|
|

This chapter describes the Cisco 6400 Service Connection Manager (SCM) deployment process. Deployment is defined as the process of creating objects in Cisco Element Manager Framework.
Deployment is the feature that informs the Cisco 6400 SCM of the presence of supported network elements.You perform the deployment process after starting the Cisco 6400 SCM for the first time or after installing new hardware or network elements.
The Cisco 6400 SCM objects can be deployed manually or automatically by launching a wizard-style deployment tool that enables you to automatically deploy a network modeled in Cisco EMF. The deployment wizard deploys objects in Cisco EMF in advance of actual deployment on a Cisco 6400 SCM in the field.
The Cisco 6400 SCM:
From the Deployment option, you can also delete a chassis and its defined objects within the relevant chassis. Deployment is the first stage of equipment provisioning. It is also referred to as pre-provisioning—meaning that part of the network hardware setup before the service is actually provisioned. After objects are deployed, the initial state of all objects is normal.
Pre-provisioning is the process of reserving and configuring a space in the system for network equipment that has not yet been physically slotted into the system rack. It refers to a particular state of the device or object. When an object or device is in a pre-provisioned state, the device or object is not present, but the system has been pre-provisioned to hold an object of similar type. Thus the node line cards in the Cisco 6400 SCM can exist in a state known as pre-provisioned and the Cisco 6400 SCM does not monitor their status.
When the cards are placed in the physical equipment, it is possible to change the node line card from the decommissioned state to the commissioned state by clicking the Commission button.
 |
Note Objects try to achieve a Commissioned state after subchassis discovery. After manual deployment the initial state of all objects is Decommissioned, unless you selected the Cisco 6400 SCM Quick Start deployment option. See the "Quick Start Deployment" section on for further details. |
You can create Site, Shelf, Chassis, NSP, NRP, NRP2, and Node Line Card objects manually from the MapViewer application. This is referred to as manual deployment. Manual deployment only creates the chassis but does not commission it. You must perform a commission (put deployed objects into service) on the deployed chassis after manual deployment.
Producing a manageable Cisco 6400 UAC in Cisco EMF is a three-stage process (Figure 4-1).
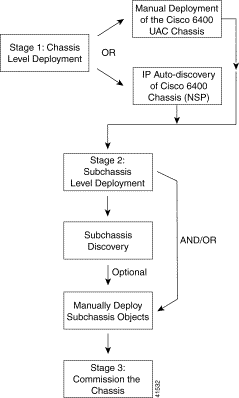
The Cisco 6400 SCM software uses a Deployment Wizard to help simplify the process of manually deploying (or creating) new objects representing the network elements to be managed. The Deployment Wizard appears as a series of windows. Each Wizard window prompts you for the information that is required by the deployment process to deploy your new object.
Table 4-1 lists the various objects that can be deployed and the objects they can be deployed from. For example, you could deploy a chassis and associated NSP from a Site object.
| Object Type to be Deployed | Launch Point to Deploy Objects From | Menu Options to Select to Launch Deployment Wizard | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cisco 6400 Views | Region,Site, Bay | Chassis | NSP | NRP | Node Line Card (NLC) | ||
Generic Objects | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Deployment, Deploy Generic Objects... |
Chassis and NSP | No | Yes | No | No | No | No | Deployment, Cisco 6400 UAC, Deploy Chassis and NSP |
NRP and NRP2 and associated Ports | No | No | No | Yes | No | No | Deployment, Cisco 6400 UAC, Deploy NRP(s) and associated Port(s) |
NLC and associated Ports | No | No | No | Yes | No | No | Deployment, Cisco 6400 UAC, Deploy Line Card(s) and associated Port(s) |
Generic objects are non-technology-specific objects. The Cisco 6400 SCM allows the following generic objects to be deployed: Bay, IP Device, Network, Region, SNMP Agent, SNMP MIB-2 Agent, SNMP Proxied Device, and Site.
When deploying a generic object, the information you are prompted to provide differs according to the type and number of generic objects you are deploying.
This section explains the deployment of a Site object as an example. The deployment process differs slightly for other types of generic objects.
To deploy a Generic object, follow these steps:
Step 2 Click and hold down the right mouse button.
Step 3 Choose the Deployment > Deploy Generic Objects... option.
The Deployment Wizard—Templates window appears (Figure 4-2) displaying a list of available generic object deployment profiles. Deployment profiles are templates that prompt you for the appropriate information required to deploy the selected object successfully.
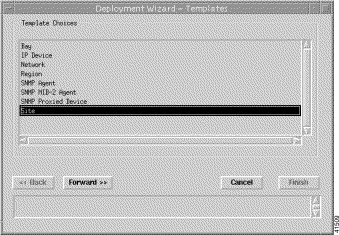
Step 4 Chose the generic object that you want to deploy from the list supplied. The example in Figure 4-2 shows a Site object deployment profile selected. The Deployment Wizard now steps through a series of windows that prompt you for the information required to deploy a Site object.
Step 5 Click Forward. The Deployment Wizard—Object Parameters window appears (Figure 4-3).
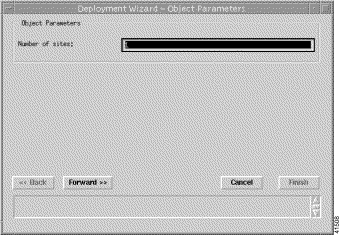
Step 6 Enter the number of sites required.
 |
Note The information that you supply differs according to the type of generic object you are deploying. More than one Deployment Wizard—Object Parameters window can appear depending upon the type of generic object you are deploying. When deploying more than one generic object of the same type, you will have to enter the object parameters for each object. |
Step 7 Click Forward. The next window of the Deployment Wizard appears (Figure 4-4).
