Read this chapter to learn how to isolate faults in the Cisco 6200 advanced digital subscriber line access multiplexer (DSLAM). Most problems in a Cisco 6200 system can be traced to one of the system's field-replaceable units (FRUs):
All Cisco 6200 FRUs are hot-swappable, except the PEM in the case where only one is operating.
| FRU Affected
| Symptom
| Steps to Take
|
|---|
| Management processor card (MPC)
| Power LED is not lit.
|
|
1 . | Check power LEDs on other cards. If none are lit, refer to the PEM section of this table. |
|
2 . | If power LEDs on other cards are lit, remove the card from its slot and check for bent or broken pins on both the card and the backplane. Return the card to its slot and screw it firmly into place. |
|
4 . | If the problem persists with a new card, there may be a fault in your backplane. Contact Cisco's TRC. |
|
Ready LED is yellow, indicating that the MPC failed its power-on self test.
| Press the reset switch on the MPC. If the problem persists, replace the card.1
|
The MPC comes up, but you cannot Telnet to the system.
|
|
1 . | Check the configuration of your LAN for both the Cisco 6200 and the Telnet source. |
|
2 . | Check the cabling and connectors between the Telnet source and the Cisco 6200. Refer to "Pin Assignments," to check pinouts. |
|
Card cannot be fully inserted into its slot.
| Inspect connectors on both the card and the backplane, looking for bent pins or other damage.
|
| FRU Affected
| Symptom
| Steps to Take
|
|---|
| Network trunk card (NTC)
| Power LED is not lit.
|
|
1 . | Check power LEDs on other cards. If none are lit, refer to the PEM section of this table. |
|
2 . | If power LEDs on other cards are lit, remove the card from its slot and check for bent or broken pins on both the card and the backplane. Return the card to its slot and screw it firmly into place. |
|
4 . | If the problem persists with a new card, there may be a fault in your backplane. Contact Cisco's TRC. |
|
Trunk fails to come up. Ready LED is yellow, indicating that the NTC failed its power-on self test.
|
|
1 . | Use the show ipc nodes command to find out whether there is a communication problem between the NTC and the MPC. There should be an entry in the resulting display for each SLC and NTC. If there is an entry for each card, skip to step 2. If one or more cards is not listed, do the following: |
- At the console, enter show int ethernet 0/1. If the port reports CRC errors or collisions, the backplane Ethernet may be improperly terminated. See the next item. If the port is administratively down, enter these commands to enable it:
c6200> configure terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
6200(config-if)# int eth0/1
6200(config-if)# no shut
6200(config-if)# exit
6200(config)# exit
6200#
- Ensure that the terminators on the backplane Ethernet connectors are in place. The backplane Ethernet connectors are BNC connectors. In most cases, they are located on the rear of the chassis, labeled ETH1 and ETH2. One is near the upper right corner and the other is near the lower right corner. (In some chassis, the backplane Ethernet connectors are at the front of the chassis, located behind panels at the top and bottom.)
- Use the MPC section of this table to troubleshoot the MPC.
|
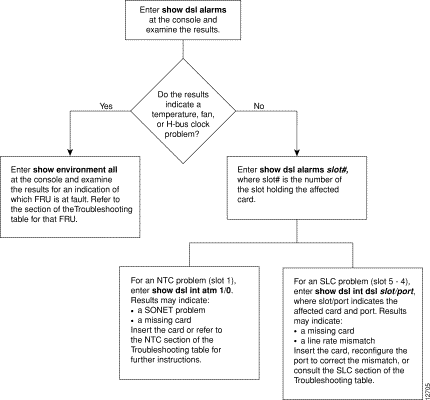
2 . | Check the alarm LEDs on the MPC or enter show dsl alarms to check the alarm status of the system. If any alarms are indicated, refer to Figure 7-1. |
|
3 . | Use the command show dsl status to ensure that the card is provisioned to be in this slot. (Nothing is displayed for slots that are not provisioned.) If necessary, update the configuration. |
|
4 . | To reset the card, pull it part way out of its slot, then push it back in and screw it into place. |
|
5 . | If the problem persists, replace the card. |
|
| Network trunk card (NTC)
| Trunk fails to come up or performs poorly.
|
|
1 . | Enter the command show dsl int atm 1/0. The results tell you about alarms, clocking mode, loopback status, and trunk status. If the trunk is administratively down, use the no shut config command to bring it up. |
|
2 . | Use the loopback command to run an OC-3 loopback test. You must install test equipment at the remote end to inject and receive data for a loopback test. See "Command Reference," for more information on the loopback command. |
|
3 . | If your cable is too long or if your optical signal passes through too many connectors, signal attenuation will cause signal quality problems. Check cable length and number of connectors. |
|
4 . | Check optical connectors for damage or for scratches on the optical surface. Replace connectors if necessary. |
|
5 . | Check optical connectors for dirt on the optical surface. If a connector is dirty, clean it by blowing compressed air from a distance of 3 inches (8 cm). You can also clean the connectors on most cables with an alcohol-moistened, lint-free wipe. Check the cable manufacturer's cleaning instructions first. |
- To prevent problems from dirty or damaged connectors, keep any unused optical connector covered with its protective cap.
