|
|

This chapter describes how to configure permanent virtual connection (PVC)-supported VLANs and PVC-supported VLANs with quality of service (QoS) traffic shaping on the ATM modules for the Catalyst 5000 and 6000 family switches.
 |
Note For information on installing Catalyst 5000 family ATM modules, refer to the Catalyst 5000 Family Module Installation Guide. For information on installing Catalyst 6000 family ATM modules, refer to the Catalyst 6000 Family Module Installation Guide. |
 |
Note For syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter, see "Command Reference." |
This chapter consists of the following sections:
PVC-based ATM links allow Catalyst 5000 and 6000 family switches to connect to each other through ATM interfaces over PVCs. You can configure one or more PVCs for each VLAN on every Catalyst 5000 or 6000 family ATM module. Connectivity can be back-to-back or through an ATM switch cloud, using RFC 1483-compliant, bridged Logical Link Control/Subnetwork Access Protocol (LLC/SNAP) packet encapsulation.
 |
Note Traffic cannot be bridged between ports in the same VLAN if these ports are configured for PVCs. |
When you create a PVC, you create a virtual channel descriptor (VCD) and attach it to the virtual path identifier (VPI) and virtual channel identifier (VCI). A VCD identifies the VPI-VCI pair for a particular packet. The ATM module requires this feature to manage packet transmission. The number chosen for the VCD is independent of the VPI-VCI pair used.
To use PVCs, you must configure PVCs in both the Catalyst 5000 or 6000 family ATM modules and the ATM switch cloud. PVCs remain active until the circuit is removed from either configuration.You can configure up to 4096 PVCs on the ATM module. In addition, you can divide the PVCs attached to the rate queues among different VLANs.
PVCs are compatible with switched virtual connection (SVC)-based LAN Emulation (LANE), with the following restrictions:
You can configure QoS traffic shaping with ATM PVC traffic-shaping software releases 50.1 or 51.1 and with ATM software releases 11.3WA4 and 12.0W5.
QoS consists of the following contracts:
In the Catalyst 5000 and 6000 family ATM module software, CoS is determined when you specify the traffic-shaping parameters. The following sections describe how CoS and traffic shaping functions in the Catalyst 5000 and 6000 ATM family modules. Traffic policing is not supported on the ATM modules.
 |
Note Software releases 50.1 and 51.1 are separate images from the Catalyst 5000 family LANE/MPOA software; software releases 50.1 and 51.1 do not support traffic shaping with LANE and support only RFC 1483-bridged Ethernet SNAP-encapsulated PVCs with peak cell-rate shaping. |
 |
Caution The ATM single PHY OC-3, dual PHY OC-3, and dual PHY DS3 modules require compatible releases of the Catalyst 5000 family supervisor engine and ATM PVC traffic-shaping software. Refer to the current release notes applicable to your module for information about software release requirements. |
Software releases 50.1 and 51.1 support unspecified bit rate (UBR) and constant bit rate (CBR) CoS. CoS for a PVC is determined by the specified traffic shaping. If you specify the peak cell rate (PCR), the PVC will have a CBR CoS. If no PCR is set, the PVC will have a UBR CoS.
Software releases 11.3 and 12.0 support UBR, CBR, and variable bit rate (VBR). As in software releases 50.1 and 51.1, the CoS is determined by the traffic shaping parameters you specify.
 |
Note The MBS should be a value between 2 and 255. If you specify an MBS of 1, the channel is opened with CBR CoS. |
Traffic shaping uses queues to constrain data bursts, limit peak data rate, and smooth jitters so that traffic will fit within the promised CoS contract.
Software releases 50.1 and 51.1 support up to ten dynamically created rate queues, and the rate queue assigned to a PVC depends on the PCR you assign to that PVC. When you specify the PCR, the software assigns the PVC to a rate queue that most closely matches that cell rate. If you do not specify the PCR, the software automatically assigns the PVC a service class of UBR and the default rate queue, which is the highest bandwidth rate queue available. See Table 4-1 for rate queue ranges in the different
software releases.
 |
Note Releases 50.1 and 51.1 allow only PCR. |
As in releases 50.1 and 51.1, in software releases 11.3WA4 and 12.0W5 rate queues are determined by the traffic shaping you specify. In software releases 11.3 and 12.0, the number of available rate queues is determined by the maximum amount of bandwidth divided by the specified PCR allocated for each PVC. As a result, software release 12.0 provides more rate-queue granularity and makes better use of the available bandwidth. See Table 4-1 for a listing of maximum available bandwidth for specific modules and software versions.