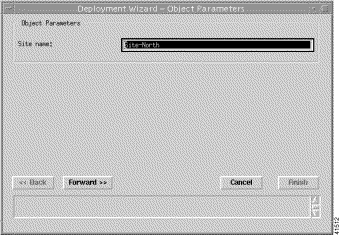
Step 8 Enter a Site name.
Step 9 Click Forward. The Deployment Wizard—Views window appears (Figure 4-5).
 |
Note Proceed to Step 17 when deploying a Network or Region object. |
The Deployment Wizard—Views window allows you to select where your new objects are placed in the Physical and genericObjects views.
Step 10 Click Select (in the Select Relationships frame) to select a Physical relationship. This step only applies when the launch point was not a generic object; otherwise the generic object is selected as the parent object, (for example, a region). The Object Selector window might appear (Figure 4-6) with the Physical view displayed.
Step 11 Select a location in the Physical view to place the generic object (when required).
Step 12 Click Apply. The Deployment Wizard—Views window appears with your selection displayed. The Cisco 6400 SCM automatically adds the same selection into the genericObjects box. Proceed to Step 14 when the selections are the same.
Step 13 Click Select (in the Select Relationships frame) to select a genericObjects relationship, when required. The Object Selector window appears with the genericObjects view displayed.
Step 14 Select a location in the genericObjects view to place the generic object.
Step 15 Click Apply. The Deployment Wizard—Views window appears (see Figure 4-5).
Step 16 Click Forward.
 |
Note Repeat Steps 8 to 16 if you entered more than one Site in Step 6. |
The Summary details appear in the Deployment—Wizard Summary window (Figure 4-7).
Step 17 Click Finish (when the Deployment Summary information is correct) to complete deployment and close the Deployment Wizard—Summary window. The new objects are created and displayed in the Map Viewer window.
 |
Note This deployment procedure can be applied to the deployment of any of the generic objects, although all of the steps might not apply to the particular generic object that you are deploying. |
 |
Note A Cisco 6400 chassis and node switch processor (NSP) card must be deployed under a Shelf object. A shelf object is automatically deployed when you deploy a chassis and NSP objects. |
Two NSPs can be deployed in either or both of two dedicated slots (0A and 0B) in the center of the Cisco 6400 chassis. One NSP is required for system operation, the second NSP provides fault tolerance.
 |
Note You can deploy the Cisco 6400 SCM objects manually or automatically by launching a wizard-style deployment tool that enables you to automatically deploy a network modeled in Cisco EMF. The deployment wizard also enables you to (optionally) deploy objects in Cisco EMF in advance of actual deployment of a Cisco 6400 UAC in the field. For information about Quick Start Deployment, see "Quick Start Deployment." |
To deploy a Cisco 6400 shelf, chassis, and NSP, follow these steps:
 |
Note You can now deploy a number of Cisco 6400 chassis into a unique site or bay. However, you must have one shelf object deployed for each chassis. A shelf object is automatically deployed when you deploy a chassis object. |
Step 2 Right-click Deployment > Cisco 6400 UAC > Deploy Cisco 6400 UAC option. The Deployment Wizard—Object Parameters window (1 of 3) appears (Figure 4-8).
Step 3 Enter a Shelf name. A Shelf is an object that acts as a container for a chassis object. Each Site object must have a unique name for deployment to be successful.
Click Forward. The Deployment Wizard—Object Parameters window (2 of 3) appears (Figure 4-9).
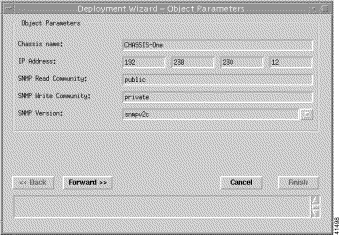
Step 4 Enter the Chassis name, IP Address (for the primary NSP), SNMP Read Community, and SNMP Write Community, and then select the value for an SNMP Version.
Step 5 Click Forward. The Deployment Wizard—Object Parameters window (3 of 3) appears (Figure 4-10).
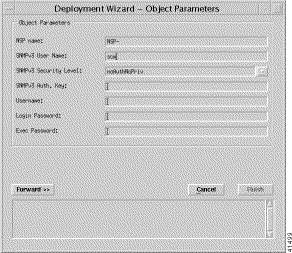
Step 6 Enter the NSP name, SNMPv3 User Name, SNMPv3 Security Level, SNMPv3 Auth. Key, Username, Login Password, and Exec. Password.
Step 7 Click Forward. The Deployment Summary details appear in the Deployment Summary window (Figure 4-11).
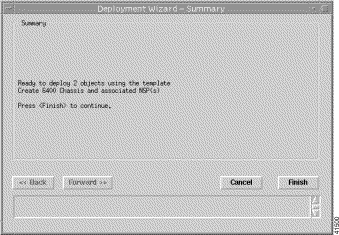
Step 8 Click Finish (when the Deployment Summary information is correct) to complete the deployment and close the Deployment Summary window. This creates the relevant objects in the Cisco EMF.
The Cisco 6400 SCM software provides a Deployment Wizard to assist you in manually deploying subchassis objects.
