|
|

This section takes the form of data sheets describing the configuration.
These sheets give, for each class:
Figure 4-1 shows the lay out of a configuration data sheet.

General password to Configuration Function.
| C0 - R0 | Access key to configurator | ||
Parameters displayed |
Meanings of parameters |
Possible values | |
0 -------- | Password | Up to 8 alphanumeric characters. Default Password: CCLAER | |
| C1 - R0 | Name, code, date of configuration | ||
Parameters displayed |
Meanings of parameters |
Possible values | |
0 -------- | Name of configuration | Up to 8 alphanumeric characters. | |
| C1 - R1 | Use of lines | ||
Parameters displayed | Meanings of parameters | Possible values | |
0 -- | Parameters 0 to 35 | "1" = line configured as X.25 synchronous | |
|
| "14" = line configured as D-channel (ISDN) with or without PLL | |
The values "14" can ONLY be used for the line numbers 0, 3, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18, 21, 24, 27, 30 or 33.
The values "15" or "16" can NOT be used for the line numbers 0, 3, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18, 21, 24, 27, 30 or 33.
The values "23", "27" and "28" can be used only on LAN type lines (line 6) (LMX case).
Parameters to connect these lines are defined in C12 and C13.
| C1 - R2 | DNIC ZO No. of the equipment | ||
Parameters displayed | Meanings of parameters | Possible values | |
0 ------ COMMAND | Private-network address of equipment (FastPAD numbering). | 6 digits obligatory. | |
| C1 - R3 | Configuration version No. | ||
Parameters displayed | Meanings of parameters | Possible values | |
0 --- | Configuration counter. | Number automatically incremented by 1 each time configuration is modified | |
| C2 - R0 | Read-protected recurrences This recurrence is used to set up the read protection codes for certain classes and/or recurrences. | ||||
Parameters displayed |
|
| Meanings of parameters |
| Possible values; Example |
0 1 5 | -,-,-,-,-,- |
| CLASS 0 CLASS 7 CLASS 8 CLASS 9 |
These parameters correspond to the classes having the same numbers that define the configuration. |
-,-,-,-,-,- | | | Nos. of protected recurrences in case of | partial protection | (up to 5 recurrences)
1 = class completely protected 0 = class partly protected if no recurrence number follows
|
18 | -,-,-,-,-,- |
| CLASS 18 CLASS 24 |
|
Example: Class 10, completely protected Class 7, only recurrences 0 and 1 are protected. The other classes are not protected. |
| C2 - R1 | Write-protected recurrences Same as C2 - R0 but the classes and/or recurrences are write-rather than read protected | |
| C2 - R2 | General system parameters | |
Parameters displayed | Meanings of parameters | Possible values |
0 -- | Number of lines configured | 1 to 36 0 = contacting |
8 - 11 - 15 COMMAND | Type of language Reserved Reserved | 0 = french, 1 = english 0 = no, 1 = yes 0 = reduced |
* (Modulo 32) for the FastPADmp6.
| C2 - R3 | Call parameters | ||
Parameters displayed | Meanings of parameters | Possible values | |
0 -- | Data frame rejection threshold | This values are percentages of the memory resources | |
. . . 15- COMMAND | Reserved Reserved Reserved |
| |
This class corresponds to the characteristics of each management function of the equipment.
| C3 - R0 | Traffic generator function | ||
Parameters displayed | Meanings of parameters | Possible values | |
0 -,--,--,------ | Characteristics of traffic generator function | -,--,--,------ | |
|
| | | | | | | 1 to 98 = Transmission delay | | | |
| C3 - R1 | Observation function | ||
Parameters displayed | Meanings of parameters | Possible values | |
0 -,------ | Characteristics of observation | -,------ | |
|
| | | Password for access to function | |
| C3 - R2 | Statistics function | ||
Parameters displayed | Meanings of parameters | Possible values | |
0 -,--,------ | Characteristics of statistics function | -,--,------ | |
|
| | | Password to access the function | |
| C3 - R3 | Outstanding events function | ||
Parameters displayed | Meanings of parameters | Possible values | |
0 -,------ | Characteristics of outstanding events function | -,------ | |
|
| | to 6 alphanumeric characters. | |
| C3 - R4 | File transfer function | |
| I |
| C3 - R5 | Telemaintenance function | ------- Same as C3 - R3 |
| | |
| C3 - R6 | Configurator function | |
| C3 - R7 | Alarm function | ||
Parameters displayed | Meanings of parameters | Possible values | |
0 - | Characteristics of alarm function | - | | |
|
| |___ 0 = function not configured | |
| C3 - R8 | Alarm function subscribers | ||
Parameters displayed | Meanings of parameters | Possible values | |
0 ---------------- | Address of two subscribers that can be called by the alarm function of the equipment (private network or public data network). | Up to 15 digits. | |
| C3 - R9 | MMI (Man-Machine Interaction) | ||
Parameters displayed | Meanings of parameters | Possible values | |
0 -,------ | Characteristics of MMI function | -,------ | |
|
| | |_ Password for access to function | |
| C3 - R10 | Billing Same as C3 - R9 |
| C3 - R11 | Extended statistics Same as C3 - R9 |
| C3 - R12 | Reserved |
| C3 - R13 | MGS Trace |
| C3 - R14 | Motor Trace |
| C3 - R15 | DLM and DAR Same as C3 - R9 |
| C3 - R16 | MAP Same as C3 - R9 |
| C3 - R17 | Reserved |
| C3 - R18 | Reserved |
| C3 - R19 | Reserved |
This class defines the subscriber number and the internal service numbers contained in the access code to the management functions. The subscriber numbers (AB) are defined in R0.
