|
|

This Troubleshooting appendix is divided into the following sections:
Problems with the StrataView Plus Workstation to DAS Server Shelf connection are divided into two categories:
When there is a problem with the StrataView Plus Workstation to DAS Server Shelf communication and they are connected over ethernet, the following is a list of things that you should check:
Step 1 Check the cabling between the StrataView Plus Workstation and a router and 10Base-T hub.
Step 2 Check the cabling between the hub or router and the DAS Server Shelf.
Step 3 If the DAS Server Shelf is on a subnet, make sure the IP Address is set correctly with respect to subnet masks.
Step 4 If the ethernet connection is through routers, make sure the routers are set up correctly.
Step 5 Check with your network system administrator to see if you need to modify the DAS Server Shelf's /etc/defaultrouter file to identify the router.
Step 6 Check with your network system administrator to see if you need to modify StrataView Plus Workstation's /etc/defaultrouter file to identify the router.
Step 7 Ping the StrataView Plus Workstation from the DAS Server Shelf:
ping hostname of StrataView Plus Workstation
then
ping IP address of StrataView Plus Workstation
If you can ping with the IP address but not with the hostname, then /etc/hosts has not been set up correctly.
Step 8 If you can talk to the StrataView Plus Workstation but not to the DAS (INS)Daemon software, make sure that the file /usr/net/fr/hosts also contains the IP address of the StrataView Plus Workstation.
Step 9 Repeat Step 7, but ping from the StrataView Plus Workstation.
When there is a problem with the StrataView Plus Workstation to DAS Server Shelf communication and they are connected via IP over frame relay, the following is a list of things that you should check:
Step 1 Check the cabling between the StrataView Plus Workstation and the router.
Step 2 Make sure that the router has been setup correctly, i.e., /etc/defaultrouter.
Step 3 Check the cabling between the router and the Cisco wide-area switch, i.e., make sure the router is connected to the Frame Relay network.
Step 4 Make sure the router's V.35 port and the remote DAS Server Shelf are on the same subnetwork. (Refer to this chapter, DAS Server Shelf Interface Connections.)
Step 5 Make sure there's a PVC between the router and the remote DAS Server Shelf and that this PVC is configured for at least 128 kbps of bandwidth.
Step 6 Use testcon to connect to test the PVC. (Refer to the Cisco WAN Switching Command Reference for more information about testcon.)
Step 7 From the StrataView Plus Workstation ping the remote DAS Server Shelf, by hostname, then by IP address.
Step 8 It may be necessary to setup a route from StrataView Plus to the remote DAS (INS) through the router as described in the chapter, DAS Server Shelf Interface Connections.
When there appears to be a problem with the PRI to DAS Server Shelf, check the following list of things:
Step 1 Ensure that the CSU connected to the Cisco wide-area switch circuit line interface (T1 or E1 FRP) is configured properly: ESF with B8ZS for T1; HDB3 with CCS for E1.
Step 2 Ensure that there is a PVC between the PRI port and the DAS Server Shelf with the correct logical channel (T1 = 24; E1 = 16) and a DLCI of 0 at the PRI end.
Step 3 Ensure that the PVC between the PRI and the DAS Server Shelf has been configured for a PIR, MIR, and QIR of 64 kbps.
Step 4 Ensure that the DAS Server Shelf has been configured for the correct Switch Type. (See the chapter, Understanding the DAS Command Line Interface for information on using the DAS (INS) Command Line Interface [INS_CLI].)
This section contains some generic hints for troubleshooting PVCs. These PVCs could be the signalling PVCs used to configure the DAS Dial-Up Frame Relay system, or the Dial-Up or Dial-Backup PVCs.
When there appears to be a problem with an existing PVC, try these things:
1 ) Use the dspportstats command to see if frames are being passed across the port. Reset the port stats counters with the clrportstats command. Look for frame errors. (The Cisco WAN Switching Command Reference describes this command in detail.)
