|
|

To alter the configuration of your Catalyst 3900, follow these steps:
Step 1 Establish a console session if one has not already been established. For information about establishing a console session, refer to the "Planning for Configuration and Management" chapter.
Step 2 At the Main Menu, select Configuration. The Configuration Menu panel (Figure 6-1) is displayed.
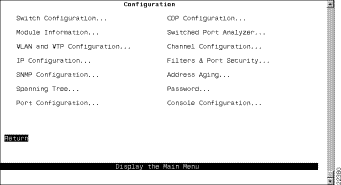
Step 3 Select the menu option you want.
Step 4 Change or enter values.
Step 5 When you have changed or entered all of the required configuration parameters, save the changes and return to the Cisco Catalyst 3900 Main Menu. Configuration is complete.
As you move through the console panels, follow these guidelines:
1-3 5 7-9
1-3,5,7-9
To view or change basic switch and stack information, such as the system name, system location, or system contact, select Switch Configuration on the Configuration Menu. The Switch Configuration panel (Figure 6-2) is displayed.
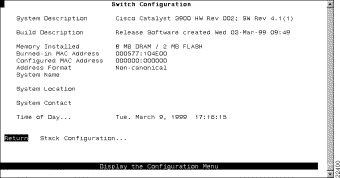
The following information is displayed on this panel:
| To | Select | Then |
|---|---|---|
Change the current settings... | The appropriate parameter... | Specify the new value. |
View additional information about the switch... | Stack Configuration | Refer to the "Configuring Stack Parameters" section. |
Save your changes... | Return |
|
To configure stack parameters, select Stack Configuration on the Switch Configuration panel. The Stack Configuration panel (Figure 6-3) is displayed.
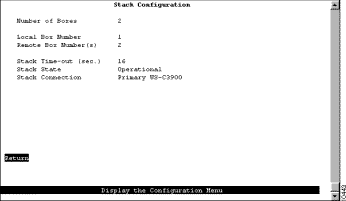
The following information is displayed on this panel:
To view general information about the Catalyst 3900 and any expansion modules installed, select Module Information on the Configuration Menu. The Module Information panel (Figure 6-4) is displayed.
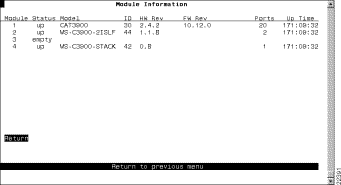
The following information is displayed on this panel:
You cannot change the information that appears on this panel.
You can partition a single Catalyst 3900 into multiple VLANs. A VLAN can be configured with its own IP address and managed with SNMP. A VLAN can contain ports from multiple switches in the same stack. Any VLAN can participate independently in the Spanning-Tree Protocol (STP). Once VLANs have been established, packets are forwarded between ports belonging to the same VLAN only.
You can use the VTP to set up and manage VLANs across an entire administrative domain. When new VLANs are added to a Catalyst switch in an administrative domain, VTP can be used to automatically distribute the information to the trunk ports of all the devices in the administrative domain. This allows VLAN naming consistency and connectivity between all devices in the administrative domain.
An administrative or management domain is a logical grouping of VLANs used by the VTP for the purpose of administration and management. VTP parameters are propagated throughout the VLANs within a single management domain. While you can have duplicate VLAN names in a network, each VLAN name within a management domain must be unique. A management domain is not device specific. Different devices may belong to the same management domain if the VLANs defined for the devices belong to the same management domain. Likewise, a device may belong to multiple management domains if the VLANs defined for the device belong to different management domains.
VTP pruning enhances network bandwidth use by reducing unnecessary flooded traffic, such as broadcast, multicast, unknown, and flooded unicast packets. VTP pruning increases available bandwidth by restricting flooded traffic only to those trunk links that the traffic must use to access the appropriate network devices. When a VLAN is pruned on an ISL trunk link, that trunk does not transmit frames destined for that VLAN. By default, VTP pruning is disabled. Before enabling VTP pruning, make sure that all the devices in the administrative domain support VTP pruning.
For more information about Token Ring VLANs, refer to the "Token Ring VLANs" section of the "Understanding Token Ring Switching" appendix. For more information about VTP, refer to the "VLAN Trunking Protocol" section of the "Understanding Token Ring Switching" appendix.
To configure VLANs and the VTP for the Catalyst 3900, select VLAN and VTP Configuration on the Configuration Menu. The VLAN and VTP Configuration panel (Figure 6-5) is displayed.
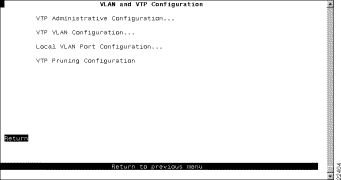
The following options are displayed on this panel:
To view or configure parameters for the VTP, select VTP Administrative Configuration on the VLAN and VTP Configuration panel. The VTP Administrative Configuration panel (Figure 6-6) is displayed.
