|
|

A frame relay connection can be setup either from StrataView Plus or via the MGX 8220 command line interface.
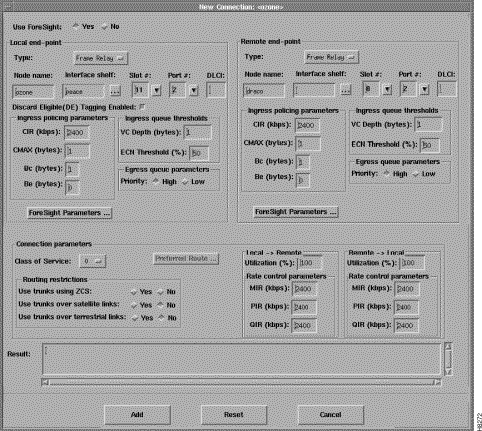
Setting up a frame relay connection is normally performed from StrataView Plus using the Connection Manager graphical user interface. An example of the StrataView Plus screen used for making an MGX 8220 frame relay connection is shown in Figure 5-1. For full details of how to set up a connection, refer to the Cisco StrataView Plus Operations Guide.
The CLI provides the capability to set up a variety of frame relay connections.
The following sections describe how to establish an end-to-end frame relay connection with network interworking and MGX 8220 FRSM end points.
Figure 5-2 shows two BPX nodes in a BPX network in which each of these two nodes is connected to an MGX 8220 shelf via an BNI card. User frame relay equipment, located at "A", is attached to one of the MGX 8220 shelves via a port on the shelf's FRSM card. User frame relay equipment, located at "B", is attached to the other MGX 8220 shelf. This chapter describes how a frame relay connection can be established to permit bidirectional communication between the frame relay equipment at "A" and "B".
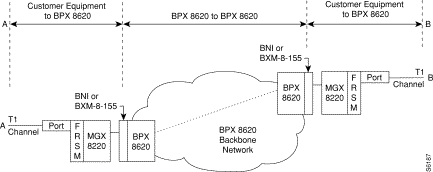
To make the connection, the path from "A" to "B" is made up of three segments as shown in Figure 5-2. When using CLI, each segment must be established and configured separately.
Two segments span from the FRSM to the BNM on the MGX 8220 shelves. These segments are part ATM and part frame relay with the conversion being made in the MGX 8220 shelves.
There is also an ATM trunk segment that spans the BPX backbone network from one of the
BPX nodes to the other BPX node, this segment terminates on a BNI feeder trunk in each node. This segment may include intermediary BPX nodes (not shown in the diagram).
The links between the segments must be configured properly so that the three segments make up one complete end to end connection from "A" to "B". This process consists primarily of ensuring that the VPI between the MGX 8220 shelf and it collocated BPX switch must contain the MGX 8220 slot number of the FRSM and the VCI must contain the logical channel number assigned to the virtual circuit.
This procedure must be performed on the MGX 8220 at BOTH ends of the connection ("A" and "B").
To establish an end to end frame relay connection, perform the following steps:
Step 2 If not enabled, enable the T1 line to be used for the frame relay connection by performing an addln command using the physical FRSM connector number (1 to 4) connected to the T1 line.
Step 3 If not configured, configure the T1 line to the frame relay equipment using the cnfln command. Specify parameters as appropriate.
If not enabled, enable the port to the frame relay equipment by performing an addport command using the parameters as follows:
For port number, specify an unused port number (1 to 96).
For line number, specify the FRSM line used to connect to the frame relay equipment
(1 to 4, with 1 being the top line).
For DS0 speed, specify either "1" for 56K or "2" for 64K bits per second.
For beginning timeslot, specify the beginning timeslot in the T1 or E1 line.
For number of timeslot, specify the number of consecutive T1 or E1 timeslots to be used for the connection.
Step 4 Enable the frame relay channel by performing an addchan command.
Select network interworking or service interworking in the chan_type parameter. 1 is for network interworking.
For channel number, enter a value between 16 and 271. THIS WILL BE THE SAME NUMBER SPECIFIED IN THE VCI FIELD TO/FROM THE BPX SWITCH.
For port number, enter the port number previously enabled.
For DLCI, enter a DLCI number to be used in communicating with the frame relay equipment.
At this point the MGX 8220 shelf segment is up with default parameters.
The following steps should be performed to establish the required BPX to BPX segments.
1. Perform an addcon command at one of the BPX nodes (not both) as follows.
2. Specify the other addcon parameters of bandwidth, and so on.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
MCR | Minimum Cell Rate |
PCR | Peak Cell Rate |
% Util | Percentage utilization of channel |
Minimum Cell Rate (MCR) is only used with ForeSight (ATFST).
MCR and Peak Cell Rated (PCR) should be specified according to the following formulae.
