 010106 00 010107 02
Function ID = 82 (Card Status)
Starting RLS = 1, 1, 6
Span = all spans
Ending RLS = 1, 1, 7
Span = spans 1 and 2
The following two $82 reports are generated for the command in Example 5-4:
04 0506 0708 091011 12 13 14 15 16 17
82 0020 003F 010C20 01 01 06 01 19 01
04 0506 0708 091011 12 13 14 15 16 17
82 0040 005F 010C20 01 01 07 01 1F 02
04 0506 0708 091011 12 13 14 15 16 17
82 0060 007F 010C20 01 01 07 02 1E 02
System Status
Same as source VCA of the command requesting this report.
The Port Status ($83) report informs the host of the status of a range of ports. The command, for which the report is generated, forms the leading portion of the report. This leading portion is followed by a series of port status report elements, each of which is three bytes long. The first two bytes specify the port address; the third byte specifies the call processing status of the port.
If the port range for which the status report is requested is such that one $83 report cannot accommodate all the port status report elements, the report is split into as many $83 reports as necessary. Such fragments are distinguished from each other through a continuity bit.
Up to 82 port status report elements can be in one $83 report, considering that the maximum length of the report is 256 bytes.
The $83 command generates the $83 report. If the $83 command is successfully processed, the network status byte is set to $01.
Figure 5-4 shows the byte formatting for this report.
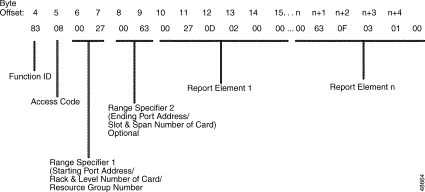
Function ID (byte offset 4)—Byte immediately following the Network Header; uniquely identifies the report from the system.
Access Code (byte offset 5)—Copied from the Port Status ($83) command for which the report is being generated. Only bit C is modified, if required.
A port address range can be specified in different ways. The access code specifies the way in which the port address range is chosen.
C000 AGR0
Range Specifier 1 (byte offsets 6 and 7)—Copied from the $83 command for which the report is being generated.
Range Specifier 2 (byte offsets 8 and 9)—This is an optional field in $83 reports. Copied from the $83 command for which the report is being generated.
Report Element 1 (byte offsets 10 to 14)—If Range Specifier 2 is not present, the first Report Element starts at byte offset 8. This forms the single report element containing the port status report for one port. Other similar report elements follow.
The first two bytes (byte offsets 10 and 11) specify the port address; the third byte (byte offset 12) specifies the call processing state of the port. Table 5-3 lists the possible port call processing major states.
| Hexadecimal Value | Major Call Processing State |
|---|---|
0 | CP_IDLE |
1 | CP_WAIT |
2 | CP_WWINK |
3 | CP_DIAL |
4 | CP_STAB |
6 | CP_WANS |
7 | CP_DCON |
9 | CP_GARD |
0xB | CP_FEXC |
0xC | CP_WTIM |
0xD | CP_MBUSY |
0xE | CP_MFWT |
0xF | CP_SETUP |
0x10 | CP_PRIMARY |
0x11 | CP_RDR |
0x12 | CP_MF |
0x13 | CP_ATT |
0x14 | CP_DIAG |
0x15 | CP_DISC |
0x16 | CP_HOST |
0x17 | CP_FDIG |
0x18 | CP_DIG |
0x19 | CP_INPULSE |
0x1A | CP_DTMF |
0x1B | CP_TALK |
0x1C | CP_TONE |
0x1D | CP_CONF |
0x1E | CP_MON |
0x1F | CP_OUTPULSE |
0x20 | CP_WTONE |
0x21 | CP_SPEECH |
0x22 | CP_SELFTEST |
0x23 | CP_WTFSUP |
0x24 | CP_ANALYZE |
0x25 | CP_RECORD |
0x26 | CP_CPAMON |
0x27 | CP_DONECOLLECT |
0x28 | CP_DELAY |
0x29 | CP_WAITACK |
0xFE1 | CP_OOS |
0xFF2 | CP_NOTINDB |
| 1If the card containing the port is OOS. 2If the card containing the port is not defined in DB. |
Byte offset 13 indicates the supplementary state of the port with respect to the major state of the port. Table 5-4 lists the possible port call processing supplementary states.
| Major State | Hexadecimal Value | Supplementary Call Processing State |
|---|---|---|
Reorder | 0x01 | RDR_FBUSY |
0x02 | RDR_QUIET | |
0x04 | RDR_DONE | |
TNK wait | 0x01 | WT_DTMF |
0x02 | DIALING | |
0x03 | WT_DIAL | |
0x04 | WT_SPC | |
0x04 | WT_ANNC | |
0x08 | WT_BEEP | |
0x10 | SPC_ATT | |
0x10 | WT_TALK | |
0x20 | WT_PSC | |
0x40 | WT_TIM | |
0x80 | WT_MF | |
Guard | 0x00 | GD_NORMAL |
0x01 | GD_WTRLS | |
0x02 | GD_WTRLSH | |
Diagnostic/maintenance busy | 0x00 | DIAG_IDLE |
0x01 | DIAG_CMAINT | |
0x02 | DIAG_PATH | |
0x03 | DIAG_OEND | |
0x04 | DIAG_AUTO | |
0x05 | DIAG_INTRN | |
0x06 | DIAG_TEST | |
Conference port | 0x01 | CF_1WAY |
0x02 | CF_2WAY | |
0x04 | CF_SET | |
0x08 | CF_ACK | |
0x10 | CF_RSRV | |
Receiver enabling | 0x01 | DLY_TIME |
0x04 | DLY_WINK | |
0x08 | DLY_ANS | |
0x10 | DLY_ANN | |
Dialing | 0x00 | D_UNK |
Outpulse rule | 0x01 | DIAL_DIG |
0x02 | WAIT_SUP | |
0x03 | WAIT_TM | |
0xFE1 | CARD_OOS_STATE | |
0xFF2 | NOT_INDB_STATE |
| 1If the card containing the port is OOS. 2Card containing the port is not defined in DB. |
Byte offset 14 indicates the ISDN state of the port. Table 5-9 lists the possible values of the port call processing ISDN major states.
| Hexadecimal Value | ISDN Major State |
|---|---|
0x00 | PT_ACTIVE |
0x01 | PT_OOS_NE |
0x02 | PT_OOS_FE |
0x03 | PT_MAINT_NE |
0x04 | PT_MAINT_FE |
0x05 | PT_DCHAN |
0x06 | PT_OOS_FE_MAINT_NE |
0xFD1 | PT_NON_CNTRLD |
0xFE2 | PT_OOS_STATE |
0xFF3 | PT_NOT_INDB |
| 1If the card containing the port is not ISDN controlled. 2If the card containing the port is OOS. 3Card containing the port is not defined in DB. |
Byte offset 15 indicates the ISDN sub-state of the port. Table 5-6 lists the possible port call processing ISDN supplementary states.
| Hexadecimal Value | ISDN Supplementary State |
|---|---|
0x00 | ISDN_IDLE |
0x01 | O_INITED |
0x02 | O_OVRLP |
0x03 | O_PRCEED |
0x04 | O_ACTIVE |
0x05 | O_DELIVRD |
0x0B | I_CPRSNT |
0x0C | I_OVRLP |
0x0D | I_PRCEED |
0x0E | I_CONNECT |
0x0F | I_DELIVRD |
0x10 | I_ACTIVE |
0x14 | DISC_IND |
0x15 | DISC_REQ |
0x16 | DISC_RLS |
0x80 | ISDN_WAIT |
0xFD1 | PORT_NON_CNTRLD |
0xFE2 | PORT_OOS |
0xFF3 | PORT_NOT_INDB |
| 1If the card containing the port is not ISDN controlled. 2If the card containing the port is OOS. 3Card containing the port is not defined in DB. |
The following command requests status reports for ports $27 and $28. The command specifies the range through port addresses:
04 05 0607 0809
83 08 0027 0028
Main command segment elements are as follows:
Function ID = 83 (Port Status)
Access Code = 0000 1000 (C000 AGRS)
Starting Port Address = 0027
Ending Port Address = 0028
The following report is generated for the command in Example 5-5.
04 0506 0708 091011121314 15161718192021
83 0800 2700 2800270D02FD FD002800000000
Function ID = 83 (Port Status)
Access Code = 0000 1000 (C000 AGRS)
Starting Port Address = 0027 (Copied from command)
Ending Port Address = 0028 (Copied from command)
Port Address = 0027 (Report Element 1)
Port Status = 0D (CP_MBUSY)
Supplementary State = 02 (DIAG_PATH)
ISDN State = fd (Unknown)
ISDN Sub-state (Unknown)
Port Address = 0028 (Report Element 2)
Port Status = 00 (CP_IDLE)
Supplementary State = 00 (IDLE)
ISDN State = 00 (PT_ACTIVE)
ISDN Sub-state (ISDN Idle)
 |
Note Unless otherwise stated, the MF processing described in this section applies to both MF and MFCR2 processing. |
Resource Control
$40
The MF Digit ($D0) report transfers MF digit collection information from the system to the host. Report indicates if the digit report is valid and the incoming port from which the digits were collected. If a collection error occurred, the present state of the Controlling Port (CP_SETUP or forced to idle) is also indicated. This report can be included as a report segment in an Inpulse Rule Complete ($DD) report.
