|
|

May 1, 2001
 |
Note The most current Cisco documentation for released products is available on Cisco.com at http://www.cisco.com. The online documents may contain updates and modifications made after the hardcopy documents were printed. |
These release notes describe the following topics:
These release notes describe command enhancements and the open and resolved caveats included in the Cisco Cache software, Release 2.3.1 for the Cisco Content Engines and Cisco Cache Engines. Software Release 2.3.1 is an extension of Release 2.3.0. To simplify terminology, both the Cache Engine and the Content Engine are referred to as the "CE." Refer to the Cisco Cache Software Configuration Guide, Software Versions 2.2.x, 2.3.x for the following information:
 |
Note WCCP is also known as the Web Cache Control Protocol and the Web Cache Coordination Protocol. |
Refer to the Cisco Cache Software Command Reference, Release 2.3.0 for global configuration, EXEC, show, and interface command descriptions. Refer to the Cisco Content Engine 500 Series Hardware Installation Guide for information on the Cisco Content Engines. See the "Related Documentation" section for information about the web sites from which to obtain related documentation.
 |
Note We recommend that you install the most recent software release available for your model of the CE. |
To determine the version of the software currently running on the Cisco CE, log on to the CE and enter the show version EXEC command.
CE Cache software can be downloaded from the Cisco Systems Software Center at the following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/cgi-bin/tablebuild.pl/cache-engine20
Two types of CE Cache software files are available on Cisco.com to download: files with the .pax suffix and files with the .bin suffix. The .pax file contains the full-image software with the graphical user interface (GUI) and is the file routinely installed. The .bin file software is for recovery situations that require booting from the network, or restoring Flash memory. Refer to the section "Recovering the System Software" in the Cisco Cache Software Configuration Guide, Software Versions 2.2.x, 2.3.x for instructions on loading your system image with the .bin file.
Step 1 Use an FTP client to transfer the .pax file to the /local directory of your CE.
Step 2 Log on to the CE, and at the privileged level EXEC command prompt enter:
install filename.pax
where filename is the name of the .pax file.
Step 3 Follow the command-line interface instructions as prompted. At the following prompt, enter y:
Copy new image to flash memory?[yes]:
Step 4 After the CE has rebooted, use the show version command to display the current
software version.
Release 2.3.1, like Release 2.3.0, operates on all models of the Cisco 500 series Cache Engines, as well as the Cisco Content Engine 507, 560, and 590.
The following topics are described in this section:
The bypass auth-traffic command now supports the bypassing of Windows NT LAN Manager (NTLM) authenticated traffic. You can now configure the Cache Engine software to bypass all the authenticated traffic using the new command option all or bypass only NTLM authenticated traffic using the new command option ntlm-only.
The following are the enhancements to the bypass auth-traffic command:
bypass auth-traffic allFor backward compatibility, the bypass auth-traffic enable command is still supported.
The show bypass list command also now provides information about bypassed NTLM authentication traffic. For example:
console# show bypass list
Client Server Entry type
------ ------ ----------
10.1.200.2:0 172.16.7.52:0 ntlm-auth-traffic
Two new radius-server command options have been added to Release 2.3.1 to ensure that the CE does not issue unnecessary user prompts during a session. These were added to resolve caveat CSCds63770. The following are the new radius-server command options:
radius-server multiple-user-prompt-timeout valueThe multiple-user-prompt-timeout command option denotes the amount of time after which the next prompt, the 401 (unauthorized) response, will be sent to the user. The default value is 25 seconds. The multiple-user-prompt-fix enable command option is used to enable the fix to caveat CSCds63770 and is enabled by default.
See the "Resolved CaveatsSoftware Release 2.3.1" section for information about caveat CSCds63770.
New Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) MIB objects have been added to the Cisco Cache software, Release 2.3.1. Most of these objects are used to obtain more information about the cache file system (cfs) disk volumes and the DOS file system (dosfs) disk volumes. One new MIB object is used to determine the duplex value of the Ethernet port. See Table 1 for information about the new 2.3.1 SNMP MIB objects.
New SNMP traps have also been added to the Cisco Cache software, Release 2.3.1. See Table 2 for information about the new 2.3.1 SNMP traps.
