|
|

Product Number: ATUC-1-4DMT-I(=)
This publication contains instructions that describe how to install and configure Cisco ATUC-4DMT-ISDN line cards. This high-density line card supports discrete multitone (DMT) over Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN) protocols that employ 2B1Q- or 4B3T-based encoding.
You can only use this line card in Cisco 6260 digital subscriber line access multiplexers (DSLAMs) that contain the NI-2 network interface processor module running Cisco IOS software. You can deploy the line cards described in this document in either of two ways:
This document includes the following sections:
You can only use ATUC-4DMT-ISDN line cards in ISDN service in Cisco 6260 DLSAM chassis.
The ATUC-4DMT-ISDN line card
In CPE installations with ISDN service on the same wire pair, you must use a DMT/ISDN signal splitter to separate and isolate ISDN and DMT signal frequency bands. The line card contains filters that reject the ISDN spectrum (or signal) during operation.
 |
Warning Means danger. You are in a situation that could cause bodily injury. Before you work on any equipment, be aware of the hazards involved with electrical circuitry and be familiar with standard practices for preventing accidents.
|
Use the following guidelines when working with equipment that is connected to telephone wiring or to other network cabling:
Electrostatic discharge (ESD) damage, which can occur when electronic line cards or components are improperly handled, results in complete or intermittent failures. Port adapters and processor line cards consist of printed circuit boards that are fixed in metal carriers. Electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding and connectors are integral components of the carrier. Although the metal carrier helps to protect the board from ESD, use a preventive antistatic strap during handling.
Observe the following guidelines to prevent equipment ESD damage:
 |
Caution Never attempt to remove the printed circuit board from the metal carrier. For safety, periodically check the resistance value of the antistatic strap. The measurement should be between 1 and 10 megohms. |
This section describes software requirements and lists the parts and tools that you need to install an ATUC-4DMT-ISDN line card in a Cisco 6260 DLSAM chassis.
Table 1 lists the Cisco IOS release you should use to configure and manage line cards in Cisco 6260 DSLAMs.
| Hardware Platform | Recommended Minimum Cisco IOS Release |
Cisco 6260 NI-2 DSLAM | Cisco IOS Release 12.1(3)DA or later |
You do not need special parts or tools to install a line card. However, you should use ESD-preventive equipment or the disposable grounding wrist strap included with the line card you receive. You also need a small standard screwdriver to rotate the line card locking tabs.
To install any line card in a Cisco 6260 DSLAM chassis, follow the procedures in the "Line Card Installation" section. To remove a line card, follow the procedures in the "Line Card Removal" section.
 |
Note You do not need to disconnect power before you insert or remove a line card from a Cisco 6260 NI-2 DSLAM chassis. |
You can install up to 30 ATUC-4DMT-ISDN line cards in the following Cisco 6260 DSLAM slots
To install a line card in a Cisco 6260 chassis slot, perform the following steps:
 |
Caution Static voltages as low as 30 volts can cause latent damage to circuitry. Be sure to observe all standard antistatic procedures (for example, wear a grounding strap). |
 |
Note If an unexpected result occurs when you perform the following procedure refer to the Cisco 6260 Hardware Installation and Troubleshooting Guide. |
| Step | Procedure |
|---|---|
Step 1 | Hold the line card vertically, with its faceplate toward you and its connector fingers facing the DSLAM line card slot. |
Step 2 | Align the upper and lower edges of the line card with the upper and lower guides in the DSLAM line card slot. |
Step 3 | Slide the line card into its DSLAM slot (Figure 1) by applying gentle pressure with both hands at the top and bottom of its faceplate until its finger contacts enter the backplane connector. |
Step 4 | Rotate the faceplate locking tab on the line card to its unlocked position (see Figure 2) and engage the locking lever at the upper front rail of the DSLAM chassis (see Figure 1). |
Step 5 | Press the locking lever down; this action inserts the line card finger contacts into the backplane connector. |
Step 6 | Rotate the line card locking tab with a small screwdriver. When you insert the line card, the green Status LED on the faceplate should light (firmware on the line card runs an internal test to ensure proper line card operation). If the Status LED does not light, replace the line card. |
Step 7 | Install a blank faceplate to cover each empty slot in the Cisco 6260 DSLAM. Secure the faceplate to the DSLAM chassis by rotating its locking tab to the locked position (see Figure 2). |
 |
Warning Blank faceplates and cover panels serve three important functions: 1) they prevent exposure to hazardous voltages and currents inside the chassis; 2) they constrain electromagnetic interference (EMI) that may otherwise disrupt other equipment; and 3) they direct the flow of cooling air through the chassis. Do not operate the system unless all line cards, blank faceplates, front covers, and rear covers are in place. |
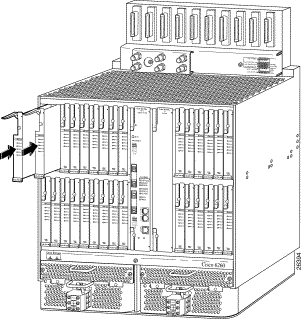
 |
Note The Cisco 6260 Hardware Installation and Troubleshooting Guide describes the Cisco 6260 DSLAM-slot modem tip and ring mapping to backplane connectors. |

This section describes how to remove a line card. You do not need to disconnect power before you remove a line card from its slot in a Cisco 6260 DSLAM chassis. The following procedure describes how to remove a line card.