The report indicates if garbled MF digits were detected by the receiver. A garbled MF digit is declared if one of the following conditions exists:
The $D0 report is generated in direct response to an MF Collection Control command ($68), or as a result of inpulse rule processing. In MF processing, KP and ST are stripped from the digit report by the system. In MFCR2 processing, Group I-15 digits are stripped from the digit report by the system.
Figure 5-5 shows the byte formatting for this report.
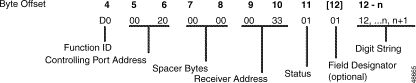
Function ID (byte offset 4)--Byte immediately following the Network Header; uniquely identifies this report from the system.
Controlling Port Address (byte offsets 5 and 6)—Hexadecimal representation of the incoming port from which the digits were collected. Omitted if the report is included as a segment in a $DD report.
Spacer Bytes (byte offsets 7 and 8)—Reserved for future enhancements; always returned as 00 00. Omitted if the report is included as a segment in a $DD report.
Receiver Address (byte offsets 9 and 10)—Hexadecimal representation of the MF/MFCR2 receiver port processing the incoming digits.
Status (byte offset 11)—In MF processing, this byte indicates the status of the digit report; convert byte from hexadecimal to binary and interpret the bits as described below.
VS000XYZ
In MFCR2 processing, this byte also indicates the status of the digit report. However, only the Y and Z bytes are converted from hexadecimal to binary as described below.
000000YZ
Optional Field Designator/Digit String (byte offsets 12 to n)—When the "Enable Digit Field Reporting" feature is enabled from either Data Base Administration Menu or Maintenance Menu of the System Administrator database, the byte at offset 12 indicates into what field the system stores the reported digits (refer to the Cisco VCO/4K System Administrator's Guide). Possible byte values are as follows:
Digit String (byte offsets 12 + n to n)—Collected MF digits; digits represented are from 1 to 9, and 0 ($A). Each nibble in the hexadecimal byte represents a single digit. The Digit String always ends with an $F. The KP, ST, ST1, ST2, and ST3 digits are stripped from the digit string before the report is sent. If the "Enable Digit Field Reporting" feature is not enabled, then the Digit String bytes begin at byte offset 12. The Optional Field Designator and Digit String are included only when Z = 1 in the MF Status byte.
The following report shows an MF receiver port at address $34 used to collect three MF digits (1, 2, 3) from the incoming port at address $18. The "Enable Digit Field Reporting" feature has not been enabled.
04 0506 0708 0910 11 12 13
D0 0018 0000 0034 01 12 3F
Main command segment elements are as follows:
Function ID = D0 (MF Digit)
Controlling Port Address = 0018
Spacer Bytes = 00 00
MF Receiver Address = 0034
MF Status = 00000001
Digit String = 123 (F marks end of string)
The report below shows the MF digit collection was aborted due to a timeout. The controlling port at address $021 was placed into CP_SETUP state to await further host action. No digits are reported.
04 0506 0708 0910 11
D0 0021 0000 0034 42
Main command segment elements are as follows:
Function ID = D0 (MF Digit)
Controlling Port Address = 0021
Spacer Bytes = 00 00
MF Receiver Address = 0034
MF Status = 01000010
No digit string attached
Resource Control
$40
The DTMF Digit ($D1) (Standard) report transfers DTMF/DP digit collection information from the system to the host. The report indicates whether the digit report is valid and the line or trunk from which the digits were collected. If a timeout occurs, any digits collected up to that point are returned. This report can also indicate if one of the following conditions occurred:
This report can be included as a report segment in an Inpulse Rule Complete ($DD) report.
The $D1 report is generated in direct response to a DTMF Collection Control ($67) command, or as a result of inpulse rule processing. No distinction is made between DTMF or DP digits. If first digit reporting was specified by the host in the DTMF Collection Control ($67) command, digit collection produces two reports: the first report indicates it is a first digit report and contains only one digit; the second is a valid digit report with all collected digits, including the first digit that was previously reported.
An exception to first digit reporting is when the first digit entered is a single-digit end of string code ($F). In this case, the first digit report is returned with bit settings in the DTMF Status byte (offset 11) indicating a first digit report without a valid digit string (V = 1 and Z = 0).
Figure 5-6 shows the byte formatting for this report.
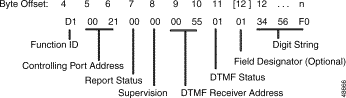
Function ID (byte offset 4)—Byte immediately following the Network Header; uniquely identifies this report from the system.
Controlling Port Address (byte offsets 5 and 6)—Hexadecimal representation of the line/trunk from which the digits were collected. Omitted if report included as a segment in a $DD report.
Report Status (byte offset 7)—Indicates if an event condition is reflected in this report, such as voice prompt abort or outgoing port detached when the first digit is detected, collection was aborted because expected supervision was not detected, or digit field overflow occurred. Omitted if the report is included as a segment in a $DD report. Convert the byte from hexadecimal to binary and interpret the bits as described below.
0VDTA000
Supervision (byte offset 8)—When T = 1 in the Report Status byte, indicates the type of supervision that was expected but not received before the supervision timer fired. If T = 0, this byte is set to $00. Omitted if report included as a segment in a $DD report. Interpret byte according to the following list.
DTMF Receiver Address (byte offsets 9 and 10)—Hexadecimal representation of the DTMF receiver port processing the incoming digits. For SLIC, DID, and UTC ports, this address is the same as the Controlling Port Address.
DTMF Status (byte offset 11)—Indicates the status of the digit report; convert byte from hexadecimal to binary and interpret the bits as described below.
0T0VWXYZ
Optional Field Designator/Digit String (byte offset 12 to n) - When the "Enable Digit Field Reporting" feature is enabled from either Data Base Administration Menu or Maintenance Menu of the System Administrator database, the byte at offset 12 indicates into what field the system stores the reported digits (refer to the Cisco VCO/4K System Administrator's Guide). Possible values are as follows:
Digit String (byte offsets 12 + n to n)—The DTMF digits collected; digits represented are from 1 to 9, and 0 ($A), plus the special characters * ($B) and # ($C). The digit string always ends with an $F. Each nibble in the hexadecimal byte represents a single digit. If the "Enable Digit Field Reporting" feature is not enabled, then the Digit String bytes begin at byte offset 12. The Optional Field Designator and Digit String are included only when Z = 1 in the DTMF Status byte.
The following report shows a DTMF receiver at address $52 collected seven DTMF digits (1 to 7) from the port at address $18. The "Enable Digit Field Reporting" feature has not been enabled.
04 0506 07 08 0910 11 12 131415
D1 0018 00 00 0052 01 12 34567F
Function ID = D1 (DTMF Digit)
Controlling Port Address = 0018
Report Status = 00000000
Supervision = 00 (supervision timer is not set in the $67 command or the timer did not fire)
DTMF Receiver Address = 0052
DTMF Status = 00000001
Digit String = 1234567 (F marks end of string)
The following report shows that a DTMF receiver at address $52 was enabled to collect digits from the port at address $18. One digit was received before the DTMF interdigit timer fired, so there is only one digit in this report. The "Enable Digit Field Reporting" feature has not been enabled.
04 0506 07 08 0910 11 12
D1 0018 00 00 0052 41 9F
Function ID = D1 (DTMF Digit)
Controlling Port Address = 0018
Report Status = 00000000
Supervision = 00 (supervision timer is not set in the $67 command or the timer did not fire)
DTMF Receiver Address = 0052
DTMF Status = 01000001
Digit String = 9 (F marks end of string)
The following report shows a DTMF receiver at address $35 has received the first digit of a string and is reporting it to the host. A voice prompt was aborted when the first digit was received. The "Enable Digit Field Reporting" feature has not been enabled.
04 0506 07 08 0910 11 12
D1 0021 40 00 0052 11 5F
Function ID = D1 (DTMF Digit)
Controlling Port Address = 0021
Report Status = 01000000
Supervision = 00 (supervision timer is not set in the $67 command or the timer did not fire)
DTMF Receiver Address = 0052
DTMF Status = 00010001
Digit String = 5 (F marks end of string)
Resource Control
$40
The DTMF Digit ($D1) (Enhanced) report transfers DTMF/DP digit collection information from the system to the host. The report indicates if the digit report is valid and the line or trunk from which the digits were collected. If a timeout occurs, any digits collected up to that point are returned. This report can also indicate if one of the following conditions occurred:
This report can be included as a report segment in an Inpulse Rule Complete ($DD) report.
The $D1 (Enhanced) report is generated in direct response to the 4th-column DTMF option being enabled, or as a result of inpulse rule processing. No distinction is made between DTMF or DP digits. If first digit reporting was specified by the host in the DTMF Collection Control ($67) command, digit collection produces two reports: the first report indicates it is a first digit report and contains only one digit; the second is a valid digit report with all collected digits, including the first digit that was previously reported.
Figure 5-7 shows the byte formatting for this report.
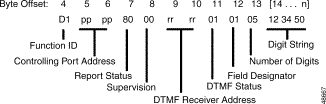
Function ID (byte offset 4)—Byte immediately following the Network Header; uniquely identifies this report from the system.
Controlling Port Address (byte offsets 5 and 6)—Hexadecimal representation of the line/trunk from which the digits were collected. Omitted if report included as a segment in a $DD report.