MCR = CIR *3/800 cells per second
PCR =AR * 3/800 cells per second but less than or equal to 6000
AR = Frame relay port speed in bps.
For example: | AR equals 64K, PCR = 237, or |
The above MCR and PCR formulae assume a fairly pessimistic frame size of 100 octects, however, even smaller frame sizes can result in worse case scenarios. For example:
For a frame size of 64 octects the PCR formula becomes | PCR = AR * 2/512 cells per sec |
For a frame size of 43 octects the PCR formula becomes | PCR = AR * 2/344 cells per sec |
% Util should normally be set to the same value as that used for the frame relay segments of the connection.
FRSM service interworking connections are made in the same manner as the network interworking connections except that chan_type in the MGX 8220 addchan command is specified as service interworking (transparent or translation) and the connection end that is remote from the MGX 8220 is an ATM UNI.
These services are setup the same as frame relay except the for port_type in the addchan command which is set as 2 for FUNI or 3 for frame forwarding.
AUSM connections can be setup either through StrataView Plus or via the CLI.
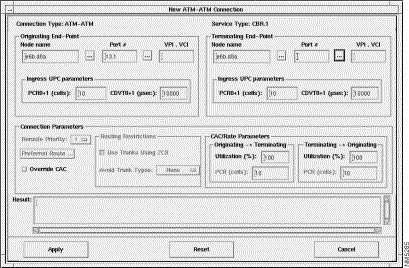
Setting up an AUSM connection is normally performed from StrataView Plus using the Connection Manager graphical user interface. An example of the StrataView Plus screen used for making an MGX 8220 ATM to ATM connection is shown in Figure 5-3. For full details of how to set up a connection, refer to the Cisco StrataView Plus Operations Guide.
Use the following sequence of commands to establish an ATM UNI/NNI connection using the AUSM card. The connection is between a T1 or E1 ATM UNI on the AUSM card and an
ATM service interface elsewhere in the IPX/BPX network.
1. Login to AUSM
2. Issue addln command, specifying the line/port number (between 1 and 4), 1 being the top line/port
3. If required, use cnfln command specifying line code, line length, and clock source
4. Issue upport command specifying the port to be upped
5. Use cnfportq to setup egress queues. Other than defaults you need to specify:
port number (1-4)
queue number (1-16)
queue priority
0 = disable queue
1 = high priority, always serve
2 = best available
3 = Min. guaranteed bandwidth
4 = Min. guaranteed bandwidth with max. rate shaping
5 =CBR with smoothing
service sequence number (1-16)
max. queue depth (1-8000)
CLP low threshold (1-8000)
CLP high threshold (1-8000)
EFCI threshold (1-8000)
6. Use addcon command to add the connection, specifying:
logical connection (LCN 16-271)
connection type (1 = vpc, 2 = vcc)
port number (1-4)
vpi (0-255)
vci (0-65535)
service type (1 = cbr, 2 = vbr, 3 = abr)
queue number (1-16)
7. For configuring UPC, use one of
cnfupc cbr
cnfupc vbr
cnfupc abr
8. Use cnfchanfst to configure ForeSight
9. If queue depths need to be changed, use cnfchanq command
The AUSM 8T1/E1 has a similar command sequence for adding ATM connections for ATM ports.
For IMA ports:
1. addln - on all constituent links
2. cnfln - if required
3. addimagrp - to add the IMA port follow the command sequence for the ATM ports
The AUSM 8Ti/E1 LCN range is 16-1015.
For the BPX segment, set up the connection in the same manner as that for FRSM. The connection type should be specified as ABR, CBR, or VBR to match the connection type used at the connection endpoint (for example, AUSM). The parameter values map directly from those specified at the connection endpoint.
Use the following procedure to setup a CESM connection.
Via the Command Line Interface (CLI)
Setting up a CESM connection is performed through the CLI. The procedure is to first add the line using the add line command (addln) and then add and configure a channel using the add channel (addchan) command. In the addchan command the channel number, the cell delay variation, the cell loss integration period and buffer size are all specified. The command sequence is:
1. addln <line #>
2. addchan "chan_num CDV CellLossIntegPeriod bufsize"
chan_num -- value ranging from 16 to 19
16 - line 1, 17 - line 2, 18 - line 3, 19 - line 4
CDV -- Cell delay variation: Range 1000-65535 microseconds
CellLossIntegPeriod -- Cell loss integration period:
Range 1000-65535 milliseconds
bufsize -- egress bufsize: Min value: 0.6*CDV-T1, 0.7*CDV-E1.
Max value: 65535, 0 to auto-compute
Example:
addln 1
addchan 16 10000 2500 0
Use the following procedures to setup a FRASM connection.
Setting up a FRASM connection is performed through the CLI. There are three basic types of connection which are:
For more information about these types of connections, refer to the "Frame Relay Access Service Module " section in Chapter 4, "MGX 8220 Service Modules".
