|
|

This appendix lists the port pinouts on the supervisor engines and the standards compliance specifications.
 |
Note Any pin not specifically listed is not connected. |
This appendix contains the following sections:
The console port on Supervisor Engines I and II is an EIA/TIA-232, data communications equipment (DCE), DB-25 receptacle. Both data set ready (DSR) and data carrier detect (DCD) are active when the system is running. The Request To Send (RTS) signal tracks the state of the Clear To Send (CTS) input. The console port does not support modem control or hardware flow control. Table A-1 lists the Supervisor Engine I and II console port pinouts.
| Pin | Signal | Direction | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
1 | GND |
| Ground |
2 | RxD | —> | Receive data |
3 | TxD | <— | Transmit data |
4 | CTS | <— | Clear to send |
5 | RTS | —> | Return to send |
7 | GND |
| Ground |
8 | DTR | —> | Data terminal ready |
20 | DCD | <— | Data carrier detect |
 |
Note The Supervisor Engine III auxiliary (AUX) port is currently not supported. |
You can connect the Supervisor Engine III console port to an ASCII terminal or PC running terminal emulation software. Table A-2 lists the pinouts for the asynchronous serial console port. In addition to the RJ-45-to-RJ-45 cable provided in the console port accessory kit (shipped with your Catalyst 5000 family switch), you will need either an RJ-45-to-DB-9, RJ-45-to-D-subminiature female, or RJ-45-to-D-subminiature male adapter (these adapters are provided in the accessory kit).
| Console Port | Console Device |
|---|---|
| Pin (signal) | Connect to |
1 is looped to pin 8 |
|
2 (DTR) | DSR |
3 (RxD) | TxD |
4 (GND) | GND |
5 (GND) | GND |
6 (TxD) | RxD |
7 (DSR) | DTR |
8 is looped to pin 1 |
|
You can connect the Supervisor Engine II G or III G console port to an ASCII terminal or PC running terminal emulation software (console port) or IOS software (RSFC console port). Table A-3 lists the pinouts for the asynchronous serial console port. Table A-4 lists the pinouts for the RSFC console port.
In addition to the RJ-45-to-RJ-45 cable provided in the console port accessory kit (shipped with your Catalyst 5000 family switch), you will need either an RJ-45-to-DB-9, RJ-45-to-D-subminiature female, or RJ-45-to-D-subminiature male adapter (these adapters are provided in the accessory kit).
| Console Port | Console Device |
|---|---|
| Pin (signal) | Connect to |
1 is looped to pin 8 |
|
2 | DTR (out) |
3 | TXD or RXD |
4 | (GND) |
5 | (GND) |
6 | RXD or TXD |
7 | RTS/DCD (in) |
8 is looped to pin 1 |
|
| Console Port | Console Device |
|---|---|
| Pin (signal) | Connect to |
9 is looped to pin 16 |
|
10 | DTR (out) |
11 | TXD or RXD |
12 | (GND) |
13 | (GND) |
14 | RXD or TXD |
15 | RTS (in) |
16 is looped to pin 9 |
|
This section describes the supervisor engine 100BASE-TX, 100BASE-FX, 1000BASE-SX, and 1000BASE-LX/LH interface ports.
Table A-5 lists the cabling specifications for the 100-Mbps uplink modules.
| Specification | Description |
|---|---|
Cable type | Category 5 UTP1 |
Transceiver speed | 100 Mbps |
Duplex mode | Full and half |
Maximum distance between stations | 328 ft (100 m) |
| 1UTP=unshielded twisted pair |
This section lists the supervisor engine 100BASE-TX port pinouts.