2 ) Use the dspchstats command at both endpoints of the PVC. Reset the channel stats counters to with the clrchstats command. (The Cisco WAN Switching Command Reference describes this command in detail.)
3 ) Use the Frame Relay Status Utility on the DAS Server Shelf to verify data on the PVC, identified by its DLCI, at the DAS Server Shelf. (The next section describes Using the Frame Relay Status Utility.)
4 ) Ensure that the factory-configured file /usr/net/fr/ fr_config file appears as it is shown in Chapter 6, DAS Server Shelf Interface Connections.
5 ) Ensure that the /usr/net/fr/fr_conv file contains the IP address to DLCI mapping for any IP networks accessible across the frame relay network, as shown in chapter, DAS Server Shelf Interface Connections.
6 ) Log in as root on the DAS Server Shelf. Change directory to /opt/ins/log. List (ls) the directory. There should be a log file for each DLCI on the DAS Server Shelf serial frame-relay (RS422/V.35) port.
7 ) In the same directory look at the IFM_LOG file, by entering more IFM_LOG. If you see 0-length received frames, you can tell there is a problem with the frames received.
8 ) If no connections can be made, look in the insd.log, described in the section DAS (INS) Daemon Log, for a specific error message. Take the appropriate action.
9 ) If a Dial-Backup cannot be made, look in the insd.log, described in the section DAS (INS) Daemon Log, for a specific error message. Take the appropriate action.
10 ) If the DAS (INS) Daemon is not accepting calls, look in the insd.log, described in the section DAS (INS) Daemon Log, for a specific error message. Take the appropriate action.
11 ) If calls are not successfully processed, look in the insd.log, described in the section DAS (INS) Daemon Log, for a specific error message. Log into the node and use dspsnmp, described in the Cisco WAN Switching Command Reference, to ensure that the node allows SNMP sets. Look for hanging PRI B channel connections. Take the appropriate action.
12 ) If the original connection cannot be restored, look in the insd.log, described in the section DAS (INS) Daemon Log, for a specific error message. Take the appropriate action.
To use the Frame Relay Status Utility, follow these steps:
Step 1 Log into the DAS Server Shelf as root.
Step 2 Change directory to /usr/net/fr.
Step 3 Type frstatus and press Enter. The Frame Relay/PPP Status Report screen, as shown in Figure C-1, appears.
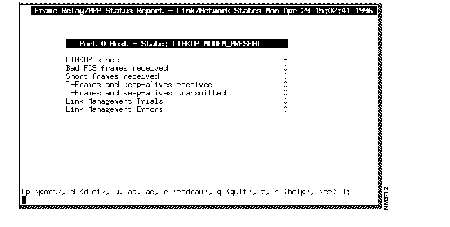
Step 4 Type ad and press enter to get a list of all the currently configured DLCIs. A DLCI Report screen, similar to Figure C-2, appears.
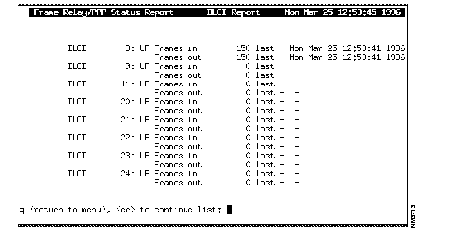
Step 5 Find the DLCI you wish to monitor and press q. You will return to the previous screen. Type d, followed by a space, then the number of the DLCI, and press Enter. A Frame Relay/PPP Status Report screen similar to Figure C-3, which includes Frames-in and Frames-out counters for the specified DLCI, will appear.
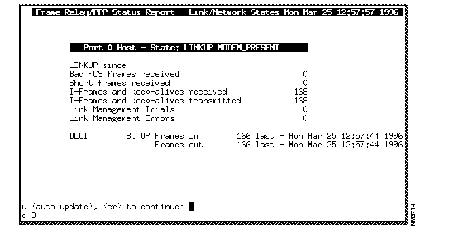
Step 6 To clear the Frames-in and Frames-out counters, press Enter, the q, and you will return to the DAS Server Shelf UNIX file directories. Type frroute and press Enter.