The sub-addresses are the internal service numbers assigned to the parameters of R1 and R3 and correspond to the functions defined by the similar parameter of R2 and R4.
|
| R2 = Function No. |
R0 = First management functions | ____________ |
|
|
| R1 = Internal Service No. = IS No. |
|
|
|
|
| R4 = Function No. |
R0 = Second management functions | ____________ |
|
|
| R3 = Internal Service No. = IS No. |
| C4 - R0 | Internal subscriber Nos. (AB) | ||
Parameters displayed | Meanings of parameters | Possible values | |
0 99 - - - - - - - - - - | First internal subscriber number | 99 by convention | |
|
|
| |
| C4 - R1 | Sub-address of the second internal subscriber | ||
Parameters displayed |
| Meanings of parameters | Possible values |
0 | 03 04 05 06 14 | Internal service Nos. (IS Nos.) allowing distribution of messages transmitted by each management function in clear language or BINARY. | The user is not allowed t modify these parameters See Table 4-1 below. |
| C4R1 = SI No. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Name of the management function | BINARY | ASCII | CLEAR | Number |
Exchange observation | 03 | 04 | - | 128 |
Statistics | 05 | 06 | 14 | 129 |
Outstanding events | 01 | 02 | 15 or 16 | 130 |
Alarm | — | — | — | 131 |
Traffic generator | — | 00 | — | 132 |
File transfer | 09 | — | — | 133 |
Telemaintenance | 11 | 12 | — | 134 |
Configuration | — | — | 10 | 135 |
MMI | — | — | 17 | 136 |
Billing | 07 | 08 | — | 137 |
MAP | — | — | 18 | 155 |
DLM | 32 | — | — | 154 |
Extended statistics | — | — | 20 | 152 |
Rad (real path) | — | 47 | — | 48 |
Rad (user interface) | — | — | 48 | 48 |
| C4 - R2 | Function No./Sub-address of first internal subscriber | ||
Parameters displayed |
| Meanings of parameters |
|
0 | 128 128 129 129 129 | Number of the management functions to which the IS N0. of the similar parameters of R1 are assigned. |
|
| C4 - R3 | Sub-address of the second internal subscriber | ||
Parameters displayed | Meanings of parameters | Possible values | |
0 | 23 24 21 22 23 | Internal service Nos. (IS Nos.) allowing distribution of messages transmitted by each management function in clear language or BINARY. | The user is not allowed t modify these parameters See Table 4-2 below. |
| C4R3 = SI No. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Name of the management function | BINARY | ASCII | CLEAR | Number |
Exchange observation | 21 | — | — | 128 |
Statistics | 22 | — | — | 129 |
Outstanding events | 23 | — | 24 | 130 |
Alarm | — | — | — | 131 |
Traffic generator | — | — | — | 132 |
File transfer | — | — | — | 133 |
Telemaintenance | 25 | — | — | 134 |
Configuration | 26 | — | — | 135 |
MMI | — | — | — | 136 |
Billing | 27 | — | — | 137 |
MAP | 33 | — | — | 155 |
DLM | — | — | — | 154 |
Rad (real path) | — | 47 | — | 48 |
Rad (user interface) | — | — | 48 | 48 |
| C4 - R4 | Function No./Sub-address of second internal subscriber | ||
Parameters displayed |
| Meanings of parameters |
|
0 | 144 144 142 143 148 | Number of the management functions to which the IS N0. of the similar parameters of R3 are assigned. |
|
This class is used to configure the events for which the system must trigger an alarm message.
Several families of events are distinguished.
There is a recurrence for each family.
| C5 - R0 | Trouble report | ||
Parameters displayed | Meanings of parameters | Possible values | |
0 --,--,--,--,--,--,-- | Parameter 0: Refer to the management functions manual for the meanings of all the possible values (these values are in hexadecimal characters). | Refer to the Management Functions manual. | |
| C5 - R1 | Management family | ||
Parameters displayed | Meanings of parameters | Possible values | |
0 --,--,--,--,--,--,-- | Parameter 1: If the first value is 99, the following values are non-alarms lines (for example: P1 - 99, 2, 3, lines 2 and 3 do not trigger any alarm messages.