Table A-6 lists the pinouts for the 40-pin MII Fast Ethernet ports.
| Pin | Signal | Pin | Signal |
|---|---|---|---|
1 | +5V | 21 | +5V |
2 | MDIO | 22 | Common |
3 | MDC | 23 | Common |
4 | RxD<3> | 24 | Common |
5 | RxD<2> | 25 | Common |
6 | RxD<1> | 26 | Common |
7 | RxD<0> | 27 | Common |
8 | Rx_DV | 28 | Common |
9 | Rx_Clk | 29 | Common |
10 | Rx_Er | 30 | Common |
11 | Tx_Er | 31 | Common |
12 | Tx_Clk | 32 | Common |
13 | Tx_En | 33 | Common |
14 | TxD<0> | 34 | Common |
15 | TxD<1> | 35 | Common |
16 | TxD<2> | 36 | Common |
17 | TxD<3> | 37 | Common |
18 | Col | 38 | Common |
19 | CRS | 39 | Common |
20 | +5V | 40 | +5V |
Table A-7 lists the pinouts for the RJ-45 MDIX Fast Ethernet ports.
| Pin | Signal | Direction | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
1 | RxD+ | <— | Receive data + |
2 | RxD- | <— | Receive data - |
3 | TxD+ | —> | Transmit data + |
4 | NC |
| No connection |
5 | NC |
| No connection |
6 | TxD- | —> | Transmit data - |
7 | NC |
| No connection |
8 | NC |
| No connection |
Use SC fiber-optic connectors (see Figure A-1) to connect to the 100BASE-FX (two port), 1000BASE-SX, and 1000BASE-LX/LH ports. Use MT-RJ fiber-optic connectors (see Figure A-2) to connect to 100BASE-FX (four port) ports. Always keep caps and plugs on the fiber-optic connectors on the cable and the switch when they are not in use.
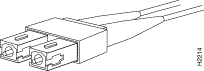
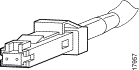
The Gigabit Interface Converter (GBIC) is a hot-swappable input/output device that plugs into a Gigabit Ethernet or EtherChannel module, linking the module with the fiber-optic network. For more information on GBICs, see the "Connecting Gigabit Ethernet Modules" section.
Table A-8 provides cabling specifications for the GBICs that you install in the Gigabit Ethernet module. Note that all GBIC ports have SC-type connectors, and the minimum cable distance for all GBICs listed (multimode fiber [MMF] and single-mode fiber [SMF]) is 6.5 feet (2 m). The minimum cabling distance for the ZX GBIC is 6.2 miles (10 km) with 8-dB attentuators installed at both ends of the link and 24.9 miles (40 km) without attenuators.
| GBIC | Wavelength (nm) | Fiber Type | Core Size (micron) | Modal Bandwidth (MHz/km) | Cable Distance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
SX1 | 850 | MMF | 62.5 | 160 | 722 ft (220 m) |
LX/LH | 1300 | MMF2 | 62.5 | 500 | 1804 ft (550 m) |
ZX3 | 1550 | SMF | 9/10 | - | 43.5 miles (70 km) |
 |
Note The mode-conditioning patch cord (CAB-GELX-625 or equivalent) is required to comply with IEEE standards. The IEEE found that link distances could not be met with certain types of fiber-optic cable cores. The solution is to launch light from the laser at a precise offset from the center by using the mode-conditioning patch cord. At the output of the patch cord, the LX/LH GBIC is compliant with the IEEE 802.3z standard for 1000BASE-LX. For more information, see the "Patch Cord (1000BASE-LX/LH Uplink Port Only)" section. |
Table A-9 lists standards compliance specifications.
| Specification | Description | |
Compliance | CE1 Marking |
|
Safety | UL2 1950, CSA3-C22.2 No. 950, EN460950, IEC5 950, TS6 001, AS/NZS7 3260 | |
EMI8 | FCC9 Class A (47 CFR10, Part 15), ICES11-003 Class A, EN55022 Class A, CISPR22 Class A, AS/NZS 3548 Class A, and VCCI12 Class A with UTP13 EN55022 Class B, CISPR22 Class B, AS/NZS 3548 Class B, and VCCI Class B (Japan) with FTP14 cables | |
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Posted: Tue Oct 3 18:55:57 PDT 2000
Copyright 1989-2000©Cisco Systems Inc.