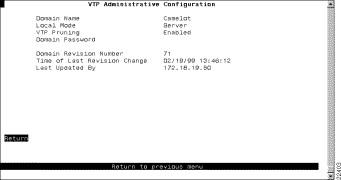
The following information is displayed on this panel:
| To | Select | Then |
|---|---|---|
Change the current settings | The appropriate parameter | Specify the value. |
Save your changes | Return |
|
You can define VLANs for the entire network from a single switch. The VLAN configuration is propagated to all switches in the same administrative domain using the VTP advertisement protocol. To define VLANs, select VTP VLAN Configuration on the VLAN and VTP Configuration panel. The VTP VLAN Configuration panel (Figure 6-7) is displayed. The panel lists the VLANs with respect to their parent-child relationships. Each TrBRF is followed by an indented list of the TrCRFs for which it is a parent. You can also sort the entries on the panel by VLAN ID. This is particularly useful when you are searching for a particular VLAN or when you want to add a VLAN and need to see the IDs that have already been assigned.

The following information is displayed on this panel:
| To | Select | Then |
|---|---|---|
View the current configuration of a VLAN, including a list of associated ports for a TrCRF... | View | Specify the VLAN ID. |
Add a new TrBRF VLAN configuration... | Add | Specify the VLAN ID. Select TrBRF. Refer to the "Adding or Changing TrBRF VLAN Parameters" section. |
Add a new TrCRF VLAN configuration... | Add | Specify the VLAN ID. Select TrCRF. Refer to the "Adding or Changing TrCRF VLAN Parameters" section. |
Change an existing TrBRF VLAN configuration... | Change | Specify the VLAN ID and refer to the "Adding or Changing TrBRF VLAN Parameters" section. |
Change an existing TrCRF VLAN configuration... | Change | Specify the VLAN ID and refer to the "Adding or Changing TrCRF VLAN Parameters" section. |
Add or remove a TrBRF or TrCRF from the list of preferred VLANS... | Change_Local_State | Specify the VLAN ID and confirm your request to add or remove the VLAN from the preferred list. Then, press any key to refresh the panel. |
Delete a VLAN... | Delete | Specify the VLAN ID. |
Display a list of VLANs sorted by VLAN ID... | Sort | Select Sort_by_VLAN_ID. |
Save your changes... | Return |
|
To add a new TrBRF, select Add on the VTP VLAN Configuration panel, enter the VLAN ID (2 through 1001) and select TrBRF. To change the definition of an existing TrBRF, select Change on the VTP VLAN Configuration panel and specify the VLAN ID. In either case, the VLAN Parameter Configuration for TrBRF panel (Figure 6-8) is displayed.
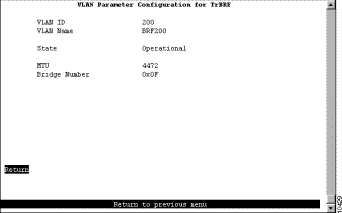
The following information is displayed on this panel:
 | Caution The Catalyst 3900 ATM module does not support MTUs greater than 4472. Therefore, configuring an MTU size larger than 4472 for a TrBRF that contains an ATM port will result in the ATM port being removed from the TrBRF. Additionally, if a TrBRF is configured for an MTU size larger than 4472, none of the TrCRFs assigned to the TrBRF can be assigned to an ATM port. |
| To | Select | Then |
|---|---|---|
Change the current settings | The appropriate parameter | Specify the value. |
Save your changes | Return |
|
To add a new TrCRF, select Add on the VTP VLAN Configuration panel, enter the VLAN ID (2 through 1001) and select TrCRF. To change the definition of an existing TrCRF, select Change on the VTP VLAN Configuration panel and specify the VLAN ID. In either case, the VLAN Parameter Configuration for TrCRF panel (Figure 6-9) is displayed.
As described in the "Token Ring VLANs and ISL" section of the "Understanding Token Ring Switching" appendix, you can configure a TrCRF as a backup path in the event that the ISL link fails. When configuring a backup TrCRF, keep the following in mind:
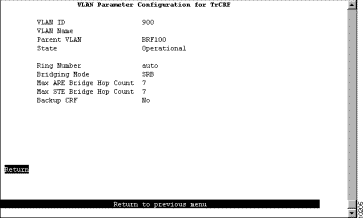
The following information is displayed on this panel:
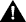 | Caution If the ports of the TrCRF VLAN are connected to a ring that contains only workstations, the port will be unable to learn the ring number. In this case, you must configure the ring number. |
| To | Select | Then |
|---|---|---|
Change the current settings | The appropriate parameter | Specify the value. |
Save your changes | Return |
|
To change the definition of the default Ethernet VLAN, select Change on the VTP VLAN Configuration panel and specify the VLAN ID. The VLAN Parameter Configuration for Ethernet panel (Figure 6-10) is displayed. You can change the values of the security association identifier, MTU, and the translationally bridged VLANs only.
The following information is displayed on this panel:
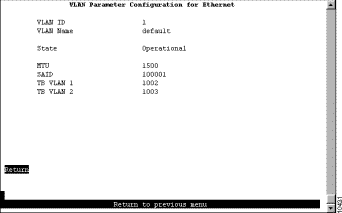
To view the definition of an existing FDDI or FDDI-Net VLAN, select View on the VTP VLAN Configuration panel and specify the VLAN ID. The VLAN Parameter Configuration for FDDI (or the VLAN Parameter Configuration for FDDI-net) panel (Figure 6-11) is displayed.