Report Status (byte offset 7)—Indicates the status of the digit report. Also, indicates if an event condition is reflected in this report, such as voice prompt abort or outgoing port detached when first digit detected, collection was aborted because expected supervision was not detected, or digit field overflow occurred. Omitted if the report is included as a segment in a $DD report. Convert the byte from hexadecimal to binary and interpret the bits as follows.
0VDTA000
Supervision (byte offset 8)—When T = 1 in the Report Status byte, indicates the type of supervision that was expected but not received before the supervision timer fired. If T = 0, this byte is set to $00. Omitted if the report is included as a segment in a $DD report. Interpret the byte according to the following list:
DTMF Receiver Address (byte offsets 9 and 10)—Hexadecimal representation of the DTMF receiver port processing the incoming digits. For SLIC, DID, and UTC ports, this address is the same as the Controlling Port Address.
DTMF Status (byte offset 11)—Specifies that this report follows the enhanced report format; convert byte from hexadecimal to binary and interpret the bits as described below.
ET0VWXYZ
Field Designator/Digit String (byte offset 12) - When the "Enable Digit Field Reporting" feature is enabled from the System Features screen of the System Configuration menu, this byte indicates into what field the system stores the reported digits (refer to the Cisco VCO/4K System Administrator's Guide). This byte is always present; if the feature is disabled, or if Z = 0 in the DTMF Status byte, then this byte is set to $05. Possible values are as follows:
Number of Digits (byte offset 13)—Specifies the number of digits contained in this report. This byte is set to $00 if Z = 0 in the DTMF status byte to indicate that there are no digits to be reported.
Digit String (byte offsets 14 - n)—The remaining bytes contain the DTMF digits collected. Digits are represented as 0 to 9, A to D, E (*), and F (#). Each byte in the digit string contains two digits. If the report contains an odd number of digits, the last nibble is set to $0; there is no digit string terminator.
The Digit string is included only when Z = 1 in the DTMF status byte to indicate that there are digits to be reported.
The following report shows that a DTMF receiver at address $52 collected seven DTMF digits (1 to 7) from the port at address $18. The "Enable Digit Field Reporting" feature has not been enabled.
04 05060708 09 10 1112 13 14 15 16
D1 00180000 00 52 9107 12 34 56 70
Function ID = D1 (DTMF Digit)
Controlling Port Address = 0018
Report Status = 00000000
Supervision = 00 (supervision timer is not set in the $67 command or the timer did not fire)
DTMF Receiver Address = 0052
DTMF Status = 10000001
Digit String = 1234567 (0 marks end of byte)
The following report shows that a DTMF receiver at address $52 was enabled to collect digits from the port at address $18. One digit was received before the DTMF interdigit timer fired, so there is only one digit in this report. The "Enable Digit Field Reporting" feature has not been enabled.
04 05060708 09 10 1112 13
D1 00180000 00 52 C101 90
Function ID = D1 (DTMF Digit)
Controlling Port Address = 0018
Report Status = 00000000
Supervision = 00 (supervision timer is not set in the $67 command or the timer did not fire)
DTMF Receiver Address = 0052
DTMF Status = 11000001
Digit String = 9 (0 marks end of byte)
The following report shows that a DTMF receiver at address $35 has received the first digit of a string and is reporting it to the host. A voice prompt was aborted when the first digit was received. The "Enable Digit Field Reporting" feature has not been enabled.
04 05060708 09 10 1112 13
D1 00214000 00 52 9101 50
Function ID = D1 (DTMF Digit)
Controlling Port Address = 0021
Report Status = 01000000
Supervision = 00 (supervision timer is not set in the $67 command or the timer did not fire)
DTMF Receiver Address = 0052
DTMF Status = 10010001
Digit String = 5 (0 marks end of byte)
Resource Control
$44
The Permanent Signal Condition ($D2) report informs the host that a line or trunk port has not released within 30 seconds of a release by the system. The report is also sent when a line/trunk that was in Permanent Signal Condition (PSC) goes back on hook.
The $D2 report is generated if the system has tried to release a line/trunk and that port is still off hook after 30 seconds of inactivity. It is generated with a PSC code of $00 when line/trunk finally does release. When port goes on hook, this report may be accompanied by an Incoming Port Change of State ($DB) or Outgoing Port Change of State ($DA) report, depending upon the settings in the Incoming Port Control ($6A) or Outgoing Port Control ($69) command used in the call. Refer to "System Commands," for more information.
The $D2 reports are never generated for ports with a class of service = A.
Figure 5-8 shows the byte formatting for this report.
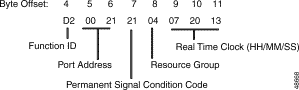
Function ID (byte offset 4)—Byte immediately following the Network Header; uniquely identifies the report from the system.
Port Address (byte offsets 5 and 6)—Hexadecimal representation of the port for which this report was generated.
Permanent Signal Condition Code (byte offset 7)—Specifies the reason this report was sent. If this byte = $00, the port has gone back on hook and the PSC no longer exists. Convert the byte from hexadecimal to binary and interpret the bits as follows:
ABCDEFGH
Resource Group (byte offset 8)—Specifies the resource group number to which the port belongs; convert byte from hexadecimal to decimal for the group number (1 to 63 inclusive).
Real Time Clock (byte offset 9 to 11)—24-hour system clock indicating the time the status change occurred; hours, minutes, and seconds are represented separately in hexadecimal. Convert each byte from hexadecimal to decimal for the time.
Assume an incoming port was linked to an outgoing port in resource group 5 and at address $0028. When the incoming port went back on hook to end the call, the outgoing port did not release within 30 seconds. The following report shows a PSC for the outgoing trunk.
04 0506 07 08 091011
D2 0028 81 05 121E00
Function ID = D2 (Permanent Signal Condition)
Port Address = 0028
Permanent Signal Condition Code = 10000001
Resource Group = 5
Real Time Clock = 6:30:00 pm ($12 = 18; $1E = 30; $00 = 00)
The following report indicates that the outgoing port in Example 5-14 released, clearing the PSC.
04 0506 07 08 091011
D2 0028 01 05 122911
Function ID = D2 (Permanent Signal Condition)
Port Address = 0028
Permanent Signal Condition Code = 00000001
Resource Group = 5
Real Time Clock = 6:41:17 pm ($12 = 18; $29 = 41; $11 = 17)
System Status
$40
The System Port Status ($D3) report informs the host of an attempted change in the status of a system resource port. The attempted change can be the result of the following:
This report is generated when a change occurs in the operating status of an individual resource port on a system card. Status changes can be caused by an action at the system administrative console, an internally detected fault, or a host command.
A report indicating a port's availability may be returned from a card in active, maintenance, diagnostic, or maintenance busy mode. When the card is in standby mode or out of service, the port cannot be used for a call and no $D3 reports are generated for the port.
Any $D3 report generated for the first port on the DTG card will always indicate no status change (this port is not supported and remains deactivated at all times). Also, port status changes applied to DTG ports are only performed on the ports residing on the active tone card. Although the ports on the standby tone card are assigned the same logical addresses as the ports on the active card, the $D3 report represents the status of the active tone card port.
Figure 5-9 shows the byte formatting for this report.
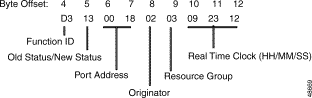
Function ID (byte offset 4)—Byte immediately following the Network Header; uniquely identifies the report from the system.
Old Status/New Status (byte offset 5)—Specifies the status of the port before the change occurred and the present status of the port. Convert the byte from hexadecimal to binary and interpret the bits as follows.
MMMMNNNN
Port Address (byte offsets 6 and 7)—Hexadecimal representation of port address for which the report is generated.
Originator (byte offset 8)—Specifies whether the change in status was originated by the system or the host and the reason for the change. Interpret the byte as follows:
Resource Group (byte offset 9)—Specifies the resource group number to which the port belongs; convert byte from hexadecimal to decimal for the group number (1 to 63).
Real Time Clock (byte offsets 10 to 12)—A 24-hour system clock indicating the time the status change occurred; hours, minutes, and seconds are represented separately in hexadecimal. Convert each byte from hexadecimal to decimal for the time.
The following report indicates that the port at address $18, in resource group 3, is currently available due to a change originated by the system.
04 05 0607 08 09 101112
D3 13 0018 02 03 092312
Function ID = D3 (System Port Status)
Old Status/New Status = 00010011
Port Address = 0018
Originator = 02 (port was returned to service by the system)
Resource Group = 3
Real Time Clock = 9:35:18 am ($09 = 9; $23 = 35; $12 = 18)
The following report indicates that the port at address $21, in resource group 3, is currently unavailable because it has been busied out from the distant end.
04 05 0607 08 09 101112
D3 31 0021 32 03 0D2D00
Function ID = D3 (System Port Status)
Old Status/New Status = 00110001
Port Address = 0021
Originator = 32 (port was busied out from distant end)
Resource Group = 3
Real Time Clock = 1:45:00 pm ($0D = 13; $2D = 45; $00 = 00)
Resource Control
$40
The Spoken Digit ($D4) report transfers spoken digit collection information from the system to the host. The report indicates the following:
If a timeout occurs, any digits collected up to that point are reported.
The $D4 report is generated in response to a Speech Collection Control ($6E) command.
Figure 5-4 shows the byte formatting for this report.