In software versions 11.3WA4 and12.0W5, you can specify PCR, SCR, and MBS traffic-shaping parameters.
The minimum PCR or SCR is 64 Kbps. If you specify a value less than 64 Kbps, the rate specified to the segmentation and reassembly sublayer (SAR) is 64 Kbps.
| Module | Product Number | Software Release | Number of Rate Queues | PCR Range |
|---|---|---|---|---|
ATM LANE PHY OC-3 | WS-X5153 | 50.1 | 8 | 2081-155,000 Kbps |
51.1 | 8 2 | 2081-155,000 Kbps 1-2080 Kbps | ||
ATM Dual PHY DS-3 | WS-X5166 | 51.1 | 8 2 | 2354-155,000 Kbps 1-2353 Kbps |
ATM Dual PHY | WS-X5161 | 11.WA43 | n | 0-622050 Kbps/n |
12.0W5 | n | 0-622050 Kbps/n | ||
ATM Dual PHY | WS-X5167 | 11.3WA4 | n | 0-155,000 Kbps |
12.0W5 | n | 0-155,000 Kbps | ||
ATM Fabric Integration | WS-X5165 | 11.3WA4 | n | 0-622,050 Kbps |
12.0W5 | n | 0-622,050 Kbps |
VTP is disabled by default on the ATM modules, even if you have enabled it to run on the supervisor engine module. If you enable VLAN Trunk Protocol (VTP) in the ATM module, the ATM module creates LAN Emulation Clients (LECs) for each VLAN configured on the supervisor engine. However, because a VLAN cannot simultaneously have LANE and PVCs configured, enabling VTP will cause any previously configured PVCs to be deleted.
 |
Note If you want to use PVCs to connect VLANs to the ATM cloud, do not enable VTP on the ATM module. VTP will override PVC configurations. |
Figure 4-1 shows two Catalyst 5000 family switches with ATM dual PHY DS3 modules in a redundant configuration running ATM PVC traffic-shaping software. The ATM dual PHY DS3 modules contain ten rate queues. Twenty-four PVCs are divided among the ten rate queues; each specifies a particular cell rate for the PVC set attached to it. In this example, PVC 1 through PVC 7 are in VLAN 1, PVC 8 through PVC 20 are in VLAN 2, and PVC 21 through PVC 24 are in VLAN 3.
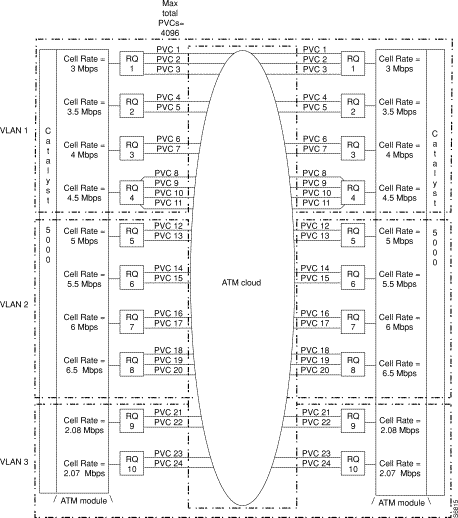
Table 4-2 shows the default PVC configuration.
| Feature | Default Configuration |
|---|---|
Clock internal | Transmit clock is generated internally |
ATM framing | C-Bit with ADM |
Line buildout | Short |
DS3-scramble | Disabled |
These sections describe how to configure PVC-supported VLANs on the Catalyst 5000 or 6000 family ATM modules:
To configure a PVC within the ATM cloud, refer to the documentation from your ATM switch vendor.