The Deployment Wizard is the graphical interface used to create new objects representing the network elements to be managed. The Deployment Wizard prompts you to enter the information that is required by the deployment process.
Node route processor cards (NRP and NRP2) can be installed in any one or all of the eight chassis slots numbered 1 to 8. Figure 4-12 shows four NRPs installed in chassis slots 1, 2, 5, and 6.
To deploy an NRP and port, follow these steps:
Step 2 Right-click Deployment > Cisco 6400 UAC > Deploy NRPs and Associated Port(s) option. The Deployment Wizard—Templates window appears (Figure 4-12) with a list of defined NRPs and NRP2s.
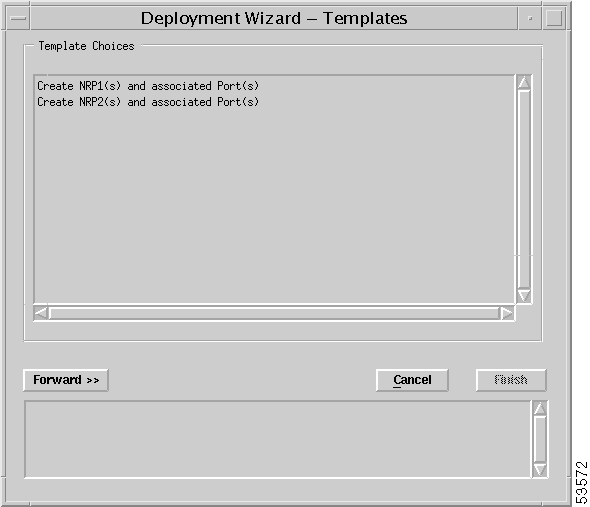
Step 3 Choose NRP1 or NRP2.
Follow these steps to deploy an NRP.
Step 2 Click Forward. The Deployment Wizard—Object Parameters (1 of 3) windows appears (Figure 4-13).
Step 3 Enter the number of NRPs that you want to deploy. The number of NRPs that you can deploy in the selected chassis depends on the number of line cards installed.
Step 4 Click Forward. The Deployment Wizard—Object Parameters (2 of 3) window appears (Figure 4-14).
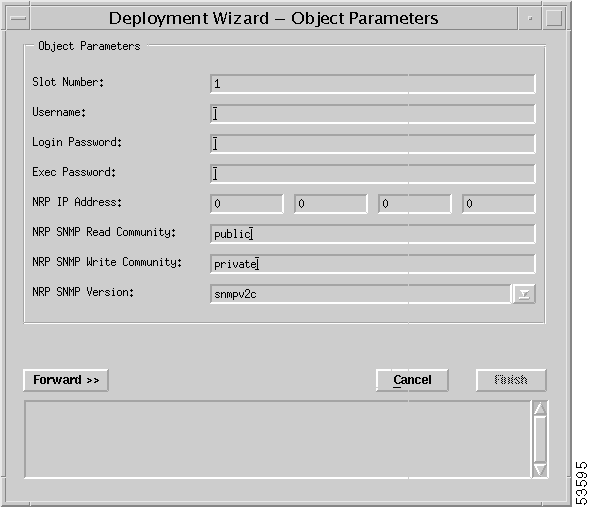
Step 5 Enter values for Slot Number, Username, Login Password, Exec Password, NRP IP Address, NRP SNMP Read Community, and NRP SNMP Write Community, and then choose an NRP SNMP Version.
Where:
Step 6 Click Forward. The Deployment The Deployment Wizard—Object Parameters (3 of 3) window appears (Figure 4-15).
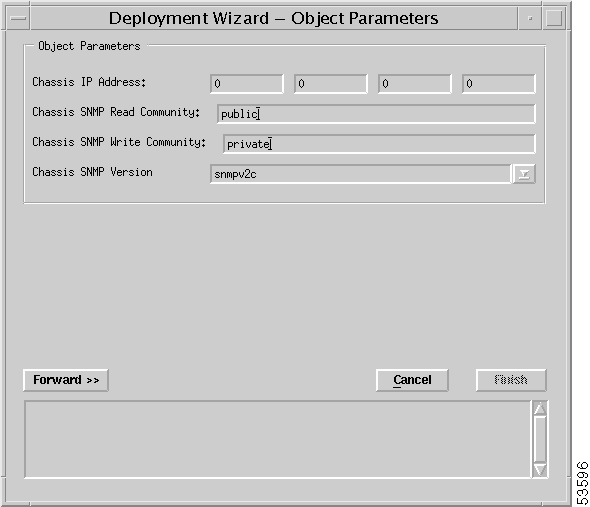
Step 7 Enter values for Chassis IP Address, Chassis SNMP Read Community, Chassis SNMP Write Community, and Chassis SNMP Version.
Where:
 |
Note If there are more NRPs to define, then the second Object Parameters window redisplays when you click Forward. |
Step 8 Click Forward. The Deployment Summary details appear in the Deployment Wizard—Summary window (Figure 4-16).
Step 9 Click Finish (when the Deployment Summary information is correct).
To deploy an NRP2, follow these steps.
Step 2 Click Forward. The Deployment Wizard—Object Parameters (1 of 3) window appears (Figure 4-17).
