|
|

Cisco MGM enforces security with user names and passwords, and manages user accounts individually and in groups. The use of access groups simplifies the process of assigning privileges to individual users because such groups enable you to define a set of privileges for each type of user.
Cisco EMF enforces security with the following types of accounts.
| Access Level | Account Type | Number of Users | Access Type | Command Groups |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Administrator | 1 | Read/Write | All categories |
2 | User defined | As many as needed | Read/Write | User can only invoke the categories of service defined by the access spec of its user group |
From Cisco EMF's Access application, an administrator can arrange Cisco EMF user accounts in groups. These groups can be used to model user roles; for example, administrators typically set up a user group for administrative users and system operators.
To add, change, or delete user accounts or groups, refer to the Cisco Element Management Framework User Guide.
You can change your own password. System administrators can change any password.
To make administrative password changes, follow these steps:
Step 2 From the Edit menu, select Change Password. For instance, to change the admin password, select Change Admin Password.
 |
Note The Change Admin Password option is available only to system administrators. |
The Change User Password window opens.
Step 3 Enter the existing password in the Old Password box.
Step 4 Enter a new password in the New Password box, and reenter the new password to verify your choice.
Step 5 Click Apply.
Step 6 If an invalid password is entered or the new password is not verified correctly, an error message is displayed. Click OK to try again.
When Cisco MGM communicates with Cisco MGX 8000 Series Carrier Voice Gateways, security is enforced with community strings. SNMP communities group workstations and servers that can manage the Cisco MGX 8000 Series gateways according to their access privileges.
For Cisco MGM to configure the gateways, both Cisco MGM and the gateways must agree on a community string. Community string configuration is a multistep process, starting with each gateway and ending with the Cisco MGM that manages them.
The following notes pertain to the configuring of community strings for Cisco MGM:
To configure Cisco MGM community strings, follow these steps:
Step 2 On the Cisco EMF Launchpad, click Viewer. The Cisco EMF MapViewer opens.
Step 3 Click the object tree, right-click on the desired site or object, and click Open SNMP Community String Config Dialog.
The SNMP Community String Config dialog box opens. (See Figure 7-1.)
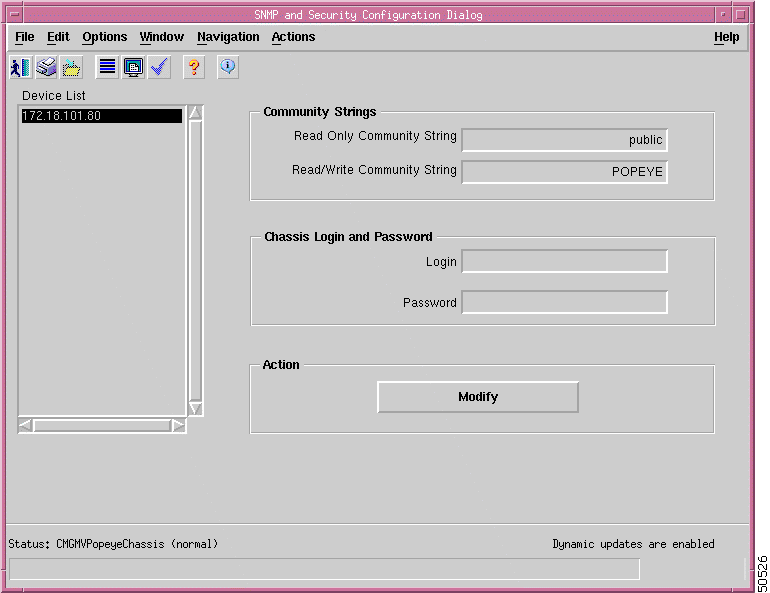
 |
Note For security reasons, the current community string values are not displayed. |
Step 4 Select one or more IP addresses from the list, using the Shift key to select multiple addresses.
Step 5 Enter a read-write community string in the Read Write Community String field.
Step 6 Click Modify Community Strings.
 |
Note Cisco EMF scrambles the community strings so you cannot view them later. |
A confirmation screen opens that reports successful and unsuccessful configuration attempts.
Step 7 Click Close.
 |
Note When subchassis synchronization is first invoked after auto-discovery, Cisco MGM uses the default read write community string: POPEYE. If the community string of the device is different from the default read write community string, objects under cards (lines and sessions) won't be found. In this case, configure the read write community string of the device in Cisco MGM to match the actual read write community string of the device, then perform a subchassis synchronization. For information about changing the default read write community string, refer to the "Inventory Discovery" section. |
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Posted: Thu Aug 8 22:10:31 PDT 2002
All contents are Copyright © 1992--2002 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Important Notices and Privacy Statement.