|
|

This chapter introduces the Cisco Subscriber Edge Services Manager (Cisco SESM) Release 3.1(3) and Cisco Subscriber Policy Engine (Cisco SPE) Version 1.01. The chapter includes the following topics:
The Cisco Subscriber Edge Services Manager (SESM) works in conjunction with other network components to provide extremely robust, highly scalable connection management to services in the broadband and mobile wireless markets.
Internet service providers (ISPs) and network access providers (NAPs) deploy SESM to provide their subscribers with a web interface, or portal, for accessing multiple Internet and other services. ISPs and NAPs can customize and brand the content of the SESM portal web pages and thereby control the user experience for different categories of subscribers.
SESM applications provide support for any platform that supports the Java Runtime Environment (JRE). Platforms tested in our labs include Sun Solaris, Windows NT, Windows 2000, Red Hat Linux, and SuSE Linux.
An SESM solution is deployed with the Cisco Service Selection Gateway (SSG), a feature set embedded in the Cisco IOS software broadband release train. Some of the devices on which SSG can run include the Cisco 7200 Series high-performance multifunction router, the Cisco 7400 Series router, and the Cisco 6400 Universal Access Concentrator (UAC).
The SESM applications run in a default network assessable to the SSG. Together, SESM and SSG provide subscriber authentication, service selection, and service connection capabilities to subscribers in the broadband and mobile wireless environments.
Subscribers interact with an SESM web portal using a standard Internet browser. They do not need to download any software or plug-ins to use the SESM web portal. After a subscriber successfully authenticates, the SESM web portal presents a list of services that the subscriber is currently authorized to use. The subscriber can gain access to one or more of those services by selecting them from the web portal. Alternatively, an automatic connection feature can automatically connect subscribers to services after authentication.
For service subscribers, the SESM solution offers flexibility and convenience, including the ability to access multiple services simultaneously.
For service providers, the SESM solution provides a way to control the subscriber experience and promote customer loyalty. Service providers can change the look and feel of their SESM web application, brand the application, and control the content of the pages displayed to their subscribers.
 |
Note The SESM product was previously called the Cisco Service Selection Dashboard (Cisco SSD). |
Two SESM deployment options are available:
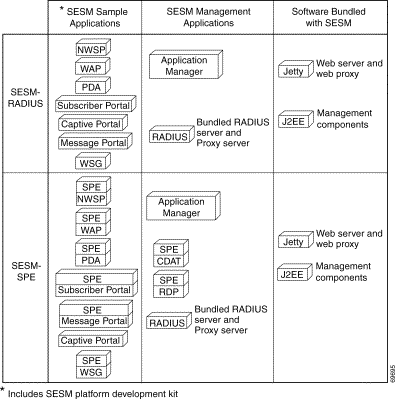
SESM includes the following sample portal applications that can be installed and configured for demonstration purposes or used as a starting point for customizations:
You can optionally install the following applications to configure an SESM captive portal solution:
SESM-SPE includes two additional supporting applications:
Figure 1-1 shows all of the applications included in SESM Release 3.1(3).
The Cisco Subscriber Policy Engine (SPE) Version 1.01 is a policy server specifically customized to provide granular subscriber service policy. SPE combines role-based access control (RBAC) functionality with an open policy server. Service providers can create differentiated subscriber groups. Service and content providers can use the SPE to provide value added and differentiated services to the subscriber population.
SPE is installed when SESM Release 3.1(3) is deployed in LDAP mode to provide the following enhanced features and capabilities:
Figure 1-2 shows the relationship between the SESM and SPE products.

You can deploy SESM portal applications in these modes:
The same SESM application programming interface (API) is used to develop and customize applications intended for either the RADIUS or the LDAP modes. Applications intended for LDAP mode deployment can include additional features provided by SPE. The Cisco Subscriber Edge Services Manager Web Developer Guide describes how to create applications for both RADIUS and LDAP mode deployments.
See the "SESM in RADIUS Mode" section for more information about the components and data flow in a RADIUS mode deployment.
An LDAP deployment stores subscriber and service profile information in a Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP)-compliant directory. An LDAP deployment requires the Cisco Subscriber Policy Engine (SPE) Version 1.01, which is available from the SESM installation package if your SESM purchase license allows it.
See the "SESM in LDAP Mode" section for more information about the components and data flow in an LDAP mode deployment.
Demo mode simulates the actions of an SESM deployment in both RADIUS and LDAP modes. It uses a local copy of a Merit RADIUS file to obtain profile information. See "Demo Quick Start," for information about installing and using SESM in Demo mode.
Do not confuse the term sample application with Demo mode. The SESM sample applications are fully functioning web applications that were built using the SESM development library. These applications use the services of the Jetty web server and the JMX management server.
Demo mode is an SESM deployment mode for SESM portal applications. You can install and run the sample portal applications (NWSP, WAP, and PDA) in any of the SESM deployment modes: RADIUS, LDAP, or Demo.
Although you can install the captive portal solution in Demo mode, you cannot demonstrate the solution without an SSG redirecting traffic to the Captive Portal application.
This section describes the SESM web development kit and suite of applications:
See the Cisco Subscriber Edge Services Manager Web Developer Guide for information about developing a customized SESM portal application. Use the configuration information in "Configuring Components after Installation," to deploy and configure the customized applications.
The Cisco Subscriber Edge Services Manager Web Developer Guide provides detailed information about each of these sample portal applications.
