|
|

This chapter describes the Web Cache Communication Protocol (WCCP) Version 2 feature. It includes information on the benefits of this feature, supported platforms, and other information you may need to work with WCCP Version 2. This chapter includes the following sections:
Cisco developed the Web Cache Communication Protocol (WCCP) within Cisco IOS software to enable routers or switches to transparently redirect packets to network appliances. It does not interfere with normal router or switch operations. Using WCCP, the router redirects requests on configured TCP and UDP ports to network appliances rather than to intended host sites. It also balances traffic load across a group of appliances (a cluster) and ensures fault-tolerant and fail-safe operation. As Content Routers are added to or deleted from a appliance cluster, the WCCP-aware router or switch dynamically adjusts its redirection map to reflect the currently available appliances, resulting in maximized performance and content availability.
WCCP Version 2 contains the following features:
WCCP Version 2 enables a series of Content Routers, called a Content Router cluster, to connect to multiple routers. This feature provides redundancy and a more distributed architecture for instances when a Content Router needs to connect to a large number of interfaces. This strategy also has the benefit of keeping all the Content Routers in a single cluster.
With WCCP Version 2, multiple routers can service a cluster. This allows any of the available routers in a service group to redirect packets to each of the Content Routers in the cluster. Figure A-1 illustrates how this configuration appears.
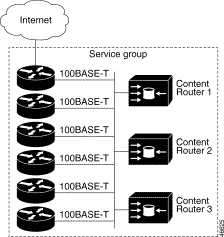
You can configure the router to run DNS boomerang (service number 50), a service that sends DNS Address (DNS A) record requests to a Content Router.
The subset of Content Routers within a cluster and routers connected to the cluster that are running the same service is known as a service group.
WCCP Version 2 addresses the issue of multiple routers being available to the cluster by allowing either a list of routers or an IP multicast address to be created on the Content Router. The difference in these two strategies is as follows:
If you are adding and removing routers dynamically, the multicast address strategy provides for easier configuration because you do not need to change the configuration for each device in the WCCP network.
The following sequence of events details how this process works:
1. Instead of having one central "home router," each Content Router defines a list of routers and stores the list in its memory.
2. Each Content Router announces its presence and view of the service group to the list of router IP addresses with which it has been configured. The routers reply with their view, which is a list of Content Router addresses in the group.
3. Once the view is consistent across all Content Routers in the cluster, one Content Router is designated the lead and sets the policy that the routers need to deploy in redirecting packets.
Also, you must perform these tasks to configure the routers that will become members of the service group:
For network configurations in which the Content Router sends to a target router a packet that needs to traverse an intervening router, the router being traversed must be configured to perform IP multicast routing. You must configure two components to enable traversal over an intervening router:
Routers and Content Routers become aware of one another and form a service group using a management protocol. Once the service group has been established, one of the Content Routers is designated to determine load assignments among the Content Routers.
If there is a group of Content Routers, the one seen by all routers and the one that has the lowest IP address becomes the lead Content Router. The role of this Content Router is to determine how traffic should be allocated across Content Routers. The assignment information is passed to the entire service group from the designated Content Router so that the routers of the group can redirect the packets properly and the Content Routers of the group can manage their load better.
WCCP Version 2 provides authentication that enables you to control which routers and Content Routers become part of the service group. You use passwords and the HMAC MD5 standard set by the ip wccp [password [0-7] password] command to control service group membership.
Cisco Express Forwarding (CEF) has been integrated into WCCP Version 2 and provides fast packet redirection.
WCCP Version 2 enables more TCP and UDP ports to have traffic redirected to the Content Router. Previously, Web-cached information could be redirected only if it was destined for TCP port 80. Many applications require packets intended for other ports to be redirected, for example, proxy-Web cache handling, FTP caching, FTP proxy handling, Web caching for ports other than 80, and RealAudio, video, and telephony applications. A UDP port is used for the interception of DNS packets for content routing.
Packets that the Content Routers do not service are tunneled back to the same router from which they were received. When a router receives a formerly redirected packet, it knows not to redirect it again.
The criteria for determining whether to redirect the traffic are:
Note that service information has been added to the protocol to indicate which service the WCCP messages refer to. This information is used to help verify that service group members are all using or providing the same service.