To set up a PVC-supported VLAN on the ATM module, perform this task in privileged mode:
| Task | Command | |
|---|---|---|
Step 1 | On the Catalyst 5000 or 6000 family switch, assign an Ethernet port to the desired VLAN. | set vlan vlan_num mod_num/port_num |
Step 2 | Establish a connection to the ATM module. | session mod_num |
Step 3 | Activate privileged mode on the ATM module. | enable |
Step 4 | Enter configuration mode. | configure terminal |
Step 5 | Select the ATM interface. | interface atm0 |
Step 6 | Set up the PVCs. | atm pvc vcd vpi vci aal5snap |
Step 7 | Bind the PVCs to the VLAN. | atm bind pvc vlan vcd vlan_num |
Step 8 | (Optional) Set up other PVCs for the same VLAN if needed by repeating Steps 6 and 7. |
|
Step 9 | Exit configuration mode. | Ctrl-Z |
Step 10 | Verify the PVC configuration. | show atm vlan |
Step 11 | Save the configuration. | write memory |
 |
Note Traffic cannot be bridged between ports in the same VLAN if these ports are configured for PVCs. |
 |
Note Traffic shaping requires software release 50.1 or release 51.1. |
To configure a PVC-supported VLAN with ATM PVC traffic shaping, perform this task in privileged mode:
| Task | Command | |
|---|---|---|
Step 1 | Assign an Ethernet port to the desired VLAN. | set vlan vlan_num mod_num/port_num |
Step 2 | Establish a connection to the ATM module. | session mod_num |
Step 3 | Activate privileged mode on the ATM module. | enable |
Step 4 | Enter configuration mode. | configure terminal |
Step 5 | Select the ATM interface. | interface atm0 |
Step 6 | (Optional) Customize the interface configuration if needed. | atm clock internal |
Step 7 | Set up the PVCs, indicating the desired peak cell rate. | atm pvc vcd vpi vci [aal-encap] aal5snap1 pcr2scr mbs [oam seconds] |
Step 8 | Bind the PVCs to the VLAN. | atm bind pvc vlan vcd vlan_num3 |
Step 9 | Set up other PVCs for the same VLAN if needed by repeating Steps 6 through 8. |
|
Step 10 | Exit configuration mode. | Ctrl-Z |
Step 11 | Verify the setup. | show atm vlan |
Step 12 | Write the configuration to NVRAM. | write memory |
 |
Note The atm bind pvc vlan vcd vlanid command is valid only for the current software release. The atm traffic-shape rate command is not available in software releases 50.1 or 51.1. |
You can unbind and remove a previously assigned PVC from a VLAN. You can also unbind a previously assigned PVC from a VLAN without removing the PVC. If you do not remove the PVC, you can bind the PVC to a different VLAN.
 |
Note The procedures in this section apply to ATM software release 4.1 and ATM PVC traffic-shaping software release 50.1. |
To remove a previously assigned PVC from a VLAN, perform this task in privileged mode:
| Task | Command | |
|---|---|---|
Step 1 | Enter privileged mode on the ATM module. | enable |
Step 2 | Enter configuration mode. | configure terminal |
Step 3 | Select the ATM interface. | interface atm0 |
Step 4 | Remove the PVC from the VLAN. | no atm pvc vcd |
Step 5 | End the session. | Ctrl-Z |
To unbind a previously assigned PVC from a VLAN without removing the PVC itself, perform this task in privileged mode:
| Task | Command | |
|---|---|---|
Step 1 | Activate privileged mode on the ATM module. | enable |
Step 2 | Enter configuration mode | configure terminal |
Step 3 | Select the ATM interface. | interface atm0 |
Step 4 | Unbind the PVC from the VLAN. | no atm bind pvc vlan vcd vlan_num |
Step 5 | End the session. | Ctrl-Z |
These sections show ATM PVC traffic-shaping configuration examples:
This example configuration describes how to configure a nonredundant PVC-supported VLAN configuration with traffic-shaping. Figure 4-2 shows the network used in this example. Assume that the ATM module in each Catalyst 5000 family switch is in slot 2. This example applies to both the single and dual PHY OC-3 ATM modules and the dual PHY DS3 ATM module.