| Refer to the Management Functions manual. | |
| C5 - R2 | Signalling family | ||
Parameters displayed |
| Meanings of parameters |
|
0 --,--,--,--,--,--,-- |
| Refer to the Management Functions manual. | |
| C5 - R3 | Procedure family | ||
Parameters displayed | Meanings of parameters | Possible values | |
0 --,--,--,--,--,--,-- | See C5 - R0 and R1 | Refer to the Management Functions manual. | |
| C5 - R4 | Link family | ||
Parameters displayed | Meanings of parameters | Possible values | |
0 --,--,--,--,--,--,-- | See C5 - R0 and R1 | Refer to the Management Functions manual. | |
| C5 - R5 | Line family - Physical level | ||
Parameters displayed | Meanings of parameters | Possible values | |
0 --,--,--,--,--,--,-- | See C5 - R0 and R1 | Refer to the Management Functions manual. | |
| C5 - R6 | Asynchronous family - Protocol level | ||
Parameters displayed | Meanings of parameters | Possible values | |
0 --,--,--,--,--,--,-- | See C5 - R0 and R1 | Refer to the Management Functions manual. | |
| C5 - R7 | Asynchronous - Command level | ||
Parameters displayed | Meanings of parameters | Possible values | |
0 --,--,--,--,--,--,-- | See C5 - R0 and R1 | Refer to the Management Functions manual. | |
| C5 - R8 | Asynchronous family - Semantic level | ||
Parameters displayed | Meanings of parameters | Possible values | |
0 --,--,--,--,--,--,-- | See C5 - R0 and R1 | Refer to the Management Functions manual. | |
| C5 - R9 | SDLC family | ||
Parameters displayed | Meanings of parameters | Possible values | |
0 --,--,--,--,--,--,-- | See C5 - R0 and R1 | Refer to the Management Functions manual. | |
| C5 - R10 | VIP family | ||
Parameters displayed | Meanings of parameters | Possible values | |
0 --,--,--,--,--,--,-- | See C5 - R0 and R1 | Refer to the Management Functions manual. | |
| C5 - R11 | T.VIP, T.BSC and T.FRAD families | ||
Parameters displayed | Meanings of parameters | Possible values | |
0 --,--,--,--,--,--,-- | See C5 - R0 and R1 | Refer to the Management Functions manual. | |
| C5 - R12 | BSC 3270 and BSC 2780/3780 families | ||
Parameters displayed | Meanings of parameters | Possible values | |
0 --,--,--,--,--,--,-- | See C5 - R0 and R1 | Refer to the Management Functions manual. | |
| C5 - R13 | Multi link protocol (MLP) family | ||
Parameters displayed | Meanings of parameters | Possible values | |
0 --,--,--,--,--,--,-- | See C5 - R0 and R1 | Refer to the Management Functions manual. | |
CLASS 5 - (Continued)
| C5 - R14 | X.25/PSTN families | ||
Parameters displayed | Meanings of parameters | Possible values | |
0 --,--,--,--,--,--,-- | See C5 - R0 and R1 | Refer to the Management Functions manual. | |
| C5 - R15 | ESV securized VC family | ||
Parameters displayed | Meanings of parameters | Possible values | |
0 --,--,--,--,--,--,-- | See C5 - R0 | Refer to the Management Functions manual. | |
| C5 - R16 | N4 securized VC family | ||
Parameters displayed | Meanings of parameters | Possible values | |
0 --,--,--,--,--,--,-- | See C5 - R0 | Refer to the Management Functions manual. | |
| C5 - R17 | IR securized VC family | ||
Parameters displayed | Meanings of parameters | Possible values | |
0 --,--,--,--,--,--,-- | See C5 - R0 | Refer to the Management Functions manual. | |
| C5 - R18 | ISDN, channel D family | ||
Parameters displayed | Meanings of parameters | Possible values | |
0 --,--,--,--,--,--,-- | See C5 - R0 and R1 | Refer to the Management Functions manual. | |
| C5 - R19 | X.29 Rerouting family | ||
Parameters displayed | Meanings of parameters | Possible values | |
0 --,--,--,--,--,--,-- | See C5 - R0 | Refer to the Management Functions manual. | |
| C5 - R20 | Ethernet Bridge family | ||
Parameters displayed | Meanings of parameters | Possible values | |
0 --,--,--,--,--,--,-- | See C5 - R1 | Refer to the Management Functions manual. | |
| C5 - R21 | Frame relay DLC/Multi-frame family | ||
Parameters displayed | Meanings of parameters | Possible values | |
0 --,--,--,--,--,--,-- | See C5 - R0 and R1 | Refer to the Management Functions manual. | |
| C5 - R22 | Compression family | ||
Parameters displayed | Meanings of parameters | Possible values | |
0 --,--,--,--,--,--,-- | See C5 - R0 and R1 | See Management Functions manual. | |
| C5 - R23 | DLM family | ||
Parameters displayed | Meanings of parameters | Possible values | |
0 --,--,--,--,--,--,-- | See C5 - R0 and R1 | See Management Functions manual. | |
| C5 - R24 | Configurator family + On line file transfer | ||
Parameters displayed | Meanings of parameters | Possible values | |
0 --,--,--,--,--,--,-- | See C5 - R0 and R1 | See Management Functions manual. | |
| C5 - R25 | LMI family See C5R0 and R1. |
| C5 - R26 | PPP family See C5R0 and R1. |
| C5 - R27 | FRSNA family See C5R0 and R1. |
This table defines the configuration of passwords and codes allowing:
| C6 - R0 | List of NUIs = Network User Identifiers | ||
Parameters displayed | Meanings of parameters | Possible values | |
0 | BREI2H I2HEL ------
------ | The values given to these parameters are the passwords allowing local subscribers to send calls to remote equipments. | Up to 6 letters. |
| C6 - R1 | List of NUAs = Network User Address | ||
Parameters displayed | Meanings of parameters | Possible values | |
0 2728 | The values given to these parameters are the codes allowing called remote subscribers to identify calling local subscribers (for billing, for example). | 0 to 4 digits | |
Example of the command: N [NUI]-[COMMAND]
This class is used to configure the abbreviated codes allowing access to the management functions of the equipment via a local or remote asynchronous terminal.
Theses codes, defined by the parameters of R0, correspond to the complete codes defined by similar parameters defined in R1, R2 and R3.