|
6 . | Check optical power at both ends of the connection. |
|
7 . | Check for a card type mismatch. You must have cards of the same type (OC3, for example) and mode (single mode or multimode) at both ends of the connection. |
|
8 . | Check for a cable type mismatch. You must use multimode cable with multimode cards, or single mode cable with single mode cards. |
|
Card cannot be fully inserted into its slot.
| Inspect connectors on both the card and the backplane, looking for bent pins or other damage.
|
| Subscriber line card (SLC)
| Power LED is not lit.
|
|
1 . | Check power LEDs on other cards. If none are lit, refer to the PEM section of this table. |
|
2 . | If power LEDs on other cards are lit, replace the card. |
|
3 . | If the problem persists with a new card, there may be a fault in your backplane. Contact Cisco's TRC. |
|
All ports on a card fail to come up (modems don't train). Ready LED may be yellow, indicating that the SLC failed its power-on self test.
|
|
1 . | Use the show ipc nodes command to find out whether there is a communication problem between the SLC and the MPC. There should be an entry in the resulting display for each SLC and NTC. If there is an entry for each card, skip to step 2. If one or more cards is not listed, do the following: |
- At the console, enter show int ethernet 0/1. If the port reports CRC errors or collisions, the backplane Ethernet may be improperly terminated. See the next item. If the port is administratively down, enter these commands to enable it:
c6200> configure terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
6200(config-if)# int eth0/1
6200(config-if)# no shut
6200(config-if)# exit
6200(config)# exit
6200#
- Ensure that the terminators on the backplane Ethernet connectors are in place. The backplane Ethernet connectors are BNC connectors. On some models, these connectors are accessible from the front of the chassis, located behind panels at the top and bottom of the unit. On other models, the connectors are accessible from the rear of the chassis, located behind the metal panels that cover the data and power connectors.
- Use the MPC section of this table to troubleshoot the MPC.
|
3 . | Use the command show dsl status to that ensure the card is provisioned to be in this slot. (Nothing is displayed for slots that are not provisioned.) If necessary, update the configuration. |
|
4 . | To reset the card, pull it part way out of its slot, then push it back in and screw it into place. |
|
5 . | If the problem persists, replace the card. |
|
| Subscriber line card (SLC)
| A line fails to come up (modems don't train), or a port LED flashes continuously.
|
|
1 . | Use the command show dsl interface dsl slot/port to display the port's configuration. Check the display to ensure the port is properly provisioned. |
Note Alternatives to steps 2 and 3, if you don't have access to perform these checks: enter the command show dsl interface dsl slot/port. On a DMT interface, look for Line Status (near the top). If this reads "CPE not detected," troubleshoot the CPE and the local loop. On a CAP interface, look in the Signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) section of the resulting display for CO receiverGain, CPE transmitPower, and CPE receiverGain:
- CO receiverGain: If the CPE and the local loop are working properly, this value should be in the single digits---ideally 1 or 2. (Ignore the parenthetical gain1 and gain2 values.)
- CPE transmitPower: Should be positive (for example, 7 db).
- CPE receiverGain: Should be negative (for example, -18 db).
If the CPE is disconnected or turned off, or if there's a break in the local loop, expect to see a CO receiverGain value over 10 db, and values of 0 db for both CPE transmitPower and CPE receiverGain.
|
4 . | (For CAP SLCs only) Use the linetest command or the Cisco 6200 Manager (GUI) to perform a CAP hardware test to determine whether the port on the SLC is healthy. |
|
5 . | Plug a modem into the line at the CO (cutting out the local loop). If the modems train over the shorter distance, the problem lies in the subscriber loop or in the CPE. |
|
Card cannot be fully inserted into its slot.
| Inspect connectors on both the card and the backplane, looking for bent pins or other damage.
|
Card experiences problems in one slot but operates normally in another.
| There may be a fault in your backplane. Contact Cisco's TRC.
|
| Fan tray and air filter
| Fans do not run.
|
|
1 . | Make sure the fan tray is fully inserted into the chassis. |
|
2 . | Check input power connections. If connections are loose or their polarity is reversed, chassis does not receive power and fans do not run. |
|
Fans run but the system overheats.
|
|
1 . | Make sure that all intake and exhaust vents on the front, rear, and sides of the chassis are free of blockages. |
|
2 . | Make sure that the ambient temperature and other environmental factors in the system area are within the ranges specified in Table 1-1. |
|
3 . | Make sure all cards, blank faceplates, and covers are in place. The cooling system cannot operate effectively unless the chassis is fully enclosed. |
|
4 . | Enter the show environment all command and check the results to see if individual fans have failed. If so, replace the fan tray. |
|
6 . | Reduce the ambient temperature. |
|
Power entry
module (PEM)
| Green LED on PEM fails to go on.
|
|
1 . | Make sure the circuit breaker on the PEM is turned on. |
|
2 . | Make sure the PEM is properly seated and screwed in place. |
|
3 . | Make sure power leads are properly connected to power connectors on the backplane. If connections are loose or their polarity is reversed, chassis does not receive power. |
|
4 . | Check the power source. |
|
5 . | Move the PEM to the other PEM slot. If the PEM still fails, replace it. |
|
PEM experiences problems in one slot but operates normally in the other.
| There may be a fault in your backplane. Contact Cisco's TRC.
|
|