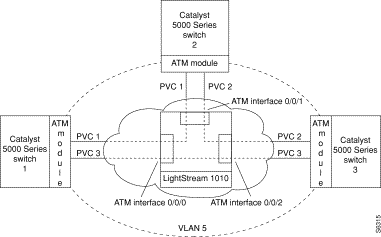
Table 4-3 shows the VLAN and switch connections, VPIs, VCIs, and traffic rates for the network shown in Figure 4-2.
| PVC | VLAN/Switch Connections | VPI | VCI | Rate in kbps |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Connects Switch 1 to Switch 2 on | 0 | 32 | 45000 |
2 | Connects Switch 2 to Switch 3 on | 0 | 33 | 2080 |
3 | Connects Switch 1 to Switch 3 on | 0 | 34 | 45000 |
These assumptions apply for this example:
Before configuring the VLAN over PVCs, you must perform these tasks:
 |
Note These procedures apply only if your ATM switch is a Cisco LightStream 1010 ATM switch. If you have a different ATM switch, consult the documentation provided by the switch vendor. |
Switch> enable
Switch#
Switch# configure terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
Switch(config)# interface atm0/0/0
Switch(config-if)# atm pvc 0 32 interface atm0/0/1 0 32
Switch(config-if)# end
Switch#
Step 2 Verify the setup of PVC 1. Enter this command on the LightStream 1010 ATM switch:
Switch# show atm vc interface atm0/0/0
Interface VPI VCI Type X-Interface X-VPI X-VCI Status
ATM0/0/0 0 5 PVC ATM2/0/0 0 32 UP
ATM0/0/0 0 16 PVC ATM2/0/0 0 33 UP
ATM0/0/0 0 18 PVC ATM2/0/0 0 34 UP
ATM0/0/0 0 32 PVC ATM0/0/1 0 32 UP
Switch#
Step 3 Create PVC 2 within the ATM cloud. Enter these commands on the LightStream 1010 ATM switch:
Switch# configure terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
Switch(config)#
Switch(config)# interface atm0/0/1
Switch(config-if)# atm pvc 0 33 interface atm0/0/2 0 33
Switch(config-if)# end
Switch#
Step 4 Verify the setup of PVC 2. Enter this command on the LightStream 1010 ATM switch:
Switch# show atm vc interface atm0/0/1
Interface VPI VCI Type X-Interface X-VPI X-VCI Status
ATM0/0/1 0 5 PVC ATM2/0/0 0 35 UP
ATM0/0/1 0 16 PVC ATM2/0/0 0 36 UP
ATM0/0/1 0 18 PVC ATM2/0/0 0 37 UP
ATM0/0/1 0 32 PVC ATM0/0/0 0 32 UP
ATM0/0/1 0 33 PVC ATM0/0/2 0 33 UP
Switch#
Step 5 Create PVC 3 within the ATM cloud. Enter these commands on the LightStream 1010 ATM switch:
Switch# configure terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
Switch(config-if)# interface atm0/0/2
Switch(config-if)# atm pvc 0 34 interface atm0/0/0 0 34
Switch(config-if)# end
Switch#
Step 6 Verify the setup of PVC 3. Enter this command on the LightStream 1010 ATM switch:
Switch# show atm vc interface atm0/0/2
Interface VPI VCI Type X-Interface X-VPI X-VCI Status
ATM0/0/2 0 5 PVC ATM2/0/0 0 38 UP
ATM0/0/2 0 16 PVC ATM2/0/0 0 39 UP
ATM0/0/2 0 18 PVC ATM2/0/0 0 40 UP
ATM0/0/2 0 33 PVC ATM0/0/1 0 33 UP
ATM0/0/2 0 34 PVC ATM0/0/0 0 34 UP
Switch#
Step 7 At the console of the Catalyst 5000 family Switch 1, establish a connection to the ATM module in
slot 2 by entering these commands:
Console> enable
Enter password:
Console> (enable) set vlan 5
Console> (enable) session 2
Trying ATM-2...
Connected to ATM-2.
Escape character is '^]'.
ATM>
Step 8 Configure PVC 1 and PVC 3 on Switch 1 by entering these commands:
ATM> enable
ATM# configure terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
ATM(config)# interface atm0
ATM(config-if)# atm pvc 10 0 32 aal5snap 45000
ATM(config-if)# atm ds3-scramble
ATM(config-if)# atm lbo long
ATM(config-if)# atm framing m23adm
ATM(config-if)# atm clock internal
ATM(config-if)# atm pvc 11 0 34 aal5snap 45000
ATM(config-if)# end
ATM#
You can perform all PVC-related configurations for all VLANs on atm0, the major interface, because the subinterface number has no significance for PVC-supported VLANs. VCDs 10 and 11 (used above) can be any unused VCDs. Enter the show atm vc command to find unused VCDs.