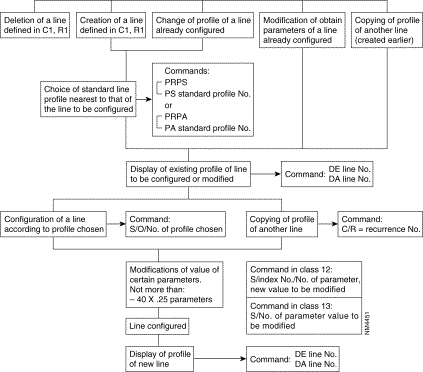
| C7 - R0 | Mnemonics | ||
Parameters displayed | Meanings of parameters | Possible values | |
0 | CONF--
------ | Abbreviated call codes | Up to 6 alphanumeric characters in capital. |
| C7 - R1 | Network address | ||||
Parameters displayed |
| Meanings of parameters
| Possible values; example (up to 15 digits). | ||
0 | 90000099------
--...-- | Complete address of equipment (private network DNIC Z0 AB or public network)
| |||
| C7 - R2 | Facilities | ||||
Parameters displayed |
| Meanings of parameters
| Example: Refer to R3 | ||
0 | 90000099------
--...-- | Complete address of equipment (private network DNIC Z0 AB or public network)
|
|
|
|
| Facility | Value |
Reverse charging | 01, 01, |
| C7 - R3 | Call data | ||||
Parameters displayed | Meanings of parameters | Possible values | |||
0 | 10CC--------
------------ | Additional call data | Up to 12 alphanumeric characters. | ||
|
|
| |||
| C7 - R4 | Minitel function key conversion |
|
| ||
Parameters displayed | Meanings of parameters | Possible values | |||
0 - | Processing carried out on the function keys of the Minitel, for each of the mnemonics stored in the R0. | 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 bit | |||
|
| not significant | PAD profile use | |||
| C7 - R5 | Call data in hexadecimal | ||
Parameters displayed | Meanings of parameters | Possible values | |
0 - | Additional call data | 12 hexadecimal characters max. | |
This class is used to configure the automatic subscriber call numbers with which a call is set up when an event is detected at the interface level.
| C8 - R0 | Address called | ||
Parameters displayed | Meanings of parameters | Possible values | |
0 | 90000099-------
--------------- | Complete address of equipment (private network DNIC Z0 AB or public network) | See C7 - R1 |
| C8 - R1 | Facilities | ||
Parameters displayed | Meanings of parameters | Possible values | |
0 . 199 | --,--,--,--
--,--,--,-- | Facilities contained in a call request packet.
| See C7 - R2 |
|
|
|
|
| C8 - R2 | Call data | ||
Parameters displayed | Meanings of parameters | Possible values | |
0. COMMAND | ------------ ------------ |
|
|
| C8 - R3 | Minitel function key conversion (Videotex line) - Number of the PVC (SDLC line) FRAD, Ethernet Bridge, IP Router | ||
Parameters displayed | Meanings of parameters | Possible values | |
0 - |
| See C7 - R4 | |
| | ||
| C8 - R4 | Call timing | ||
Parameters displayed | Meanings of parameters | Possible values | |
0 --- | Call retransmission timing value. | 0 to 99 (unit of 10 seconds) | |
|
|
| |
| C8 - R5 | Call data in hexadecimal | ||
Parameters displayed | Meanings of parameters | Possible values | |
0 00AF-------- | Additional call data | 12 digits in hexa. | |
| The table gives the relations between the value of the DAU and the type of encapsulation: |
| |
| Contents | Encapsulation | DAU value |
IP | MONO (RFC877) | CC | followed by |
* Example: CC, 08, 00
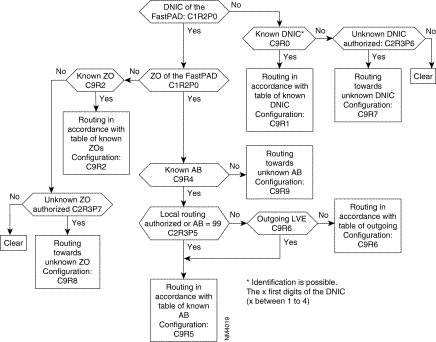
This class specifies the routing of calls between subscribers.
| C9 - R0 | List of known DNICs | ||
Parameters displayed | Meanings of parameters | Possible values | |
0 | 2222 1 3 444
---- | Each parameter corresponds to the 1, 2, 3, 4 first digits of the "called" address to be routed. | 1, 2, 3, or 4 digits (value 0 to 9) |
| C9 - R1 | Routing to known DNICs | ||
Parameters displayed | Meanings of parameters | Possible values | |
0 | -,-,-,--,--,--,--,--,--
-,-,-,--,--,--,--,--,-- | Each parameter corresponds to the type of routing chosen for the known DNICs listed in R0. | -,-,-,--,--,--,--,--,-- |
|
| | | | The max. number of lines per | |
CLASS 9 - (Continued) | Routing type | Examples: |
| 1 = routing on one line 2 = routing on n(*) lines, with:
3 = routing on n lines with equal distribution (shared). | 1,1,0,1 routing on line 1 3, 4, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4 |
4 = routing on n with:
= routing with DLM | 4, 4, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4 Preferred | line Backup lines: line 2 preferred, line 2 out of service line 3 out of service
4, 3, 0, 49, 1, 2
5, 3, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4 lines 1, 2, 3 share calls equally | |
| 6 = Shared routing (See type 3) 7 = Preferred routing (See type 4) | 6, 8, 0, 5, 2 |
| 8 = Preferential routing, module (See |
|
|
|
|
(*) Routing example (type 2) on 17 lines:
| |||
0 | 2,17,0,1,2,3,4,5,6 7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15, 16,17 | Caution: In this case, the DNICs of parameters 1 and 2 of recurrence 0 are not significant. |
|
| C9 - R2 | List of known ZOs | ||
Parameters displayed | Meanings of parameters | Possible values | |
0 -- | Numbers of other equipment known to the FastPAD belonging to the same private network. | 2 digits obligatory. | |
| C9 - R3 | Routing to known ZOs | ||
Parameters displayed | Meanings of parameters | Possible values | |
0 | -,-,-,--,--,--,--,--,-- -,-,-,--,--,--,--,--,-- | Type of routing chosen to the known ZOs configured in R2. | Same C9 - R1 |
| C9 - R4 | List of known ABs | ||
Parameters displayed | Meanings of parameters | Possible values | |
