|
|

This chapter contains an alphabetical listing of the debug commands. Documentation for each command includes a brief description of its use, command syntax, usage guidelines, sample output, and a description of that output.
Output formats vary with each debug command. Some generate a single line of output per packet, whereas others generate multiple lines of output per packet. Some generate large amounts of output; others generate only occasional output. Some generate lines of text, and others generate information in field format. Thus, the way the debug commands are documented also varies. For example, for debug commands that generate lines of text, the output is described line by line. For debug commands that generate output in field format, tables are used to describe the fields.
By default, the network server sends the output from the debug commands to the console terminal. Sending output to a terminal (virtual console) produces less overhead than sending it to the console. Use the privileged EXEC command terminal monitor to send output to a terminal. For more information about redirecting output, see the "Using Debug Commands" chapter.
Use the debug apple arp EXEC command to enable debugging of the AppleTalk address resolution protocol (AARP). The no form of this command disables debugging output.
debug apple arp [interface unit]| interface unit | (Optional) Information for a particular interface is to be displayed. For example, Ethernet0 specifies the first Ethernet interface; Ethernet1 specifies the second Ethernet interface. If you include this argument, you must specify both the interface type and unit number. |
EXEC
This command is helpful when you experience problems communicating with a node on the network you control (a neighbor). If the debug apple arp display indicates that the router is receiving AARP probes, you can assume that the problem does not reside at the physical layer.
Figure 2-1 shows sample debug apple arp output.

Explanations for representative lines of output in Figure 2-1 follow.
The following line indicates that the router has requested the hardware MAC address of the host at network address 4160.26:
Ether0: AARP: Sent resolve for 4160.26
The following line indicates that the host at network address 4160.26 has replied, giving its MAC address (0000.0c00.0453). For completeness, the message also shows the network address to which the reply was sent and its hardware MAC address (also in parentheses).
Ether0: AARP: Reply from 4160.26(0000.0c00.0453) for 4160.154(0000.0c00.8ea9)
The following line indicates that the MAC address request is complete:
Ether0: AARP: Resolved waiting request for 4160.26(0000.0c00.0453)
Use the debug apple errors EXEC command to display errors occurring in the AppleTalk network. The no form of this command disables debugging output.
debug apple errors [interface unit]| interface unit | (Optional) Information for a particular interface is to be displayed. For example, Ethernet0 specifies the first Ethernet interface; Ethernet1 specifies the second Ethernet interface. If you include this argument, you must specify both the interface type and unit number. |
EXEC
In a stable AppleTalk network, the debug apple errors command produces little output.
To solve encapsulation problems, enable debug apple errors and debug apple packet together.
Figure 2-2 shows sample debug apple errors output when a router is brought up with a zone that does not agree with the zone list of other routers on the network.
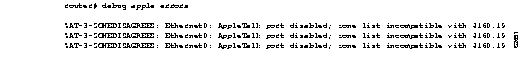
As Figure 2-2 suggests, a single error message indicates zone list incompatibility; this message is sent out periodically until the condition is corrected or debug apple errors is turned off.
Most of the other messages that debug apple errors can generate are obscure or indicate a serious problem with the AppleTalk network. Some of these other messages follow.
In the following message, RTMPRsp, RTMPReq, ATP, AEP, ZIP, ADSP, or SNMP could replace NBP, and "llap dest not for us" could replace "wrong encapsulation":
Packet discarded, src 4160.12-254,dst 4160.19-254,NBP,wrong encapsulation
In the following message, in addition to invalid echo packet, other possible errors are unsolicited AEP echo reply, unknown echo function, invalid ping packet, unknown ping function, and bad responder packet type.
Ethernet0: AppleTalk packet error; no source address available
AT: pak_reply: dubious reply creation, dst 4160.19
AT: Unable to get a buffer for reply to 4160.19
Processing error, src 4160.12-254,dst 4160.19-254,AEP, invalid echo packet
The debug apple errors command can print out additional messages when other debugging commands are also turned on. When you turn on both debug apple errors and debug apple events, the following message can be generated:
Proc err, src 4160.12-254,dst 4160.19-254,ZIP,NetInfo Reply format is invalid
In the preceding message, in addition to NetInfo Reply format is invalid, other possible errors are NetInfoReply not for me, NetInfoReply ignored, NetInfoReply for operational net ignored, NetInfoReply from invalid port, unexpected NetInfoReply ignored, cannot establish primary zone, no primary has been set up, primary zone invalid, net information mismatch, multicast mismatch, and zones disagree.
When you turn on both debug apple errors and debug apple nbp, the following message can be generated:
Processing error, ...,NBP,NBP name invalid
In the preceding message, in addition to NBP name invalid, other possible errors are NBP type invalid, NBP zone invalid, not operational, error handling brrq, error handling proxy, NBP fwdreq unexpected, No route to srcnet, Proxy to "*" zone, Zone "*" from extended net, No zone info for "*", and NBP zone unknown.
When you turn on both debug apple errors and debug apple routing, the following message can be generated:
Processing error, ...,RTMPReq, unknown RTMP request
In the preceding message, in addition to unknown RTMP request, other possible errors are RTMP packet header bad, RTMP cable mismatch, routed RTMP data, RTMP bad tuple, and Not Req or Rsp.
Use the debug apple events EXEC command to display information about AppleTalk special events, neighbors becoming reachable/unreachable, and interfaces going up/down. Only significant events (for example, neighbor and route changes) are logged. The no form of this command disables debugging output.
debug apple events [interface unit]| interface unit | (Optional) Information for a particular interface is to be displayed. For example, Ethernet0 specifies the first Ethernet interface; Ethernet1 specifies the second Ethernet interface. If you include this argument, you must specify both the interface type and unit number. |
EXEC
The debug apple events command is useful for solving AppleTalk network problems because it provides an overall picture of the stability of the network. In a stable network, the debug apple events command does not return any information. If, however, the command generates numerous messages, they can indicate where the problems might lie.
When configuring or making changes to a router or interface for AppleTalk, enable debug apple events. Doing so will alert you to the progress of the changes or to any errors that might result. Also use this command periodically when you suspect network problems.
The debug apple events command is also useful to determine whether network flapping (nodes toggling on- and off-line) is occurring. If flapping is excessive, look for routers that only support 254 networks.
When you enable debug apple events, you will also see any messages that the configuration command apple event-logging normally displays. Turning on debug apple events, however, will not cause apple event-logging to be maintained in nonvolatile memory. Only turning on apple event-logging explicitly will store it in nonvolatile memory. Furthermore, if apple event-logging is already enabled, turning on or off debug apple events will not affect apple event-logging.
Figure 2-3 shows sample debug apple events output that describes a nonseed router coming up in discovery mode.

