|
|

HDLC Serial links can be used as VLAN trunks in IEEE 802.10 virtual LANs to extend a virtual topology beyond a LAN backbone.
AppleTalk can be routed over virtual LAN (VLAN) subinterfaces using the ISL or IEEE 802.10 VLAN encapsulation protocols. The AppleTalk Routing over IEEE 802.10 Virtual LANs feature provides full-feature Cisco IOS software AppleTalk support on a per-VLAN basis, allowing standard AppleTalk capabilities to be configured on VLANs.
AppleTalk users can now configure consolidated VLAN routing over a single VLAN trunking interface. Prior to introduction of this feature, AppleTalk could be routed only on the main interface on a LAN port. If AppleTalk routing was disabled on the main interface or if the main interface was shut down, the entire physical interface would stop routing any AppleTalk packets. With this feature enabled, AppleTalk routing on subinterfaces will be unaffected by changes in the main interface with the main interface in the "no-shut" state.
To enable AppleTalk routing on IEEE 802.10 interfaces, perform this task in global configuration mode:
| Task | Command |
|---|---|
| Enable AppleTalk routing globally. | appletalk routing [eigrp router-number] |
After you enable AppleTalk globally and define the encapsulation format, you need to enable it on the subinterface by specifying the cable range and naming the AppleTalk zone for each interface. To enable the AppleTalk protocol on the subinterface, perform these tasks in interface configuration mode:
| Task | Command |
|---|---|
| Assign the AppleTalk cable range and zone for the subinterface. | appletalk cable-range cable-range [network.node] |
| Assign the AppleTalk zone for the subinterface. | appletalk zone zone-name |
To define the VLAN encapsulation format as either ISL or 802.10, perform these tasks in interface configuration mode:
The configuration example illustrated in Figure 16 shows AppleTalk being routed between different ISL and IEEE 802.10 VLAN encapsulating subinterfaces.
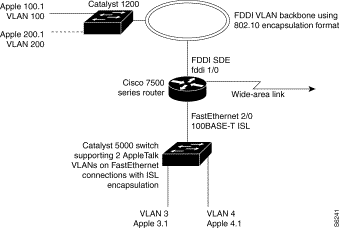
As shown in Figure 16, AppleTalk traffic is routed to and from switched VLAN domains 3, 4, 100, and 200 to any other AppleTalk routing interface. This example shows a sample configuration file for the Cisco 7500 series router with the commands entered to configure the network shown in Figure 16.
!
interface Fddi 1/0.100
encapsulation sde 100
appletalk cable-range 100-100 100.2
appletalk zone 100
!
interface Fddi 1/0.200
encapsulation sde 200
appletalk cable-range 200-200 200.2
appletalk zone 200
!
interface FastEthernet 2/0.3
encapsulation isl 3
appletalk cable-range 3-3 3.2
appletalk zone 3
!
interface FastEthernet 2/0.4
encapsulation isl 4
appletalk cable-range 4-4 4.2
appletalk zone 4
!
|
|