WCCP Version 2 filters packets to determine which redirected packets have been returned from the Content Router and which ones have not. It does not redirect the ones that have been returned because the Content Router has determined that the packets should not be routed. WCCP Version 2 returns packets that the Content Router does not service to the same router from which they were transmitted. Typical reasons why a Content Router would reject packets and initiate packet return are:
WCCP Version 2 has the capability to adjust the load being offered to individual Content Routers to provide more effective use of the resources available and at the same time help to ensure high quality of service to the clients. It uses three techniques to perform this task:
The following limitations apply to WCCP Version 2:
WCCP is implemented within "software-switching" paths of all of the supported platforms shown in Table A-1. It is available for process-, fast- and CEF-based forwarding paths. IOS software Release 12.0(11)S introduces a distributed CEF (dCEF) implementation for 75xx+VIP environments.
The Cisco Content Router 4400 supports only WCCP Version 2.
| Platform | IOS 11.1 CA | IOS 11.2 P | IOS 12.0(3)T | IOS 12.0(5)T |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Cisco 1600/1700 | n/a | n/a | n/a | v21 |
Cisco 2500 series | v12 | v1 | v2 | v1/v2 |
Cisco 4000 series | v1 | v1 | v2 | v1/v2 |
Cisco 4500 series | v1 | v1 | v2 | v1/v2 |
Cisco 4700 series | v1 | v1 | v2 | v1/v2 |
Cisco 5200 series | n/a |
|
|
|
Cisco 5300 series | n/a |
|
|
|
Cisco 6400 series |
|
|
|
|
Cisco 7200 series | v1 | v1 | v2 | v1/v2 |
Cisco 7500 series | v1 | v1 | v1 | v1/v2 |
Catalyst RSM |
|
|
|
|
Catalyst MSFC |
|
|
|
|
| 1v2 = WCCP Version 2 2v1 = WCCP Version 1 |
For descriptions of supported MIBs and how to use MIBs, see Cisco's MIB Web site on CCO at http://www.cisco.com/public/sw-center/netmgmt/cmtk/mibs.shtml.
None
None
Before you use WCCP Version 2, you must complete the following tasks:
You can configure a router to run the DNS boomerang, custom Web cache, and reverse proxy services associated with WCCP Version 2. The services can be configured simultaneously. Perform the following tasks to configure a cluster with multiple routers.
| Command | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
Step 1 | Router(config)# ip wccp {web-cache |
service-number} [group-address
groupaddress] [redirect-list access-list]
[group-list access-list] [password [0-7]
password]
| Turns the WCCP feature on or off for the specified service. |
Step 2 | Router(config-if)# ip wccp {web-cache |
service-number} redirect out
| Specifies "out" because in the future, WCCP may have the ability to redirect incoming packets as well as outgoing packets. |
Step 3 | Router(config-if)# ip wccp redirect
exclude in
| Allows inbound packets on this interface to be excluded from redirection. |
| Command | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
Step 1 | Router(config)# ip wccp 50
| Turns on the protocol for DNS packet redirection. |
Step 2 | Router(config)# interface type-number
| Specifies an interface for packet redirection. |
Step 3 | Router(config-if)# ip wccp 50 redirect out
| Enables the check on packets to determine whether they need to be redirected to a Content Router. |
| Command | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
Step 1 | Router(config)# ip wccp 50 group-address
groupaddress
| Configures the group address for the service group. |
Step 2 | Router(config)# interface type-number
| Specifies an interface that will listen for the multicast address. (For example, Eth 0, Eth0, Ser 0, Ser0, Eth 0/0.) |
Step 3 | Router(config-if)# ip wccp 50 group-listen
| Configures an interface on a router to enable or disable the reception of IP multicast packets for WCCP. |
| Command | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
Step 1 | Router(config)# ip wccp 50 group-list
access-list
| Indicates to the router which Content Router IP addresses to allow packets from. |
Step 2 | Router(config)# access-list access-list
number permit host host-address
| Creates an access list that enables or disables traffic redirection to the Content Router. |
| Command | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
Step 1 | Router(config)# ip wccp 50 password | Sets a password for the Content Router that the router is trying to access. |
| Command | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
Step 1 | Router(config)# ip wccp 50 redirect-list
access-list number
| Sets the access list used to enable redirection. |
Step 2 | Router(config)# access-list access-list
number deny host host-address
| Creates an access list that enables or disables traffic redirection to the Content Router. |
Console# show running-config
Building configuration...