Table 1 provides the name of each new SNMP MIB object and its description.
| Variable Name | Description |
|---|---|
cceUsageDiskVolumeName | Name of the cfs disk volume. |
cceUsageDiskVolumeEverMounted | Indicates whether the cfs disk volume was ever mounted. |
cceUsageDiskVolumeCurrentlyMounted | Indicates whether the cfs disk volume is currently mounted. |
cceUsageDiskVolumeUnmountReason | Indicates the reason why the cfs disk volume is currently unmounted. The possible reasons for the unmounted state are:
If the given cfs disk volume is unmounted because of an error, then a trap (cacheTrapDiskVolUnmounted) is generated to notify the managing station. See Table 2. |
cceUsageDiskVolumeCurrent | Specifies the percentage of the cfs disk volume currently being used. |
cceUsageDiskVolumePeak | Specifies the percentage of the cfs disk volume that was used during its peak usage. |
cceIfFullDuplex | Specifies the duplex value of the Ethernet port. The possible duplex values are:
|
cceLoggingWriteFailReason | Indicates the reason the last translog write operation failed. If the last operation was successful, this object displays as "NotApplicable." |
cceUsageDosfsVolumeName | Specifies the dosfs volume name. |
cceUsageDosfsVolumeState | Specifies the state of a given dosfs volume. The following are the possible state values and associated descriptions:
|
cceUsageDosfsVolumeFreeSpace | Specifies the amount of free space available on a given dosfs volume. |
cceUsageDosfsVolumeTotalSpace | Specifies the total space available on a given dosfs volume. |
| Trap Name | Description |
|---|---|
cacheTrapDiskVolUnmounted | Indicates the cfs disk volume has been unmounted because of an error. |
cacheTrapDosfsVolFull | Indicates the dosfs volume is full. |
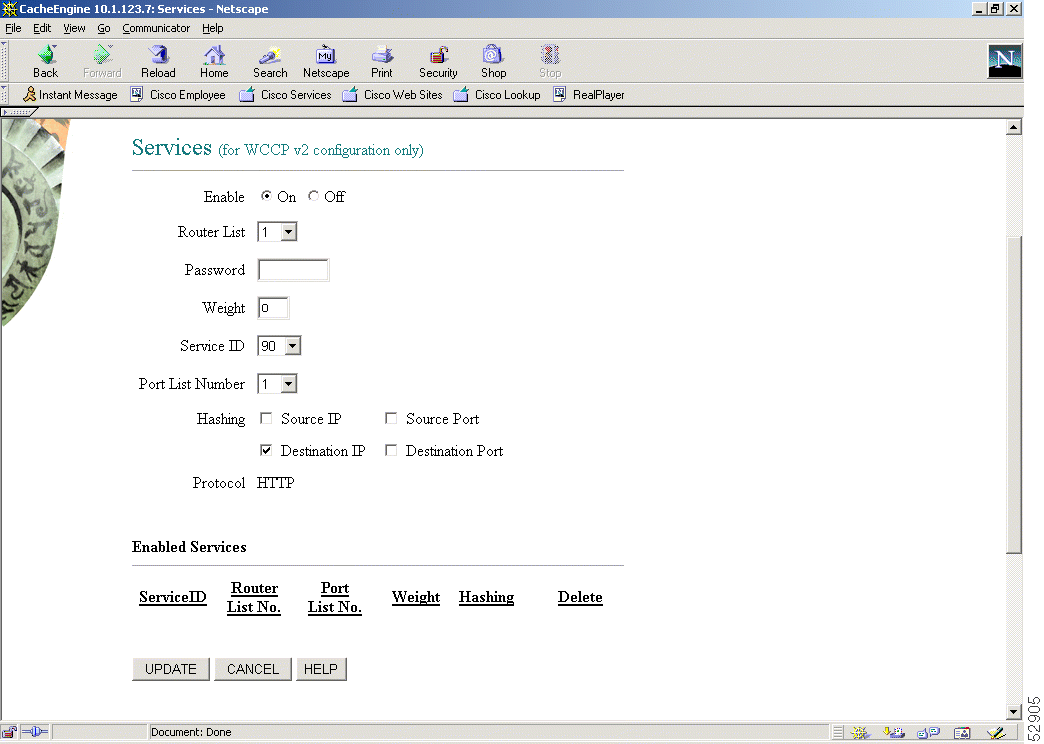
The graphical user interface WCCP Services page shown in Figure 1 has been enhanced to display the list of enabled services. The WCCP Services page now also provides an option to selectively delete the individual services. Refer to the WCCP Services page online help for more information.
The following sections describe the open and resolved caveats for Release 2.3.1. Caveats describe unexpected behavior in the Cisco Cache software.
The following section lists and describes the open caveats for Release 2.3.1:
CSCdt18114
Console> (enable) set spantree portfast 1/2 enable
The following section lists and describes the caveats from previous releases that are resolved in Release 2.3.1:
Use this document in conjunction with the following Cisco Cache Software and Cisco Content Engine documentation:
You can find this document and the above listed documents at the following sites:
The following sections provide sources for obtaining documentation from Cisco Systems.