The following information is displayed on this panel:
If the VLAN type is FDDI, the following additional information is displayed for FDDI VLANs:
If the VLAN type is FDDI-Net, the following additional information is displayed for FDDI-Net VLANs:
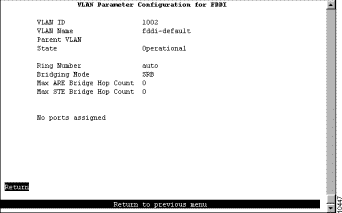
To display a list of the TrCRFs and TrBRFs to which ports are assigned, select Local VLAN Port Configuration on the VLAN and VTP Configuration panel. The Local VLAN Port Configuration panel (Figure 6-12) is displayed.
By default, all local TrCRFs and TrBRFs that are defined on a switch when the switch is started (or restarted) are enabled for the ISL port. However, you can disable a TrCRF or TrBRF for the ISL port.
This panel displays the following information about the VLAN port assignments:
| To | Select | Then |
|---|---|---|
Change the TrCRF to which the port is assigned... | Change | Select the VLAN from the displayed list of TrCRFs. |
Change the TrCRFs or TrBRFs enabled for an ISL port... | Change | Specify the ISL port to change, select the TrBRF from the list of TrBRFs and enable or disable the TrCRF as desired. |
Save your changes... | Return |
|
When changing VLAN assignments for an ISL module, keep the following in mind:
You can set the pruning eligibility for a VLAN regardless of whether VTP pruning has been enabled for the administrative domain. However, traffic from the VLAN will not be pruned until VTP pruning has been enabled for the administrative domain.
VLANs that are not configured to be eligible for pruning are always considered to be in a joining state on every trunk. VLAN 1, the default TrBRF (1005), and TrCRFs are not eligible for pruning.
For information about enabling VTP pruning on the administrative domains, refer to the "Configuring VTP Parameters" section.
The VTP Pruning Configuration panel displays all TrBRFs, excluding the default TrBRF (1005), that are currently configured.
When changing the VTP pruning configuration for a TrBRF, keep the following in mind:
To view or change IP information associated with a TrBRF, such as the IP address, subnet mask, or IP state, or to send PINGs, select IP Configuration on the Configuration Menu. The IP information that you can configure is associated with a TrBRF. Therefore, if the ports of the Catalyst 3900 are assigned to more than one TrBRF, when you select IP configuration you will be presented with a list of possible TrBRFs from which to choose. The IP Configuration panel (Figure 6-14) is displayed.
The following information is displayed on this panel:
When you select either of the BootP options for the IP state, the Catalyst 3900 repeats BootP requests at regular intervals, beginning at 1 second intervals and eventually decreasing to 5 minute intervals until it has received a valid response.
The following BootP response parameters are recognized and recorded in NVRAM:
The BootP requests will also cease if a valid IP address is configured via the console panels or if the IP state is set to IP Disabled. Once the Catalyst 3900 stops sending BootP requests on a domain, it does not resume sending requests or recognize BootP responses on that domain unless the Catalyst 3900 is reset.
For more information about BootP, refer to the "Understanding BootP" appendix.
| To | Select | Then |
|---|---|---|
Change the current settings... | The appropriate parameter... | Specify the value. |
Verify the network availability of a particular resource... | Specify the IP address of the resource. | |
Save your changes... | Return |
|
To allow the Catalyst 3900 to be managed by an SNMP manager, you must first configure the SNMP parameters. To view or set SNMP parameters, such as the community names, where traps are to be sent, whether authentication failure traps should be sent, and whether the collection of soft error statistics is enabled or disabled, select SNMP Configuration on the Configuration Menu. The SNMP Configuration panel (Figure 6-15) is displayed.
The following information is displayed on this panel:
| To | Select | Then |
|---|---|---|
Change the current settings | The appropriate parameter | Specify the value. |
View or change SNMP community names and privileges | Community Strings | Refer to the "Specifying Community Names" section. |
View or change which SNMP managers are to receive traps for which domains | Trap Receivers | Refer to the "Specifying Trap Receivers" section. |
View or change the soft error monitoring configuration for the ports on the switch... | Soft Error Monitoring | Refer to the "Configuring Soft Error Monitoring" section. |
Save your changes | Return |
|
A community name is a password that a set of SNMP managers use to manage a specified device. Each community name is associated with a specific privilege level of management. To view or change the community names for the domains of the Catalyst 3900, select Community Strings on the SNMP Configuration panel. The Community Strings panel (Figure 6-16) is displayed.