Step 7 To return to the Frame Relay Status Utility, type frstatus and press Enter. Type z and press Enter to zero the other Frame Relay Status counters.
Step 8 Type d, followed by a space, then the number of the DLCI, and press Enter. The Frame Relay Status Report screen will appear with all counters zeroed.
Step 9 Type u 1, to update the screen at one second intervals. Observe the seconds indicators in the current time at the top of the screen are incrementing. This screen is now being refreshed and you can observe the counters to detect what is happening on the selected DLCI.
DAS (INS) Daemon messages are stored in usr/users/svplus/insd.log on the StrataView Plus Workstation. These messages can also be helpful in resolving DAS Dial-Up Frame Relay Application problems. (The next sub-section lists all the insd.log Error Messages.)
To view the insd.log, follow these steps:
Step 1 Log into the StrataView Plus Workstation as root.
Step 2 Change directory to /usr/users/svplus/log.
Step 3 Look at the insd.log, which will appear similar to Figure C-4, with a UNIX-level command, such as more insd.log.

UNIX provides multiple ways to view the insd.log, such as
You can find out more about these methods of viewing the insd.log by using the UNIX man command. For example, man view will provide the details about view.
If you do use view to display the insd.log, the following list of commands are helpful:
| control-f | pages forward |
| control-b | pages backward |
| G | goes to the end of the file |
| :# | (where number is an integer) goes to a specific line number |
| /pattern | searches for the pattern, e.g., /ERROR will search for ERROR |
| :q! | quits the file |
| :set number | displays the file with line numbers |
| :set ic | makes the search pattern case insensitive |
Remember that UNIX is normally case sensitive.
If you happen to get stuck in an editing mode, use the esc (Escape) key to return to the command mode.
The DAS (INS) daemon error messages are listed in Table C-1. Some common abbreviations used in these error messages are:
| · emd | Equipment Manager daemon |
| · cmgrd | Connection Manager daemon |
| · ConnManager | Connection Manager daemon |
· <Connection end point 1.DLCI> represents a frame-relay connection end point | |
All mentions of records in these messages are related to the data base.
| Error Message | Description |
|---|---|
| ERROR: received invalid msg (integer value) | Invalid message received by a task. |
| ERROR: request from invalid station | An unconfigured DAS (INS) station (i.e., DAS Server Shelf) has made a service request. |
| ERROR: invalid calling number (character string) | A call request with an invalid ANI has been received.
Appropriate action: Configure the ANI. |
| ERROR: cannot find ANI end-point | Failed to find other end-point of the PVC that connects the DAS (INS) (i.e., DAS Server Shelf) to the PRI; i.e., cannot find the PRI end-point. |
| ERROR: can't send disconnect to INS. INS is down | DAS (INS) Daemon cannot find the DAS Server Shelf for a call it is trying to disconnect in the station list. The DAS (INS) Daemon initializes a disconnect when the PVCs of a call have failed. |
| ERROR: no conns for calling number (character string) | There are no Dial-Up/Dial-Backup connections for this ANI.
Appropriate action: Configure Dial-Up PVC. |
| ERROR: dialup conn to conn translation failure | Error in translating a dial-up connection to a connection record suitable for connection creation. |
| ERROR: setFrPort failure | Cannot set the Frame Relay Port to the attributes specified by the insAniConfig program.
Appropriate action: 1. Ensure that Cisco wide-area switch allows SNMP sets with dspsnmp command; 2. Look for hanging PRI B channels. |
| ERROR: back-up conn has no assoc | The Dial-Backup connection in the database is not associated to a standard frame relay connection.
Appropriate action: Set up an associate normal PVC for this Back-Up PVC. |
| ERROR: user_connection db has no assoc conn | Cannot find a matching standard frame relay connection for the Dial-Backup connection.