As Figure 2-3 shows, the debug apple events command can be useful in tracking the discovery mode state changes through which an interface progresses. When no problems are encountered, the state changes progress as follows:
Explanations for individual lines of output in Figure 2-3 follow.
The following message indicates that a port is set. In this case, the zone multicast address is being reset:
Ether0: AT: Resetting interface address filters
The following messages indicate that the router is changing to restarting mode:
%AT-5-INTRESTART: Ether0: AppleTalk port restarting; protocol restarted
Ether0: AppleTalk state changed; unknown -> restarting
The following message indicates that the router is probing in the startup range of network numbers (65280-65534) to discover its network number:
Ether0: AppleTalk state changed; restarting -> probing
The following message indicates that the router is enabled as a nonrouting node using a provisional network number within its startup range of network numbers. This type of message only appears if the network address the router will use differs from its configured address. This is always the case for a discovery-enabled router; it is rarely the case for a nondiscovery-enabled router.
%AT-6-ADDRUSED: Ether0: AppleTalk node up; using address 65401.148
The following messages indicate that the router is sending out GetNetInfo requests to discover the default zone name and the actual network number range in which its network number can be chosen:
Ether0: AppleTalk state changed; probing -> acquiring
%AT-6-ACQUIREMODE: Ether0: AT port initializing; acquiring net configuration
Now that the router has acquired the cable configuration information, the following message indicates that it restarts using that information:
Ether0: AppleTalk state changed; acquiring -> restarting
The following messages indicate that the router is probing for its actual network address:
Ether0: AppleTalk state changed; restarting -> line down
Ether0: AppleTalk state changed; line down -> restarting
Ether0: AppleTalk state changed; restarting -> probing
The following message indicates that the router has found an actual network address to use:
%AT-6-ADDRUSED: Ether0: AppleTalk node up; using address 4160.148
The following messages indicate that the router is sending out GetNetInfo requests to verify the default zone name and the actual network number range from which its network number can be chosen:
Ether0: AppleTalk state changed; probing -> acquiring
%AT-6-ACQUIREMODE: Ether0: AT port initializing; acquiring net configuration
The following message indicates that the router is requesting the list of zones for its cable:
Ether0: AppleTalk state changed; acquiring -> requesting zones
The following messages indicate that the router is sending out GetNetInfo requests to make sure its understanding of the configuration is correct:
Ether0: AppleTalk state changed; requesting zones -> verifying
AT: Sent GetNetInfo request broadcast on Ethernet0
The following message indicates that the router is rechecking its list of zones for its cable:
Ether0: AppleTalk state changed; verifying -> checking zones
The following message indicates that the router is now fully operational as a routing node and can begin routing:
Ether0: AppleTalk state changed; checking zones -> operational
Figure 2-4 shows sample debug apple events output that describes a nondiscovery-enabled router coming up when no other router is on the wire.

As Figure 2-4 shows, a nondiscovery-enabled router can come up when no other router is on the wire; however, it must assume that its configuration (if accurate syntactically) is correct, because no other router can verify it. Notice that the last line in Figure 2-4 indicates this situation.
Figure 2-5 shows sample debug apple events output that describes a discovery-enabled router coming up when there is no seed router on the wire.

As Figure 2-5 shows, when you attempt to bring up a nonseed router without a seed router on the wire, it never becomes operational; instead, it hangs in the acquiring mode and continues to send out periodic GetNetInfo requests.
Figure 2-6 shows sample debug apple events output when a nondiscovery-enabled router is brought up on an AppleTalk internetwork that is in compatibility mode (set up to accommodate extended as well as nonextended AppleTalk) and the router has violated internetwork compatibility.

The three configuration command lines that follow indicate the part of the router's configuration that caused the configuration mismatch shown in Figure 2-6:
lestat(config)#int e 0
lestat(config-if)#apple cab 41-41
lestat(config-if)#apple zone Marketign
The router shown in Figure 2-6 had been configured with a cable range of 41-41 instead of 40-40, which would have been accurate. Additionally, the zone name was configured incorrectly; it should have been Marketing, rather than being misspelled as Marketign.
Use the debug apple nbp EXEC command to display debugging output from the Name Binding Protocol (NBP) routines. The no form of this command disables debugging output.
debug apple nbp [interface unit]| interface unit | (Optional) Information for a particular interface is to be displayed. For example, Ethernet0 specifies the first Ethernet interface; Ethernet1 specifies the second Ethernet interface. If you include this argument, you must specify both the interface type and unit number. |
EXEC
To determine whether the router is receiving NBP lookups from a node on the AppleTalk network, enable debug apple nbp at each node between the router and the node in question to determine where the problem lies.
Figure 2-7 shows sample debug apple nbp output.