Step 9 Bind PVC 1 and PVC 3 to VLAN 5 on Switch 1 by entering these commands:
ATM# configure terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
ATM(config)# interface atm0
ATM(config-if)# atm bind pvc vlan 10 5
ATM(config-if)# atm bind pvc vlan 11 5
ATM(config-if)# end
ATM#
Enter the VCD numbers used in Step 8. The last option in the atm bind pvc command specifies
VLAN 5.
Step 10 Verify the setup on Switch 1 by entering these commands:
ATM# show atm vlan
VCD VLAN-ID
10 5
11 5
ATM#
ATM# show atm vc
AAL/ Peak Avg. Burst
Interface VCD VPI VCI Type Encapsulation Kbps Kbps Cells Status
ATM0 10 0 32 PVC AAL5-SNAP 45000 0 0 ACTIVE
ATM0 11 0 34 PVC AAL5-SNAP 45000 0 0 ACTIVE
ATM#
Step 11 Save the configuration as follows:
ATM# write memory
Building configuration...
[OK]
ATM#
Step 12 At the console of the Catalyst 5000 family Switch 2, establish a connection to the ATM module in
slot 2 by entering these commands:
Console> enable
Enter password:
Console> (enable) set vlan 5
Console> (enable) session 2
Trying ATM-2...
Connected to ATM-2.
Escape character is '^]'.
ATM#
Step 13 Configure PVC 1 and PVC 2 on Switch 2 by entering these commands:
ATM> enable
ATM# configure terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
ATM(config)# interface atm0
ATM(config-if)# atm pvc 10 0 32 aal5snap 45000
ATM(config-if)# atm ds3-scramble
ATM(config-if)# atm lbo long
ATM(config-if)# atm framing m23adm
ATM(config-if)# atm clock internal
ATM(config-if)# atm pvc 11 0 33 aal5snap 2080
ATM(config-if)# end
ATM#
You can perform all PVC-related configurations for all VLANs on atm0, the major interface, because the subinterface number has no significance for PVC-supported VLANs. VCDs 10 and 11 (used above) can be any unused VCDs. Enter the show atm vc command to find unused VCDs.
Step 14 Bind PVC 1 and PVC 2 to VLAN 5 on Switch 2 by entering these commands:
ATM# configure terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
ATM(config)# interface atm0
ATM(config-if)# atm bind pvc vlan 10 5
ATM(config-if)# atm bind pvc vlan 11 5
ATM(config-if)# end
ATM#
Enter the VCDs used in Step 13. The last option in the atm bind pvc command specifies VLAN 5.
Step 15 Verify the setup on Switch 2 by entering these commands:
ATM# show atm vlan
VCD VLAN-ID
10 5
11 5
ATM#
ATM# show atm vc
AAL / Peak Avg. Burst
Interface VCD VPI VCI Type Encapsulation Kbps Kbps Cells Status
ATM0 10 0 32 PVC AAL5-SNAP 45000 0 0 ACTIVE
ATM0 11 0 33 PVC AAL5-SNAP 2080 0 0 ACTIVE
ATM#
Step 16 Save the configuration as follows:
ATM# write memory
Building configuration...
[OK]
ATM#
Step 17 At the console of the Catalyst 5000 family Switch 3, establish a connection to the ATM module in
slot 2 by entering these commands:
Console> enable
Enter password:
Console> (enable) set vlan 5
Console> (enable) session 2
Trying ATM-2...
Connected to ATM-2.
Escape character is '^]'.
ATM>
Step 18 Configure PVC 2 and PVC 3 on Switch 3 by entering these commands:
ATM> enable
ATM# configure terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
ATM(config)# interface atm0
ATM(config-if)# atm pvc 10 0 33 aal5snap 2080
ATM(config-if)# atm pvc 11 0 34 aal5snap 45000
ATM(config-if)# end
ATM#
You can perform all PVC-related configurations for all VLANs on atm0, the major interface, because the subinterface number has no significance for PVC-supported VLANs. VCDs 10 and 11 (used above) can be any unused VCDs. Enter the show atm vc command to find unused VCDs.