Appropriate action: Set up a normal Frame Relay connection. |
| ERROR: cannot find the conn in user_connection table using conn backup info | This is part of the failure recovery mechanism: if the normal connection is not in the network, but is found in the ins_conn_backup table, the DAS (INS) Daemon (insd) will assume that the previous call from the user may not have terminated appropriately. It will attempt to verify that the previous dial-up connection is removed and will attempt to remove it again if it is not.
This error message is then notifying you that a record in the ins_conn_backup table suggesting that there is still a connection in the network is not valid. |
| ERROR: Problem conn <Connection end point 1.DLCI> <Connection end point 2.DLCI> | This identifies a "problem connection"--one that was not previously removed successfully. |
| ERROR: connBackup create failure | This indicates a failure in creating a record of the standard frame relay connection that is about to be removed from the database.
Appropriate action: Look for duplicate entry in data base. |
| ERROR: connBackup record delete failure | Failure to delete a record in the ins_conn_backup database from a previous run that is no longer needed. |
| ERROR: assoc conn <Connection end point 1.DLCI> <Connection end point 2.DLCI> | Could not remove a standard frame relay connection that is associated with a Dial-Backup connection. |
| ERROR: activeConnDb create failure | Failure to create a record in the ins_active_conn table.
Appropriate action: 1. Look for duplicate entry in data base; |
| ERROR: activeConnDb ani (character string) remote record delete failure | Failure to delete a record in the ins_active_conn table. |
| ERROR: activeConnDb ani (character string) remote <Connection end point 1.DLCI> record create failure | Failure to create a record in the ins_active_conn table. |
| ERROR: conn <Connection end point 1.DLCI> <Connection end point 2.DLCI> create failure | Failure to create a connection. |
| ERROR: conn
<Connection end point 1.DLCI> | Failure to restore a standard frame relay connection after an attempt to replace it with a dial-backup connection has failed. |
| ERROR: conn record restore failure | Failure to remove a record from the ins_conn_backup database after successfully restoring the standard frame relay connection due to the back-up connection creation failure. |
| ERROR: no conn for assoc | There are no connections in the ins_conn_backup table to be restored for this ANI. |
| ERROR: active con ani (character string) <Connection end point 1.DLCI> record delete failure | Failed to remove a record from the ins_active_conn table. |
| ERROR: getNodeName on (integer value) failure | Cannot get node name using node id from database. |
| ERROR: getNodeInfo on (integer value) failure | Cannot get node info such as platform type from the database. |
| ERROR: <Connection end point1.DLCI> getFrPortSpeed | Cannot get the speed of the Frame Relay Port from the database. |
| ERROR: <Connection end point1.DLCI> getFrPortEcn failure | Cannot get the Frame Relay Port ECN threshold from the database. |
| ERROR: invalid 1_cir of 0 | Invalid CIR of 0 for the connection. |
| ERROR: invalid conn for dlci (integer value) | Cannot find a connection associated with the DLCI at the INS (i.e., DAS Server Shelf) end-point in order to resolve the PRI end-point. |
| ERROR: cannot get results of downFrPort | SNMP request failure. |
| ERROR: cannot get results of deleteFrPort | SNMP request failure. |
| ERROR: failed to down the port | SNMP request for downing a Frame Relay Port has failed. |
| ERROR: failed to delete the port | SNMP request for deleting a Frame Relay Port has failed. |
| ERROR: failed to add the port in (integer value) tries | Failed to add a Frame Relay Port. |
| ERROR: failed to up the port in (integer value) tries | Failed to up a Frame Relay Port. |
| ERROR: failed to set the port in (integer value) tries | Failed to set a Frame Relay Port's attributes. |
| ERROR: failed to add the port | Failed to set an MGX 8220 FRSM port. |
| ERROR: no stationList available | There are no INS (i.e., DAS Server Shelf) stations configured. |