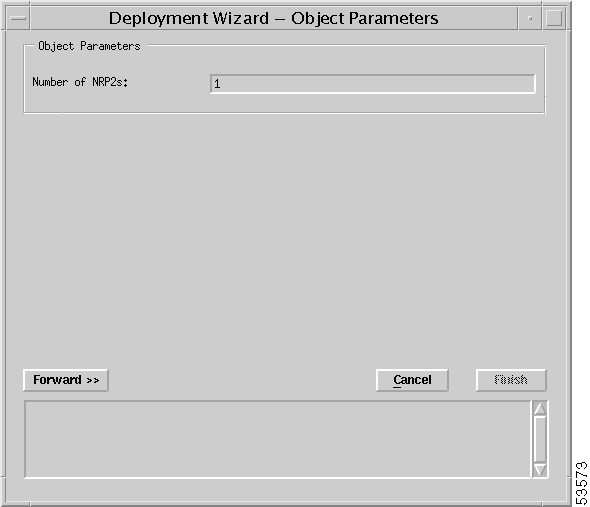
Step 3 Enter the number of NRP2s that you want to deploy. The number of NRP2s that you can deploy in the selected chassis depends on the number of line cards installed.
Step 4 Click Forward. The Deployment Wizard—Object Parameters (2 of 3) window appears (Figure 4-18).
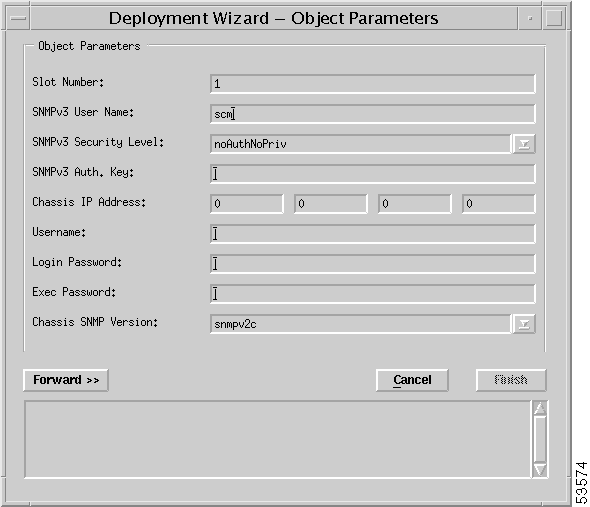
Step 5 Enter values for Slot Number, SNMPv3 User Name, SNMPv3 Security Level, SNMPv3 Auth. Key, Chassis IP Address, Username, Login Password, Exec. Password, and Chassis SNMP Version.
Where:
Step 6 Click Forward. The Deployment Wizard—Object Parameters (3 of 3) window appears (Figure 4-19).
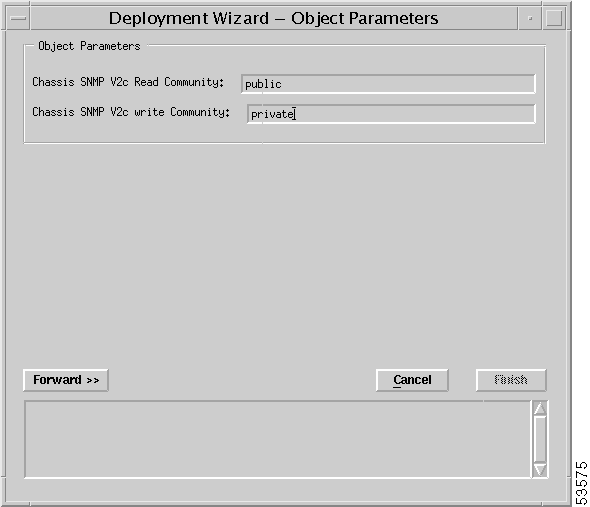
Step 7 Enter values for Chassis SNMP V2c Read Community and Chassis SNMP V2c Write Community. Where:
 |
Note If there are more NRP2s to define, then the second Object Parameters window redisplays when you click Forward. |
Step 8 Click Forward. The Summary details appear in the Deployment Wizard—Summary window (Figure 4-20).
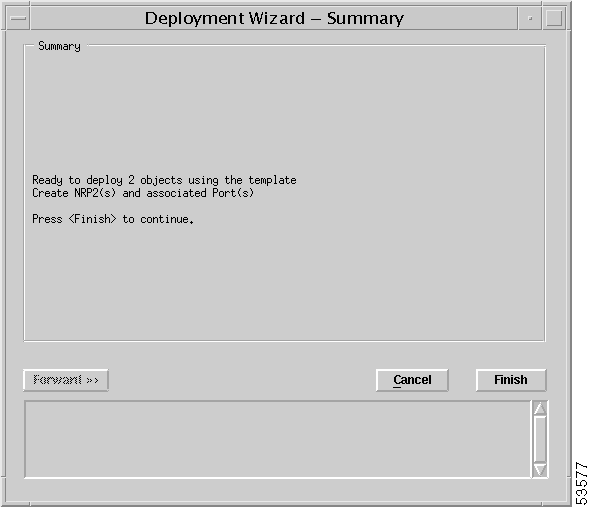
Step 9 Click Finish (when the Deployment Summary information is correct).
Half-height node line cards (NLCs) can be installed in any one or all of the eight slots numbered 1 to 8. One or two OC-3 NLCs can be installed in each slot, for a maximum of 16 per chassis.
To deploy an OC-3 node line card and ports, follow these steps:
Step 2 Right-click Deployment > Cisco 6400 UAC > Deploy OC-3 Line Card(s) and associated Port(s) option. The Deployment Wizard—Object Parameters (1 of 2) window appears (Figure 4-21).