Current configuration:
!
version 12.0
service timestamps debug uptime
service timestamps log uptime
no service password-encryption
service udp-small-servers
service tcp-small-servers
!
hostname router4
!
enable secret 5 $1$nSVy$faliJsVQXVPW.KuCxZNTh1
enable password alabama1
!
ip wccp subnet zero
ip wccp 50
ip domain-name cisco.com
ip name-server 10.1.1.1
ip name-server 10.1.1.2
ip name-server 10.1.1.3
!
!
!
interface Ethernet0
ip address 10.3.1.2 255.255.255.0
no ip directed-broadcast
ip wccp 50 redirect out
no ip route-cache
no ip mroute-cache
!
interface Ethernet1
ip address 10.4.1.1 255.255.255.0
no ip directed-broadcast
no ip route-cache
no ip mroute-cache
!
interface Serial0
no ip address
no ip directed-broadcast
no ip route-cache
no ip mroute-cache
shutdown
!
interface Serial1
no ip address
no ip directed-broadcast
no ip route-cache
no ip mroute-cache
shutdown
!
ip default-gateway 10.3.1.1
ip classless
ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 10.3.1.1
no ip http server
!
!
!
line con 0
transport input none
line aux 0
transport input all
line vty 0 4
password alaska1
login
!
end
Step 2 To view values associated with WCCP variables, enter the show ip wccp command. The following output is displayed:
Console# show ip wccp
Global WCCP Information:
Service Name: 50
Number of Content Routers:1
Number of Routers:2
Total Packets Redirected:198
Redirect access-list:-none-
Total Packets Denied Redirect:0
Total Packets Unassigned:0
Group access-list:11
Total Messages Denied to Group:0
Total Authentication failures:0
| Command | Purpose |
|---|---|
Router# show ip wccp
or
Router# show ip wccp {web-cache | 0-99}
| Displays global statistics related to WCCP. |
Router# show ip wccp
{web-cache | 0-99} detail
| Queries the router for information about which Content Routers the router has detected in a specific service group. The information can be displayed for either a Web cache or another service, which is indicated by a value of 99. |
Router# show ip interface
| Shows whether any ip wccp direct commands are configured on an interface. |
Router# show ip wccp {web-cache | 99}
view
| Displays which devices in a particular service group have been detected and which Content Routers are not visible to all other routers to which the current router is connected. The information can be displayed for either a Web cache or another service. |
This section provides the following configuration examples:
The following example shows a Web cache service configuration session:
configure terminal
ip wccp service 50
interface ethernet 0
ip wccp 50 redirect out
The following example shows how to register a router to a multicast address of 192.168.1.1:
configure terminal
ip wccp 50 group-address 192.168.1.1
interface ethernet 0
ip wccp 50 group-listen
To achieve better security, you can use a standard access list to notify the router which IP addresses are valid addresses for a Content Router attempting to register with the current router. The following example shows a standard access list configuration session where the access list number is 10 for some sample hosts:
configure terminal
access-list 10 permit host 10.1.1.1
access-list 10 permit host 10.1.1.2
access-list 10 permit host 10.1.1.3
ip wccp 50 group-list 10
The following example shows a WCCP Version 2 password configuration session in which the password is alabama2:
configure terminal
ip wccp 50 password alabama2
To disable caching for certain clients, servers, or client/server pairs, you can use WCCP access lists. The following example shows any requests coming from 10.1.1.1 or going to 10.2.2.2 will bypass the cache, whereas all other requests will be serviced normally:
configure terminal
ip wccp 50 redirect-list 120
access-list 120 deny host 10.1.1.1
access-list 120 deny host 10.2.2.2
access-list 120 permit host 10.1.1.3
The following example displays WCCP settings, using the show running-config command:
Console# show running-config
Building configuration...