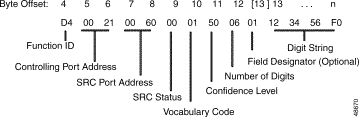
Function ID (byte offset 4)—Byte immediately following the Network Header; uniquely identifies the report from the system.
Controlling Port Address (byte offsets 5 and 6)—Hexadecimal representation of the circuit address to which the SRC port is attached.
SRC Port Address (byte offsets 7 and 8)—Hexadecimal representation of the SRC port processing the digits.
SRC Status (byte offset 9)—Indicates the status of the digit report; convert byte from hexadecimal to binary and interpret the bits as described below.
00WSCIFD
Vocabulary Code (byte offset 10)—Indicates if the SRC collected a digit string (0 to 9 and "oh") or a word (yes or no). Interpret the byte as follows:
Confidence Level (byte offset 11)—Hexadecimal representation calculated by the SRC to represent the degree to which it believes the information contained in the report to be accurate. Convert to decimal for the per cent confidence level (0 to 99%, with 0 indicating no indication was received and 99 indicating almost complete accuracy).
Number of Digits (byte offset 12)—Hexadecimal representation of the number of digits included in the attached digit string. If 00, no digit string attached and this is the final byte of the report.
Optional Field Designator/Digit String (byte offset 12)—When the "Enable Digit Field Reporting" feature is enabled from either the Data Base Administration Menu or Maintenance Menu of the System Administrator database, the byte at offset 12 indicates into what field the system stores the reported digits or words (refer to the Cisco VCO/4K System Administrator's Guide). Possible values are as follows:
Digit String (byte offsets 13 to n)—The spoken digits/word collected. Digits are nibble packed; each nibble in the hexadecimal byte represents a single digit/word. When the Vocabulary Code = 00, digits are represented from 1 to 9, and 0 ($A). When the Vocabulary Code = 01, possible values are "Yes" (1) and "No" (0). The digit string always ends with an $F. If the "Enable Digit Field Reporting" feature is not enabled, then the Digit String bytes begin at byte offset 12. The Optional Field Designator and Digit String are included only when D = 1 in the SRC Status byte.
The following report indicates that the SRC port at port address $29 has collected seven spoken digits with an 84% confidence level. The "Enable Digit Field Reporting" feature has not been enabled.
04 0506 0708 09 10 11 12 13 141516
D4 0060 0029 01 00 84 07 62 54A5AF
Function ID = D4 (Spoken Digit)
Controlling Port Address = 0060
SRC Port Address = 0029
SRC Status = 00000001
Vocabulary Code = 00 (digit string collected)
Confidence Level of Collection = 54 (84 percent, decimal)
Number of Digits = 07
Spoken Digits Collected = 6254A5A (F marks end of digit string)
The following example shows a typical $D4 report for a "Yes" or "No" speech recognition attempt on an SRC port located at port address $2A. The "Enable Digit Field Reporting" feature has not been enabled.
04 0506 0708 09 10 11 12 13
D4 0062 002A 01 01 63 01 1F
Function ID = D4 (Spoken Digit)
Controlling Port Address = $0062
SRC Port Address = 002A
SRC Status = 00000001
Vocabulary Code = 01 (word collected)
Confidence Level of Collection = $63 (99%, decimal)
Number of Digits = 01
Spoken Digits Collected = 1F ("Yes" was recognized)
System Status
$44
Use the Resource Limitation ($D6) report to inform the host when a resource limitation condition has been detected or cleared. When the condition is detected, the system informs the host there are no units in a specific resource group available to satisfy an allocation request (resource control command, inpulse rule, outpulse rule, etc.). This report is sent only the first time a limitation condition is detected for a resource group. No subsequent limitation condition reports are sent until after the condition has cleared. If the report is generated in response to a resource control command, the original command packet with the appropriate status ($1F in the network status byte) is returned.
For the resource limitation to clear, the system informs the host that resources in a group for which a $D6 report was generated have been successfully allocated for three consecutive requests.
The $D6 report is generated for the first occurrence in a specific group until the condition clears. A limitation condition is declared in response to a host resource control command, inpulse rule processing, or outpulse rule processing when all resources of the type requested are busy or otherwise unavailable. The command must specify to hunt a resource group instead of requesting a specific port address.
For the Conference Control ($6D) command, this report is generated when all ports in the conference resource group are busy or unavailable.
For internal service circuits (DRCs, MRCs, DVCs, IPRCs, DCCs, and CPAs), if no group exists that contains the resource type requested, this report is not sent.
This report is also generated after three consecutive successful allocations have occurred from a resource group for which allocation attempts have previously failed.
Figure 5-11 shows the byte formatting for this report.
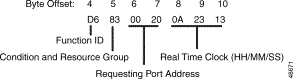
Function ID (byte offset 4)—Byte immediately following the Network Header; uniquely identifies the report from the system.
Condition (byte offset 5)—Specifies whether a limitation condition is present and the resource group for which the request was made. Convert the byte from hexadecimal to binary and interpret the bits as follows.
C0GGGGGG
Requesting Port Address (byte offsets 6 and 7)—Hexadecimal representation of the port specified in the resource control command, inpulse rule, or outpulse rule for which a resource was requested. For a conference control command, this byte is the hexadecimal representation of the conference number for which the port was requested. If the port address is in the range $80 00 to $80 FF. The requesting port is a virtual port.
Real Time Clock (byte offsets 8 to 10)—A 24-hour system clock indicating the time the $D6 report was generated. Hours, minutes, and seconds are represented separately in hexadecimal. Convert each byte from hexadecimal to decimal for the time.
The following report indicates that all ports in resource group 3 are unavailable. This report is sent the first time an allocation attempt fails for this group until the condition has cleared.
04 05 0607 080910
D6 83 0020 0A2313
Function ID = D6 (Resource Limitation)
Condition and Resource Group = 10000011
Requesting Port Address = 0020
Real Time Clock = 10:35:19am ($0A = 10; $23 = 35; $13 = 19)
The following report indicates that the limitation condition reported in Example 5-20 has cleared (three consecutive allocations from this group have been successfully performed).
04 05 0607 080910
D6 03 0038 0A3522
Function ID = D6 (Resource Limitation)
Condition and Resource Group = 00000011
Requesting Port Address = 0038
Real Time Clock = 10:53:34am ($0A = 10; $35 = 53; $22 = 34)
System Status
$40
The System Card Status ($D9) report informs the host of a change in the status of a system resource card. The card location is represented both by the port address and the physical rack, level, slot (R-L-S) address.
The $D9 report is generated when a change occurs in the operating status of a system card. Status changes can be caused by an action at the System Administration console, a host command, or physical removal and/or replacement of the card. The report is also sent for each card in the system as it comes on line after a system boot.
For T1, the card is reported as on line when the carrier and remote carrier alarms clear. If either the carrier alarm or remote carrier alarm reoccurs, the card is reported as being off line.
For DVC and IPRC, the card is reported as on line when the card download is complete.
Figure 5-12 shows the byte formatting for this report.
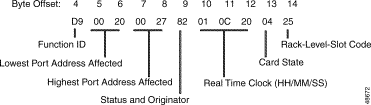
Function ID (byte offset 4)—Byte immediately following the Network Header; uniquely identifies the report from the system.
Lowest Port Address Affected (byte offsets 5 and 6)—Hexadecimal representation of the first port address on the card for which the report is sent.
Highest Port Address Affected (byte offsets 7 and 8)—Hexadecimal representation of the last port address on the card for which the report is sent.
Status and Originator (byte offset 9)—Specifies if the card is on line or off line, if the card was just added to or deleted from the database, and whether the change in status was originated by the system or the host. Convert the byte from hexadecimal to binary and interpret the bits as follows:
LDA000SH
Real Time Clock (byte offsets 10 to 12)—A 24-hour system clock indicating the time the status change occurred. Hours, minutes, and seconds are represented separately in hexadecimal. Convert each byte from hexadecimal to decimal for the time.
Card State (byte offset 13)—Indicates the present status of the card for which the report is generated. Interpret this byte as follows:
Rack-Level-Slot Code (byte offset 14)—Specifies the rack, level, and slot in which the card is located. Convert the byte from hexadecimal to binary and interpret as follows:
LLLSSSSS
 |
Note For a multispan card, the command includes a port range of 24 channels. If the card is removed or deleted, the report is issued multiple times. |
The following report indicates that the card at rack 1, level 1, slot 5 was taken out of service through a System Administration console command.
04 0506 0708 09 101112 13 14
D9 0020 0027 82 010C20 04 25
Function ID = D9 (System Card Status)
Lowest Port Address Affected = 0020
Highest Port Address Affected = 0027
Status and Originator = 10000010
Real Time Clock = 1:12:32 am ($01 = 1; $0C = 12; $20 = 32)
Card State = 04 (card out of service)
Rack-Level-Slot Code = 00100101
The following report indicates that the card at rack 2, level 0, slot 20 was added to the system database but is still off line.
04 0506 0708 09 101112 13 14
D9 0018 001F A2 142D00 04 94
Function ID = D9 (System Card Status)
Lowest Port Address Affected = 0018
Highest Port Address Affected = 001F
Status and Originator = 10100010
Real Time Clock = 8:45:00 pm ($14 = 20; $2D = 45; $00 = 00)
Card State = 04 (card out of service)
Rack-Level-Slot Code = 10010100
 |
Note Unless otherwise stated, the MF processing described in this section applies to both MF and MFCR2 processing. |
Resource Control
$40
In MF processing, the Outgoing Port Change of State ($DA) report informs the host of a change in the hardware state of an outgoing system port. Note that in-band signaling is only detected during outpulse rule processing when a CPA port is attached. This report can also be issued to indicate that an outpulse rule has successfully completed for the outgoing port.