The first three lines in Figure 2-7 describe an NBP lookup request:
AT: NBP ctrl = LkUp, ntuples = 1, id = 77
AT: 4160.19, skt 2, enum 0, name: =:ciscoRouter@Low End SW Lab
AT: LkUp =:ciscoRouter@Low End SW Lab
Table 2-1 describes the fields in the first line of output shown in Figure 2-7.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| AT: NBP | Indicates that this message describes an AppleTalk NBP packet. |
| ctrl = LkUp | Identifies the type of NBP packet. Possible values include:
LkUp--NBP lookup request. LkUp-Reply--NBP lookup reply. |
| ntuples = 1 | Indicates the number of name-address pairs in the lookup request packet. Range: 1-31 tuples. |
| id = 77 | Value that identifies the NBP lookup request. |
Table 2-2 describes the fields in the second line of output shown in Figure 2-7.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| AT: | Indicates that this message describes an AppleTalk packet. |
| 4160.19 | Network address of the requester. |
| skt 2 | Internet socket address of the requester. The responder will send the NBP lookup reply to this socket address. |
| enum 0 | Enumerator field. Used to identify multiple names registered on a single socket. Each tuple is assigned its own enumerator, incrementing from 0 for the first tuple. |
| name: =:ciscoRouter@Low End SW Lab | Entity name for which a network address has been requested. The AppleTalk entity name includes three components:
Object (in this case, a wildcard character ( Type (in this case, ciscoRouter) Zone (in this case, Low End SW Lab) |
The third line in Figure 2-7 essentially reiterates the information in the two lines above it, indicating that a lookup request has been made regarding name-address pairs for all objects of the ciscoRouter type in the Low End SW Lab zone.
Since the router is defined as an object of type ciscoRouter in zone Low End SW Lab, it sends an NBP lookup reply in response to this NBP lookup request. The following two lines of output from Figure 2-7 show the router's response.
AT: NBP ctrl = LkUp-Reply, ntuples = 1, id = 77
AT: 4160.154, skt 254, enum 1, name: lestat.Ether0:ciscoRouter@Low End SW Lab
In the first line, ctrl = LkUp-Reply identifies this NBP packet as an NBP lookup request. The same value in the id field (id = 77) associates this lookup reply with the previous lookup request. The second line indicates that the network address associated with the router's entity name (lestat.Ether0:ciscoRouter@Low End SW Lab) is 4160.154. The fact that no other entity name/network address is listed indicates that the responder only knows about itself as an object of type ciscoRouter in zone Low End SW Lab.
Use the debug apple packet EXEC command to display per-packet debugging output. The output reports information online when a packet is received or a transmit is attempted. The no form of this command disables debugging output.
debug apple packet [interface unit]| interface unit | (Optional) Information for a particular interface is to be displayed. For example, Ethernet0 specifies the first Ethernet interface; Ethernet1 specifies the second Ethernet interface. If you include this argument, you must specify both the interface type and unit number. |
EXEC
This command allows you to monitor the types of packets being slow switched. It will display at least one line of debugging output per AppleTalk packet processed.
When invoked in conjunction with the debug apple routing, debug apple zip, and debug apple nbp commands, the debug apple packet command adds protocol processing information in addition to generic packet details. It also reports successful completion or failure information.
When invoked in conjunction with the debug apple errors command, the debug apple packet command reports packet-level problems, such as those concerning encapsulation.
Figure 2-8 shows sample debug apple packet output.

Table 2-3 describes the fields in the first line of output shown in Figure 2-8.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Ether0: | Name of the interface through which the router received the packet. |
| AppleTalk packet | Indicates that this is an AppleTalk packet. |
| enctype SNAP | Encapsulation type for the packet. |
| size 60 | Size of the packet (in bytes). |
| encaps000000000000000000000000 | Encapsulation. |
Table 2-4 describes the fields in the second line of output shown in Figure 2-8.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| AT: | Indicates that this is an AppleTalk packet. |
| src = Ethernet0:4160.47 | Name of the interface sending the packet, as well as its AppleTalk address. |
| dst = 4160-4160 | Cable range of the packet's destination. |
| size = 10 | Size of the packet (in bytes). |
| 2 rtes | Indicates that there are two routes in the routing table that link these two addresses. |
| RTMP pkt sent | Indicates the type of packet sent. |
The third line in Figure 2-8 indicates the type of packet received and its source AppleTalk address. This message is repeated in the fourth line because AppleTalk hosts can send multiple replies to a given GetNetInfo request.
Use the debug apple routing EXEC command to enable debugging output from the Routing Table Maintenance Protocol (RTMP) routines. The no form of this command disables debugging output.
debug apple routing [interface unit]| [interface unit] | (Optional) Information for a particular interface is to be displayed. For example, Ethernet0 specifies the first Ethernet interface; Ethernet1 specifies the second Ethernet interface. If you include this argument, you must specify both the interface type and unit number. |
EXEC
This command can be used to monitor acquisition of routes, aging of routing table entries, and advertisement of known routes. It also reports conflicting network numbers on the same network if the network is misconfigured.
Figure 2-9 shows sample debug apple routing output.