Current configuration:
!
version 12.0
service timestamps debug uptime
service timestamps log uptime
no service password-encryption
service udp-small-servers
service tcp-small-servers
!
hostname router4
!
enable secret 5 $1$nSVy$faliJsVQXVPW.KuCxZNTh1
enable password alabama1
!
ip subnet-zero
ip wccp 50
ip domain-name cisco.com
ip name-server 10.1.1.1
ip name-server 10.1.1.2
ip name-server 10.1.1.3
!
!
!
interface Ethernet0
ip address 10.3.1.2 255.255.255.0
no ip directed broadcast
ip wccp 50 redirect out
no ip route-cache
no ip mroute-cache
!
interface Ethernet1
ip address 10.4.1.1 255.255.255.0
no ip directed-broadcast
no ip route-cache
no ip mroute-cache
!
interface Serial0
no ip address
no ip directed-broadcast
no ip route-cache
no ip mroute-cache
shutdown
!
interface Serial1
no ip address
no ip directed-broadcast
no ip route-cache
no ip mroute-cache
shutdown
!
ip default-gateway 10.3.1.1
ip classless
ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 10.3.1.1
no ip http server
!
!
!
line con 0
transport input none
line aux 0
transport input all
line vty 0 4
password alaska1
login
!
end
This section documents new or modified commands that configure the WCCP Version 2 feature.
In Cisco IOS Release 12.0(1)T or a later release of 12.0 T, you can search and filter the output for show and more commands. This functionality is useful when you need to sort through large amounts of output, or if you want to exclude output that you do not need to see.
To use this functionality, enter a show or more command followed by the "pipe" character (|), one of the keywords begin, include, or exclude, and an expression that you want to search or filter on:
command | {begin | include | exclude} regular-expressionFollowing is an example of the show atm vc command in which you want the command output to begin with the first line where the expression "PeakRate" appears:
show atm vc | begin PeakRateFor more information on the search and filter functionality, refer to the Cisco IOS Release 12.0(1)T feature module titled CLI String Search.
To remove Web Cache Communication Protocol (WCCP) statistics maintained on the router either for a particular service or for all the services, use the clear ip wccp EXEC command.
clear ip wccp {web-cache | service-number}
Syntax Description
web-cache Directs the router to remove statistics for the Web cache service. service-number Directs the router to remove statistics for a specified Web cache service. The number can be from 0 to 99. The DNS boomerang service is indicated by a value of 50.
Defaults
No default behavior or values.
Command Modes
EXEC
Command History
11.1 CA This command was introduced. 11.2 P This command was introduced. 12.0(3)T This command has been expanded to be explicit about service.
Release
Modification
Usage Guidelines
Use the show ip wccp and show ip wccp detail commands to display WCCP statistics.
Examples
clear ip wccp 50
Related Commands
ip wccp
show ip wccp
To direct a router to enable or disable the support for a Content Router service group, use the ip wccp global configuration command. To remove the ability of a router to control support for a service group, use the no form of this command.
ip wccp {web-cache | service-number} [group-address groupaddress] [redirect-list access-list] [group-list access-list] [password [0-7] password]
Syntax Description
web-cache Enables the Web cache service. service-number The identification number of the Web Cache Communication Protocol (WCCP) service being controlled by a router. The number can be from 0 to 99. The DNS boomerang service is indicated by a value of 50. group-address (Optional.) Directs the router to use a specified multicast IP address for communication with the WCCP service group. groupaddress (Optional.) A multicast address used by the router to determine which Content Router should receive redirected messages. redirect-list (Optional.) Directs the router to use an access list to control traffic redirected to this service group. access-list (Optional.) A string (not to exceed 64 characters) that is the name of the access list that determines which traffic is redirected to a Content Router. group-list (Optional.) Directs the router to use an access list to determine which Content Routers are allowed to participate in the service group. access-list (Optional.) A string (not to exceed 64 characters) that is the name of the access list that determines which Content Routers are allowed to participate in the service group. password (Optional.) A string that directs the router to apply MD5 authentication to messages received from the service group specified by the service name given. Messages that are not accepted by the authentication are discarded. 0-7 (Optional.) A value that indicates the HMAC MD5 algorithm used to encrypt the password. This value is generated when an encrypted password is created for the Content Router. password (Optional.) The password name that is combined with the HMAC MD5 value to create security for the connection between the router and the Content Router.
Defaults
This command is disabled by default.
Command Modes
Global configuration
Command History
12.0(3)T This command was introduced.