| ERROR: connDb getList failure | Database failure on access to a list of possible connections leftover on the B-channel (that the call has been received). |
| ERROR: existing conn delete failure | Failed to delete leftover connections on the B-channel. |
| ERROR: lost cmgrd connection | No connection to Connection Manager daemon. |
| ERROR: cannot reconnect to cmgrd | Failed to reconnect to Connection Manager daemon. |
| ERROR: cannot connect to ConnManager | Failed to reconnect to Connection Manager daemon. |
| ERROR: time out on request | Connection Manager daemon response timed out. |
| ERROR: cmgrd returned (integer value) | Connection Manager daemon returned an ERROR (-1) or PARTIAL (1) error code. |
| ERROR: source (integer value) (character string) code (integer value), (character string) | Error code and strings returned by server processes. (Note that there can be multiple errors returned per request.) |
| ERROR: invalid cmgrd response | An unrecognized return value received from the Connection Manager daemon. |
| ERROR: cmgrd failure response (integer value) | Connection Manager daemon returned failure. |
| ERROR: cmgrd partial failure response (integer value) | Connection Manager daemon returned a partial failure; i.e., it is possible the request was only carried out partially--not all segments of the connection were successfully handled by the Connection Manager daemon. |
| ERROR: lost emd connection | No connection to Equipment Manager daemon. |
| ERROR: cannot reconnect to emd | Failed to reconnect to Equipment Manager daemon. |
| ERROR: timed out on request | Equipment Manager daemon timed out. |
| ERROR: emd returned (integer value) | Equipment Manager daemon response code. |
| ERROR: invalid emd response (integer value) | An unrecognized return value received from the Equipment Manger daemon. |
| ERROR: emd failure response (integer value) | Equipment Manager daemon returned failure. |
| ERROR: assoc_conn match failure | Failed to find an end-point match between a Dial-Backup connection and a connection in the database when attempting to use its remote DLCI. |
| ERROR: unsupported msg (integer value) (integer value) | An unsupported feature is being exercised by INS. |
| ERROR: invalid command line argument (character) | An invalid command line argument specified. |
| ERROR: cannot register with ILOG | Failed to establish communications with the ILOG broker. |
| ERROR: init_ipc_watchdog failure | IPC failure; cannot connect with socket daemon. |
| ERROR: gethostbyname failure | Gethostbyname function failure; cannot resolve the hostname. |
| ERROR: InitRpc failure | IPC failure; cannot initialize the IPC library. |
| ERROR: database open failure | Database name does not exist or the database daemons have not been started.
Appropriate action: Ensure that the DAS (INS) Daemon is installed on the SV + Workstation. |
| ERROR: cannot connect to EMDAEMON | Cannot connect to the Equipment Manger daemon. |
| ERROR: invalid asnType (integer value) | Error creating a varbind list; invalid data type. |
| ERROR: send failed | Error sending SNMP requests. |
| ERROR: request failed, error (integer value) index (integer value) reqId %lu | SNMP request failed. |
Alarms are generated by the INS processes in response to the detection of any fault conditions during normal operation of the INS. These alarms may be system or call related. As shown in Figure B-5, the alarms generated on the DAS Server Shelf by the INS processes are reported to the resident SNMP agent. These alarms are then transmitted via SNMP traps to "registered" RTM (robust trap mechanism) processes on StrataView Plus Workstations. Figure C-5 shows two StrataView Plus Workstations; one with an active DAS (INS) Daemon (INSD) and the other with a passive INSD. (The RTM trap manager processes on any StrataView Plus Workstation in the network may register with the INS for receiving the alarms.) In Figure C-5, the StrataView Plus Workstation with the passive INSD is also connected to a Customer network management systems (CNMS). The CNMS may then be informed or collect the INS alarm information from the appropriate RTM processes.