 |
Caution Static voltages as low as 30 volts can cause latent damage to circuitry. Be sure to observe all standard antistatic procedures (for example, wear a grounding strap). |
| Step | Procedure |
|---|---|
Step 1 | Rotate the line card locking tab to its unlocked position (see Figure 2). |
Step 2 | Grasp the line card extraction lever (see Figure 1). Pull up the locking lever to disengage the line card contact fingers from the backplane connector. |
Step 3 | Slide the line card out of the chassis. |
Step 4 | Place the line card on an antistatic surface. For extended storage, insert the line card into a static-shielding bag or into a box lined with static-shielding material. |
Step 5 | If you do not replace the removed line card with another line card, install a blank faceplate (refer to "Line Card Installation" section). |
In addition to its locking mechanism (Figure 3), the faceplate contains two LEDs that show you line card activity and status, and four other LEDs that show the activity of each modem during operation.
The Status and Active light-emitting diode (LED) indicators on the line card faceplate indicate line card activity during operation. The faceplate also includes four modem-status LED indicators, one for each modem in the line card. Table 2 describes LEDs on the ATUC-4DMT-ISDN line card.
| LED | Color and State | Indication | |
Status | Solid green | No internal faults, line card is communicating with the NI-2 processor card. | |
Blinking slow green | No internal faults, line card is establishing connection with the NI-2 processor. | ||
Off | This line card has not booted or is operating improperly. (During reboot, this line card might be off for 2 to 3 seconds.) | ||
Blinking slow red | An internal fault has occurred or the line card cannot boot. | ||
Active | Solid green | Running application code, no digital signal processor (DSP) microcode is downloading. | |
Blinking fast green | Running application code and DSP microcode is downloading.
| ||
ATU-C 1 through ATU-C 4 modem ports | Solid green | The port is active and trained with its CPE device. | |
Blinking green | The port is training with its CPE device. | ||
Off | The port is shut down or no CPE device detected. |
After the line card detects the CPE and completes the initialization sequence, it configures itself for one of the following types of operation
After a reset, the NI-2 network interface processor executes boot Flash EPROM routines. Boot flash code also contains the serial management bus (SMB) boot loader. The NI-2 network interface processor module sends each line card its run-time image over the SMB and loads the main executable code into SRAM. After the main-code image loads and runs, the line card loads its serial data bus (SDB) Utopia field programmable gate array (FPGA) and initializes all modems.
Each line card supports up to 256 virtual channel identifiers (VCIs) and virtual path identifiers (VPIs) per port. Each line card also enables use of default VPI/VCI mapping or provisioning of VPI/VCI mapping by means of Cisco IOS configuration commands.
For Cisco IOS software configuration information and support, refer to the Configuration Guide for Cisco 6000 Family DSLAMs with NI-2 and to the Command Reference for Cisco 6000 Family DSLAMs with NI-2 in the Cisco IOS software configuration documentation set that corresponds with the software release installed on your Cisco 6260 NI-2 DSLAM hardware.
Figure 4 shows the physical DMT data and installed interface relationships among devices in a typical ATUC-4DMT-ISDN direct connect line card deployment in a Cisco 6260 DSLAM.