Release
Modification
Examples
The following example shows a router configured to run WCCP DNS boomerang service, using (listening to) the multicast address of 192.168.1.2:
ip wccp 50 group-address 192.168.1.2
Related Commands
ip wccp group-listen
To configure an interface on a router to enable or disable the reception of IP multicast packets for the Web Cache Communication Protocol (WCCP) feature, use the ip wccp group-listen interface configuration command. To remove control of the reception of IP multicast packets for the WCCP feature, use the no form of this command.
ip wccp {web-cache | service-number} group-listen
Syntax Description
web-cache Directs the router to transmit packets to the Web cache service. service-number Identification number of the Content Router service group being controlled by a router. The number can be from 0 to 99. The DNS boomerang service is indicated by a value of 50.
Defaults
This command is disabled by default.
Command Modes
Interface configuration
Command History
12.0(3)T This command was introduced.
Release
Modification
Examples
The following example shows that multicast packets have been enabled for DNS boomerang with an address of 192.168.1.2.
configure terminal
ip wccp 50 group-address 192.168.1.2
interface ethernet 0
ip wccp 50 group-listen
Related Commands
ip wccp
ip wccp redirect out
To configure an interface to enable or disable excluding packets received on an interface from being redirected to a Content Router, use the ip wccp redirect exclude in interface configuration command. To disable a router's ability to verify that only appropriate packets are being redirected to a Content Router, use the no form of this command.
ip wccp redirect exclude inSyntax Description
This command has no arguments or keywords.
Defaults
No default behavior or values.
Command Modes
Interface configuration
Command History
12.0(3)T This command was introduced.
Release
Modification
Usage Guidelines
Note that the command is global to all the services and should be applied to any inbound interface that has been configured to be excluded from redirection on an outbound interface that the traffic will traverse.
Examples
configure terminal
ip wccp 50
interface ethernet0
ip wccp redirect exclude in
Related Commands
ip wccp
ip wccp redirect out
To configure an interface to enable a router's ability to verify that appropriate packets are being redirected to a Content Router, use the ip wccp redirect out interface configuration command. To disable a router's ability to verify that only appropriate packets being redirected to a Content Router, use the no form of this command.
ip wccp {web-cache | service-number} redirect out
Syntax Description
web-cache Enables the Web cache service. service-number The identification number of the Content Router service group being controlled by a router. The number can be from 0 to 99. The DNS boomerang service is indicated by a value of 50.
Defaults
No default behavior or values.
Command Modes
Interface configuration
Command History
12.0(3)T This command was introduced.
Release
Modification
Examples
configure terminal
ip wccp 50
interface ethernet0
ip wccp 50 redirect out
Related Commands
ip wccp redirect exclude in
To change the WCCP version number, use the ip wccp version global configuration command.
ip wccp version {1 | 2}
Syntax Description
1 Enables WCCP Version 1 2 Enables WCCP Version 2
Defaults
Version 2 is the default.
Command Modes
Global configuration
Command History
12.0(5)T This command was introduced.
Release
Modification
Usage Guidelines
To use boomerang features, you must use WCCP Version 2. The default WCCP version is Version 2.
Examples
ip wccp version 2
To display status about any ip wccp direct commands configured on an interface, use the show ip interface EXEC command.
show ip interface [type-number]
Syntax Description
type-number (Optional.) The interface number whose status is being displayed.
Defaults
No default behavior or values.
Command Modes
EXEC
Command History
10.0 This command was introduced. 12.0 This command was enhanced. 12.0(3)T This command was enhanced to include status of the ip wccp redirect out and ip wccp redirect exclude add in commands.
Release
Modification
Usage Guidelines
The Cisco IOS software automatically enters a directly connected route in the routing table if the interface is usable. A usable interface is one through which the software can send and receive packets. If the software determines that an interface is not usable, it removes the directly connected routing entry from the routing table. Removing the entry allows the software to use dynamic routing protocols to determine backup routes to the network (if any).
If the interface can provide two-way communication, the line protocol is indicated to be up. If the interface hardware is usable, the interface is indicated to be up.
If you specify an optional interface type, you will see information on that specific interface only.
If you specify no optional arguments, you will see information on all the interfaces.