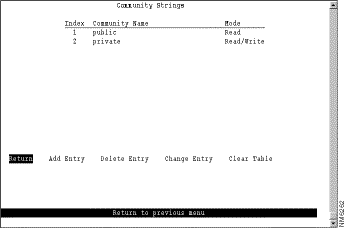
The following information is displayed on this panel:
Entries are displayed in the order in which they are entered. Only five community names can be entered.
| To | Select | Then |
|---|---|---|
Add a community name | Add Entry | Specify the community name and privilege. |
Delete a community name | Delete Entry | Specify the name to be deleted. |
Change a community name or privilege | Change Entry | Specify the index number of the entry to be changed and enter the new information. |
Delete all community names | Clear Table |
|
Save your changes | Return |
|
To view or change the list of SNMP managers to which traps are sent, select Trap Receivers on the SNMP Configuration panel. The Trap Receivers panel (Figure 6-17) is displayed.
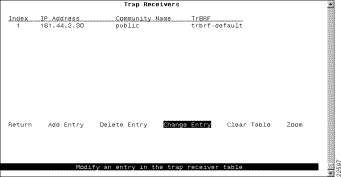
The following information is displayed on this panel:
The trap receivers list can contain a maximum of 10 entries.
The SNMP Trap Receivers information that you can configure is associated with a TrBRF. Therefore, if the ports of the Catalyst 3900 are assigned to more than one TrBRF and you select Add Entry or Change Entry on the Trap Receivers panel, after specifying the community name, you will be presented with a list of possible TrBRFs from which to choose.
| To | Select | Then |
|---|---|---|
Add an entry to the list | Add Entry | Specify the IP address, community name, and TrBRF. |
Delete an entry | Delete Entry | Specify the index number of the entry to be deleted. |
Change an entry in the list | Change Entry | Specify the index number of the entry to be changed and enter the new information. |
Delete all entries | Clear Table |
|
Display the complete list of TrBRFs assigned to an IP address | Zoom | Specify the index number. |
Save your changes | Return |
|
To view or change the soft error monitoring configuration for a port, select Soft Error Monitoring on the SNMP Configuration panel. The Soft Error Monitoring panel is displayed (Figure 6-18).
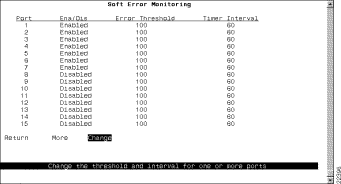
The following information is displayed on this panel.
| To | Select | Then |
|---|---|---|
Change the soft error monitoring configuration for a port or ports in the list | Change | Specify the port or port list to be changed and enter the new information as prompted. Enter the port, range of ports, or both and separate by spaces or commas. When entering a range of ports, enter the lowest port first and separate with a hyphen (for example, 8-16). To enter all ports on a switch, type an asterisk (*). |
Save your changes | Return |
|
For more information about spanning tree, refer to the "Spanning-Tree Protocol" section of the "Understanding Token Ring Switching" appendix.
To view or change the spanning-tree parameters associated with a VLAN, such as the switch priority and the port path cost, select Spanning Tree on the Configuration Menu and then select the desired TrBRF. The Spanning Tree for TrBRF panel (Figure 6-19) is displayed.
When you configure spanning-tree parameters for a TrBRF, you:
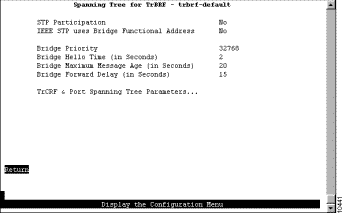
The following information is displayed on this panel:
| To | Select | Then |
|---|---|---|
Change the current settings | The appropriate parameter | Specify the value. |
View or change the spanning-tree parameters for one of the TrCRFs associated with this TrBRF | TrCRF & Port Spanning Tree Parameters | Refer to the "Changing Spanning-Tree Parameters for a TrCRF" section. |
Save your changes | Return |
|
To view or change the spanning-tree parameters for a TrCRF associated with the selected TrBRF, select TrCRF & Port Spanning Tree Parameters on the Spanning Tree panel and then select the desired TrCRF. The Spanning Tree for TrCRF panel (Figure 6-20) is displayed.
When you configure the spanning-tree parameters for a TrCRF, you:
The STP that is run on the ISL link depends on the type of TrCRF:
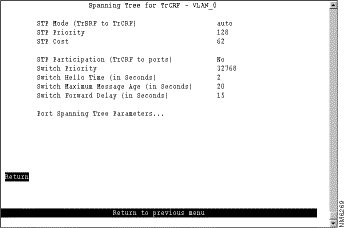
The following information is displayed on this panel:
| To | Select | Then |
|---|---|---|
Change the current settings | The appropriate parameter | Specify the value. |
View or change the spanning-tree parameters for the ports that belong to this TrCRF... | Port Spanning Tree Parameters | Refer to the "Changing Spanning-Tree Parameters for a Port" section. |
Save your changes | Return |
|
To view or change the priority, path cost, and spanning-tree mode of a port, select Port Spanning Tree Parameters on the Spanning Tree panel. The Port Spanning Tree Parameters panel (Figure 6-21) is displayed.