Supervision errors are indicated by the appropriate value in the Change byte. The Change byte also indicates when a rehunt of an outgoing port is performed. When a rehunt occurs, the new outgoing port is indicated in byte offsets 14 and 15.
For the system to generate this report indicating outpulse rule completion, a REP END token must be contained in the outpulse rule.
In MFCR2 processing, this report indicates the final backward supervision tone detected to the host as part of the R2 signaling on outgoing trunks. This tone is indicated in the Answer Supervision Code (byte offset 9). Values of 33 xx indicate the backward supervision tone, where xx indicates the Group-A or Group-B tone (the tone meaning is subject to the context of the call).
The supervision template (byte offset 13) indicates the number of the outpulse rule used during MFCR2 outpulsing.
The $DA report is generated in response to a change in the hardware state of an outgoing port or the end of outpulse rule processing (REP END in outpulse rule).
Figure 5-13 shows the byte formatting for this report.
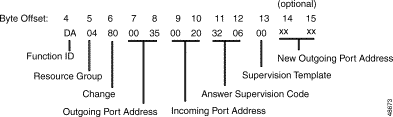
Function ID (byte offset 4)—Byte immediately following the Network Header; uniquely identifies the report from the system.
Resource Group (byte offset 5)—Specifies the resource group number to which the port belongs; convert byte from hexadecimal to decimal for the group number (1 to 63).
Change (byte offset 6)—Type of change detected. The following list provides a general indication of the change that occurred for the outgoing port.
Outgoing Port Address (byte offsets 7 and 8)—Hexadecimal representation of the address of the port for which the state change was detected.
Incoming Port Address (byte offsets 9 and 10)—Hexadecimal representation of the incoming port address to which this outgoing port was connected.
Answer Supervision Code (byte offset 11 and 12)—For Change = 01, 02, 05, 08, 10, 20, or 80, indicates the type of answer supervision activity present on this outgoing port. If Change = 40, these bytes are set to 00 00. If Change = 04, byte offset 11 contains the number of the outpulse rule processed; byte offset 12 is set to 00.
Table 5-7 lists the standard supervision codes for MF/MFCR2 processing.
| Code | Meaning |
|---|---|
30 01 | Simultaneous seizure at both ends of a trunk (glare condition). |
30 02 | Attempt made to answer a non-ringing port. |
30 04 | Supervision timer expired. |
30 05 | No current on line. |
31 01 | Reorder tone detected. |
31 02 | Busy signal detected. |
31 03 | Ringback detected. |
31 04 | Dial tone detected. |
31 05 | SIT tones detected. |
31 06 | Pager cue tone detected. |
31 07 | ISUP tone detected. |
31 08 | ISUP tone cessation. |
32 01 | Grace time completed. |
32 02 | Ringback cessation. |
32 03 | Wink detected. |
32 04 | Hook flash detected. |
32 06 | True answer detected. |
32 07 | Voice detected. |
32 08 | Voice cessation. |
32 09 | Outgoing port returned to CP_SETUP. |
Table 5-8 lists the R2 backward signaling codes for MFCR2 processing.
| Code | Backward Tone Detected |
|---|---|
33 00 | A-10/B-10 |
33 01 | A-1/B-1 |
33 02 | A-2/B-2 |
33 03 | A-3/B-3 |
33 04 | A-4/B-4 |
33 05 | A-5/B-5 |
33 06 | A-6/B-6 |
33 07 | A-7/B-7 |
33 08 | A-8/B-8 |
33 09 | A-9/B-9 |
33 0B | A-11/B-11 |
33 0C | A-12/B-12 |
33 0D | A-13/B-13 |
33 0E | A-14/B-14 |
33 0F | A-15/B-15 |
Supervision Template (byte offset 13)—For MFCR2 processing, this byte indicates the outpulse rule used for R2 outdialing.
For MF processing, this byte indicates whether the outgoing port is considered answered (ANS condition token processed in answer supervision template or FINAL SUP [xx] outpulse rule token satisfied), and specifies the number of the answer supervision template used. The byte is set to 00 for call failures and supervision errors. Convert the byte from hexadecimal to binary and interpret the bits as follows:
A0NNNNNN
New Outgoing Port (byte offset 14 and 15)—For Change = 02, indicates new Outgoing Port selected by the system as a result of a rehunt operation (outgoing supervision error encountered). The type of error is indicated in the Answer Supervision Code bytes. Not included unless Change = 02.
The following report indicates that the outgoing port which is at address $35 and connected to the incoming port at address $20 has gone off hook. Answer supervision has been detected (SLIC, T1, E+M, or UTC only).
04 05 06 0708 0910 1112 13
DA 04 80 0035 0020 3206 00
Function ID = DA (Outgoing Port Change of State)
Resource Group = 4
Change = off hook ($80)
Outgoing Port Address = 0035
Incoming Port Address = 0020
Answer Supervision Code = 3206 (true answer detected - answered with reversal)
Supervision Template = 00 (no answer supervision template used)
The following report indicates that the outgoing port which is at address $35 and was connected to the incoming port at address $20 has gone on hook.
04 05 06 0708 0910 1112 13
DA 04 40 0035 0020 0000 00
Function ID = DA (Outgoing Port Change of State)
Resource Group = 4
Change = on hook ($40)
Outgoing Port Address = 0035
Incoming Port Address = 0020
Answer Supervision Code = 00 00 (because Change = $40)
Supervision Template = 00 (no answer supervision template used)
The following report indicates that a supervision error occurred on an outgoing port at address $35 that was being connected to the incoming port at address $20. The outgoing port ($35) is removed from the call and the incoming port ($20) is placed into CP_SETUP state (no rehunt performed). Answer supervision template #2 specifies detection of SIT tones as an error condition.
04 05 06 0708 0910 1112 13
DA 04 20 0035 0020 3105 02
Function ID = DA (Outgoing Port Change of State)
Resource Group = 4
Change = supervision error detected ($20) Outgoing Port Address = $0035
Incoming Port Address = 0020
Answer Supervision Code = 31 05 (SIT tones detected)
Supervision Template = 02 (answer supervision template used)
The following report indicates that supervision was received outside of outpulse rule processing. The circuit at 00 35 is a T1 port.
04 05 06 0708 0910 1112 13
DA 04 08 0035 0020 3203 00
Function ID = DA (Outgoing Port Change of State)
Resource Group = 4
Change = supervision detected outside an outpulse rule ($08)
Outgoing Port Address = 0035
Incoming Port Address = 0020
Answer Supervision Code = 32 03 (wink detected)
Supervision Template = 00 (no answer supervision template used)
The following report indicates that a supervision error caused the system to rehunt to replace the outgoing port at address $035. The new outgoing port is supplied in the final two bytes.
04 05 06 0708 0910 1112 13 1415
DA 04 02 0035 0020 3101 00 0038
Function ID = DA (Outgoing Port Change of State)
Resource Group = 4
Change = outgoing rehunt performed; new outgoing port in final two bytes
Outgoing Port Address = 0035
Incoming Port Address = 0020
Answer Supervision Code = 3101 (reorder signal detected)
Supervision Template = 00 (no answer supervision template used)
New Outgoing Port Address = 0038
Resource Control
$40
The Incoming Port Change of State ($DB) report informs the host of a change in the hardware state of an incoming system port. Also indicates if an outpulse rule has been processed for the incoming port. This report can be included as a report segment in an Inpulse Rule Complete ($DD) report.
The $DB report is generated in response to a change in the hardware state of an incoming port or completion of an outpulse rule.
Figure 5-14 shows the byte formatting for this report.
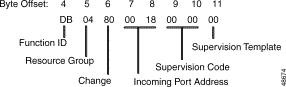
Function ID (byte offset 4)—Byte immediately following the Network Header; uniquely identifies the report from the system.
Resource Group (byte offset 5)—Specifies the resource group number to which the port belongs; convert byte from hexadecimal to decimal for the group number (1 to 63 inclusive). Omitted if the report is included as a segment in a $DD report.
Change (byte offset 6)—Type of change detected. Interpret the byte as follows:
Incoming Port Address (byte offsets 7 and 8)—Hexadecimal representation of the address of the port for which the state change was detected. Omitted if the report included as a segment in a $DD report.
Answer Supervision Code (byte offsets 9 and 10)—Specifies the supervision error or the number of the outpulse rule completed. If Change = 40, these bytes are set to 00 00. When Change = 01, 02, 05, 08, 10, 20, or 80, interpret the bytes as follows:
Supervision Template (byte offset 11)—Specifies the number of the answer supervision template used. The byte is set to 0 for call failures and supervision errors. Convert the byte from hexadecimal to binary and interpret the bits as follows:
A00NNNNNN
The following report indicates that the port at address $20 has gone off hook.
04 05 06 0708 0910 11
DB 04 80 0020 0000 00
Function ID = DB (Incoming Port Change of State)
Resource Group = 4
Change = off hook ($80)
Incoming Port Address = 0020
Supervision Code = 00 00
Supervision Template = 00 (no answer supervision template used)
The following report indicates that the port at address $20 has gone on hook.