When an asynchronous interface is encapsulated with Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) or Serial Line Internet Protocol (SLIP), IP fast switching is enabled. A show ip interface command on an asynchronous interface encapsulated with PPP or SLIP displays a message indicating that IP fast switching is enabled.
Examples
The following example displays output from the show ip interface command, using the interface e3/0:
show ip interface e3/0
Ethernet3/0 is up
Internet address is 17.1.1.38/24
Broadcast address is 255.255.255.255
Address determined by non-volatile memory
MTU is 1500 bytes
Helper address is not set
Directed broadcast forwarding is enabled
Outgoing access list is not set
Inbound access list is not set
Proxy ARP is enabled
Security level is default
Split horizon is enabled
ICMP redirects are always sent
ICMP unreachables are always sent
ICMP mask replies are never sent
IP fast switching is enabled
IP fast switching on the same interface is disabled
IP Optimum switching is enabled
IP multicast fast switching is enabled
Router Discovery is disabled
IP output packet accounting is disabled
IP access violation accounting is disabled
TCP/IP header compression is disabled
Probe proxy name replies are disabled
Gateway Discovery is disabled
Policy routing is disabled
Network address translation is disabled
WCCP Redirect outbound is enabled
WCCP Redirect exclude is disabled
Table A-2 describes the fields shown in the example.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
Ethernet 3/0 is up | If the interface hardware is usable, the interface is marked "up." For an interface to be usable, both the interface hardware and line protocol must be up. |
Internet address | Shows the IP address of the interface. |
Broadcast address | Shows the broadcast address. |
Address determined by | Indicates how the IP address of the interface was determined. |
MTU | Shows the Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU), or the maximum size of packets allowed to be transmitted from the router to a Content Router. |
Helper address | Shows a helper address, if one has been set. |
Directed broadcast forwarding | Shows a secondary address, if one has been set. |
Outgoing access list | Indicates whether the interface has an outgoing access list set. |
Inbound access list | Indicates whether the interface has an incoming access list set. |
Proxy ARP | Specifies the IP Security Option (IPSO) security level set for this interface. |
Security level | Specifies the default IPSO security level for this interface. |
Split horizon | Specifies that routing updates sent to a particular neighbor router should not contain information about routes that were learned from that neighbor. |
ICMP redirects | Indicates whether Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) redirects will be sent on this interface. |
ICMP unreachables | Indicates whether unreachable messages will be sent on this interface. |
ICMP mask replies | Indicates whether ICMP mask messages that tests node reachability across the network will be suppressed. |
IP fast switching | Indicates whether fast switching has been enabled for this interface. It is generally enabled on serial interfaces, such as this one. |
IP fast switching on the same interface | Indicates whether fast switching has been disabled for this interface. It is generally enabled on serial interfaces, such as this one. |
IP Optimum switching | Indicates whether the IP optimum switching feature has been turned on. |
IP multicast fast switching | Indicates whether the IP multicast fast switching feature has been turned on. |
Router Discovery | Indicates whether the Cisco Discovery Protocol has been turned off. |
IP output packet accounting | Indicates whether the output packet counter has been turned off. |
IP access violation accounting | Indicates whether the feature that counts unauthorized access events on the router has been turned off. |
TCP/IP header compression | Indicates whether compression is enabled or disabled. |
Probe proxy name replies | Indicates whether HP Probe proxy name replies are generated. |
Gateway Discovery | Indicates whether the gateway discovery option has been turned off. |
Policy routing | Indicates whether the policy routing option has been turned off. |
Network address translation | Indicates whether the status of the network address translation feature has been enabled or disabled. |
WCCP Redirect outbound | Indicates whether packets received on an interface are redirected to a Content Router. This field can be enabled or disabled. |
WCCP Redirect exclude | Indicates whether packets targeted for an interface will be excluded from being redirected to a Content Router. This field can be enabled or disabled. |
Related Commands
show ip wccp
To display global statistics related to the Web Cache Communication Protocol (WCCP) feature, use the show ip wccp EXEC command.
show ip wccp {web-cache | service-number} [view | detail]
Syntax Description
web-cache Directs the router to display statistics for the Web cache service. service-number Identification number of the Content Router service group being controlled by a router. The number can be from 0 to 99. The DNS boomerang service is indicated by a value of 50. view (Optional.) Directs the router to display statistics for the WCCP view configuration. detail (Optional.) Directs the router to display statistics for the WCCP detail configuration.