Step 19 Bind PVC 2 and PVC 3 to VLAN 5 on Switch 3 by entering these commands:
ATM# configure terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
ATM(config)# interface atm0
ATM(config-if)# atm bind pvc vlan 10 5
ATM(config-if)# atm bind pvc vlan 11 5
ATM(config-if)# end
ATM#
Enter the VCDs used in Step 18. The last option in the atm bind pvc command specifies VLAN 5.
Step 20 Verify the setup on Switch 3 by entering these commands:
ATM# show atm vlan
VCD VLAN-ID
10 5
11 5
ATM#
ATM# show atm vc
AAL / Peak Avg. Burst
Interface VCD VPI VCI Type Encapsulation Kbps Kbps Cells Status
ATM0 10 0 33 PVC AAL5-SNAP 2080 0 0 ACTIVE
ATM0 11 0 34 PVC AAL5-SNAP 45000 0 0 ACTIVE
ATM#
Step 21 Save the configuration as follows:
ATM# write memory
Building configuration...
[OK]
ATM#
Figure 4-3 shows the PVCs needed for complete redundancy if PHY A or PHY B on either Switch 1 or Switch 2 fails. This example (referred to as example 2) applies to the dual PHY DS3 module, but you can use the same configuration for dual PHY OC-3 modules (with appropriate PCRs).
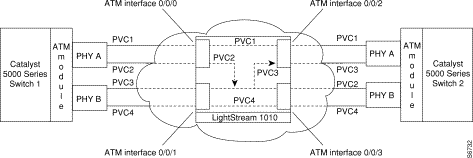
In Figure 4-3, you see Catalyst 5000 family Switch 1 and Catalyst 5000 family Switch 2, each with an ATM dual PHY DS3 module, connected to a LightStream 1010 ATM switch in the ATM cloud.
Assume PHY A on Switch 1 goes down and transmits no data to PHY A on Switch 2 over PVC 1, even though PHY A on Switch 2 remains active. When PHY A on Switch 1 goes down, PHY B on Switch 1 becomes active and transmits data to PHY B on Switch 2 over PVC 2.
Similarly, if PHY A on Switch 2 goes down and transmits no data to Switch 1 over PVC 1, PHY B on Switch 2 becomes active and transmits data to PHY B on Switch 1 over PVC 3.
Table 4-4 shows the PVCs used to transmit data when the specified PHYs for the Catalyst 5000 family switches in Figure 4-3 are active. For example, if PHY A on Switch 1 and PHY A on Switch 2 are both active, data is transmitted on PVC 1.
| Switch 1 | Switch 2 | PVC Used |
|---|---|---|
PHY A— active | PHY A—active | 1 |
PHY A—active | PHY B—active | 2 |
PHY B—active | PHY A—active | 3 |
PHY B—active | PHY B—active | 4 |
 |
Note To ensure redundancy for data transmission using dual PHYs, you must set up PVCs 1, 2, 3, and 4 on the same VLAN and configure the same data rate for each PVC. |
The following assumptions apply for this example configuration:
| PVC | Switch Connections | VPI | VCI | kbps Rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Connects PHY A on Switch 1 to PHY A on Switch 2 | 0 | 32 | 45000 |
2 | Connects PHY A on Switch 1 to PHY B on Switch 2 | 0 | 33 | 45000 |
3 | Connects PHY B on Switch 1 to PHY A on Switch 2 | 0 | 34 | 45000 |
4 | Connects PHY B on Switch 1 to PHY B on Switch 2 | 0 | 35 | 45000 |
Before configuring the VLAN over PVCs, you must perform these tasks:
To configure the devices in this example, follow these steps:
 |
Note These procedures apply only if your ATM switch is a Cisco LightStream 1010 ATM switch. If you have a different ATM switch, consult the publication that accompanied the switch. |
Switch> enable
Switch# configure terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
Switch(config)# interface atm0/0/0
Switch(config-if)# atm pvc 0 32 int atm0/0/2 0 32
Switch(config-if)# end
Switch#