In direct connect deployments, Cisco ATUC-4DMT-ISDN line cards are a principal component of the Cisco 6260 DSLAM normally located in a CO facility rack. You install from 1 to N (where N has any value up to 30) line cards in a single Cisco 6260 DSLAM.
The network configuration consists of the following two principal hardware groups
The CPE hardware group (see Figure 4) consists of customer and telco equipment. Customer PC equipment connected to a customer Ethernet LAN receives and transmits Ethernet data only. The Cisco 677i modem is telco equipment that interfaces with an Ethernet line and converts Ethernet data to DMT signals. Customers must use a telco-provided Cisco 677i modem to produce DMT signals for proper ATUC-4DMT-ISDN line card operation.
This section describes how the component configuration illustrated in Figure 4 relates to proper line card operation.
At a customer site, you must use the Cisco 677i modem to provide the Ethernet LAN interface (see Figure 4) at the downstream end of the line. The 677i modem provides the interface between a customer Ethernet and a line card. Specifically, the customer Cisco 677i modem provides the network ATUC-R DMT signaling function, which
The CO facility hardware group (see Figure 4) consists of
The CO facility equipment routes signals DMT1, DMT2, and DMT3 through DMTN between the CPE 677i modems and the MDF.
In the:
Cisco equipment using these line cards includes
The MDF (see Figure 4) is telco equipment that distributes customer DMT signals from a Cisco 677i modem to its corresponding internal modem on a line card through suitable MDF to Cisco 6260 DSLAM cabling. Cisco product offerings include prefabricated Champion cable assemblies in various lengths for connection of customer lines between a CO facility MDF and the line card connectors on Cisco 6260 DSLAM backplanes. You make these cable connections at Cisco 6260 backplane receptacles. Refer to the Cisco 6260 Hardware Installation and Troubleshooting Guide for cabling instructions.
In Figure 4, Cisco ATUC-4DMT-ISDN line cards LC1 and LC2 through LCN convert upstream DMT signals to AMT cells and downstream AMT cells to DMT signals. The Cisco NI-2 interface processor module controls each line card, which
A full complement of line cards in a single Cisco 6260 DSLAM can handle network communications from and to as many as 120 customers.
You can install up to four Cisco 6260 DSLAMs, populated with ATUC-4DMT-ISDN line cards in a direct connect configuration, in a standard NEBS compliant 7-foot CO facility rack.
The Cisco NI-2 network interface processor module (see Figure 4) in the Cisco 6260 DSLAM and the Cisco IOS software running on the Cisco NI-2 control how ATM cells are processed when transported between the line cards and the WAN network trunk.
The NI-2 processor module
The Cisco NI-2 Card Installation and Configuration for the Cisco 6260 document describes the NI-2 network interface processor module.
Figure 5 shows the DMT/ISDN data and system interface relationships among devices in a typical ATUC-4DMT-ISDN line card deployment using DMT/ISDN splitters.

In DMT/ISDN line card deployments, you use CPE and CO splitters to separate the two signals.
DMT/ISDN splitters permit both telephone voice and data signals to be transported as data from and to the CPE. You can install as many as 30 ATUC-4DMT-ISDN line cards in a single splitter-configured Cisco 6260 DSLAM.
The network configuration consists of the two following principal hardware groups:
The CPE hardware group (see Figure 5) consists of customer and telco equipment that transmits and receives both ISDN and DMT signals and PC equipment that transmits and receives Ethernet data. A typical CPE hardware group (for example, CPE1) consists of
The following sections describe the components that make up a typical splitter-configured CPE hardware group.
ISDN terminal equipment
The NT1 device (see Figure 5) includes two ports that typically provide an interface to the customer ISDN terminal equipment and the CPE DMT/ISDN splitter. The NTI device passes properly formatted 2B1Q or 4B3T signals (see Table 3) to the splitter.
In this deployment, the Cisco 677i modem (seeFigure 5 ) also provides the Ethernet primary interface. The Cisco 677i modem transmits and receives DMT signals or Ethernet data passed between the local DMT/ISDN CPE splitter and the customer LAN. Specifically, the Cisco 677i modem provides the required ATUC-R function, which
The DMT port interfaces physically with the CPE DMT/ISDN splitter. The modem ports must be used to transport data traffic over an ADSL access network.