A sample captive portal solution is included with SESM that illustrates all supported types of redirection. The sample solution includes the following applications:
Most deployers will use the captive portal application as installed but provide their own content applications for the HTTP redirections. The content applications can be any web application. When they are SESM web portals, they can use all of the features in the SESM web development kit, including the device and locale awareness features.
See "Deploying a Captive Portal Solution," for more information about captive portal features and how to install and configure the captive portal solution.
You can configure the RDP to run in two modes:
RDP is a Java2 application that uses the services of a JMX server for configuration. It is not a web application and therefore does not run in a J2EE container.
This guide describes how to install and configure RDP. RDP is intended to be used as installed but it is extensible for special purpose deployments. For information, see "RDP Packet Handlers."
CDAT is a J2EE web application. It runs in a J2EE container and uses the services of a JMX server for configuration.
This guide describes how to install and configure CDAT. For information about using CDAT, creating profiles in the RBAC model, and the SPE directory extensions, see the Cisco Distributed Administration Tool Guide.
See the Cisco Distributed Administration Tool Guide for information about the RBAC model, the DESS and AUTH extensions to an LDAP directory, and how to develop subscriber and service profile information in the RBAC model.
You can install the following items from the SESM installation package:
The sample SESM portal applications and CDAT are installed with configuration files and startup scripts that are ready to run using the Jetty web server and the Sun example JMX server. RDP is installed with configuration files and a startup script that is ready to run using the JMX server. However, SESM is designed to allow the use of any J2EE web server and any JMX-compliant server.
 |
Note See the "Port-Bundle Host Key Feature on SSG" section before deploying a J2EE server other than the Jetty server. For SESM Release 3.1(3), the host key feature works only with a Jetty server. |
The SESM portal applications and CDAT are J2EE applications. They require an HTTP listener and must run in a J2EE-compliant server container.
During SESM installation, the sample portal applications and CDAT and their corresponding configuration files and startup scripts are set up to use the Jetty server components from Mort Bay Consulting. If desired, web developers at your site can deploy a J2EE-compliant server other than the Jetty server.
All of the SESM applications (portals, RDP, and CDAT) require the services of a Java Management Extensions (JMX) server.
The installed sample applications, the configuration files, and the startup scripts are set up to use the Sun example JMX server from Sun Microsystems. The SESM installation program installs the JMX server along with the Jetty server. If desired, web developers at your site can deploy a JMX-compliant server other than the Sun example server.
This section describes the network components that are required in an SESM deployment but are not provided by the SESM installation package:
The Cisco Service Selection Gateway (SSG) is a software feature module embedded in the Cisco IOS broadband release train. The SSG feature can operate in standalone mode to provide Layer 2 service connection support, or it can be configured to work with SESM, which offers enhanced service-related features to subscribers. The SSG runs on a Cisco router or other Cisco device. For a list of Cisco devices currently verified to work with SESM, see the "SSG Devices" section.
An SESM deployment requires the services of SSG. SESM is deployed in an SSG default network. SSG performs authentication and service connection tasks on behalf of an SESM portal application.
For information about SSG in the Cisco IOS Release 12.2(4)B, see the following documents:
Regardless of the SESM deployment mode (RADIUS or LDAP), SSG and an SESM web portal application communicate using the RADIUS protocol.
The port-bundle host key feature provides the following advantages to SESM portal applications:
When port-bundle host key is enabled on the SSG, the SSG preserves the port number of the incoming HTTP request. This remote port number becomes the key that uniquely identifies each subscriber. The key is included in the request that is forwarded to the SESM web application.
The following scenarios require a RADIUS server:
SESM works with any RADIUS server that accepts vendor-specific attributes (VSAs). The VSAs define the subscriber and service profile information required in the SESM deployment. The Cisco Access Registrar is a carrier class RADIUS platform that is fully tested with SESM. See the "Configuring Cisco Access Registrar for SESM Deployments" section for more information about using Cisco Access Registrar in SESM deployments.
Also see the following references for more information about configuring a RADIUS server in an SESM deployment:
An LDAP directory allows interactive updates, a feature that is not readily supported by a RADIUS server. The LDAP mode uses this update capability to offer SESM features that the RADIUS mode cannot provide, such as:
An SESM deployment includes the following hardware platforms:
This section describes the supported platforms for the SESM applications, which include the web portal applications, the Captive Portal application, RDP, and CDAT.
SESM provides support for applications on any platform that supports the Java Runtime Environment (JRE). Platforms tested in our labs are listed below.
Subscribers can use any type of web browser to access an SESM portal application. However, each web browser and access device has its own limitations, such as differences in display capabilities. Developers of SESM portals must consider the end users of the deployed application and design the application to accommodate the media and browser versions that their subscribers commonly use.
Table 1-1 lists the browsers and devices for which the SESM sample portal applications were designed. The Cisco Subscriber Edge Services Manager Web Developer Guide includes information about obtaining and configuring simulators.
 |
Note These browser limitations apply only to the sample applications and are listed to ensure predictable results during demonstrations. |
| SESM Portal Application | Device | Other Requirements |
|---|---|---|
NWSP |
| |
WAP | WAP devices and simulators | |
PDA | PDA devices and simulators |
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Posted: Mon Aug 26 08:41:50 PDT 2002
All contents are Copyright © 1992--2002 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Important Notices and Privacy Statement.