Explanations for representative lines of the debug apple routing output in Figure 2-9 follow.
Table 2-5 describes the fields in the first line of sample debug apple routing output.
The following two messages indicate that the ager has started and finished the aging process for the routing table and that this table contains 97 entries.
AT: Route ager starting (97 routes)
AT: Route ager finished (97 routes)
Table 2-6 describes the fields in the following line of debug apple routing output.
AT: RTMP from 4160.19 (new 0,old 94,bad 0,ign 0, dwn 0)
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| AT: | Indicates that this is AppleTalk debugging output. |
| RTMP from 4160.19 | Indicates the source address of the RTMP update the router received. |
| new 0 | Number of routes in this RTMP update packet that the router did not already know about. |
| old 94 | Number of routes in this RTMP update packet that the router already knew about. |
| bad 0 | Number of routes the other router indicates have gone bad. |
| ign 0 | Number of routes the other router indicates it does not care about. |
| dwn 0 | Number of poisoned tuples included in this packet. |
Use the debug apple zip EXEC command to display debugging output from the Zone Information Protocol (ZIP) routines. The no form of this command disables debugging output.
debug apple zip [interface unit]| interface unit | (Optional) Information for a particular interface is to be displayed. For example, Ethernet0 specifies the first Ethernet interface; Ethernet1 specifies the second Ethernet interface. If you include this argument, you must specify both the interface type and unit number. |
EXEC
This command reports significant events such as discovery of new zones and zone list queries. It generates information similar to that generated by debug apple routing, but generates it for ZIP packets instead of RTMP packets.
The debug apple zip command can be used to determine whether a ZIP storm is taking place in the AppleTalk network. You can detect the existence of a ZIP storm when you see that no router on a cable has the zone name corresponding to a network number that all the routers have in their routing tables.
Figure 2-10 shows sample debug apple zip output.

Explanations of the lines of output shown in Figure 2-10 follow.
The first line indicates that the router has received an RTMP update that includes a new network number and is now requesting zone information:
AT: Sent GetNetInfo request broadcast on Ether0
The second line indicates that the neighbor at address 4160.19 replies to the zone request with a default zone:
AT: Recvd ZIP cmd 6 from 4160.19-6
The third line indicates that the router responds with three queries to the neighbor at network address 4160.19 for other zones on the network:
AT: 3 query packets sent to neighbor 4160.19
The fourth line indicates that the neighbor at network address 4160.19 responds with a ZIP extended reply, indicating that one zone has been assigned to network 31902:
AT: 1 zones for 31902, ZIP XReply, src 4160.19
The fifth line indicates that the router responds that the zone name of network 31902 is US-Orlando, and the zone length of that zone name is 10:
AT: net 31902, zonelen 10, name US-Orlando
Use the debug arp EXEC command to display information on Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) transactions. The no form of this command disables debugging output.
debug arpThis command has no arguments or keywords.
EXEC
Use this command when some nodes on a TCP/IP network are responding, but others are not. It shows whether or not the router is sending or receiving ARPs.
Figure 2-11 shows sample debug arp output.