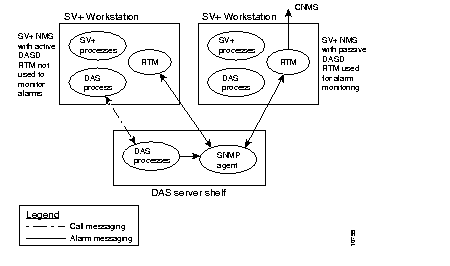
INS alarms include only essential and unique information. There is only a minimum of data that may be derived from other information. This reduces the real-time impact of alarm generation and transmission on system resources.
INS alarms are classified under two categories:
System alarms provide status information on individual system entities. Table C-2 lists and describes the INS system alarms. System alarm messages are sent as SNMP Traps. Each trap usually has a number associated with it corresponding to a value in the INS Management Information Base (MIB). The trap normally includes the system name, the host name of the DAS Server Shelf in ASCII, and a timestamp. The timestamp variable (insEventTimeStamp) is in 1/100 of a second, referenced to January 1, 1970 UTC. The traps will also include other variables that help define the alarm as necessary.
| TRAP | Description |
|---|---|
| coldStart | Standard SNMP trap generated whenever the DAS Server Shelf is powered on or reset. |
| v35InterfaceFailure | Generated whenever the DAS Server Shelf cannot communicate with the co-located IGX or Cisco wide-area switch. |
| v35InfterfaceCleared | Generated when the problem with the ipxCommunicationFailure has cleared. |
| insServerCommunicationFailure | Generated whenever there is a transition in the connectivity status between the INS and the INSD process running on an associated StrataView Plus Workstation.
Note: This alarm will be effective only if the alarm monitoring process (i.e., RTM in Figure B-5 is located on a separate StrataView Plus Workstation from the active INSD.) |
| insServerCommunicationFailureCleared | Generated when the connectivity status problem between the INS and the INSD process has cleared. |
| insAlarmStatusChanged | Generated whenever the insAlarmStatus changes. |
| insOperStatusChanged | Generated when the DAS Server Shelf Operation Status changes. |
| InsFRInterfaceFailure InsFRInterfaceFailureCleared | Generated whenever the state of the frame-relay link between the DAS Server Shelf and the Cisco wide-area switch changes. The link state is determined by LMI (Annex-D) protocol running on the Frame Relay Interface Card (RS422 to V.35). The frame-relay link is operated in the UNI mode. The LMI is configured such that the DAS Server Shelf port is considered to be the user-side, and the Cisco wide-area switch (IPX FRP) is the network side.
Even though Annex-D LMI issues and expects full status reports on all configured DLCIs, the status of individual virtual connections is not retrievable by the INS/DAS software from the Frame Relay Card software. Thus, this alarm is not generated on individual connection failures (see the isdnNetworkCommunicationFailure alarm.) This alarm is sent once for every transition in the frame-relay link status. |
| isdnNetworkComunicationFailure isdnNetworkCommunicationFailureCleared | Generated when the DAS (INS) processes detect a PRI failure.
In addition to the DAS Server Shelf system name and time stamp, this alarm will include: insDialupSwitchDlci variable-the DAS Server Shelf end of the PRI D-channel PVC; insPRIFailCause variable-1) Link down, 2)Process error. |
| insConfigCleared | Generated when the configuration of the DAS (INS) is cleared. |
| diskThresholdReached | Generated when one or more disk partitions have been filled beyond a configured threshold. (The DAS (INS) usually clears itself.) |
| diskThresholdReachCleared | Generated when the problem with the disk partitions being full has been fixed. |
Call progress alarms provide call progress information and flags call-related problems. Table C-3 lists and describes the DAS (INS) call progress alarms. Call progress alarm messages are sent as SNMP Traps. Each trap usually has a number associated with it corresponding to a value in the DAS (INS) Management Information Base (MIB). The trap normally includes the system name, the host name of the DAS Server Shelf in ASCII, and a timestamp. The timestamp variable (insEventTimeStamp) is in 1/100 of a second, referenced to January 1, 1970 UTC. The traps will also include other variables that help define the alarm as necessary.
|
|