0 -- | Numbers of FastPAD parameters. | 2 digits mandatory | |
| C9 - R5 | Routing to known ABs | ||
Parameters displayed | Meanings of parameters | Possible values | |
0 COMMAND | -,-,-,--,--,--,--,--,-- -,-,-,--,--,--,--,--,-- | Type of routing chosen to the subscribers configured in R4. | Same C9 - R1 |
| C9 - R6 | Outgoing routing | ||
Parameters displayed | Meanings of parameters | Possible values | |
0 | -,-,-,--,--,--,--,--,-- -,-,-,--,--,--,--,--,-- | Type of routing chosen for equipment on a higher hierarchical level. | Same C9 - R1 |
| C9 - R7 | Routing to an unknown DNIC | ||
Parameters displayed | Meanings of parameters | Possible values | |
0 | -,-,-,--,--,--,--,--,-- -,-,-,--,--,--,--,--,-- | Type of routing chosen when the DNIC is unknown. | Same C9 - R1 |
| C9 - R8 | Routing to unknown ZO | ||
Parameters displayed | Meanings of parameters | Possible values | |
0 | -,-,-,--,--,--,--,--,-- ,-,-,--,--,--,--,--,- | Type of routing chosen when the ZO is unknown. | Same C9 - R1 |
| C9 - R9 | Routing to unknown subscriber | ||
Parameters displayed | Meanings of parameters | Possible values | |
0 1 | -,-,-,--,--,--,--,--,--,-- -,-,-,--,--,--,--,--,-- | Type de routing chosen when the AB is unknown. | Same C9 - R1 |
| C9 - R10 | Recurrence reserved |
| C9 - R11 | Incoming address conversion (Class 12 Par. 89) | ||
Parameters displayed | Meanings of parameters | Possible values | |
0 . | 1234AA--------- 9000------------ --------------- | Address conversion on incoming call accessing the FastPAD.
| Up to 15 numerical characters. |
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
| C9 - R12 | Outgoing address conversion (Class 12 par. 89) | ||
Parameters displayed | Meanings of parameters | Possible values | |
0 --------------- | Address conversion on outgoing call coming from the FastPAD | Same C9 - R11 | |
| C9 - R13 | Reserved |
| C9 - R14 | Reserved |
| C10 - R0 | PDN numbers | ||
Parameters displayed | Meanings of parameters | Possible values | |
0 | ---------------
--------------- | This number allows configuration of the lines connected to the public network (packet or circuit switching). |
|
| PSPDN case: Number, authorizing access to the public network | Up to 15 figures per parameter | |
| C11 - R0 | contacting index | ||
Parameters displayed | Meanings of parameters | Possible values | |
0 | -
- | (IZ) Number of digits forming the compacted ZO AB number | 1: digit from 1 to 4
|
|
|
| |
| C11 - R1 | Relations ZO AB and compacted ZO AB | ||
Parameters displayed | Meanings of parameters | Possible values | |
0 | ----,----
----,----- | Assignment of compacted ZO AB numbers to private-network ZO AB numbers | ----,---- |
|
|
| |
| C11 - R2 | Correspondence between DNIC/compacted DNIC (Subsequent availability) | ||
Parameters displayed | Meanings of parameters | Possible values | |
0 | ----,----
----,----- | Assignment of compacted DNICs for DNICs in clean language | 1 |
|
|
| |
This class contains the recurrences specifying the lines profiles:
This class contains the recurrences (R0 to R35) and per recurrence, a number of parameters which vary with the selected line extension profile.
The meanings and possible values of the parameters are defined in:
PROFILE OF A SYNCHRONOUS LINE | PROFILE OF A LINE EXTENSION |
A synchronous line is defined by an X.25 profile (class 12). | The VIP, BSC, PSTN and ISDN lines are defined by the VIP, BSC, PSTN and ISDN profiles in class 13 and one of the VIP, BSC, PSTN and ISDN profiles in class 12. |
PROFILE OF A B-CHANNEL (ISDN) |
|
The channel B profiles are defined in class 30 (X.25 profile without interface signals management). |
|
* Not available
CLASS 12 | ----- (Continued) |
|
|
| CONFIGURATION OF AN X.25 LINE OR A |
| CONFIGURATION OF AN AYNCHRONOUS LINE |
|
|
| The configuration of an asynchronous line is identical to that of a synchronous line, but an asynchronous X.25 profile (class 12) and an X.3 profile (class 13) must be chosen. |
Note To configure a new line or change the type of profile of an already configured line, it is necessary to: — have declared the considered line in class 1, recurrence 1, parameter 0 to 35, — selected an ITO or ISE type reset. |
CLASS 12 | ----- (Continued) |
|
|
CONFIGURATION OF A VIP or BSC LINE |
| CONFIGURATION OF A PSTN LINE |
|
| |
CONFIGURATION OF A FRAME RELAY LINE (FRA or FRTE) |
| CONFIGURATION OF A D-CHANNEL MANAGING THE PLLs (ISDN) |
|
| - in class 13 for the PLL numbers, the TEI value and the recurrence number in class 30 defining the dynamic X.25 parameters, |
|
| |
|
| |

| CLASS 12 CLASS 13 | ----- (Continued) |
| C12 - R0 to R35 |
|
| C13 - R0 to R35 |
|
Parameters displayed |
|
|
|
| |
|
| Only the modified parameters and their new values are displayed in the various recurrences of classes 12 and 13. |
index 0 is reserved for the no of the standard profile chosen
WARNING: concerning class 12 | 0 | -- --,-- --,-- --,-- --,-- |
| . | --,-- New value of parameter ¿---- No. of modified parameter |
| CLASS 12 CLASS 13 | ----- (Continued) |
Meanings and possible value of parameters
Appendix B for X.25, SDLC, VIP, BSC, frame relay and channel B or D (ISDN) parameters.