04 05 06 0708 0910
DB 04 40 0020 0000
Function ID = DB (Incoming Port Change of State)
Resource Group = 4
Change = on hook ($40)
Incoming Port Address = 0020
Supervision Code = 00 00
Supervision Template = 00 (no answer supervision template used)
The following report indicates that the system attempted to answer a nonringing incoming port. This port must be a UTC circuit (only UTC ports report this condition).
04 05 06 0708 0910 11
DB 04 20 0020 3002 00
Function ID = DB (Incoming Port Change of State)
Resource Group = 4
Change = supervision error ($20)
Incoming Port Address = 0020
Supervision Code = 30 02
Supervision Template = 00 (no answer supervision template used)
The following report indicates that an outpulse rule has completed processing for the port at $0020. The outpulse rule included a REP END to generate this report.
04 05 06 0708 0910 11
DB 04 04 0020 0500 00
Function ID = DB (Incoming Port Change of State)
Resource Group = 4
Change = Outpulse rule complete ($04)
Incoming Port Address = 0020
Supervision Code = Outpulse rule 5
Supervision Template = 00 (no answer supervision template used)
Configuration Control
$40
The Active/Standby Mode ($DC) report informs the host of a system boot, system initialization, or transfer in control between the active and standby sides of a redundant system. It also reports when a link between the host and the system becomes established. In a redundant system, both the active and standby sides report a transfer.
A $DC report is sent when system boots, system initialization is complete, or when a transfer of control occurs. Transfer could be caused by a Change Active Controllers ($C0 01) command or an event internal to the system.
The $DC report is also sent over a host-system link when that link becomes active. A report is sent by each link in the system. System reboot causes all links to reset.
Figure 5-15 shows the byte formatting for this report.

Function ID (byte offset 4)—Byte immediately following the Network Header; uniquely identifies the report from the system.
Action Code (byte offset 5)—Specifies why the report is sent, which side sent the report, and whether that side is active or standby. Convert the byte from hexadecimal to binary and interpret the bits as follows:
RI0000SM
Spacer Byte (byte offset 6)—Reserved for future enhancements; always = $00.
The following report indicates a system boot for a redundant system with a link on each side. When the system initially comes on line, the Alarm Arbiter Card (AAC) determines which processor is active (in this example, the A side). The first report shows the event from the A side, the second from the B side.
04 05 06
DC 81 00
Function ID = DC (Active/Standby Mode)
Action Code = 10000001
Spacer Byte = 00 (no meaning) DC 82 00
Function ID = DC (Active/Standby Mode)
Action Code = 10000010
Spacer Byte = 00 (no meaning)
The following reports reflect a change in active and standby sides initiated by a host command or an action at the administrative console or the Alarm Arbiter Card.
04 05 06
DC 00 00
Function ID = DC (Active/Standby Mode)
Action Code = 00000000
Spacer Byte = 00 (no meaning)
04 05 06
DC 03 00
Function ID = DC (Active/Standby Mode)
Action Code = 00000011
Spacer Byte = 00 (no meaning)
The following report indicates that one of the host-to-system links has just become active.
 |
Note This report is not interpreted as a system reboot when received from only one link. |
04 05 06
DC 81 00
Function ID = DC (Active/Standby Mode)
Action Code = 00000000
Spacer Byte = 00 (no meaning)
Resource Control
$40
The Inpulse Rule Complete (Macro) ($DD) report informs the host that an inpulse rule has been processed. The content of the report is controlled by the type of reporting specified in the inpulse rule. If REP EACH is specified, the report will indicate only that inpulse rule processing has ended. If REP END is specified, the report is a macro containing Resource Control reports (segments) to represent all actions taken during inpulse rule execution. Resource report segments included in the macro can include the following:
Segments are reported in the following order:
Digit segments follow the general format for their report, but the Controlling Port Address and Spacer bytes are omitted in MF collections, and the Controlling Port Address, Report Status and Supervision bytes are omitted in DTMF collections. Incoming Port Change of State segments contain only the function ID and Change Code.
This report is generated when inpulse rule processing is terminated. Termination can be caused by: the successful completion of the rule; an error in rule processing; a looping rule which only contains setup to reporting tokens; a host command overriding the rule; or by the controlling port going on hook.
Figure 5-16 shows the byte formatting for this report.
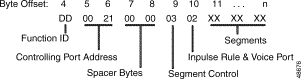
Function ID (byte offset 4)—Byte immediately following the Network Header; uniquely identifies the report from the system.
Controlling Port Address (byte offsets 5 and 6)—Hexadecimal representation of the port for which the inpulse rule is being executed.
Spacer Bytes (byte offsets 7 and 8) - Reserved for future enhancements; always returned as 00 00.
Segment Control (byte offset 9)—Specifies the number of segments included in this report, if the rule was processed for an incoming or outgoing port and if the TeleRouter overlay performed a routing action. Convert the byte from hexadecimal to binary and interpret the bits as described below. If inpulse rule executed specified REP EACH, this byte will be $00, indicating there are no segments.
ABC00NNN
Inpulse Rule/Voice Port (byte offset 10)—Specifies the inpulse rule number executed, whether it completed normally or was aborted, whether rule was aborted due to outpulse channel exhaust (DO ORULE token in inpulse rule), and whether a voice port was available on the first attempt as required by that rule. Convert the byte from hexadecimal to binary and interpret the bits as follows:
ASTRRRRR
Segments (byte offset 11 to n)—Resource report segments included in this macro; segment format follows that of the report the segment represents, with the following exceptions: the Controlling Port Address and Spacer Bytes are omitted in MF ($D0) collections, and the Controlling Port Address, Report Status and Supervision bytes are omitted in DTMF ($D1) collections, and Incoming Port Change of State ($DB) segments contain only the Function ID and Change Code.
The following report indicates that inpulse rule 3 was executed on the incoming port at address $28. Three MF digits (1, 2, 3) and seven DTMF digits were collected (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7).
04 0506 0708 09 10 1112131415161718192021222324
DD 0028 0000 02 03 00003401123FD10052011234567F
Function ID = DD (Inpulse Rule Complete (macro))
Controlling Port Address = 0028
Spacer Bytes = 00 00
Segment Control = 00000010
Inpulse Rule/Voice Port = 00000011
A = 0 (voice port available on initial request)
S = 0 (Inpulse rule processing completed normally)
T = 0 (rule not aborted due to Outpulse Channel exhaust condition)
RRRRR = 3
Segment 1 is as follows:
Function ID = MF Digit ($D0)
Controlling Port Address = omitted
Spacer Bytes = omitted
MF Receiver Address = 0034
MF Status = 00000001
Digit String = 123 (F marks end of string)
Segment 2 is as follows:
Function ID = D1 (DTMF Digit)
Controlling Port Address = omitted
Report Status = omitted
Supervision = omitted
DTMF Receiver Address = 0052
DTMF Status = 00000001
Digit String = 1234567 (F marks end of string)
The following report indicates that the incoming port at address $35 went off hook and executed inpulse rule 16. During the execution of that rule, the system made two attempts before allocating a voice port (processing a SPEAK token). Three DTMF digits (4, 4, 2) were collected.
04 0506 0708 09 10 1112131415161718
DD 0035 0000 02 90 DB80D1003505442F
Function ID = DD (Inpulse Rule Complete (macro))
Controlling Port Address = 0035
Spacer Bytes = 00 00
Segment Control = 00000010
Inpulse Rule/Voice Port = 10010000
Segment 1 is as follows:
Function ID = Incoming Port Change of State ($DB)
Resource Group = omitted
Change = off hook ($80)
Incoming Port Address = omitted
Supervision Code = omitted
Segment 2 is as follows:
Function ID = D1 (DTMF Digit)
Controlling Port Address = omitted
Report Status = omitted
Supervision = omitted
DTMF Receiver Address = 0035 (SLIC, DID, or UTC port with onboard receiver)
DTMF Status = 00000101
Digit String = 442 (F marks end of string)
Resource Control
$40
The Voice Port Status ($DE) report indicates when all voice prompts specified in a Voice Port Control ($6C) command have completed. This reporting is controlled by a bit setting in the $6C command.
The $DE report is generated when all voice prompts specified in a $6C command have completed if specified in the command.
Figure 5-17 shows the byte formatting for this report.
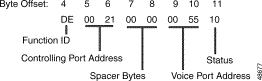
Function ID (byte offset 4)—Byte immediately following the Network Header; uniquely identifies the report from the system.
Controlling Port Address (byte offsets 5 and 6)—Hexadecimal representation of the incoming port to which the voice prompts were played.
Spacer Bytes (byte offsets 7 and 8)—Reserved for future enhancements; always returned as 00 00.
Voice Port Address (byte offsets 9 and 10)—Hexadecimal representation of the port used to present prompts.
Status (byte offset 11)—Indicates the status of the digit report. A byte value of 10 indicates that all specified voice prompts have been presented.
A $6C command specified to present five voice prompts and report to the host upon completion. The following report shows that all specified prompts have been presented.
04 0506 0708 0910 11
DE 0042 0000 0056 10
Function ID = DE (Voice Port Status)
Controlling Port Address = 0042
Spacer Bytes = 00 00
Voice Port Address = 0056
Status = all prompts presented ($10)
Resource Control
$40
Use the ISDN Port Change of State ($EA) report to inform the host of a change in the state of an ISDN call. Both the controlling and associated ports are represented. The port can be represented by B-channel, or by D-channel and Call ID.