Step 3 Enter the Number of OC-3 node line cards you want to deploy.
Step 4 Click Forward. The Deployment Wizard—Object Parameters (2 of 2) window (Figure 4-22) appears.
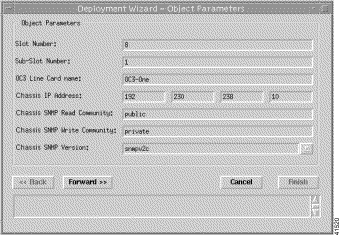
Step 5 Enter values for Slot Number, Sub-Slot Number, OC-3 Node Line Card name, Chassis IP Address, Chassis SNMP Read Community, and Chassis SNMP Write Community. Choose the Chassis SNMP Version.
 |
Note You must enter an unused Slot and subslot number or deployment will fail. |
Step 6 Click Forward.
Step 7 Repeat Steps 5 and 6 for the number of OC-3 node line cards entered in Step 3.
The Deployment Summary details appear in the Deployment Summary window (Figure 4-23).
Step 8 Click Finish (when the Deployment Summary information is correct).
The OC-12 node line card occupies a full slot in the chassis and has a single port.
To deploy an OC-12 node line card and port, follow these steps:
Step 2 Right-click Deployment > Cisco 6400 UAC > Deploy OC-12 Line Card(s) and associated Port(s) option. The Deployment Wizard—Object Parameters (1 of 2) window appears (Figure 4-24).
Step 3 Enter the Number of OC-12 node line cards you want to deploy.
Step 4 Click Forward. The Deployment Wizard—Object Parameters (2 of 2) window appears (Figure 4-25).
Step 5 Enter values for the Slot Number, OC-12 Node Line Card name, Chassis IP Address, Chassis SNMP Read Community, and Chassis SNMP Write Community. Choose the Chassis SNMP Version.
Step 6 Click Forward.
Step 7 Repeat Steps 5 and 6 for the number of OC-12 node line cards entered in Step 3.
The Deployment Summary details appear in the Deployment Summary window (Figure 4-26).
Step 8 Click Finish (when the Deployment Summary information is correct).
Half-height node line cards (NLCs) can be installed in any one or all of the eight slots numbered 1 to 8. One or two NLCs can be installed in each slot, for a maximum of 16 per chassis.
To deploy DS3 node line cards and ports, follow these steps:
Step 2 Right-click Deployment > Cisco 6400 UAC > Deploy DS3 Line Card(s) and associated Port(s) option. The Deployment Wizard—Object Parameters (1 of 2) window appears (Figure 4-27).
Step 3 Enter the Number of OC-3 node line cards you want to deploy.
Step 4 Click Forward. The Deployment Wizard—Object Parameters (2 of 2) window appears (Figure 4-28).
Step 5 Enter values for Slot Number, Sub-Slot Number, DS3 Node Line Card name, Chassis IP Address, Chassis SNMP Read Community, and Chassis SNMP Write Community. Choose the Chassis SNMP Version.
 |
Note You must enter an unused slot and sub-slot number or deployment will fail. |
Step 6 Click Forward.
Step 7 Repeat Steps 5 and 6 for the Number of DS3 node line cards entered in Step 3. The Deployment Summary details appear in the Deployment Summary window (Figure 4-29).
Step 8 Click Finish (when the Deployment Summary information is correct).
This section describes how to delete a chassis and objects within the chassis from your network configuration.
To delete a Cisco 6400 chassis from the configuration, you must perform the following functions:
To disconnect subscribers from any Cisco 6400 chassis, follow these steps:
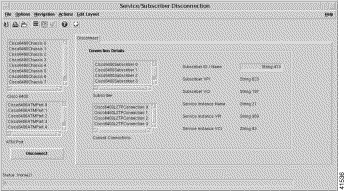
See the "Service/Subscriber Disconnection Window" section for further details on the parameters contained in the Service/Subscriber Disconnection window.
Step 2 Choose the Cisco 6400 chassis and ATM Port from the lists displayed on the left side of the window.
Step 3 Choose a Subscriber and Current Connections from the from the lists displayed in the Connection Details panel.
Step 4 Click Disconnect. A pop up window appears (Figure 4-31) to inform you that the selected subscriber is about to be disconnected.
Step 5 Click Yes to disconnect the subscriber. The Action Report window appears (Figure 4-32) confirming that the subscriber was disconnected.
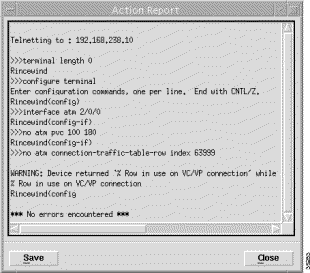
Step 6 Review the Action Report and then click the Close button to close the Action Report window or click the Save button to save the Action Report. The Action Report can be saved and used for diagnostic purposes. The "*** No errors encountered *** " message appears to show that disconnection was successful.
Step 7 Repeat these steps for each subscriber and ATM port listed.
Step 8 For every service you created, you must decommission each service. (That is, the services defined in the Cisco IOS must be removed.)
To decommission services, follow these steps:
Step 2 From the list of services, choose each service and then click the Decommission Service button.
Step 3 After all services have been decommissioned, go to the next procedure and decommission the discovered chassis.
