|
|

This management function makes it possible to observe the blocks exchanged on the lines when difficulties arise in the course of the procedure. The blocks observed are frames in the case of synchronous lines and messages in the case of asynchronous lines. The function never clears or resets the virtual circuit, transmits no interrupts, and ignores received data and interrupt packets. It deletes all exchanges acquired and not distributed upon reception of a reset.
The syntax of the access code is:
Refer to Chapter 1 for a detailed breakdown of this code.
· IS No | 03: BINARY MODE 04: ASCII MODE |
· PASSWORD: | Exists if configured (OO by default). |
· ACO No: |
|
The breakdown of the suffix is:
ACO = NL + NO (for a synchronous line) | |
ACO = NL + TM + NO (for the asynchronous line) | |
where: |
|
NL = | Number of the line (00 to 35) + virtual lines (65 to 124 and 160 to 239) of which the exchanges are to be observed. Exchange observation is possible only on line on which the function was called. |
NO = | Number of bytes to be observed for each exchange from 1 up to 40 bytes, starting from: |
| · the first byte of the frame for the synchronous lines, |
| · the first byte of the message for the asynchronous line. |
| · (NO = 40 default value). |
TM = | Type of message to observe for each exchange on an asynchronous lines, i.e.: |
| TM = A: observation of overall traffic |
| TM = C: observation of commands |
| TM = I: observation of indications |
| TM = E: observation of transmissions |
| TM = R: observation of receptions |
A message transmitted by the exchange observation function is in the following form:
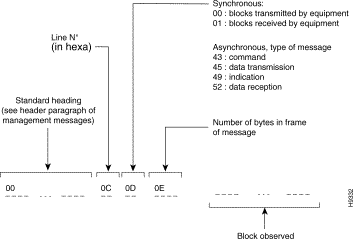

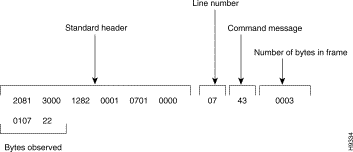
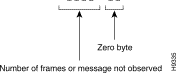
The number of messages or frames not observed are indicated to the operator by the display of the following type of message (when the standard heading is not present):
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Posted: Thu Jan 25 13:47:01 PST 2001
All contents are Copyright © 1992--2001 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Important Notices and Privacy Statement.