In Figure 2-11, each line of output represents an ARP packet that the router sent or received. Explanations for the individual lines of output follow.
The first line indicates that the router at IP address 131.108.22.7 and MAC address 0000.0c01.e117 sent an ARP request for the MAC address of the host at 131.108.22.96. The series of zeros (0000.0000.0000) following this address indicate that the router is currently unaware of the MAC address.
IP ARP: sent req src 131.108.22.7 0000.0c01.e117, dst 131.108.22.96 \
0000.0000.0000
The second line indicates that the router at IP address 131.108.22.7 receives a reply from the host at 131.108.22.96 indicating that its MAC address is 0800.2010.b908:
IP ARP: rcvd rep src 131.108.22.96 0800.2010.b908, dst 131.108.22.7
The third line indicates that the router receives an ARP request from the host at 131.108.6.10 requesting the MAC address for the host at 131.108.6.62:
IP ARP: rcvd req src 131.108.6.10 0000.0c00.6fa2, dst 131.108.6.62
The fourth line indicates that another host on the network attempted to send the router an ARP reply for the router's own address. The router ignores such bogus replies. Usually, this can happen if someone is running a bridge in parallel with the router and is allowing ARP to be bridged. It indicates a network misconfiguration.
IP ARP: rep filtered src 131.108.22.7 aa92.1b36.a456, dst 255.255.255.255 \
ffff.ffff.ffff
The fifth line indicates that another host on the network attempted to inform the router that it is on network 131.108.9.7, but the router does not know that that network is attached to a different router interface. The remote host (probably a PC or an X terminal) is misconfigured. If the router were to install this entry, it would deny service to the real machine on the proper cable.
IP ARP: rep filtered src 131.108.9.7 0000.0c00.6b31, dst 131.108.22.7 \
0800.2010.b908
Use the debug atm errors EXEC command to display ATM errors. The no form of this command disables debugging output.
debug atm errorsThis command has no arguments or keywords.
EXEC
Figure 2-12 shows sample debug atm errors output.
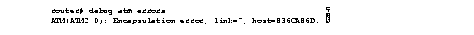
The line of output in Figure 2-12 indicates that a packet was routed to the ATM interface, but no static map was set up to route that packet to the proper virtual circuit.
Use the debug atm events EXEC command to display ATM events. The no form of this command disables debugging output.
debug atm eventsThis command has no arguments or keywords.
EXEC
This command displays ATM events that occur on the ATM interface processor and is useful for diagnosing problems in an ATM network. It provides an overall picture of the stability of the network. In a stable network, the debug atm events command does not return any information. If the command generates numerous messages, they can indicate where the problems might lie.
When configuring or making changes to a router or interface for ATM, enable debug atm events. Doing so will alert you to the progress of the changes or to any errors that might result. Also use this command periodically when you suspect network problems.
Figure 2-13 shows sample debug atm events output.
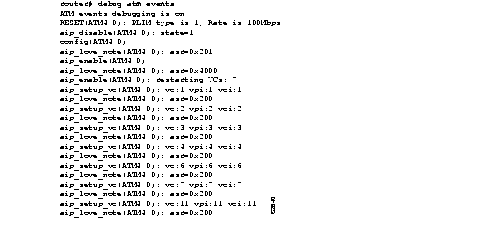
Table 2-7 describes significant fields in the output shown in Figure 2-13.
Explanations for representative lines of output in Figure 2-13 follow.
The following line indicates that the AIP was reset. The PLIM TYPE detected was 1, so the maximum rate is set to 100 Mbps.
RESET(ATM4/0): PLIM type is 1, Rate is 100Mbps
The following line indicates that the AIP was given a shutdown command, but the current configuration indicates that the AIP should be up:
aip_disable(ATM4/0): state=1
The following line indicates that a configuration command has been completed by the AIP:
aip_love_note(ATM4/0): asr=0x201
The following line indicates that the AIP was given a no shutdown command to take it out of shutdown:
aip_enable(ATM4/0)
The following line indicates that the AIP detected a carrier state change. It does not indicate that the carrier is down or up, only that it has changed:
aip_love_note(ATM4/0): asr=0x4000
The following line of output indicates that the AIP enable function is restarting all PVCs automatically:
aip_enable(ATM4/0): restarting VCs: 7
The following lines of output indicate that PVC 1 was set up and a successful completion code was returned:
aip_setup_vc(ATM4/0): vc:1 vpi:1 vci:1
aip_love_note(ATM4/0): asr=0x200
Use the debug atm packet EXEC command to display per-packet debugging output. The output reports information online when a packet is received or a transmit is attempted. The no form of this command disables debugging output.
debug atm packetThis command has no arguments or keywords.
EXEC
The debug atm packet command displays all process-level ATM packets for both outbound and inbound packets. This command is useful for determining whether packets are being received correctly or are being transmitted correctly.
For transmitted packets, the information is displayed only after the protocol data unit (PDU) is entirely encapsulated and a next hop virtual circuit (VC) is found. If information is not displayed, the address translation has probably failed during encapsulation. When a next hop VC is found, the packet is displayed exactly as it will be presented on the wire. Having a display indicates the packets are properly encapsulated for transmission.
For received packets, information is displayed for all incoming frames. The display can show whether the transmitting station properly encapsulates the frames. Because all incoming frames are displayed, this information is useful when performing back-to-back testing and corrupted frames cannot be dropped by an intermediary ATM switch.
The debug atm packet command also displays the initial bytes of the actual PDU in hexadecimal. This information can be decoded only by qualified support or engineering personnel.
Figure 2-14 shows sample debug atm packet output.

Table 2-8 describes significant fields shown in Figure 2-14.
The following two lines of output are the binary data, which are the contents of the protocol PDU before encapsulation at the ATM:
4500 002E 0000 0000 0209 92ED 836C A26E FFFF FFFF 1108 006D 0001 0000 0000
A5CC 6CA2 0000 000A 0000 6411 76FF 0100 6C08 00FF FFFF 0003 E805 DCFF 0105
Use the debug broadcast EXEC command to display information on MAC broadcast packets. The no form of this command disables debugging output.
debug broadcastThis command has no arguments or keywords.
EXEC
Depending on the type of interface and the type of encapsulation used on that interface, the debug broadcast command can produce a wide range of messages.
Figure 2-15 shows sample debug broadcast output. Notice how similar it is to the debug packet output.

Table 2-9 describes significant fields shown in Figure 2-15.
Use the debug clns esis events EXEC command to displays uncommon ES-IS events, including previously unknown neighbors, neighbors that have aged out, and neighbors that have changed roles (ES to IS, for example). The no form of this command disables debugging output.
debug clns esis eventsThis command has no arguments or keywords.
EXEC
Figure 2-16 shows sample debug clns esis events output.

Explanations for individual lines of output from Figure 2-16 follow.
The following line indicates that the router received a hello packet (ISH) from the IS at MAC address aa00.0400.2c05 on the Ethernet1 interface. The hold time (or number of seconds to consider this packet valid before deleting it) for this packet is 30 seconds.
ES-IS: ISH from aa00.0400.2c05 (Ethernet1), HT 30
The following line indicates that the router received a hello packet (ESH) from the ES at MAC address aa00.0400.9105 on the Ethernet1 interface. The hold time is 150 seconds.
ES-IS: ESH from aa00.0400.9105 (Ethernet1), HT 150
The following line indicates that the router sent an IS hello packet on the Ethernet0 interface to all ESs on the network. The router's NET address is 49.0001.AA00.6904.00, the hold time for this packet is 299 seconds, and the header length of this packet is 20 bytes.
ES-IS: ISH sent to All ESs (Ethernet1): NET 49.0001.AA00.0400.6904.00, HT 299, HLEN 20
Use the debug clns esis packets EXEC command to enable display information on ES-IS packets that the router has received and sent. The no form of this command disables debugging output.
debug clns esis packetsThis command has no arguments or keywords.
EXEC
Figure 2-17 shows sample debug clns esis packets output.