Step 2 Verify the setup of PVC 1. Enter this command on the LightStream 1010 ATM switch:
Switch# show atm vc interface atm0/0/0
Interface VPI VCI Type X-Interface X-VPI X-VCI Status
ATM0/0/0 0 5 PVC ATM2/0/0 0 32 UP
ATM0/0/0 0 16 PVC ATM2/0/0 0 33 UP
ATM0/0/0 0 18 PVC ATM2/0/0 0 34 UP
ATM0/0/0 0 32 PVC ATM0/0/2 0 32 UP
Switch#
Step 3 Create PVC 2 within the ATM cloud. Enter these commands on the LightStream 1010 ATM switch:
Switch# configure terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
Switch(config)# interface atm0/0/2
Switch(config-if)# atm pvc 0 33 int atm0/0/1 0 33
Switch(config-if)# end
Switch#
Step 4 Verify the setup of PVC 2. Enter this command on the LightStream 1010 ATM switch:
Switch# show atm vc interface atm0/0/2
Interface VPI VCI Type X-Interface X-VPI X-VCI Status
ATM0/0/2 0 5 PVC ATM2/0/0 0 38 UP
ATM0/0/2 0 16 PVC ATM2/0/0 0 39 UP
ATM0/0/2 0 18 PVC ATM2/0/0 0 40 UP
ATM0/0/2 0 32 PVC ATM0/0/0 0 32 UP
ATM0/0/2 0 33 PVC ATM0/0/1 0 33 UP
Switch#
Step 5 Create PVC 3 within the ATM cloud. Enter these commands on the LightStream 1010 ATM switch:
Switch# configure terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
Switch(config)# interface atm0/0/3
Switch(config-if)# atm pvc 0 34 int atm0/0/0 0 34
Switch(config-if)# end
Switch#
Step 6 Verify the setup of PVC 3. Enter this command on the LightStream 1010 ATM switch:
Switch# show atm vc interface atm0/0/3
Interface VPI VCI Type X-Interface X-VPI X-VCI Status
ATM0/0/3 0 5 PVC ATM2/0/0 0 41 UP
ATM0/0/3 0 16 PVC ATM2/0/0 0 42 UP
ATM0/0/3 0 18 PVC ATM2/0/0 0 43 UP
ATM0/0/3 0 34 PVC ATM0/0/0 0 34 UP
Switch#
Step 7 Create PVC 4 within the ATM cloud. Enter these commands on the LightStream 1010 ATM switch:
Switch# configure terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
Switch(config)# interface atm0/0/1
Switch(config-if)# atm pvc 0 35 interface atm0/0/3 0 35
Switch(config-if)# end
Switch#
Step 8 Verify the setup of PVC 4. Enter this command on the LightStream 1010 ATM switch:
Switch# show atm vc interface atm0/0/1
Interface VPI VCI Type X-Interface X-VPI X-VCI Status
ATM0/0/1 0 5 PVC ATM2/0/0 0 35 UP
ATM0/0/1 0 16 PVC ATM2/0/0 0 36 UP
ATM0/0/1 0 18 PVC ATM2/0/0 0 37 UP
ATM0/0/1 0 33 PVC ATM0/0/2 0 33 UP
ATM0/0/1 0 35 PVC ATM0/0/3 0 35 UP
Switch#
Step 9 At the console of the Catalyst 5000 family Switch 1, session to the ATM module in slot 2 by entering these commands:
Console> enable
Enter password:
Console> (enable) session 2
Trying ATM-2...
Connected to ATM-2.
Escape character is '^]'.
ATM>
Step 10 Configure PVCs 1, 2, 3, and 4 on Switch 1 by entering these commands:
ATM> enable
ATM# configure terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
ATM(config)# interface atm0
ATM(config-if)# atm pvc 1 0 32 aal5snap 45000
ATM(config-if)# atm ds3-scramble
ATM(config-if)# atm lbo long
ATM(config-if)# atm framing m23adm
ATM(config-if)# atm clock internal
ATM(config-if)# atm pvc 2 0 33 aal5snap 45000
ATM(config-if)# atm pvc 3 0 34 aal5snap 45000
ATM(config-if)# atm pvc 4 0 35 aal5snap 45000
ATM(config-if)# end
ATM#
You can perform all PVC-related configurations for all VLANs on atm0, the major interface, because the subinterface number has no significance for PVC-supported VLANs. VCDs 10 and 11 (used above) can be any unused VCDs. Enter the show atm vc command to find unused VCDs.