The CPE DMT/ISDN splitter (Figure 5) electrically couples the ISDN signal from the NT1 device and the DMT signal from the modem onto the pair carrying the DMT/IDSN traffic between the CPE facility and the MDF at the CO facility. The CPE splitter provides a filtering function that
The CO facility hardware group consists of Cisco and telco equipment that processes both ISDN and DMT signals (see Figure 5). The CO facility Cisco equipment transfers DMT signals between local DSL subscribers and the wide area network (WAN) trunk interface through the MDF, the DMT/ISDN CO splitter, and the line cards. Cisco equipment includes
Other equipment at the CO facility associated with DMT/ISDN signal processing includes
This section describes the relationship between the line cards and the components in the CO facility hardware group illustrated in Figure 5.
The MDF distributes DMT/ISDN signals (see Figure 5)
The telco facility DMT/ISDN CO splitter (see Figure 5):
ATUC-4DMT-ISDN line cards function as described in the "Line Cards" section. In Figure 5, Cisco line cards LC1 and LC2 through LCN convert upstream DMT signals to AMT cells and downstream AMT cells to DMT signals.
Because a CO DMT/ISDN splitter is required with each 6260 DSLAM, you can only install two Cisco 6260 DSLAMs, populated with ATUC-4DMT-ISDN line cards, in a splitter-configured standard NEBS compliant 7-foot CO facility rack.
The "Cisco NI-2 Network Interface Processor Module" section briefly describes the Cisco NI-2 network interface processor module (see Figure 4 and Figure 5).
Table 3 defines the following terms that are used in this guide.
| Acronym/Term | Definition |
|---|---|
2B1Q | An ISDN line coding technique used in the USA and Europe |
4B3T | An ISDN line coding technique used in Germany |
AAL5 | ATM adaption Layer 5 |
ADSL | Asymmetric digital subscriber line |
ANSI | American National Standards Institute |
ATM | Asynchronous Transfer Mode |
ATUC or ATU-C | Central office ADSL transceiver unit |
CCO | Cisco Connection Online |
CO | Central office |
CPE | Customer premises equipment |
DMT | Discrete multi-tone |
DSB | Data serial bus |
DSP | Digital signal processor |
DSLAM | Digital subscriber line access multiplexer |
DSL | Digital subscriber line |
EMI | Electromagnetic interference |
EPROM | Erasable programmable read-only memory |
ESD | Electrostatic discharge |
FAQ | Frequently asked questions |
FCC | Federal Communications Commission |
FPGA | Field programmable gate array |
FTP | File Transfer Protocol |
G.dmt | Standard that defines ADSL over splitter-coupled interfaces. |
GFR | Guaranteed frame rate |
GND | Ground |
HEC | Header error control |
I/O | Input/output |
ISDN | Integrated Services Digital Network |
ITU | International Telecommunications Union |
LED | Light emitting diode |
MIB | Management Information Base |
NI-2 | Network interface module type 2 |
NT1 | ISDN network terminal type 1 |
PEM | Power entry module |
PSTN | Public switched telephone network |
SDB | Serial data bus |
SMB | Serial management bus |
SRAM | Serial random-access memory |
TAC | Cisco technical assistance center |
VCI | Virtual channel identifier |
VPI | Virtual path identifier |
VIS | Visible |
Your Cisco 6260 NI-2 DSLAM and Cisco IOS software running on an NI-2 module installed in Cisco 6260 NI-2 DSLAMs have extensive features and functionality, which are documented in the following resources:
Refer to the following documents for more information about the operation and components of the Cisco 6100 series DSLAMs:
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class A digital device, pursuant to part 15 of the FCC rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference when the equipment is operated in a commercial environment. This equipment generates, uses, and can radiate radio-frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with the instruction manual, may cause harmful interference to radio communications. Operation of this equipment in a residential area is likely to cause harmful interference, in which case users will be required to correct the interference at their own expense.
You can determine whether your equipment is causing interference by turning it off. If the interference stops, it was probably caused by the Cisco equipment or one of its peripheral devices. If the equipment causes interference to radio or television reception, try to correct the interference by using one or more of the following measures:
 |
Note The ATUC-4DMT-ISDN line card is designed to meet these requirements. Modifications to this product that are not authorized by Cisco Systems, Inc., may void various approvals and negate your authority to operate this product. |
Cisco Connection Online (CCO) is the Cisco Systems primary real-time support channel. Maintenance customers and partners may self-register at CCO to obtain additional information and services.