Explanations for individual lines of output from Figure 2-17 follow.
The following line indicates that the router has sent an IS hello packet on Ethernet0 to all ESs on the network. This hello packet indicates that the router's NET is 47.0005.80ff.ef00.0000.0001.5940.1600.8906.4023.00. The hold time for this packet is 299 seconds. The packet header is 33 bytes in length.
ES-IS: ISH sent to All ESs (Ethernet0): NET 47.0005.80ff.ef00.0000.0001.5940.1600.8906.4023.00, HT 299, HLEN 33
The following line indicates that the router has sent an IS hello packet on Ethernet1 to all ESs on the network. This hello packet indicates that the router's NET is 47.0005.80ff.ef00.0000.0001.5940.1600.8906.4023.00. The hold time for this packet is 299 seconds. The packet header is 33 bytes in length.
ES-IS: ISH sent to All ESs (Ethernet1): NET 47.0005.80ff.ef00.0000.0001.5940.1600.8906.4023.00, HT 299, HLEN 34
The following line indicates that the router received a hello packet on Ethernet0 from an intermediate system, aa00.0400.6408. The hold time for this packet is 299 seconds.
ES-IS: ISH from aa00.0400.6408 (Ethernet0), HT 299
The following line indicates that the router has sent an IS hello packet on Tunnel0 to all ESs on the network. This hello packet indicates that the router's NET is 47.0005.80ff.ef00.0000.0001.5940.1600.8906.4023.00. The hold time for this packet is 299 seconds. The packet header is 33 bytes in length.
ES-IS: ISH sent to All ESs (Tunnel0): NET 47.0005.80ff.ef00.0000.0001.5940.1600.8906.4023.00, HT 299, HLEN 34
The following line indicates that on Ethernet0, the router received a hello packet from an end system with an SNPA of 0000.0c00.bda8. The hold time for this packet is 300 seconds.
IS-IS: ESH from 0000.0c00.bda8 (Ethernet0), HT 300
Use the debug clns events EXEC command to display CLNS events that are occurring at the router. The no form of this command disables debugging output.
debug clns eventsThis command has no arguments or keywords.
EXEC
Figure 2-18 shows sample debug clns events output.

Explanations for individual lines of output from Figure 2-18 follow.
The following line indicates that the router received an echo PDU on Ethernet3 from source NSAP 39.0001.2222.2222.2222.00. The exclamation point at the end of the line has no significance.
CLNS: Echo PDU received on Ethernet3 from 39.0001.2222.2222.2222.00!
The following lines indicate that the router at source NSAP 39.0001.3333.3333.3333.00 is sending a CLNS echo packet to destination NSAP 39.0001.2222.2222.2222.00 via an IS with System ID 2222.2222.2222. The packet is being sent on the Ethernet3 interface, with a MAC address of 0000.0c00.3a18.
CLNS: Sending from 39.0001.3333.3333.3333.00 to 39.0001.2222.2222.2222.00
via 2222.2222.2222 (Ethernet3 0000.0c00.3a18)
The following lines indicate that a CLNS echo packet 117 bytes in size is being sent from source NSAP 39.0001.2222.2222.2222.00 to destination NSAP 49.0002.0001.AAAA.AAAA.AAAA.00 via the router at NSAP 49.0002. The packet is being forwarded on the Ethernet3 interface, with a MAC address of 0000.0c00.b5a3.
CLNS: Forwarding packet size 117
from 39.0001.2222.2222.2222.00
to 49.0002.0001.AAAA.AAAA.AAAA.00
via 49.0002 (Ethernet3 0000.0c00.b5a3)
The following lines indicate that the router sent a redirect packet on the Ethernet3 interface to the NSAP 39.0001.2222.2222.2222.00 at MAC address 0000.0c00.3a18 to indicate that NSAP 49.0002.0001.AAAA.AAAA.AAAA.00 can be reached at MAC address 0000.0c00.b5a3.
CLNS: RD Sent on Ethernet3 to 39.0001.2222.2222.2222.00 @ 0000.0c00.3a18,
redirecting 49.0002.0001.AAAA.AAAA.AAAA.00 to 0000.0c00.b5a3
Use the debug clns igrp packets EXEC command to display debugging information on all ISO-IGRP routing activity. The no form of this command disables debugging output.
debug clns igrp packetsThis command has no arguments or keywords.
EXEC
Figure 2-19 shows sample debug clns igrp packets output.

Explanations for individual lines of output from Figure 2-19 follow.
The following line indicates that the router is sending a hello packet to advertise its existence in the DOMAIN_green1 domain:
ISO-IGRP: Hello sent on Ethernet3 for DOMAIN_green1
The following line indicates that the router received a hello packet from a certain NSAP on the Ethernet3 interface. The hold time for this information is 51 seconds.
ISO-IGRP: Received hello from 39.0001.3333.3333.3333.00, (Ethernet3), ht 51
The following lines indicate that the router is generating a Level 1 update to advertise reachability to destination NSAP 2222.2222.2222 and that it is sending that update to all systems that can be reached through the Ethernet3 interface:
ISO-IGRP: Originating level 1 periodic update
ISO-IGRP: Advertise dest: 2222.2222.2222
ISO-IGRP: Sending update on interface: Ethernet3
The following lines indicate that the router is generating a Level 2 update to advertise reachability to destination area 1 and that it is sending that update to all systems that can be reached through the Ethernet3 interface:
ISO-IGRP: Originating level 2 periodic update
ISO-IGRP: Advertise dest: 0001
ISO-IGRP: Sending update on interface: Ethernet3
The following lines indicate that the router received an update from NSAP 3333.3333.3333 on Ethernet3. This update indicated the area the router at this NSAP could reach.
ISO-IGRP: Received update from 3333.3333.3333 (Ethernet3)
ISO-IGRP: Opcode: area
The following lines indicate that the router received an update advertising that the source of that update can reach area 1 with a metric of 1100. A station opcode indicates that the update included system addresses.
ISO-IGRP: Received level 2 adv for 0001 metric 1100
ISO-IGRP: Opcode: station
Use the debug clns packet EXEC command to display information about packet receipt and forwarding to the next interface. The no form of this command disables debugging output.
debug clns packetThis command has no arguments or keywords.
EXEC
Figure 2-20 shows sample debug clns packet output.

