Figure A-1, Figure A-2, and Figure A-3 illustrate the frame conversions used in both Source-Route Transparent bridging (SRT), discussed in Chapter 21, "Configuring Transparent Bridging," and Source-Route/Translational Bridging (SR/TLB), discussed in Chapter 22, "Configuring Source-Route Bridging."
The following abbreviations are used in the illustrations:
- ACFC--Access Control/Frame Control
- DASA--Destination Address/Source Address
- LENGTH--IEEE 802.3 Length field
- TYPE--Ethernet Type field or type field used in SNAP encapsulated frames
- RIF--Routing Information Field
- 80D5 Header--3-byte field; first two bytes are length of the LLC portion of frame; third byte is padding byte (contents unimportant)
- SAP--DSAP/SSAP combination
- CONTROL--LLC control information
- INFO--Data portion of frame; higher layers begin here
Note For all frame formats, when going from a source-route bridged domain to a transparent-bridged interface, any existing RIF is removed, and the routing information indicator in the source address is removed.When going from a transparent-bridged network to a source-route bridged interface, a RIF is added, and the routing information indicator is added into the source address. This is shown with a RIF (SRB) field in the figures, indicating that the RIF field exists in the frame if source-route bridging is in use on the Token Ring media. Also, for all formats, the source and destination addresses are byte-swapped between the media.

Figure A-1: Frame Conversion Between IEEE 802.3 and Token Ring
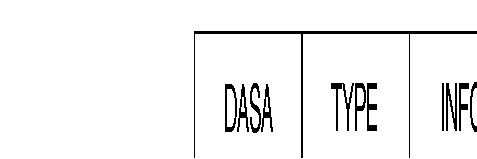
Figure A-2: Frame Conversion Between Ethernet Type II and Token Ring SNAP

Figure A-3: Frame Conversion Between Ethernet Type II "0x80D5" Format and Token Ring



