|
|
Because the DPA 7630/7610 depends on information from the Octel voice messaging system and Cisco CallManager, you must verify that these systems are set up properly before configuring the DPA 7630/7610. You must also obtain some information from these systems to set up the DPA 7630/7610.
This guide does not contain details about configuring the Cisco CallManager and Octel systems. Refer to the documentation provided with those systems for installation and configuration instructions.
These sections provide details about the configuration requirements on the Cisco CallManager and Octel systems:
Cisco CallManager recognizes the DPA 7630/7610 as another IP telephony device. So, to add the device to the database, you need some information from the DPA 7630/7610. Additionally, to set up the DPA 7630/7610, you need information from both the Cisco CallManager and Octel systems. Refer to Table 3-1 for an overview of the tasks and information you need from them to configure the DPA 7630/7610.
| Task | For More Information | |
|---|---|---|
| Cisco CallManager Configuration | ||
q | Add the DPA 7630/7610 to the Cisco CallManager database. | See "Adding the DPA 7630/7610 to Cisco CallManager" section. |
q | Configure the ports from the DPA 7630/7610 as Cisco IP Phones in Cisco CallManager. | |
q | Verify that the options for enabling and disabling MWI on the Cisco IP Phones are configured in Cisco CallManager. | |
q | Verify that the voice mail hunt group is set up properly. | |
| Octel Configuration | ||
q | Set dialing sequence for message waiting indicator. | See the "Setting Dialing Sequence for Message Waiting Indicator" section. |
q | Determine incoming call method. | |
q | Assign lines to handle incoming calls, outgoing calls, and MWI commands. | See the "Assigning Incoming, Outgoing, and MWI Lines" section. |
The DPA 7630/7610 connects to Cisco CallManager to provide the following capabilities:
When reviewing the following tasks, if you need additional instructions, refer to the Cisco CallManager Administration Guide or the online help in the Cisco CallManager application:
If you are using Cisco CallManager clusters, note that MWI commands do not propagate across inter-cluster links. The DPA 7630/7610 can set MWIs only for those extensions located on the same Cisco CallManager cluster as the DPA 7630/7610 itself.
When the DPA 7630/7610 and Cisco CallManager connect, the ports on the DPA 7630/7610 appear as IP phones in the Cisco CallManager database. An additional "virtual" port also appears as an IP phone to Cisco CallManager, but it does not have any correspondence to a physical port. It is created by the DPA 7630/7610 to handle MWI commands to Cisco CallManager.
You can choose to have the DPA 7630/7610 automatically added to Cisco CallManager using auto-registration. To do this, you must verify that auto-registration is enabled in Cisco CallManager. Refer to the documentation or online help included with the Cisco CallManager application for details.
Cisco CallManager only recognizes these IP phones after the Octel voice mail system is up and running. Therefore, verify that the Octel system and the Cisco DPA 7630/7610 systems are up before completing these tasks in Cisco CallManager.
Auto-registration automatically assigns phones a directory number. The directory number assigned is the next one available in sequential order within the device pool assigned to this phone type in Cisco CallManager. However, if you need to, you can modify this directory number for each emulated phone (see the "Configuring the DPA Ports and Phones" section).
During auto registration, the host name assigned to the DPA 7630/7610 is entered in the Description field in the record for the emulated phone in Cisco CallManager. If you do not enter a host name, the following sequence applies for the device description: SEP + the last 10 digits of the MAC address.
1. The first two digits for the MAC address are dropped.
2. The number is shifted two places to the left.
3. The two-digit port number is added to the right.
For example, if the MAC address is000039A44218
the MAC address registered for port 12 in CallManager is0039A4421812
The 25th (virtual) port is automatically assigned the MAC address of0039A4421825.
If you want to assign specific directory numbers to the emulated IP phones on the DPA 7630/7610 without using auto-registration, you must manually add each phone to the Cisco CallManager database. Keep in mind several important facts:
From the perspective of the DPA 7630/7610, several types of ports exist:
To Cisco CallManager, these ports on the DPA appear as IP phones, but the PBX MWI ports do not appear in Cisco CallManager. The Cisco CallManager database also contains records of all the end-user phones. You must configure each of these phones in Cisco CallManager to ensure that calls are processed properly. You access the phones using the Devices > Phone menu in Cisco CallManager.
These sections provide details about the required settings in Cisco CallManager for the different ports:
Use call ports to connect lines from the Octel system that handle incoming messages, such as voice mail access, and outgoing calls such as fax calls, outgoing calls to pagers, and so on. However, a particular line from the Octel system must support either incoming or outgoing calls; it cannot support both.
Outgoing Calls
Do not include the call ports supporting outgoing calls in the voice mail hunt groups. Otherwise, configure these lines in Cisco CallManager as you normally would, assigning directory numbers to them.
Incoming Calls
The call ports supporting incoming calls require additional configuration in Cisco CallManager. In these cases, these lines and their corresponding call ports compose the voice mail hunt groups. See Figure 3-1 for an example of the following settings:
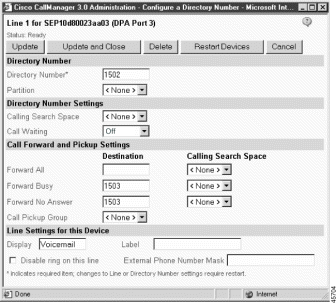
The DPA 7630/7610 uses the Octel MWI ports to handle MWI messages from the Octel system. You can also enable these lines to support outgoing call processing. However, you must not configure these ports to handle any incoming call processing. See Figure 3-2 for an example of the following settings:
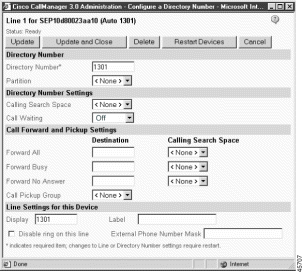
The DPA 7630/7610 automatically creates and uses the virtual port to send MWI messages to Cisco CallManager. One virtual port is created regardless of the number of Octel MWI ports you have. The virtual phone settings are similar to the Octel MWI port. See Figure 3-2 for an example of the following settings:
Although the DPA 7630/7610 does not directly interact with the end-user phones, verify that you configured these phones properly to forward to voice mail. Ensure that you set the forwarding options (Forward Busy and Forward No Answer settings) to the voice mail access number for their assigned hunt group. You might want to divide users into different hunt groups to access the voice mail system. See Figure 3-3 for an example of an end-user phone configuration.