In interworking scenarios, a pair of reports is produced when a port change of state affects both an ISDN port and a non-ISDN port. A non-ISDN port can be either the controlling port or the associated port. If the port is non-ISDN, the appropriate Incoming Port Change of State ($DB) or Outgoing Port Change of State ($DA) report is generated. Use the $EA report for ISDN-related events only.
The $EA report may be truncated if the network header segment, base report, and IEs exceed 255 bytes in length. No indication of truncation is provided to the host.
The $EA report is generated in response to a change in the state of an ISDN call or B-channel.
Figure 5-18 shows the byte formatting for this report.
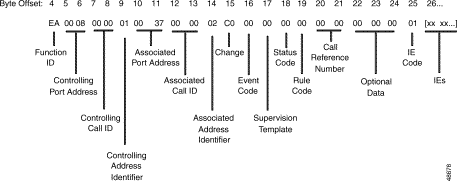
Function ID (byte offset 4)—Byte immediately following the Network Header; uniquely identifies the report from the system.
Controlling Port Address (byte offsets 5 and 6)—Hexadecimal representation of the controlling port circuit address for which the report is sent. If the Controlling Address Identifier (byte offset 9) is $01, these bytes represent the specific B-channel assigned to the call or a non-ISDN port. If the Controlling Address Identifier is $02, these bytes represent the D-channel; the Controlling Call ID is identified in byte offset 7 and 8.
Controlling Call ID (byte offsets 7 and 8)—Specifies the ISDN Call ID for the controlling port. Use Call ID only when the controlling port is specified by the D-channel. You must set the Controlling Address Identifier (byte offset 9) to $02.
Controlling Address Identifier (byte offset 9)—Specifies whether the controlling port is identified by D-channel and Call ID or by B-channel/non-ISDN port address. Interpret the byte as follows:
Associated Port Address (byte offsets 10 and 11)—Hexadecimal representation of the report's associated (outgoing) port circuit address. If the Associated Address Identifier (byte offset 14) is $01, these bytes represent the specific B-channel used. If the Associated Address Identifier is $02, these bytes represent the D-channel and Call ID.
Associated Call ID (byte offsets 12 and 13)—Specifies the ISDN Call ID for the associated (outgoing) port.
Associated Address Identifier (byte offset 14)—Specifies whether the associated (outgoing) port is identified by D-channel or by B-channel/non-ISDN port/resource group. Interpret the byte as follows:
Change (byte offset 15)—Specifies the type of change detected. The following list indicates the change that occurred for the outgoing port.
Event Code (byte offset 16)—Specifies the D-channel message received. Codeset 0 Q.931 message coding is used for all event codes. Interpret the byte as follows:
 |
Note If the system receives a NOTIFY message from the network and the ISDN state is ACTIVE (10), the system passes the NOTIFY message to the host in bytes 26 to n. In all other states, the system ignores network NOTIFY messages. |
Supervision Template (byte offset 17)—Specifies whether the outgoing port is considered answered (ANS condition token processed in ISDN supervision template) and the number of the ISDN supervision template used. If no ISDN supervision template is being used, or call failures and errors occur, set the byte to 00. Convert the byte from hexadecimal to binary and interpret the bits according to the following descriptions:
A0NNNNNN
Status Code (byte offset 18)—Indicates if an error was encountered. Interpret the byte as follows:
Rule Code (byte offset 19)—For Change = 04, indicates the number of the outpulse rule processed. Otherwise, this byte is 00.
Call Reference Number (byte offsets 20 and 21)—Indicates a call reference number that is reported to the host; call references are numbered sequentially.
 |
Note Set the Enable Host Call Reference feature flag to Y in the System Features administration screen when using the Call Reference Number bytes to enable the reporting of a call reference number to the host. Refer to the Cisco VCO/4K System Administrator's Guide for further information on the Enable Host Call Reference feature and feature flag setting instructions. |
Optional Data (byte offsets 22 to 24)—Reserved for future enhancements.
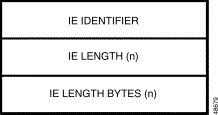
IE Code (byte offset 25)—Indicates the number of IEs included in this report. IE reporting is controlled by ISDN message templates. A value of $00 indicates that no IEs follow this byte. IEs are reported exactly as they were received from the D-channel.
IEs (byte offsets 26 to n)—For IE Code > 00, these bytes contain any IEs received over the specified D-channel. Each IE has either a multibyte or single-byte format. Figure 5-19 shows the multibyte format and Figure 5-20 shows the single-byte format.

 |
Note Single-byte IEs have bit 8 set to 1. |
Resource Control
$40
Use the ISDN Inpulse Rule Complete ($ED) report to inform the host that an inpulse rule has been processed either in response to a SETUP message received over the D-channel or for a specific B-channel. Digits collected in-band can also be included in this report. The content of the report is controlled by the type of reporting you specify in the inpulse rule and in the ISDN Receive Message Template. Information included in this report can include:
Received IEs are reported in the same format as they were received.
Digit segments are presented in the following order:
Digit segments follow the general format for their report, but the Controlling Port Address and Spacer Bytes are omitted in MF collections, and the Controlling Port Address, Report Status and Supervision bytes are omitted in DTMF collections.
This report may be truncated if the network header segment, base report, digit segments, and IEs exceed 255 bytes in length. Indication of truncation is provided as an Inpulse Rule Status byte value of 8F (byte offset 12-n).
This report is generated when inpulse rule processing is terminated. Termination can be caused by:
Figure 5-21 shows the byte formatting for this report.
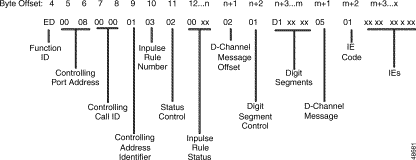
Function ID (byte offset 4)—Byte immediately following the Network Header; uniquely identifies the report from the system.
Controlling Port Address (byte offsets 5 and 6)—Hexadecimal representation of the controlling port circuit address for which the report is sent. If the Controlling Address Identifier (byte offset 9) is $01, these bytes represent the specific B-channel assigned to the call or a non-ISDN port. If the Controlling Address Identifier is $02, these bytes represent the D-channel; the Controlling Call ID is identified in byte offset 7 and 8.
Controlling Call ID (byte offsets 7 and 8)—Specifies the ISDN Call ID for the controlling port.
Controlling Address Identifier (byte offset 9)—Specifies whether the controlling port is identified by D-channel and Call ID or by B-channel/non-ISDN port address. Interpret the byte as follows:
Inpulse Rule Number (byte offset 10)—Specifies the inpulse rule number executed. Convert from hexadecimal to decimal for the inpulse rule.
Status Control (byte offset 11)—Specifies the number of Inpulse Rule Status bytes that follow. At least one Inpulse Rule Status byte is included in the report. The maximum number of status bytes allowed in a report is 10.
Inpulse Rule Status (byte offsets 12 to n)—Specifies whether the inpulse rule completed normally or was aborted due to error condition. Multiple status bytes can be included in a single report; the number of status bytes is indicated by the Status Control value. Interpret the bytes as follows:
D-Channel Message Offset (byte offset n + 1)—Specifies the number of hexadecimal bytes until the D-Channel Message byte (offset m + 1). This byte always contains a value of at least $02 to account for a Digit Segment Control byte (assuming no Digit Segments are included in the report).
Digit Segment Control (byte offset n + 2)—Specifies the number of DTMF or MF Digit report segments that follow. If this byte = 00, no digit segments are included in this report.
Digit Segments (byte offset n + 3 - m)—Optional DTMF and MF Digit report segments included in this macro; segment format follows that of the report the segment represents, with the exclusion of the Incoming Port Address byte.
D-Channel Message (byte offset m + 1)—Specifies the received D-channel message. When Digit Segment Control = 00, this byte immediately follows it. Otherwise, it appears after the final digit segment. Interpret this byte as follows:
 |
Note If a NOTIFY message from the network is received by the system and the ISDN state is ACTIVE (10), the system passes the NOTIFY message to the host in bytes 26 through n. In all other states, the system ignores NOTIFY messages from the network. |
IE Code (byte offset m + 2)—Indicates the number of IEs included in this report. IE reporting is controlled by ISDN Message Templates. A value of $00 indicates that no IEs follow this byte. IEs are reported exactly as they were received from the D-channel.
IEs (byte offset m + 3 - x)—For IE Code > 00, these bytes contain any IEs received over the specified D-channel. Each IE has either a multibyte format or a single-byte format. Figure 5-22 shows the multibyte format and Figure 5-23 shows the single-byte format.

 |
Note Single-byte IEs have bit 8 set to 1. |
System Status
$44
The Alarm Condition ($F0) report indicates the presence or clearance of a system alarm. Additionally, alarm severity and the number of occurrences is reported.
The report is generated upon alarm detection (any occurrence), severity change, or clearance. Additionally, an alarm is set or cleared for:
Because multiple occurrences of one card alarm are normal during system initialization, reports of card alarms that were set during system initialization do not supply a card's physical location. Similar alarms are reported in one $F0 report; the number of occurrences reflects the number of cards for which the alarm was detected. When a card becomes active, an $F0 report is generated; use the additional data bytes to indicate the Rack, Level, Slot location, and the span number.