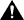 | Caution Use caution when modifying port STP values in networks in which parallel ISL-ATM or ISL-Token Ring configurations exist. Changing the port STP values from the defaults in these environments can cause the ISL port to become blocked. A blocked ISL port in an ISL-ATM parallel configuration prevents VLAN trunking information from being propagated across the network. If an ATM or Token Ring port becomes the forwarding path to the root switch instead of the ISL link, the switch on the other end might incorrectly limit AREs to the incoming TrCRF. Therefore, when modifying STP values, always ensure that the STP port path costs are configured such that the ISL port is the preferred path. In an ISL parallel configuration, a Token Ring or ATM link should never have a lower cost to the root bridge than the ISL link. |
The following information is displayed on this panel:
| To | Select | Then |
|---|---|---|
Change a parameter associated with a port | Change | Specify the port number, select the appropriate parameter, and then specify the new value. |
Save your changes | Return |
|
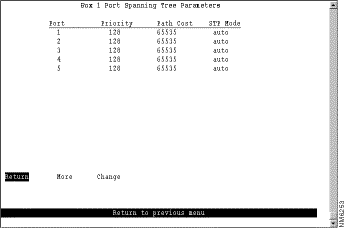
To view or change the configuration parameters of a port such as the mode, type, and speed, select Port Configuration on the Configuration Menu and specify the port number. The Token Ring Port Configuration panel (Figure 6-22) is displayed. If you specify the port number of an ATM module, the ATM Port Configuration panel is displayed. Refer to the "Configuring the ATM Port" section for more information. If you specify the port number of an ISL module, the ISL Port Configuration panel is displayed. Refer to the "Configuring the ISL Port" section" for more information.
The following information is displayed on this panel:
| To | Select | Then |
|---|---|---|
Change the current settings... | The appropriate parameter... | Specify the new value. |
Save your changes | Return |
|
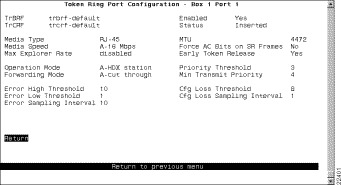
To configure your ATM expansion module, select Port Configuration from the Configuration Menu panel. You are prompted to specify the port you want to configure. When you specify a port on an ATM module, the ATM Port Configuration panel (Figure 6-23) is displayed. The possible port numbers for the ATM module are 21 (if the module is installed in slot 1) and 25 (if the module is installed in slot 2).
The following information is displayed on this panel:
The following options are displayed on this panel:
When you change a parameter on a panel and select Return, the change is saved in NVRAM. The change will not be implemented, however, until you restart the Catalyst 3900 or select Apply Changes.
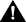 | Caution Selecting Apply Changes will cause all ELANs to close and could, therefore, disrupt the network. |
To configure ATM physical-layer network parameters, select ATM Network Setup from the ATM Configuration panel. The ATM Network Setup panel (Figure 6-24) is displayed.
The following information is displayed on this panel:
| To | Select | Then |
|---|---|---|
Change the current settings... | The appropriate parameter... | Specify the value. |
Configure advanced ATM parameters... | Advanced Parameters | Refer to the "Configuring Advanced ATM Parameters" section. |
Save your changes... | Return |
|
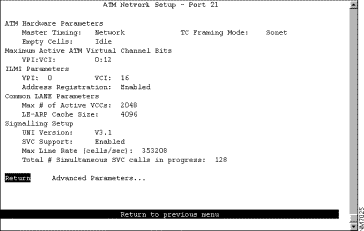
To configure advanced ATM parameters, select Advanced Parameters on the ATM Network Setup panel. The Advanced Parameters panel (Figure 6-25) is displayed. We recommend only experienced users configure the parameters listed on this panel. Changing these parameters may impact your network, therefore, use caution when altering the values for these parameters.
The following information is displayed on this panel:
| To | Select | Then |
|---|---|---|
Change the current settings... | The appropriate parameter... | Specify the value. |
Save your changes... | Return |
|
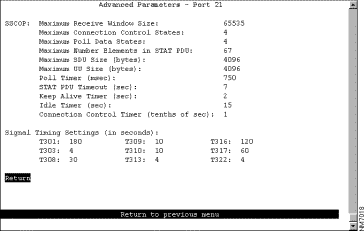
To configure LEC parameters, select ATM LEC Setup from the Configuration panel. Select the TrCRF to which the module is assigned. The ATM LEC Setup panel (Figure 6-26) is displayed.
The following information is displayed on this panel:
| To | Select | Then |
|---|---|---|
Change the current settings... | The appropriate parameter... | Specify the value. |
Save your changes... | Return |
|
Map traffic profiles for this ELAN... | Traffic Profile Mapping | Refer to the "Configuring Traffic Profile Mapping" section. |
Configure LAN emulation parameters for this ELAN... | LANE Parameters | Refer to the "Configuring LANE Parameters" section. |
To define the list of traffic profiles to be used for mapping outgoing traffic, select Traffic Profile Mapping on the ATM LEC Setup panel and specify the map number (0 through 9). The Traffic Profile Mapping panel (Figure 6-27) is displayed.