Appendix C for X.3 parameters.
Appendix D for PSTN parameters.
Appendix E for VIP parameters.
Appendix F for BSC 3270 parameters.
Appendix G for BSC 2780/3780 parameters.
Appendix H for transparent BSC parameters.
Appendix I for parameters related to PLL management in a D channel.
Appendix J for the parameters related to LMI management.
Profile of an asynchronous terminal
| C14 - R0 | X.3 customer profile | ||
Parameters displayed | Meanings of parameters | Possible values | |
0 | 80 | The X.3 profile defined in this recurrence has the standard profile No. 80. | See Appendix C. |
This class is used to compose the Videotex welcome page.
The messages configured in R1 are displayed with the attributes configured in R0.
| C15 - R0 | Message attributes | ||
Parameters displayed | Meanings of parameters | Possible values | |
0 --,--,--,--,--,--,--,--,--,-- | Each parameter corresponds to one block.
The blocks displayed are made up of up to 10 terms. These terms describe the attributes used for the composition of the welcome messages configured in R1. | --,--,--,--,--,--,--,--,--,-- 10 hexadecimal terms | |
|
| 1st term: Delimiter of beginning of positioning attributes | |
| C15 - R0 | (Continued) | ||
Parameters displayed | Meanings of parameters | Meaning of terms and possible values | |
|
|
| |
| C15 - R0 | (Continued) | ||
Parameters displayed | Meanings of parameters | Meaning of terms and possible values | |
|
|
| |
| C15 - R1 | Contents of message | ||
Parameters displayed | Meanings of parameters | Meaning of terms and possible values | |
0 | ------------
------------ | Each parameter corresponds to the parameter having the same number in R0 and is used to compose a welcome message. | Message consisting of up to 12 alphanumeric characters per parameter. |
This class is used to compose the PAD welcome page.
The messages configured in R1 are displayed with the attributes configured in R0.
| C16 - R0 | Message attributes | ||
Parameters displayed | Meanings of parameters | Meaning of terms and possible values | |
0 --,--,--,--,--,--,--,--,--,-- | Each parameter corresponds to one block. | --,--,--,--,--,--,--,--,--,-- | | | 10 hexadecimal terms | |
|
| When the terminal connected to the PAD permits, the attributes have the same meaning as those of a Prestel type Videotex terminal (see C15R0) | |
| C16 - R1 | Message contents | ||
Parameters displayed | Meanings of parameters | Possible values | |
0 ------------ | Each parameter corresponds to the parameter having the same No. in R0 and is used to compose a welcome message. | Message made up of 12 alphanumeric characters. | |
| C17 - R0 | Table of PVCs/DLCI | ||
Parameters displayed | Meanings of parameters | Possible values | |
0 --,-,----,---- | Configuration of Permanent Virtual Circuits or the DLCI number or LLC (virtual router). | --,-,----,---- | |
|
| | | | or emergency LLC No | |
| Note: |
| |
| C18 - R0 to R35 | CUG for the lines 0 to 35 | ||
Parameters displayed | Meanings of parameters | Possible values | |
0 --,--,-- |
| --,--,-- | | | | |
|
| | | |
| C18 - R36 | CUG for management functions | ||
Parameters displayed | Meanings of parameters | Possible values | |
0 | --,--,--
--,--,--, | Control of access to management functions is enhanced by up to 4 specific configurable CUGs configurable for each function. | --,--,-- | | | |
| (C0, R0): encoding is the same as other recurrences in the class. | Processing | |
| PARAMETERS | FUNCTIONS | |
|---|---|---|
0 to 3 | Observation |
|
4 to 7 | Statistics |
|
8 to 11 | Outstanding events |
|
12 to 15 | Alarms |
|
16 to 19 | Traffic generator |
|
20 to 23 | File transfer |
|
24 to 27 | Maintenance |
|
28 to 31 | Configuration |
|
32 to 35 | MMI |
|
36 to 39 | Billing |
|
40 to 43 | Extended statistics |
|
44 to 47 | Reserved |
|
48 to 51 | Reserved |
|
52 to 55 | MAP |
|
56 to 59 | | |
|
60 to 63 | | |
|
64 to 67 | | |
|
68 to 71 | | |
|
72 to 75 | | | Reserved |
76 to 79 | | |
|
80 to 83 | | |
|
84 to 87 | | |
|
88 to 91 | | |
|
92 to 95 | | |
|
| C18 - R37 to R49 | CUG for the virtuals functions | ||
Parameters displayed | Meanings of parameters | Possible values | |
0 | --,--,--
--,--,-- | See C18R0 to R35. | See C18R0 to R35. |
| C19 - R0 | SDLC clusters, VIP controllers, BSC 3270 and BSC 2780/3780 | |||
Parameters displayed | Meanings of parameters | Possible values |
| |
0 | --,---
--,--,--,-- | Position of clusters or controllers | SDLC |
|
|
| Position of automatic call (1 to 200) defined in |
| |
|
| | | if = 0 polling station | or station |
| |
| C19 - R0 | (Continued) | |||
Parameters displayed | Meanings of parameters | Possible values | ||
|
| BSC 3270 | ||
|
| | | | C | ||
|
| A, B and C are the terminal addresses to be used in BSC 3780; in BSC 2780, these bytes are not used.