To decommission the chassis, follow these steps:
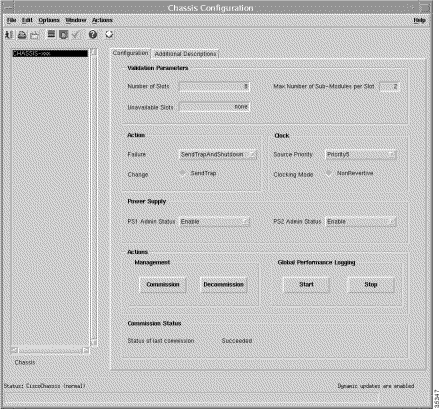
Step 2 Choose an appropriate Chassis from the Chassis selection list displayed at the left side of the Chassis Configuration window (Figure 4-33).
Step 3 Click Decommission. The state of the selected chassis and its objects changes to decommissioned.
Step 4 From the same Chassis Configuration window (Figure 4-33), click the appropriate entry in the chassis name list.
Step 5 Right- click Deployment > Delete Objects... option. The popup Deployment Wizard — Summary window appears prompting you to delete the chassis (Figure 4-34).
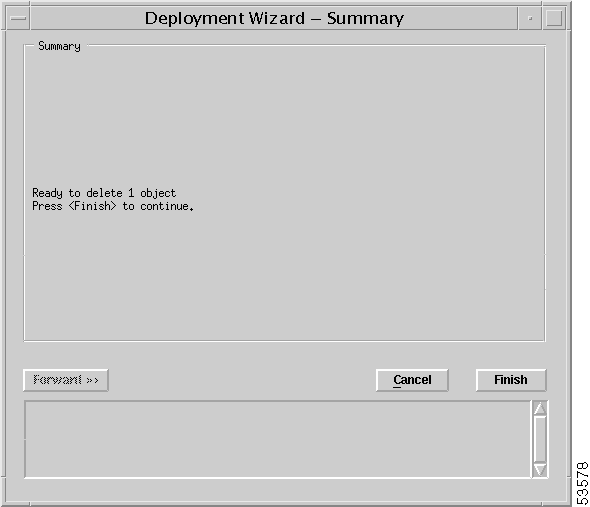
Step 6 Click Finish to delete the relevant chassis and the objects within it. The chassis name is removed from the Chassis Name list. (Click the Cancel button if you do not want to delete the chassis.)
Auto-discovery is used to discover an existing network. You can examine the network for IP and SNMP devices and create an object for each new device discovered.
Auto-discovery is also used to identify new SCM chassis and NSP cards within that chassis.
The Auto-discovery application has three mechanisms for discovering devices:
Auto-discovery can detect devices on more than one subnetwork using multihop discovery. This option is available when using SNMP or IP and SNMP discovery. When Cisco EMF discovers a device that is connected to more than one network, it can run auto-discovery on the next network. This happens when the hop count is greater than zero. It can be scheduled to run at preset times. An option is available to specify the physical location under which discovered objects are created.
 |
Note After Auto-discovery, you should launch IOS/Command Line Security information and then enter SNMP management information. See the "After Auto-Discovery" section on for further information. |
To auto-discover IP and SNMP devices, follow these steps:
Step 2 Choose the object within the Map Viewer window that Auto-discovery will be launched from. Right-click Deployment > Auto Discovery... option. The Discover Network Devices window appears (Figure 4-35).
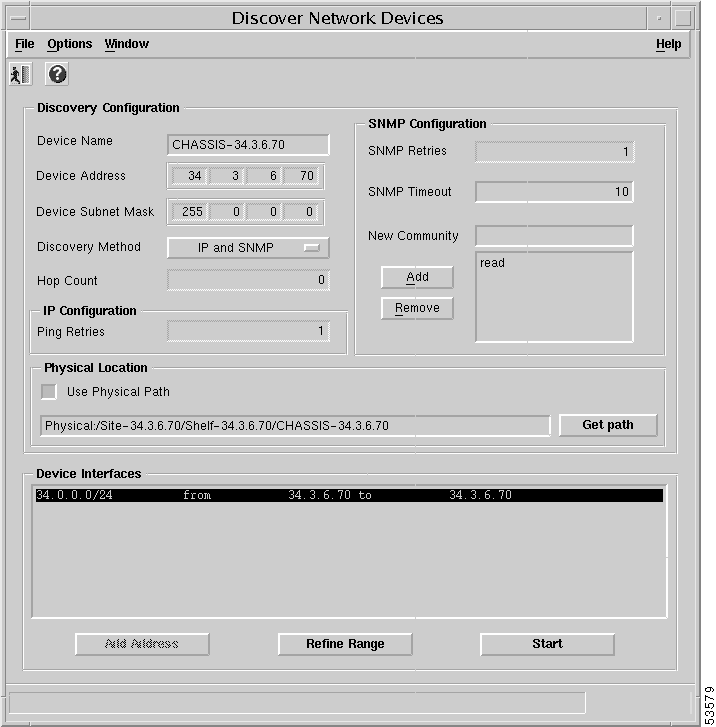
The Discover Network Devices window (Figure 4-35) displays the object name and address in the Discovery Configuration panel.
Step 3 Enter the IP address of the chassis or the beginning address of a range of addresses in the Device Address field. To discover a single Cisco 6400 UAC, use the NSP address as the start address.
Step 4 Enter the appropriate mask value in the Device Subnet Mask field.
Step 5 Click the drop-down list next to Discovery Method and choose IP and SNMP (default value) from the displayed list.
Step 6 In the Hop Count data entry box, type the number of distant networks that you want to discover away from the local subnet that you can discover devices on. The maximum number is 16.