For all three types of connections the procedure is to first establish a physical line for the connection using the add line command (addln) in which the physical back card port is specified and then to establish and configure ports on that line using the add port (addport) command for each port.
In the addport command the port number, line number, line speed, time slot, the port type, the encoding type, and the interface type are specified.
To complete the connection, additional commands are used which are specific to the type of connection being set up (FRAS BNN, STUN, or BSTUN).
To complete the FRAS BNN connection, proceed as follows:
1. Use the addln command to specify the physical port number (from 1 to 8) which is to be used for the FRAS BNN connection.
2. Use the addport command to specify a port number for the connection and to specify its parameters. Specify the port speed, the slot number, the encoding to be used and the type of
DS0 interface. The port type field is used to specify the connection as a FRAS BNN connection. The role (primary, secondary, and so forth) of the FRASM port to be used in the link protocol must be specified.
addport <port_num> <line_num> <line_speed> <begin_slot> <port_type> <port_role> <encoding> <interface>
where:
<port_num> | port number in the range 1-192 |
<line_num> | value ranging from 1 to 8 |
<ds0_speed> | 1 for 2.4K, 2 for 4.8K, 3 for 9.6K, 4 for 56K, 5 for 64Kbps |
<begin_slot> | time slot number in the T1 frame |
<port_type> | 1, 2, or 3: 1 = STUN, 2 = FRAS, 3=BSTUN |
<port_role> | 1, 2, 3, or 4: 1 = Primary, 2 = Secondary, 3 = Negotiable, |
<MUX encoding> | 1 or 2: 1 = NRZ, 2 = NRZI |
<MUX interface> | 1 or 2: 1 = DS0, 2 = DS0A |
3. Once the line and port have been specified, use the add link station command (addls) to specify the FRASM port link station address and xid. A link consists of two link stations and the connecting transmission medium. In order to start an SNA session a link between the two nodes needs to be established. In a FRAS BNN connection the SNA part of the connection is terminated at the FRASM; a session requires that the FRAS BNN port act as a link station. The link station name and the xid (exchange ID) are used during the process of establishing a link.
addls <port_num><lsaddress><xid>
<port_num> | port number in the range 1-192 |
<lsaddress> | LS address in the range 0x01-0xFE |
<xid> | 4-byte Hex number that is to be exchanged for this station in the range 0000-FFFFFFFF |
4. The add channel (addchan) command is used to specify the frame relay end of the connection. This consists of specifying the DLCI and committed rate for the channel.
addchan <chan_num> <port_num> <dlci_num> <cir>
where
<chan_num> | channel number is in the range 16-1015 |
<port_num> | port number is in the range 1-192 |
<dlci_num> | DLCI is in the range 0-1023 |
<cir> | committed information rate: 0-1536000 bps for T1; 0-2048000 bps for E1 (FRASM does not support E1) |
5. Use the add FRAS BNN route command (addfrasbnnroute) to establish a connection between the frame relay channel number and the link station.
addfrasbnnroute <port_num> <lsaddress> <chan_num> <lsap> <rsap>
<port_num> | port number of the FrasBNN connection to be routed in the range 1-192 |
<lsaddress> | address of the link station in the range 0x01-0xFE |
<chan_num> | channel number of the connection to be routed in the range 16-1015 |
<lsap> | number in the range 0x01-0xFF (even numbers only) |
<rsap> | number in the range 0x01-0xFF (even numbers only) |
To complete the STUN connections, proceed as follows:
1. Use the addln command to specify the physical port number (from 1 to 8) which is to be used for the STUN connection.
2. Use the add STUN group command (addstungroup) command to create a STUN group. This command is used to specify the group number and the protocol type. When a STUN connection is made, the connection is assigned to a group in the add STUN port command.
3. Use the addport command to specify a port number for the connection and to specify its parameters. Specify the port speed, the slot number, the encoding to be used and the type of
DS0 interface. The port type field is used to specify the connection as a STUN connection. The role (primary, secondary, and so forth) of the FRASM port to be used in the link protocol must be specified.