You can access the most current Cisco documentation on the World Wide Web at the following sites:
Cisco documentation and additional literature are available in a CD-ROM package, which ships with your product. The Documentation CD-ROM is updated monthly and may be more current than printed documentation. The CD-ROM package is available as a single unit or as an annual subscription.
Cisco documentation is available in the following ways:
If you are reading Cisco product documentation on the World Wide Web, you can submit technical comments electronically. Click Feedback in the toolbar and select Documentation. After you complete the form, click Submit to send it to Cisco.
You can e-mail your comments to bug-doc@cisco.com.
To submit your comments by mail, use the response card behind the front cover of your document, or write to the following address:
Attn Document Resource Connection
Cisco Systems, Inc.
170 West Tasman Drive
San Jose, CA 95134-9883
We appreciate your comments.
Cisco provides Cisco.com as a starting point for all technical assistance. Customers and partners can obtain documentation, troubleshooting tips, and sample configurations from online tools. For Cisco.com registered users, additional troubleshooting tools are available from the TAC website.
Cisco.com is the foundation of a suite of interactive, networked services that provides immediate, open access to Cisco information and resources at anytime, from anywhere in the world. This highly integrated Internet application is a powerful, easy-to-use tool for doing business with Cisco.
Cisco.com provides a broad range of features and services to help customers and partners streamline business processes and improve productivity. Through Cisco.com, you can find information about Cisco and our networking solutions, services, and programs. In addition, you can resolve technical issues with online technical support, download and test software packages, and order Cisco learning materials and merchandise. Valuable online skill assessment, training, and certification programs are also available.
Customers and partners can self-register on Cisco.com to obtain additional personalized information and services. Registered users can order products, check on the status of an order, access technical support, and view benefits specific to their relationships with Cisco.
To access Cisco.com, go to the following website:
The Cisco TAC website is available to all customers who need technical assistance with a Cisco product or technology that is under warranty or covered by a maintenance contract.
If you have a priority level 3 (P3) or priority level 4 (P4) problem, contact TAC by going to the TAC website:
P3 and P4 level problems are defined as follows:
In each of the above cases, use the Cisco TAC website to quickly find answers to your questions.
To register for Cisco.com, go to the following website:
http://www.cisco.com/register/
If you cannot resolve your technical issue by using the TAC online resources, Cisco.com registered users can open a case online by using the TAC Case Open tool at the following website:
http://www.cisco.com/tac/caseopen
If you have a priority level 1(P1) or priority level 2 (P2) problem, contact TAC by telephone and immediately open a case. To obtain a directory of toll-free numbers for your country, go to the following website:
http://www.cisco.com/warp/public/687/Directory/DirTAC.shtml
P1 and P2 level problems are defined as follows:
This document is to be used in conjunction with the documents listed in the "Related Documentation" section.
AccessPath, AtmDirector, Browse with Me, CCDA, CCDE, CCDP, CCIE, CCNA, CCNP, CCSI, CD-PAC, CiscoLink, the Cisco NetWorks logo, the Cisco Powered Network logo, Cisco Systems Networking Academy, the Cisco Systems Networking Academy logo, Fast Step, Follow Me Browsing, FormShare, FrameShare, GigaStack, IGX, Internet Quotient, IP/VC, iQ Breakthrough, iQ Expertise, iQ FastTrack, the iQ Logo, iQ Net Readiness Scorecard, MGX, the Networkers logo, Packet, RateMUX, ScriptBuilder, ScriptShare, SlideCast, SMARTnet, TransPath, Unity, Voice LAN, Wavelength Router, and WebViewer are trademarks of Cisco Systems, Inc.; Changing the Way We Work, Live, Play, and Learn, Discover All That's Possible, and Empowering the Internet Generation, are service marks of Cisco Systems, Inc.; and Aironet, ASIST, BPX, Catalyst, Cisco, the Cisco Certified Internetwork Expert logo, Cisco IOS, the Cisco IOS logo, Cisco Systems, Cisco Systems Capital, the Cisco Systems logo, Enterprise/Solver, EtherChannel, EtherSwitch, FastHub, FastSwitch, IOS, IP/TV, LightStream, MICA, Network Registrar, PIX, Post-Routing, Pre-Routing, Registrar, StrataView Plus, Stratm, SwitchProbe, TeleRouter, and VCO are registered trademarks of Cisco Systems, Inc. and/or its affiliates in the U.S. and certain other countries.
All other brands, names, or trademarks mentioned in this document or Web site are the property of their respective owners. The use of the word partner does not imply a partnership relationship between Cisco and any other company. (0104R)
Copyright © 2001, Cisco Systems, Inc.
All rights reserved.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Posted: Tue Oct 1 05:12:35 PDT 2002
All contents are Copyright © 1992--2002 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Important Notices and Privacy Statement.