|
| |
| C20 - R0 | Modem initialization table | ||
Parameters displayed | Meanings of parameters | Possible values | |
0 | ----...---- ----...---- ----...---- | Each parameter stands for a string of characters allowing to initialize the modem. | A string contains up to 50 alphanumeric characters. |
| C21 - R0 | 1st XID frame | ||
Parameters displayed | Meanings of parameters | Possible values | |
0 | ----...----
----...---- | A XID frame can contains from 0 to 256 bytes; 10 parameters of 26 bytes each are use to describe it. | Each parameter contains up to 26 hexadecimal characters. |
| C21 - R2 | 3rd XID frame |
| C21 - R2 | 3rd XID frame |
| C21 - R3 | 4th XID frame |
| C22 - R0 | X.121 address table | ||
Parameters displayed | Meanings of parameters | Possible values | |
0 | 1234567-------- 891011==1415---- 19>----------- ;
--------------- | Each parameter corresponds to an X.25 address. It is matched with the equivalent parameter number of recurrences 1 and 2. | The X.121 address is coded in quartets on 8 bytes. |
|
| The ">" character is used as an extraction marker. The digits to the left of this marker constitute a prefix to be ignored. | |
| C22 - R1 | PNTN/ISDN E.164 address table | ||
Parameters displayed | Meanings of parameters | Possible values | |
0 | 12345678 4629 45361521 112233== 46879656:1234 | In the case of conversion without extraction, the parameter corresponds to an E.164 or PSTN number. | The E.164 or PSTN address is coded in quartet on 14 bytes (number + sub-address). |
| represent respectively the X.121 address and the behavior. | < : pulse dialling | |
| C22 - R1 | (Continued) | ||
Parameters displayed | Meanings of parameters | Possible values | |
| Case of ISDN on outgoing call:
|
| |
| C22 - R1 | (Continued) | ||
Parameters displayed | Meanings of parameters | Possible values | |
| Case of ISDN: checking of E.164 address on incoming call.
| When this address begins with the ";" character, the behavior defined in recurrence 2 is applied to all calls, regardless of the caller, even if it is not furnished by the network. | |
CLASS 22 - (Continued)
| C22 - R2 | Additional information on outgoing and incoming call | ||
Parameters displayed | Meanings of parameters | Possible values | |
0 | -,-,-,-,-,-,-,-
-,-,-,-,-,-,-,- | These parameters define the behavior to be adopted on outgoing and incoming calls. | 8 bytes defined as follows: | | | | | | | | |
| When these options are not defined, a default behavior is adopted:
| | | | Type of protocol 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 bit | |
|
| A5 - Number of attempts associated with the ISDN number (multiple backup)
|
|
| C22 - R2 | (Continued) | ||
Parameters displayed | Meanings of parameters | Possible values | |
|
| byte 2: | |
|
| byte 3: | |
| C22 - R2 | (Continued) | ||
Param. displayed | Meanings of parameters | Possible values | |
|
| Action 2: Direction assigned to ISDN number (towards an MLP bundle) (not used for PSTN) | |
| C22 - R2 | (Continued) | ||
Parameters displayed | Meanings of parameters | Possible values | |
|
| Action 4: Extraction of E.164 address from X.25 address of call request packet | |
| C22 - R2 | (Continued) | ||
Parameters displayed | Meanings of parameters | Possible values | |
|
| Action 6: Number of attempts associated with the last number of the ISDN number list (multiple backup) (not used for PSTN) . . . . . . . 7F = 15 Highest priority | |
| C20 - R0 | Flow control | ||
Parameters displayed | Meanings of parameters | Possible values | |
0 1 | 4,4,3,3,2,2,2,2,2,2, -,-,-,-,-,-,-,-,-,- | Each parameter has 10 packet windows sizes (values from 1 to 7) corresponding to the 10 possible packet lengths (16, 32, 64, 128, 256, 512, 1024, 2048, 4096, 8192). | P0 = default value |
| C24 - R0 | Internal subscriber of management functions |
This recurrence is defined the same way a recurrence in C12 is defined and it uses the X.25 profile 06.
|
Parameters displayed |
|
|
|
| |
|
| Only the modified parameters and their new values are displayed in the various recurrences of class 24. |
Index 0 is reserved for profile No. 06.
WARNING: concerning class 24. | 0 | 06 |
The characters in the left-hand column on the screen are no longer the parameter nos. but the positioning indices of modified parameters | 34 . | --,-- |
|
| . |
Attention ! Barring exceptions, the parameters can not be modified.
C24 - R1 = ESV-N4 securized lines with profile number 45.
C24 - R2 = IR securized lines with profile number 46.
C24 - R3 = X.29 rerouting with profile number 81.
C24 - R4 = Compression with profile number 96.
C24 - R5 = DLM with profile number 110.
C24 - R6 to R8 = Virtual router (FastPAD modules) with profile number 112.