Step 7 In the SNMP Retries data entry box, enter the number retry attempts that the system should try to communicate with a device without receiving an expected reply, before it is discarded as not being an SNMP device. The maximum number is 10.
 |
Note If SNMP Retries is left at zero, only the initial attempt to ping a device is made. If the device does not respond or responds with an error, the device is ignored. |
Step 8 In the New Community data entry box, enter a new SNMP read community name, then click the Add button. The new community name displays along with the existing community names.
 |
Note You can remove any of the displayed community names by choosing a name and then clicking the Remove button. There must be at least one community name. |
Step 9 In the SNMP Timeout data entry box, enter the amount of time that you specify the system to time out before getting a response from a device. The default is 10 seconds.
Step 10 In the Physical Location panel, click the Use Physical Path button. Make sure the correct path is shown. Choose Get path and select the correct Physical View if required.
 |
Note If the object used to launch Auto-discovery already has a physical location, it is shown by default. This path should be selected. Also, the Get Path selection allows you to use the hierarchical browser if you did not choose the Physical Path button. |
Step 11 If you want to restrict or increase the IP address range, click the Refine Range button (Figure 4-35). The Discovery Interface window (Figure 4-36) appears. You can specify a range of IP addresses by entering a start address and an end address. Only IP addresses within the specified address range are discovered.
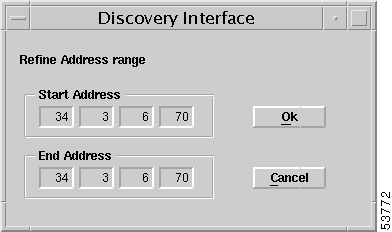
Step 12 In the Ping Retries data entry box, type the number of retry attempts that the system should try to identify if an active machine is connected at a specified address. The maximum number is 10.
 |
Note If IP Retries is left at zero, only the initial attempt to ping a device is made. If the device does not respond or responds with an error, the device is ignored. |
Step 13 To add a second address, type in the new address and then press the Add Address button. This function allows you to add a second address to be discovered.
 |
Note The Hop Count field must have a value of at least one for you to be able to add another address, otherwise the button is not active. To get distant subnets, you must enter a hop count value. |
Step 14 To start the discovery process, choose the device from the Device Interfaces list, then click the Start button. The Discovery Progress window appears similar to Figure 4-37.
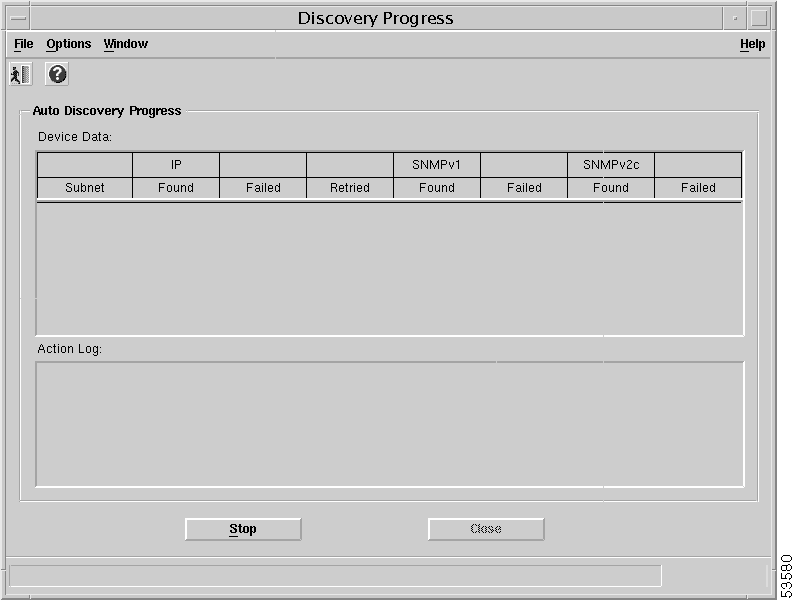
The Discovery Progress window displays the progress of the auto-discovery process in two ways. The Device Data panel displays information on the number of devices found and information on the success of IP and SNMP queries performed on the devices. The data is presented in a spreadsheet format with each row representing a subnet being discovered. This provides an indication of the current state of the auto-discovery process.
Some messages that can display in the Discovery Progress window are: Starting Discovery, Total devices discovered, and Device object creation complete.
 |
Note You can stop the discovery and creation of objects by clicking the Stop button. |
 |
Note When auto-discovery is started, the system checks for existing devices in a selected address range. Any existing devices are ignored by the discovery process and the Stop button is greyed out. |
When all the relevant IP devices on the network have been discovered, an object class is created and stored under the Network view for each device. These devices can then be accessed by the Map Viewer.
Step 15 After all devices have been discovered, click the Close button.
At this point, the chassis is discovered with its NSP in a decommissioned state. After you auto-discover a chassis and before you commission that chassis, perform the following functions:
 |
Note Auto-discovery from the Cisco 6400 UAC does not deploy NRPs (like manual deployment). The following procedures ensure that all NRPs are discovered in the correct state (commissioned). |
To enter the CLI password for the relevant chassis, follow these steps:
Step 2 From the Management Information window (see Figure 5-51), click the IOS/Command Line Security tab. The IOS/Command Line Security Tab window appears (Figure 4-38).