The following information is displayed on this panel:
| To | Select | Then |
|---|---|---|
Change the current settings... | The appropriate parameter... | Specify the value. |
Save your changes... | Return |
|
To configure LANE parameters for this LEC, select LANE Parameters on the ATM LEC Setup panel. The LANE Parameters panel (Figure 6-28) is displayed.
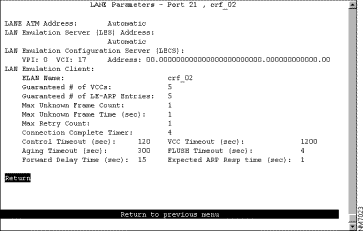
The following information is displayed on this panel:
| To | Select | Then |
|---|---|---|
Change the current settings... | The appropriate parameter... | Specify the value. |
Save your changes... | Return |
|
To configure the traffic profile table, select Traffic Profiles Table on the ATM Configuration panel. The Traffic Profiles Table panel (Figure 6-29) is displayed.
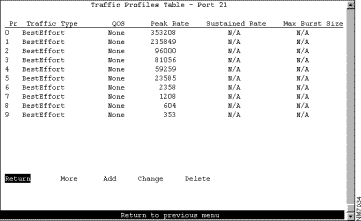
The following information is displayed on this panel:
| To | Select | Then |
|---|---|---|
Add an entry | Add | Specify the profile identifier, traffic type, QOS, peak rate, sustained rate, and maximum burst size. |
Change the current settings... | Change | Specify the profile identifier, traffic type, QOS, peak rate, sustained rate, and maximum burst size. |
Remove an entry | Delete | Specify the profile identifier. |
Save your changes... | Return |
|
To configure port parameters your ISL expansion module, select Port Configuration from the Configuration Menu panel. You are prompted to specify the port you want to configure. When you specify a port on an ISL module, the ISL Port Configuration panel (Figure 6-30) is displayed. The possible port values for the 2-port ISL expansion module are 21 and 23 (if the module is inserted in slot 1) and 25 and 27 (if the module is inserted in slot 2).
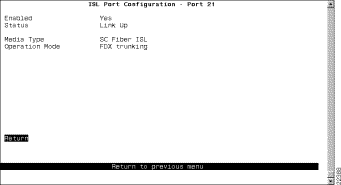
The following information is displayed on this panel:
Each device configured for CDP sends periodic messages to a multicast address. Each device advertises at least one address at which it can receive SNMP messages. The advertisements also contain time-to-live, or holdtime, information, which indicates the length of time a receiving device should hold CDP information before discarding it.
To configure CDP parameters, select CDP Configuration on the Configuration Menu. The CDP Configuration panel (Figure 6-31) is displayed.
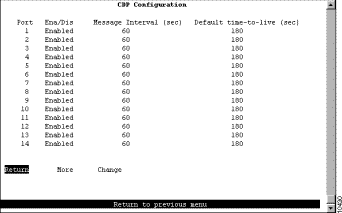
The following information is displayed on this panel:
| To | Select | Then |
|---|---|---|
Change a parameter associated with a port | Change | Specify the port number, select the appropriate parameter, and then specify the new value. |
Save your changes | Return |
|
An active port monitor allows you to use a customer-supplied trace tool, such as a Network General Sniffer, to monitor only the LLC traffic that is switched by the monitored port. The MAC frames are not monitored.
Configuring a port to be a SPAN port removes the port from the TrCRF to which it is currently assigned. If you then disable the SPAN port, or configure a new port to be the SPAN port, the port remains unassigned to a TrCRF until you reassign it to a TrCRF.
To insert into a ring, ports must be assigned to a TrCRF (unless they are configured as a SPAN port). Therefore, ports that are not configured as SPAN ports and are unassigned will not be able to insert into the ring until you reassign them to a TrCRF or configure them as a SPAN port. For information about how to assign a port to a TrCRF, refer to the "Displaying VLAN Port Assignments" section.
To configure a SPAN port, select Switched Port Analyzer on the Configuration Menu. The Switched Port Analyzer panel (Figure 6-32) is displayed.
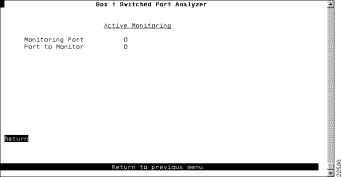
The following information is displayed on this panel:
| To | Select | Then |
|---|---|---|
Change the current settings | The appropriate parameter | Specify the value. |
Disable the SPAN port | Port to Monitor | Specify 0. |
Save your changes | Return |
|
To view or change the Channel definitions, select Channel Configuration on the Configuration Menu. The Channel Configuration panel (Figure 6-33) is displayed.
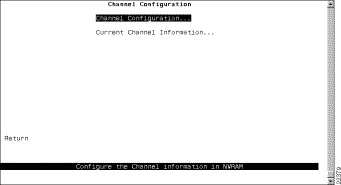
The following options are displayed on this panel:
To configure one or more TokenChannels or ISL Channels, select Channel Configuration on the Channel Configuration panel. The Channel Configuration panel (Figure 6-34) is displayed.