Explanations for individual lines of output from Figure 2-20 follow.
In the following lines, the first line indicates that a CLNS packet of size 157 bytes is being forwarded. The second line indicates the NSAP and system name of the source of the packet. The third line indicates the destination NSAP for this packet. The fourth line indicates the next-hop system ID, interface, and SNPA of the router interface used to forward this packet.
CLNS: Forwarding packet size 157
from 47.0023.0001.0000.0000.0003.0001.1920.3614.3002.00 STUPI-RBS
to 47.0005.80ff.ef00.0000.0001.5940.1600.8906.4017.00
via 1600.8906.4017 (Ethernet0 0000.0c00.bda8)
In the following lines, the first line indicates that the router received an Echo PDU on the specified interface from the source NSAP. The second line indicates which source NSAP is used to send a CLNS packet to the destination NSAP, as shown on the third line. The fourth line indicates the next-hop system ID, interface, and SNPA of the router interface used to forward this packet.
CLNS: Echo PDU received on Ethernet0 from 47.0005.80ff.ef00.0000.0001.5940.1600.8906.4017.00!
CLNS: Sending from 47.0005.80ff.ef00.0000.0001.5940.1600.8906.4023.00 to 47.0005.80ff.ef00.0000.0001.5940.1600.8906.4017.00
via 1600.8906.4017 (Ethernet0 0000.0c00.bda8)
Use the debug clns routing EXEC command to display debugging information of all CLNS routing cache updates and activities involving the CLNS routing table. The no form of this command disables debugging output.
debug clns routingThis command has no arguments or keywords.
EXEC
Figure 2-21 shows sample debug clns routing output.
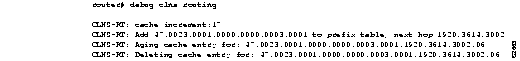
Explanations for individual lines of output from Figure 2-21 follow.
The following line indicates that a change to the routing table has resulted in an addition to the fast-switching cache:
CLNS-RT: cache increment:17
The following line indicates that a specific prefix route was added to the routing table, and indicates the next-hop system ID to that prefix route. In other words, when the router receives a packet with the prefix 47.0023.0001.0000.0000.0003.0001 in that packet's destination address, it forwards that packet to the router with the MAC address 1920.3614.3002.
CLNS-RT: Add 47.0023.0001.0000.0000.0003.0001 to prefix table, next hop 1920.3614.3002
The following lines indicate that the fast-switching cache entry for a certain NSAP has been invalidated and then deleted:
CLNS-RT: Aging cache entry for: 47.0023.0001.0000.0000.0003.0001.1920.3614.3002.06
CLNS-RT: Deleting cache entry for: 47.0023.0001.0000.0000.0003.0001.1920.3614.3002.06
Use the debug compress EXEC command to display compression information. The no form of this command disables debugging output.
debug compressThis command has no arguments or keywords.
EXEC
Figure 2-22 shows sample debug compress output.

Table 2-10 describes significant fields shown in Figure 2-22.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| COMPRESS xmt_paks | The sequence count of this frame is modulo 256 (except zero only occurs on initialization). This value is part of the compression header sent with each frame. |
| DECOMPRESS xmt_paks | The sequence count in the compression header received with this frame. |
| DECOMPRESS rcv_sync | The received internal sequence count, which is verified against the DECOMPRESS xmt_paks count. If these counts do not match, a LAPB reset will occur. On LAPB reset, a compression reinitialization occurs. Compression reinitialization initializes the dictionaries and xmt_paks and rcv_sync counts. |
Use the debug decnet adj EXEC command to display debugging information on DECnet adjacencies. The no form of this command disables debugging output.
debug decnet adjThis command has no arguments or keywords.
EXEC
Figure 2-23 shows sample debug decnet adj output.

Explanations for representative lines of output in Figure 2-23 follow.
The following line indicates that the router is sending hellos to all routers on this segment, which in this case is Ethernet 0:
DNET-ADJ: Sending hellos to all routers on interface Ethernet0, blksize 1498
The following line indicates that the router has heard a hello from 1.5 and is creating an adjacency entry in its table. The initial state of this adjacency will be initializing.
DNET-ADJ: 1.5 adjacency initializing
The following line indicates that the router is sending an unscheduled (triggered) hello as a result of some event, such as new adjacency being heard:
DNET-ADJ: sending triggered hellos
The following line indicates that the adjacency with 1.5 is now up, or active:
DNET-ADJ: 1.5 adjacency up
The following line indicates that the adjacency with 1.5 has timed out, because no hello has been heard from adjacency 1.5 in the time interval originally specified in the hello from 1.5:
DNET-ADJ: 1.5 adjacency down, listener timeout
The following line indicates that the router is sending an unscheduled hello, as a result of some event, such as the adjacency state changing:
DNET-ADJ: hello update triggered by state changed in dn_add_adjacency
Use the debug decnet connects EXEC command to display debugging information of all connect packets that are filtered (permitted or denied) by DECnet access lists. The no form of this command disables debugging output.
debug decnet connectsThis command has no arguments or keywords.
EXEC
When using connect packet filtering, it may be helpful to use the decnet access-group configuration command to apply the following basic access list:
access-list 300 permit 0.0 63.1023
access-list 300 permit 0.0 63.1023 eq any
You can then log all connect packets transmitted on interfaces to which you applied this list, in order to determine those elements on which your connect packets must be filtered.
Figure 2-24 shows sample debug decnet connects output.