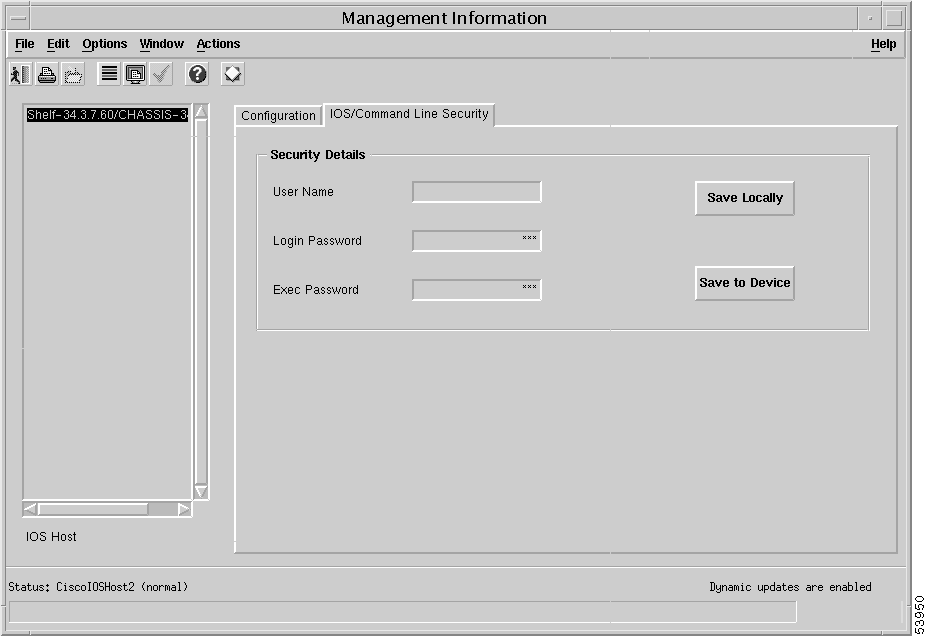
Step 3 In the Security Details panel, enter the User Name (optional). If you enter a name in this field, then this name must match the user name specified in the Cisco IOS on the NSP card.
Step 4 Enter the Login Password. This password must match the Line tty password configured in the Cisco IOS on the NSP card.
Step 5 Enter the Exec.Password. This is the encrypted enable password and must match the enable password configured in the Cisco IOS for the NSP card.
Step 6 Choose Save from the File menu to save your parameters.
Step 7 Click the Save Locally button to save the configuration management information to the local SCM database.
 |
Note If there are NRP2s defined in this chassis, then you must perform Step 7 and Step 8 before you commission the chassis. |
Step 8 From the selected chassis, right-click Cisco 6400 UAC > Chassis > Manage > SNMP Management option. The SNMP Management window appears (see Figure 5-10).
Step 9 Enter values for the SNMPv3 Specific panel parameters. For details, refer to "Viewing the SNMP Management Window" section.
Step 10 Commission the chassis. See "Commissioning a Chassis" section. The NRP and NRP2 cards are discovered in the correct state.
 |
Note Failure to set the CLI passwords causes subchassis-discovered NRPs to enter the alarmed state, leaves them decommissioned and does not set their IP addresses. NRP passwords must also be set before using the Service and Subscriber options on the Cisco 6400 SCM. |
Commissioning a chassis within a shelf initiates subchassis discovery. Subchassis discovery discovers all of the cards installed in the chassis being commissioned.
 |
Note Objects that are pre-provisioned but not in the chassis are shown as decommissioned (hatched). Any objects that are discovered but not pre-provisioned are created as new objects. |
A selected chassis can be commissioned in two ways:
To commission a chassis (from the Chassis Configuration window), follow these steps:

Step 2 Choose an appropriate Chassis from the Chassis list displayed at the left side of the Chassis Configuration window.
Step 3 Configure the parameters displayed on the Configuration tab.
 |
Note Validation Parameters are set at the time of deployment and represent the correct number of slots or subslots in the Cisco 6400 chassis. Changing these parameters will mean that slot restriction tests could fail deployment; for example, setting the number of slots to 7 and then attempting to deploy a card in slot 8. |
Step 4 Enter additional descriptions when required (optional) on the Additional Descriptions tab. Descriptions 1 and 2 (optional) allow you to specify additional description information for a selected chassis. These data entry fields allow you to enter any additional text descriptions for identification purposes (for example, CLLI codes could be entered).
Step 5 Click the Commission button on the Chassis Configuration window. Subchassis discovery starts and all cards that were not pre-provisioned are discovered and added to the chassis Map Viewer. The NSP and all related cards are now in a commissioned state. Figure 4-40 shows a sample view of the chassis after subchassis discovery.
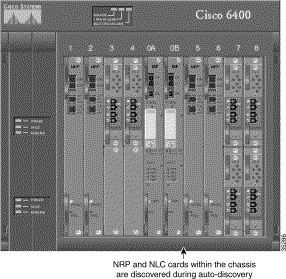
A selected chassis can be decommissioned in two ways:
To decommission a chassis (from the Chassis Configuration window), follow these steps:
Step 2 Choose an appropriate Chassis from the Chassis list displayed at the left side of the Chassis Configuration window.
Step 3 Click Decommission. The state of the selected chassis and all related cards changes to decommissioned.
 |
Note If you want to delete a Cisco 6400 device from the configuration, then you must first decommission that device. |
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Posted: Tue May 29 10:32:15 PDT 2001
All contents are Copyright © 1992--2001 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Important Notices and Privacy Statement.