C24 - R9 = Reserved
Any modification of this class leads to a total reset (ITO) of the equipment.
| C25 - R0 to R8 | MLP line bundles |
|
|
Parameters displayed | Meanings of parameters | Possible values | Example
|
0 - | Bundle function number defining the main line (number of main line) | 0 to 35 01to 32 |
32 32 20 |
17 ---- 18 --- 19 --- 20 --- 21 - 22 --- 23 --- COMMAND | MT1 frame loss time-out Supervision time-out, reset MPL, MT3 Line out of service to MT4 Maximum number of frames sent on a link Reserved Transmission of restart upon reception of MLP reset TNS3 level 3 supervision time-out | 01 to 255 steps = 1 S 00 to 255 steps = 1 S 001 to 255 - 0 = NO 1 1 = YES 000 to 255 (step = 10 S) (if 000 = supervision not active) | 10 40 3
1
10 10 |
Remarks: |
|
| |
|
| |
Important: | MLP parameters must be symmetrical at the two ends of the bundle. |
|
| C26 - R0 | |||
Parameters displayed | Meanings of parameters | Possible values | |
0 --------- | Only the following combinations are managed:
| A Reserved | |
Ex : | Parameter 0 | : | DACE90402180BFF701000 | X.25 field: E called party address |
| . DA | : | Destruction of calling address | F Facility |
| . CE90402180 | : | Change the called address to 90402180. |
|
| . BF701000 | : | Addition of reliability 701000 at output of switch. |
|
This class contains the recurrences (R0 to R15) defining the dynamic connection parameters of the packets in B or D channels or frame relay.
This class also contains the static connection, parameters of the PLLs of the network FR (FRTE). The lines making reference to it are defined in class 32, recurrence 1.
These recurrences are defined the same way as a recurrence in class 12.
Parameters displayed |
|
|
|
| |
|
| Only the modified parameters and their new values are displayed in the various recurrences of class 30. |

Index 0 is reserved for the profile number
WARNING: concerning class 30 |
| 0 -- |
|
| 3 . . |
|
| . |
The meaning of the values of parameter values are given in AppendixB.
| C31 - R0 | Reserved | ||
| C31 - R1 | Reserved | ||
| C31 - R2 | Reserved | ||
| C31 - R3 | Reserved | ||
| C31 - R4 | Reserved | ||
| C31 - R5 | Reserved | ||
| C31 - R6 | Reserved |
| C31 - R7 | Definition of IP addresses on WAN interface | ||
Parameters displayed | Meanings of parameters | Possible values | |
0 | --,--,--,--
--,--,--,-- | Primary IP addresses on WAN side. | 4 bytes in decimal separated by commas. |
| C31 - R8 | Definition of IP addresses on LAN interface | ||
Parameters displayed | Meanings of parameters | Possible values | |
0 | --,--,--,--
--,--,--,-- --,--,--,-- | Primary IP address of router on LAN side. | 4 bytes in decimal separated by commas. |
| C31 - R9 | Reserved | ||
| C31 - R10 | Reserved | ||
| C31 - R11 | Definition of LAN interfaces | ||
Parameters displayed | Meanings of parameters | Possible values | |
0 | --,--,--,--,--,-- | Definition of primary and secondary interfaces on LAN side, of associated LLC Helpers and type of encapsulation. | --,--,--,-- reserved |
|
| | | | |
| C31 - R12 | Table of minimum IP addresses | ||
Parameters displayed | Meanings of parameters | Possible values | |
0 | --,--,--,-- | IP address defining the minimum of an address range. | 4 bytes in decimal separated by commas. |
| C31 - R13 | Table of maximum IP addresses | ||
Parameters displayed | Meanings of parameters | Possible values | |
0 | --,--,--,-- | IP address defining the maximum of an address range. | 4 bytes in decimal separated by commas. |
| C31 - R14 | IP routing table (to WAN) | ||
Parameters displayed | Meanings of parameters | Possible values | |
0 | --,---,--
--,--,--, -- | Definition of IP address ranges and of associated LLC. | --,---,-- |
|
| R13 (1 to 200) | |
| C31 - R15 | Default routing | ||
Parameters displayed | Meanings of parameters | Possible values | |
0. | --- | Definition of default route. | --- |
| C31 - R16 | Reserved | ||
| C31 - R17 | Reserved | ||
| C31 - R18 | Reserved | ||
| C31 - R19 | List of community names for SNMP | ||
Parameters displayed | Meanings of parameters | Possible values | |
0 | ------... | Community name for reading only of MIB. | String of characters up to 14 bytes. |
| C31 - R20 | Table of IP address of SNMP managers | ||
Parameters displayed | Meanings of parameters | Possible values | |
0 | --,--,--,--,-- | IP address of managers authorized to use the SNMP agent and associated community name. | --,--,--,--,-- |
| C31 - R21 | Table of broadcast IP addresses for SNMP traps | ||
Parameters displayed | Meanings of parameters | Possible values | |
0 | --,--,--,-- | IP address for traps. | 4 bytes in decimal separated by commas. |
| C31 - R22 | Value of ports | ||
Parameters displayed | Meanings of parameters | Possible values | |
0 | ---- | UDP port No. for SNMP. | 2 bytes in hexadecimal. |
| C31 - R23 | Reserved | ||
| C32 - R0 | a = line,, type, priority (optional) | ||
Parameters displayed | Meanings of parameters | Possible values | |
0 | --,,----,-
--,,---- | PLL. | ---,,----,- |
|
| | | |
| C32 - R1 | b = line, PLL, rec C30 | ||
Parameters displayed | Meanings of parameters | Possible values | |
0 | --,,----,--
--,-,---- | PLL. | ---,-,----,-- |
|
| | Type of PLL | |
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Posted: Thu Jan 25 13:43:45 PST 2001
All contents are Copyright © 1992--2001 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Important Notices and Privacy Statement.