The benefits of using channels are the following:
 | Caution While you can use TokenChannels to interconnect Catalyst 3900s and Catalyst 3920s, you cannot use TokenChannels to interconnect different models of switches. For example, you cannot use a TokenChannel to interconnect a Catalyst 2600 and a Catalyst 3900. Likewise, you cannot use a TokenChannel to interconnect a Catalyst 3900 and a non-Cisco switch. |
TokenChannels and ISL Channels are fault-tolerant. This feature enables channels to continue to function as long as there is at least one link active in the channel. This capability ensures that large portions of a network are not disrupted in the event a port or cable fails within the channel by transferring the traffic to one or more of the remaining ports in the channel. A channel displays in a a reduced state when some, but not all of the ports assigned to the channel are up.
Before you configure a TokenChannel or an ISL Channel, be aware of the following:
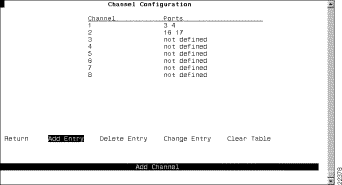
The following information is displayed on this panel:
| To | Select | Then |
|---|---|---|
Define a new channel | Add Entry | Specify the ports that compose the new channel, separated by spaces. You cannot specify more than 8 ports. |
Delete the definition for a channel | Delete Entry | Specify the identifier of the channel you want to delete. |
Change the definition of a channel | Change Entry | Specify the identifier of the channel definition you want to change and enter the new information. Disable or disconnect the ports associated with a channel before changing the channel definition. |
Delete all channel definitions | Clear Table | Confirm the deletion of all channel definitions. |
Save your changes | Return |
|
To view the configuration of currently defined channels, select Current Channel Information on the Channel Configuration panel. The Current Channel Information panel (Figure 6-35) is displayed.
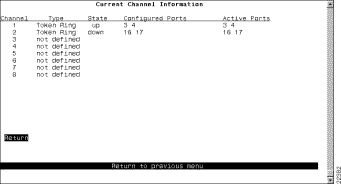
The following information is displayed on this panel:
To limit access, you can do the following:
To limit the scope and access of users on segments attached to the Catalyst 3900, select Filters & Port Security from the Configuration Menu. The Filters & Port Security panel (Figure 6-36) is displayed.
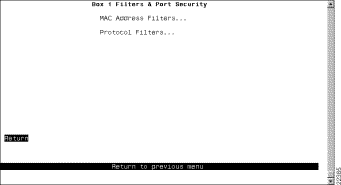
The following options are displayed on this panel:
To restrict certain users from communicating with other users or resources (such as printers or servers), select MAC Address Filters on the Filters & Port Security panel. The MAC Address Filters panel (Figure 6-37) is displayed.
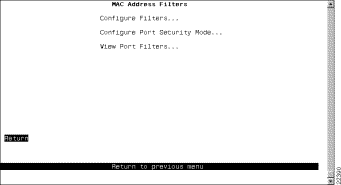
The following options are displayed on this panel:
To configure a new MAC address filter, select Configure Filters on the MAC Address Filters panel. The Configure Filters panel (Figure 6-38) is displayed.
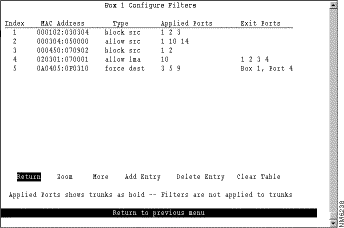
The following information is displayed on this panel:
You can define up to 250 source or destination MAC addresses to be filtered at the port of entry into the Catalyst 3900. MAC addresses can be unicast, multicast (group), or broadcast. All 250 addresses can be associated with one port or divided among the available ports.
| To | Select | Then |
|---|---|---|
Display the complete list of Entry Ports and Exit Ports for a filter | Zoom | Specify the index number. |
Add a filter | Add Entry | Specify the filter type, the MAC address, and the ports. The port numbers should be listed from lowest to highest and be separated by spaces. If you do not specify a port number, the filter will be applied to all ports. |
Delete a filter | Delete Entry | Specify the index number of the filter to be deleted. |
Delete all filters | Clear Table | Confirm the deletion of all filters. |
Save your changes | Return |
|
The Catalyst 3900 also allows you to totally block (secure) communication at selected ports, unless explicitly allowed by a MAC filter. Addresses that have been allowed or forced by a configured filter are not blocked. To define the security attributes of each port, select Configure Port Security Mode on the MAC Address Filters panel. The Configure Port Security Mode panel (Figure 6-39) is displayed.
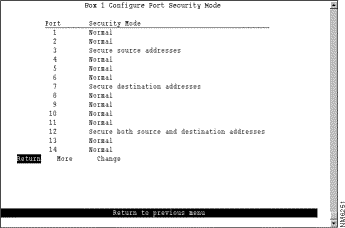
The following information is displayed on this panel:
| To | Select | Then |
|---|---|---|
Change the security mode for a port | Change | Specify the port and the desired security mode. |
Save your changes | Return |
|
To display the defined filters for a specific port, select View Port Filters on the Filters & Port Security panel and specify the port number. The View Port Filters panel (Figure 6-40) is displayed.