In Cisco CallManager, you must set the option to enable the message waiting light on Cisco IP Phones. Once configured, you can access the values used to enable and disable the message waiting light by following these procedures. These options appear under the Service > Service Parameters menu in Cisco CallManager. You must configure these settings for each Cisco CallManager system in a cluster, and you must stop and restart Cisco CallManager after making these changes.
In these examples, the MessageWaitingOffDN value is 1998, and the MessageWaitingOnDN value is 1999. Record these values. You need them to configure the DPA 7630/7610.
You must configure several settings in Cisco CallManager to ensure that the voice mail hunt groups function properly. These options appear under the Service > Service Parameters menu in Cisco CallManager: You must configure these settings for each Cisco CallManager system in a cluster, and you must stop and restart Cisco CallManager after making these changes.
The pilot directory number is the number users dial on their Cisco IP Phones to access voice mail. Typically, it is the first directory number in the hunt group. You can configure this number to be easily accessed on Cisco IP Phones, such as with the messages button on a Cisco IP Phone 7960.
To configure the pilot directory number perform the following steps:
Step 2 Click the name of your Cisco CallManager system.
Step 3 Select the VoiceMailDn service parameter.
Step 4 Enter the pilot directory number in the Value field.
Refer to the Cisco CallManager Administration Guide or online help in the Cisco CallManager application if you need additional assistance.
You can specify the number of times Cisco CallManager forwards a call before generating an error tone. The default setting is 12, but you should set it to a number larger than the number of extensions in the largest hunt group.
To configure the hop count perform the following steps:
Step 2 Click the name of your Cisco CallManager system.
Step 3 Select the ForwardMaximumHopCount service parameter.
Step 4 Enter the maximum number of hops required in the Value field.
Refer to the Cisco CallManager Administration Guide or online help in the Cisco CallManager application if you need additional assistance.
The no-answer timeout setting determines how much time is spent contacting a directory number before forwarding to voice mail. You can specify the number of seconds allowed before the system determines that a call to an extension forwarded to the voice mail system.
The Octel systems have similar settings, which are determined by the number of rings. When performing supervised transfers, the Octel system expects a certain number of rings before the call is forwarded, and the Octel system stops the call.
You must not configure Cisco CallManager in such a way that it does not designate a call as unanswered before the Octel system designates that same call as unanswered. If Cisco CallManager prematurely designates the call as unanswered, the Octel system might incorrectly designate the call as busy, or it might drop the call.
To ensure that the Cisco CallManager system allows enough time for the number of expected rings to occur on the Octel system, you must set the no-answer timeout. In Cisco CallManager, you should set this setting to be 7 seconds times the number of rings configured on the Octel system. Seven seconds is slightly longer than the ring duration on a Definity or Meridian 1 PBX system.
For example, if you have the Octel system set to four rings, set the setting in Cisco CallManager to 28 seconds.
To configure the number of seconds before a no-answer timeout occurs perform the following steps:
Step 2 Click the name of your Cisco CallManager system.
Step 3 Select the ForwardNoAnswerTimeout service parameter.
Step 4 Enter the number of seconds in the Value field.
Refer to the Cisco CallManager Administration Guide or online help in the Cisco CallManager application if you need additional assistance.
You should not need to make any changes to your Octel system. However, you should verify your configuration and obtain information from the Octel system to properly set up the DPA 7630/7610. This information should already be configured if you previously used Octel and Definity or Meridian 1 systems together.
On Definity and Octel systems, you must set the dialing sequence that is used to enable and disable the MWI on phones connected to the Definity system. After you configure this setting on the Definity and Octel systems, record the setting. You need it when you configure the DPA 7630. Meridian 1 PBX systems set MWI differently so you do not need to set this for the DPA 7610.
The Octel system has two methods of receiving incoming calls on a Meridian 1 system, using Hunt or Automatic Call Distribution (ACD). The Hunt method involves groups of forwarded phones, which is similar to the method used in Cisco CallManager. However, the Meridian 1 system has a restriction on the number of hops in a forwarding chain (similar to the ForwardMaxHopCount setting in Cisco CallManager). This setting is fixed between 18 and 30 hops (depending on the PBX version), and you cannot modify it. This restriction limits both the number of phones available to the hunt group and the number of Octel ports that can be part of the group.
To avoid this restriction, you can use ACD groups, which can be much larger than the hunt groups.
Regardless of the method you use, you must verify the method in use so you can set the proper setting on the DPA 7610. To quickly verify this method, on the Meridian 1 system, check the configuration of key 0 on the phones connected to the Octel system:
On the Octel system, you must specify how each line is used, following these guidelines:
You have some flexibility in determining the number of lines used for each of these tasks. For example, a company with a 144-port Octel voice mail system using a DPA 7630 in hybrid integration mode might use the following configuration:
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Posted: Thu Mar 15 09:11:44 PST 2001
All contents are Copyright © 1992--2001 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Important Notices and Privacy Statement.