Defaults
No default behavior or values.
Command Modes
EXEC
Command History
11.1 CA and 11.2 P This command was introduced. 12.0(3)T The user was allowed to query the router for the current global configuration information in use by either a single service or all services.
Release
Modification
Usage Guidelines
Use the clear ip wccp command to reset the counter for the "Total Packets Redirected" information.
Examples
The following example displays output from the show ip wccp command:
show ip wccp
Global WCCP Information:
Service Name: 50
Number of Cache Engines:1
Number of Routers:2
Total Packets Redirected:198
Redirect access-list:-none-
Total Packets Denied Redirect:0
Total Packets Unassigned:0
Group access-list:11
Total Messages Denied to Group:0
Total Authentication failures:0
Table A-3 describes the fields shown in the example.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
Service Name | Service that is detailed in the display output. |
Number of Content Routers | Number of Content Routers using the router as their home router. |
Number of Routers | Number of routers in the service group. |
Total Packets Redirected | Total number of packets redirected by the router. |
Redirect access-list | Name or number of the access list that determines which packets will be redirected. |
Total Packets Denied Redirect | Total number of packets that were not redirected because they did not match the access list. |
Total Packets Unassigned | Number of packets that were not redirected because they were not assigned to any Content Router. Packets may not be assigned during initial discovery of Content Routers or when a Content Router is dropped from a cluster. |
Group access-list | Content Router that is allowed to connect to the router. |
Total Messages Denied to Group | Number of messages disallowed by the router because they did not meet all the requirements of the service group. |
Total Authentication failures | Number of password authentication failures. |
The following example displays output from the show ip wccp 50 detail EXEC command. This command displays Content Router and WCCP router statistics for a particular service group:
show ip wccp 50 detail
WCCP Router information:
IP Address: 192.168.88.10
Protocol Version: 2.0
WCCP Cache-Router Information
IP Address: 192.168.88.11
Protocol Version: 2.0
State: Usable
Initial Hash Info: AAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAA
AAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAA
Assigned Hash Info: FFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFF
FFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFF
Hash Allotment: 256 (100.00%)
Packets Redirected: 21345
Connect Time: 00:13:46
Table A-4 describes the fields shown in the example.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
WCCP Router information | Header for the area that contains fields for the IP address and version of WCCP associated with the router connected to the Content Router in the service group. |
IP Address | IP address of the router connected to the Content Router in the service group. |
Protocol Version | Version of WCCP being used by the router in the service group. |
WCCP Cache-Router information | Fields for information on Content Routers. |
IP Address | IP address of the Content Router in the service group. |
Protocol Version | Version of WCCP being used by the Content Router in the service group. |
State | Indicates whether the Content Router is operating properly and can be contacted by a router and other Content Routers in the service group. |
Initial Hash Info | Initial state of the hash bucket assignment. |
Assigned Hash Info | Current state of the hash bucket assignment. |
Hash Allotment | Percentage of buckets assigned to the current Content Router. Both a value and a percentage figure are displayed. |
Packets Redirected | Number of packets that have been redirected to the Content Router. |
Connect Time | Length of time the Content Router has been connected. |
The following is sample output from the show ip wccp view EXEC command. In this case, the service number 50 has been specified.
show ip wccp service 50 view
WCCP Router Informed of:
192.168.88.10
192.168.88.20
WCCP Content Routers Visible
192.168.88.11
192.168.88.12
WCCP Content Routers Not Visible:
-none-
If any Content Router is displayed under the WCCP Content Routers Not Visible field, the Content Router needs to be reconfigured to add this router to it. Table A-5 describes the fields shown in the example.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
WCCP Routers Informed of | List of routers detected by the current router. |
WCCP Content Routers Visible | List of Content Routers that are visible to the router and other Content Routers in the service group. |
WCCP Content Routers Not Visible | List of Content Routers in the service group that are not visible to the router and other Content Routers in the service group. |
Related Commands
ip wccp detail
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Posted: Fri Dec 29 10:11:44 PST 2000
Copyright 1989-2000©Cisco Systems Inc.