addport <port_num> <line_num> <line_speed> <begin_slot> <port_type> <port_role> <encoding> <interface>
where:
<port_num> | port number in the range 1-192 |
<line_num> | value ranging from 1 to 8 |
<ds0_speed> | 1 for 2.4K, 2 for 4.8K, 3 for 9.6K, 4 for 56K, 5 for 64Kbps |
<begin_slot> | beginning timeslot number in the T1 frame |
<port_type> | 1, 2, or 3: 1 = STUN, 2 = FRAS, 3=BSTUN |
<port_role> | 1, 2, 3, or 4: 1 = Primary, 2 = Secondary |
<MUX encoding> | 1 or 2: 1 = NRZ, 2 = NRZI |
<MUX interface> | 1 or 2: 1 = DS0, 2 = DS0A |
4. Use the add STUN port command (addstunport) to establish a group number for the connection.
addstunport<port_num><group_num>
where
<port_num> | port number in the range 1-192 |
<group number> | the group number to which the connection is to be assigned |
5. Once the group, line and port have been specified, use the add link station command (addls) to specify the FRASM port link station address and xid. A link consists of two link stations and the connecting transmission medium. In order to start an SNA session a link between the two nodes needs to be established. Since in a STUN connection the SNA can be terminated at the FRASM, a session requires that the FRAS BNN port act as a link station. The link station name and the xid (exchange ID) are used during the process of establishing a link.
addls <port_num><lsaddress><xid>
<port_num> | port number in the range 1-192 |
<lsaddress> | LS address in the range 0x01-0xFF. If virtual multidrop and |
<xid> | 4-byte Hex number that is to be exchanged for this station in the range 0000-FFFFFFFF |
6. Use the add channel (addchan)command is used to specify the frame relay portion of the connection. This consists of specifying the DLCI and committed rate for the channel.
addchan <chan_num> <port_num> <dlci_num> <cir>
where
<chan_num> | channel number is in the range 16-1015 |
<port_num> | port number is in the range 1-192 |
<dlci_num> | DLCI is in the range 0-1023 |
<cir> | committed information rate: 0-1536000 bps for T1; 0-2048000 bps for E1 (FRASM does not support E1) |
7. Use the add STUN route command (addstunroute) to establish a connection between the frame relay channel number and the link station.
addstunroute <port_num><lsaddress><chan_num><lsap>
<port_num> | port number of the STUN connection to be routed in the range 1-192 |
<lsaddress> | address of the SDLC LS in the range 0x01-0xFF |
<chan_num> | channel number of the STUN connection to be routed in the range 16-1015 |
<lsap> | number in the range 0x01-0xFF (even numbers only) |
To complete the BSTUN connections, proceed as follows:
1. Use the addln command to specify the physical port number (from 1 to 8) which is to be used for the BSTUN connection.
2. Use the add BSTUN group command (addbstungroup) command to create a BSTUN group. This command is used to specify the group number and whether local acknowledge is to be. When a BSTUN connection is made, the connection is assigned to a group in the add BSTUN port command.
3. Use the addport command to specify a port number for the connection and to specify its parameters. Specify the port speed, the slot number, the encoding to be used and the type of DS0 interface. The port type field is used to specify the connection as a BSTUN connection. The role (primary, secondary, and so forth) of the FRASM port to be used in the link protocol must be specified.
addport <port_num> <line_num> <line_speed> <begin_slot> <port_type> <port_role> <encoding> <interface>
where:
<port_num> | port number in the range 1-192 |
<line_num> | value ranging from 1 to 8 |
<ds0_speed> | 1 for 2.4K, 2 for 4.8K, 3 for 9.6K, 4 for 56K, 5 for 64Kbps |
<begin_slot> | time slot number in the T1 frame |
<port_type> | 1, 2, or 3: 1 = STUN, 2 = FRAS, 3=BSTUN |
<port_role> | 1, 2, 3, or 4: 1 = Primary, 2 = Secondary, 3 = Negotiable |
<MUX encoding> | 1 or 2: 1 = NRZ, 2 = NRZI |
<MUX interface> | 1 or 2: 1 = DS0, 2 = DS0A |
4. Use the add BSTUN port command (addbstunport) to establish a group number for the connection.
addbstunport<port_num><group_num>
where
<port_num> | port number in the range 1-192 |
<group number> | the group number to which the connection is to be assigned |
5. Use the add channel (addchan)command to specify the frame relay portion of the connection. This consists of specifying the DLCI and committed rate for the channel.
addchan <chan_num> <port_num> <dlci_num> <cir>
where
<chan_num> | channel number is in the range 16-1015 |
<port_num> | port number is in the range 1-192 |
<dlci_num> | DLCI is in the range 0-1023 |
<cir> | committed information rate: 0-1536000 bps for T1; 0-2048000 bps for E1 (FRASM does not support E1) |
6. Use the add BSTUN route command (addbstunroute) to establish a connection between the frame relay channel number and the 3270 control unit.
addbstunroute <port_num><cuaddress><chan_num><lsap>
<port_num> | port number of the BSTUN connection to be routed in the range 1-192 |
<cuaddress> | address of the control unit in the range 0x01-0xFF |
<chan_num> | channel number of the BSTUN connection to be routed in the range 16-1015 |
<lsap> | number in the range 0x01-0xFF |
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Posted: Mon Jan 15 16:30:05 PST 2001
All contents are Copyright © 1992--2001 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Important Notices and Privacy Statement.