The No Alarm Reports During System Initialization feature lets you enable/disable Disable alarm reporting during system initialization. Y disables system alarm reports until the system comes into service; N enables the system alarm reports. Access the System Feature Configuration screen from the Main menu.
From the System Feature Configuration screen, define the alarm severity for the No Hosts alarm ($0B) as wether Major or Fatal. If the Fatal Alarm for No Hosts feature=Y, all failed host links cause the affected system controller to reset after system initialization.
Figure 5-24 shows the byte formatting of this report.
Function ID (byte offset 4)—Byte immediately following the Network Header that identifies the report.
Alarm Code (byte offset 5)—Identifies the reported alarm. The system alarms, their meanings, and severity levels are described in Table 5-9. For more information on system alarms, refer to the Cisco VCO/4K System Administrator's Guide and Cisco VCO/4K System Messages.
| Value | Alarm Message | Alarm Severity |
|---|---|---|
01 | ALM001: Insufficient Timed IPC Memory | Minor |
02 | ALM002: Network Manager Failure | Fatal |
03 | ALM003: Host Manager Failure | Fatal |
04 | ALM004: Redundancy Manager Failure | Minor |
0A | ALM010: Host Communications Failure | Minor |
0B | ALM011: No Hosts Available | Major |
0C | ALM012: ADLC Sub-System Failure | Major |
0D | ALM013: Ethernet Sub-System Failure | Major |
0E | ALM014: Overlay Sub-System Failure | Major |
0F | ALM015: Resource Group Limitation Pending | Minor |
10 | ALM016: Resource Group Limitation Exists | Minor |
11 | ALM017: Internet Host Ping Failure | Major |
14 | ALM020: Start Record Exhaust | Major |
15 | ALM021: End Record Exhaust | Major |
16 | ALM022: D-Channel Pool Exhaust | Major |
17 | ALM023: NBC Does Not Respond | Fatal |
18 | ALM024: NBC DMA Output Failure | Fatal |
19 | ALM025: CP Transmit Overrun | Critical |
1A | ALM026: No NBC In System | Critical |
1B | ALM027: NBC Failure | Fatal |
1C | ALM028: NBC Loss of Internal Sync. | Fatal |
1D | ALM029: NBC Comm. Bus Failure | Minor |
1E | ALM030: No Tone Card In System | Critical |
1F | ALM031: Rack 1, Level 2 Failure | Critical |
20 | ALM032: Rack 1, Level 3 Failure | Critical |
21 | ALM033: Rack 2, Level 0 Failure | Critical |
22 | ALM034: Rack 2, Level 1 Failure | Critical |
23 | ALM035: Rack 2, Level 2 Failure | Critical |
24 | ALM036: Rack 2, Level 3 Failure | Critical |
25 | ALM037: Redundant Controller Failure | Minor |
26 | ALM038: PRI D-Channel Failure | Major |
27 | ALM039: PRI/T1/E1 Carrier Lost | Major |
28 | ALM040: PRI/T1/E1 Card Failure | Major |
29 | ALM041: PRI/T1/E1 Remote Alarm | Major |
2A | ALM042: PRI/T1/E1 Out Of Frame | Major |
2B | ALM043: PRI/T1/E1 Signaling Bit Alarm | Minor |
2C | ALM044: PRI/T1/E1 Slip Maint. Threshold | Minor |
2D | ALM045: PRI/T1/E1 OOF Maint. Threshold | Minor |
2E | ALM046: PRI/T1/E1 BPV Maint. Threshold | Minor |
2F | ALM047: Loss Of All Call Progress Analyzers | Minor |
30 | ALM048: Loss Of All Speech Recognizers | Minor |
31 | ALM049: Loss Of All MF Receivers | Minor |
32 | ALM050: Loss Of All DTMF Receivers | Minor |
33 | ALM051: Loss Of Announcement Capability | Minor |
34 | ALM052: Card Failure In System | Minor |
35 | ALM053: Fatal Host Alarm | Fatal |
36 | ALM054: Critical Host Alarm | Critical |
37 | ALM055: Major Host Alarm | Major |
38 | ALM056: Minor Host Alarm | Minor |
39 | ALM057: Aux-1 Host Alarm | Aux 1 |
3A | ALM058: Aux-2 Host Alarm | Aux 2 |
3B | ALM059: NFAS D-Channel Failure | Critical |
3C | ALM060: Loss of All MFCR2 Transceivers | Minor |
3D | ALM061: T1/E1 Blue Alarm | Minor |
3E | ALM062: E1 CRC Error | Minor |
3F | ALM063: Loss of All Subrate Functionality | Major |
40 | ALM064: Loss of Subrate Redundancy | Major |
41 | ALM065: Subrate Timeslot Threshold | Major |
42 | ALM066: Subrate Timeslot Exhausted | Major |
43 | ALM067: All Ports on Card Deactivated | Minor |
44 | ALM068: DS0 Port Slip Maintenance Threshold | Minor |
45 | ALM069: DS0 Port Loss of Clock | Major |
46 | ALM070: NBC Loss of External Synchronization | Major |
47 | ALM071: Wrong Hardware Installed | Major |
48 | ALM072: Interface Hardware Failure | Major |
49 | ALM073: Module Hardware Failure | Major |
4A | ALM074: Loss of All SPC OUTPULSERS | Minor |
4B | ALM075: No SPC Static Tone In System | Minor |
4C | ALM076: Incoming Timing Changed to Internal | Minor |
4D | ALM077: ICC Card Congestion Alarm | Minor |
50 | ALM080: Update Channel Failure | Minor |
51 | ALM081: UPD DMA Output Failure | Non-alarm event |
52 | ALM082: UPD Transmit Overrun | Minor |
53 | ALM083: UPD Receive Overrun | Minor |
54 | ALM084: UPD Receive Timeout | Non-alarm event |
55 | ALM085: UPD DMA Output Timeout | Non-alarm event |
5A | ALM090: Printer Offline | Non-alarm event |
5D | ALM093: Available Disk Space Less Than 30 MB | Major |
5E | ALM094: Available Disk Space Less Than 15 MB | Major |
5F | ALM095: Failed to Create 30 MB of Available Disk Space | Major |
60 | ALM096: Trace File Exceeded 1 MB Size | Major |
61 | ALM097: Log File Exceeded 1 MB Size | Major |
64 | ALM100: Queue Overflow | Fatal |
65 | ALM101: Queue Overflow | Critical |
66 | ALM102: Queue Overflow | Major |
67 | ALM103: Queue Overflow | Minor |
68 | ALM104: Queue Overflow | Non-alarm event |
69 | ALM105: Memory Allocation Failure | Fatal |
6A | ALM106: Memory Allocation Failure | Critical |
6B | ALM107: Memory Allocation Failure | Major |
6C | ALM108: Memory Allocation Failure | Minor |
6D | ALM109: Memory Allocation Failure | Non-alarm event |
96 | ALM150: Live Upgrade Start | Non-alarm event |
97 | ALM151: Live Upgrade Software Installed | Non-alarm event |
98 | ALM152: Optional S/W Configuration Initiated | Non-alarm event |
99 | ALM153: Rebooting Generic with New Release | Non-alarm event |
9A | ALM154: Card Cutover Initiated | Non-alarm event |
9B | ALM155: Live Upgrade Failed | Non-alarm event |
9C | ALM156: Live Upgrade Successful | Non-alarm event |
9D | ALM157: Live Upgrade Aborted by User | Non-alarm event |
Severity (byte offset 6)—Indicates an alarm's severity. Possible severity levels are as follows:
Occurrences (byte offset 7)—Indicates the number of alarm occurrences in hexadecimal. Convert to decimal for the number of occurrences.
Occurrence Severity (byte offset 8)—Indicates an alarm's occurrence severity. Possible severity levels are as follows:
Additional Data Bytes (byte offsets 9 to 12)—Supplies additional information for the following alarm codes. Additional information bytes are not supplied for alarms set during system initialization processing. Refer to the "Action Causing Report Generation" section.
 |
Note Byte 12 is optional and used for multispan cards only. |
At system initialization, the following report is generated to indicate a card alarm set for 20 T1 cards as part of normal processing. This reporting assumes the No Alarm Reports During System Initialization feature is disabled (set to N).
04 05 06 07 08
F0 27 05 14 05
Function ID = F0 (Alarm Condition)
Alarm Code = 27 (ALM039: PRI/T1/E1 Carrier Loss)
Severity = 05 (Major)
Occurrences = 14 (20 occurrences)
Occurrence Severity = 05 (Major)
No Additional Data Bytes
The following report indicates the T1 card located at the R-L-S position 1,2,21 comes into service following system initialization (the card out of service condition is cleared). The location is indicated in the additional data bytes.
04 05 06 07 08 091011
F0 27 00 01 00 010215
Function ID = F0 (Alarm Condition)
Alarm Code = 27 (ALM039: PRI/T1/E1 Carrier Loss)
Severity = 00 (Alarm Cleared)
Occurrences = 01 (1 occurrence)
Occurrence Severity = 00 (Alarm Cleared)
Additional Data Bytes = 01 02 15 (1, 2, 21)
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Posted: Sat Sep 28 14:33:51 PDT 2002
All contents are Copyright © 1992--2002 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Important Notices and Privacy Statement.