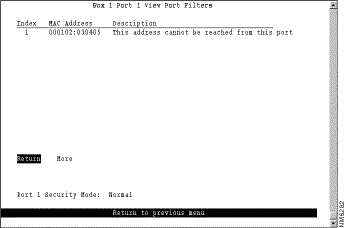
The following information is displayed on this panel:
You cannot change any information on this panel.
To filter data based on protocol, select Protocol Filters on the Filters & Port Security panel. The Protocol Filters panel (Figure 6-41) is displayed.
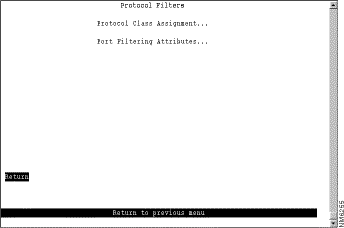
The following options are displayed on this panel:
To use protocol filtering, you must first define the protocol classes. You can define up to 15 protocol classes for use in protocol filtering. To define the protocol classes, select Protocol Class Assignment on the Protocol Filters panel. The Protocol Class Assignment panel (Figure 6-42) is displayed.
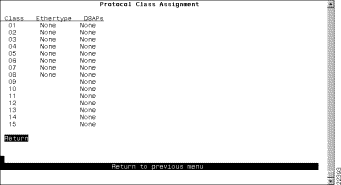
The following information is displayed on this panel:
| To | Select | Then |
|---|---|---|
Change the current settings | The appropriate port... | Specify the value. |
Save your changes | Return |
|
After you have defined your protocol classes, you can define how a port handles frames for each protocol class. To define how each class is handled, select Port Filtering Attributes on the Protocol Filters panel and specify the port number. The Port Filtering Attributes panel (Figure 6-43) is displayed.
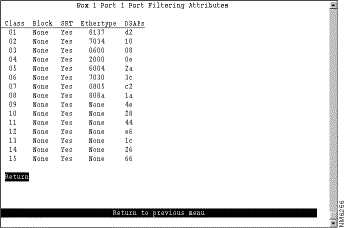
The following information is displayed on this panel:
| To | Select | Then |
|---|---|---|
Change the current settings | The appropriate parameter... | Specify the value. |
Save your changes | Return |
|
To ensure that the address tables (per port and master) are kept to a minimum size, you can configure an aging limit. The aging limit is used to determine when inactive MAC addresses are removed from the address table. To define address table aging limits, select Address Aging from the Configuration Menu. The Address Aging panel (Figure 6-44) is displayed.
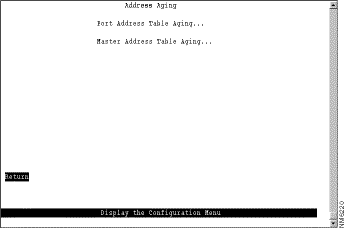
The following options are displayed on this panel:
To define the address aging limits of each port, select Port Address Table Aging on the Address Aging panel. The Port Address Table Aging panel (Figure 6-45) is displayed.
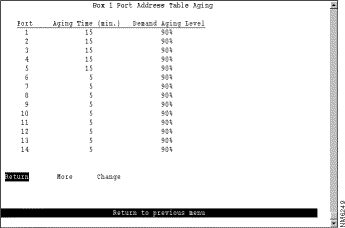
The following information is displayed on this panel:
| To | Select | Then |
|---|---|---|
Change the aging time limit and the address table aging level | Change | Specify the port, the new aging time, and the new aging level. |
Disable address removal for a port based on address age | Change | Specify an Aging Time of 0. |
Disable address removal for a port based on address table capacity | Change | Specify a Demand Aging Level of Disable. |
Save your changes | Return |
|
To define the address aging limits of the master address table, select Master Address Table Aging on the Address Aging panel. The Master Address Table Aging panel (Figure 6-46) is displayed.
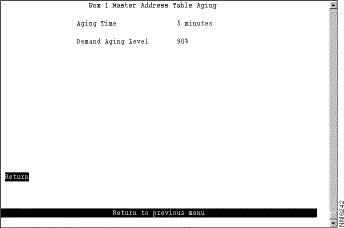
The following information is displayed on this panel:
| To | Select | Then |
|---|---|---|
Change the aging time limit or the address table aging level | The appropriate parameter | Specify the new value. |
Disable address removal based on address age | Aging Time | Specify 0. |
Disable address removal based on address table aging level | Demand Aging Level | Specify Disable. |
Save your changes | Return |
|
The Catalyst 3900 allows you to set a password to protect its configuration. If you establish a password, users must enter it to obtain access to the Main Menu. To set a password, select Password on the Configuration Menu. The Password panel (Figure 6-47) is displayed.
| To | Select | Then |
|---|---|---|
Add a password | Set Password | Press Enter at the Old Password prompt and specify a new password. |
Change the password | Set Password | Specify the current password and the new password. |
Delete the password | Delete Password | Specify the current password. |
Save your changes | Return |
|
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Posted: Tue Oct 12 11:52:51 PDT 1999
Copyright 1989-1999©Cisco Systems Inc.