Available 24 hours a day, 7 days a week, CCO provides a wealth of standard and value-added services to Cisco customers and business partners. CCO services include product information, product documentation, software updates, release notes, technical tips, the Bug Navigator, configuration notes, brochures, descriptions of service offerings, and download access to public and authorized files.
CCO serves a wide variety of users through two interfaces that are updated and enhanced simultaneously: a character-based version and a multimedia version that resides on the World Wide Web (WWW). The character-based CCO supports Zmodem, Kermit, Xmodem, FTP, and Internet e-mail, and it is excellent for quick access to information over lower bandwidths. The WWW version of CCO provides richly formatted documents with photographs, figures, graphics, and video, as well as hyperlinks to related information.
You can access CCO in the following ways:
For a copy of CCO Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ), contact cco-help@cisco.com. For additional information, contact cco-team@cisco.com.
If you are a network administrator and need personal technical assistance with a Cisco product that is under warranty or covered by a maintenance contract, contact the Cisco Technical Assistance Center (TAC) at 800 553-2447, 408 526-7209, or tac@cisco.com. To obtain general information about Cisco Systems, Cisco products, or upgrades, contact 800 553-6387, 408 526-7208, or cs-rep@cisco.com.
Cisco documentation and additional literature are available in a CD-ROM package, which ships with your product. The Documentation CD-ROM, a member of the Cisco Connection Family, is updated monthly. Therefore, it might be more current than printed documentation. To order additional copies of the Documentation CD-ROM, contact your local sales representative or call customer service. The CD-ROM package is available as a single package or through an annual subscription.
If you are reading Cisco product documentation on the World Wide Web, you can submit comments electronically. Click Feedback in the toolbar and select Documentation. After you complete the form, click Submit to send it to Cisco. We appreciate your comments.
If you are reading Cisco product documentation on the World Wide Web, you can submit comments electronically. Click Feedback in the toolbar and select Documentation. After you complete the form, click Submit to send it to Cisco. We appreciate your comments.
Copyright © 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Access Registrar, AccessPath, Are You Ready, ATM Director, Browse with Me, CCDA, CCDE, CCDP, CCIE, CCNA, CCNP, CCSI, CD-PAC, CiscoLink, the Cisco NetWorks logo, the Cisco Powered Network logo, Cisco Systems Networking Academy, Fast Step, FireRunner, Follow Me Browsing, FormShare, GigaStack, IGX, Intelligence in the Optical Core, Internet Quotient, IP/VC, iQ Breakthrough, iQ Expertise, iQ FastTrack, iQuick Study, iQ Readiness Scorecard, The iQ Logo, Kernel Proxy, MGX, Natural Network Viewer, Network Registrar, the Networkers logo, Packet, PIX, Point and Click Internetworking, Policy Builder, RateMUX, ReyMaster, ReyView, ScriptShare, Secure Script, Shop with Me, SlideCast, SMARTnet, SVX, TrafficDirector, TransPath, VlanDirector, Voice LAN, Wavelength Router, Workgroup Director, and Workgroup Stack are trademarks of Cisco Systems, Inc.; Changing the Way We Work, Live, Play, and Learn, Empowering the Internet Generation, are service marks of Cisco Systems, Inc.; and Aironet, ASIST, BPX, Catalyst, Cisco, the Cisco Certified Internetwork Expert Logo, Cisco IOS, the Cisco IOS logo, Cisco Press, Cisco Systems, Cisco Systems Capital, the Cisco Systems logo, Collision Free, Enterprise/Solver, EtherChannel, EtherSwitch, FastHub, FastLink, FastPAD, IOS, IP/TV, IPX, LightStream, LightSwitch, MICA, NetRanger, Post-Routing, Pre-Routing, Registrar, StrataView Plus, Stratm, SwitchProbe, TeleRouter, are registered trademarks of Cisco Systems, Inc. or its affiliates in the U.S. and certain other countries.
All other brands, names, or trademarks mentioned in this document/website are the property of their respective owners. The use of the word partner does not imply a partnership relationship between Cisco and any of its resellers. (0008R)
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Posted: Wed Jul 24 19:56:00 PDT 2002
All contents are Copyright © 1992--2002 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Important Notices and Privacy Statement.