Step 11 Bind the PVCs to VLAN 5 on the Switch 1 by entering these commands:
ATM# configure terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
ATM(config)# interface atm0
ATM(config-if)# atm bind pvc vlan 1 5
ATM(config-if)# atm bind pvc vlan 2 5
ATM(config-if)# atm bind pvc vlan 3 5
ATM(config-if)# atm bind pvc vlan 4 5
ATM(config-if)# end
ATM#
Enter the VCD numbers used in Step 8. The last option in the atm bind pvc command specifies
VLAN 5.
Step 12 Verify the setup on the Switch 1 by entering these commands:
ATM# show atm vlan
VCD VLAN-ID
1 5
2 5
3 5
4 5
ATM#
ATM# show atm vc
AAL / Peak Avg. Burst
Interface VCD VPI VCI Type Encapsulation Kbps Kbps Cells Status
ATM0 1 0 32 PVC AAL5-SNAP 45000 0 0 ACTIVE
ATM0 2 0 33 PVC AAL5-SNAP 45000 0 0 ACTIVE
ATM0 3 0 34 PVC AAL5-SNAP 45000 0 0 ACTIVE
ATM0 4 0 35 PVC AAL5-SNAP 45000 0 0 ACTIVE
ATM#
Step 13 Save the configuration as follows:
ATM# write memory
Building configuration...
[OK]
ATM#
Step 14 At the console of the Catalyst 5000 family Switch 2, session to the ATM module in slot 2 by entering these commands:
Console> enable
Enter password:
Console> (enable) set vlan 5
Console> (enable) session 2
Trying ATM-2...
Connected to ATM-2.
Escape character is '^]'.
ATM>
Step 15 Configure PVCs 1, 2, 3, and 4 on Switch 2 by entering these commands:
ATM> enable
ATM# configure terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
ATM(config)# interface atm0
ATM(config-if)# atm pvc 1 0 32 aal5snap 45000
ATM(config-if)# atm ds3-scramble
ATM(config-if)# atm lbo long
ATM(config-if)# atm framing m23adm
ATM(config-if)# atm clock internal
ATM(config-if)# atm pvc 2 0 33 aal5snap 45000
ATM(config-if)# atm pvc 3 0 34 aal5snap 45000
ATM(config-if)# atm pvc 4 0 35 aal5snap 45000
ATM(config-if)# end
ATM#
You can perform all PVC-related configurations for all VLANs on atm0, the major interface, because the subinterface number has no significance for PVC-supported VLANs. VCDs 10 and 11 (used above) can be any unused VCDs. Enter the show atm vc command to find unused VCDs.
Step 16 Bind the PVCs to VLAN 5 on the Catalyst 5000 family Switch 2 by entering these commands:
ATM# configure terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
ATM(config)# interface atm0
ATM(config-if)# atm bind pvc vlan 1 5
ATM(config-if)# atm bind pvc vlan 2 5
ATM(config-if)# atm bind pvc vlan 3 5
ATM(config-if)# atm bind pvc vlan 4 5
ATM(config-if)# end
ATM#
Step 17 Verify the setup on the Catalyst 5000 family Switch 2 by entering these commands:
ATM# show atm vlan
VCD VLAN-ID
1 5
2 5
3 5
4 5
ATM#
ATM# show atm vc
AAL / Peak Avg. Burst
Interface VCD VPI VCI Type Encapsulation Kbps Kbps Cells Status
ATM0 1 0 32 PVC AAL5-SNAP 45000 0 0 ACTIVE
ATM0 2 0 33 PVC AAL5-SNAP 45000 0 0 ACTIVE
ATM0 3 0 34 PVC AAL5-SNAP 45000 0 0 ACTIVE
ATM0 4 0 35 PVC AAL5-SNAP 45000 0 0 ACTIVE
ATM#
Step 18 Save the configuration as follows:
ATM# write memory
Building configuration...
[OK]
ATM#
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Posted: Tue Nov 28 00:18:51 PST 2000
Copyright 1989-2000©Cisco Systems Inc.