Table 2-11 describes significant fields shown in Figure 2-24.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| DNET-CON: | Indicates that this is a debug decnet connects packet. |
| list 300 item #2 matched | Indicates that a packet matched the second item in access list 300. |
| src = 19.403 | Indicates the source DECnet address for the packet. |
| dst = 19.309 | Indicates the destination DECnet address for the packet. |
| on Ethernet0: | Indicates the router interface on which the access list filtering the packet was applied. |
permitted
| Indicates that the access list permitted the packet. |
| srcname = "RICK" | Indicates the originator user of the packet. |
| srcuic = [0,017] | Indicates the source UIC of the packet. |
| dstobj = 42 | Indicates that DECnet object 42 is the destination. |
| id="USER" | Indicates the access user. |
Use the debug decnet events EXEC command to display debugging information on DECnet events. The no form of this command disables debugging output.
debug decnet eventsThis command has no arguments or keywords.
EXEC
Figure 2-25 shows sample debug decnet events output.

Explanations for representative lines of output in Figure 2-25 follow.
The following line indicates that the router received a hello from a router whose area was greater than the max-area parameter with which this router was configured:
DNET: Hello from area 50 rejected - exceeded 'max area' parameter (45)
The following line indicates that the router received a hello from a router whose node ID was greater than the max-node parameter with which this router was configured:
DNET: Hello from node 1002 rejected - exceeded 'max node' parameter (1000)
Use the debug decnet packet EXEC command to display debugging information on DECnet packet events. The no form of this command disables debugging output.
debug decnet packetThis command has no arguments or keywords.
EXEC
Figure 2-26 shows sample debug decnet packet output.

Explanations for individual lines of output from Figure 2-26 follow.
The following line indicates that the router is sending a converted packet addressed to node 1.10 to Phase V:
DNET-PKT: src 1.3 dst 1.10 sending to PHASEV
The following line indicates that the router forwarded a packet from node 1.4 to node 1.5. The packet is being sent to the next hop of 1.5 whose SNPA (MAC address) on that interface is 0000.3080.cf90.
DNET-PKT: Packet fwded from 1.4 to 1.5, via 1.5, snpa 0000.3080.cf90, TokenRing0
Use the debug decnet routing EXEC command to display all DECnet routing-related events occurring at the router. The no form of this command disables debugging output.
debug decnet routingThis command has no arguments or keywords.
EXEC
Figure 2-27 shows sample debug decnet routing output.

Explanations for individual lines of output from Figure 2-27 follow.
The following line indicates that the router has received a level 1 update on interface Ethernet 0:
DNET-RT: Received level 1 routing from 1.3 on Ethernet0 at 1:16:34
The following line indicates that the router is sending its scheduled updates on interface Ethernet 0:
DNET-RT: Sending normal routing updates on Ethernet0
The following line indicates that the route will send an unscheduled update on this interface as a result of some event. In this case, the unscheduled update is a result of a new entry created in the interface's routing table.
DNET-RT: route update triggered by after split route pointers in dn_rt_input
The following line indicates that the router sent the unscheduled update on Ethernet 0:
DNET-RT: Sending L1 triggered routes
DNET-RT: Sending L1 triggered routing updates on Ethernet0
The following line indicates that the router removed the entry for node 1.5 because the adjacency with node 1.5 timed out, or the route to node 1.5 through a next-hop router went away:
DNET-RT: removing route to node 5
Use the debug dialer EXEC command to display debugging information about the packets that have been received on a Frame Relay interface. The no form of this command disables debugging output.
debug dialerThis command has no arguments or keywords.
EXEC
Table 2-12 describes the error messages that the debug dialer command can generate for a serial interface being used as a V.25bis dialer for dial-on-demand routing (DDR).
| Message | Description |
|---|---|
| Serial 0: Dialer result = xxxxxxxxxx | This message displays the result returned from the V.25bis dialer. It is useful in debugging if calls are failing. On some hardware platforms, this message cannot be displayed due to hardware limitations. Possible values for the xxxxxxxxxx variable depend on the V.25bis device with which the router is communicating. |
| Serial 0: No dialer string defined. Dialing cannot occur. | This message is displayed when a packet is received that should cause a call to be placed. However, there is no dialer string configured, so dialing cannot occur. This message usually indicates a configuration problem. |
| Serial 0: Attempting to dial xxxxxxxxxx | This message indicates that a packet has been received that passes the dial-on-demand access lists. That packet causes dialing of a phone number. The xxxxxxxxxx variable is the number being called. |
| Serial 0: Unable to dial xxxxxxxxxx | This message is displayed if for some reason, the phone call could not be placed. This might be due to a lack of memory, full output queues, or other problems. |
| Serial 0: disconnecting call | This message is displayed when the router attempts to hang up a call. |
| Serial 0: idle timeout
Serial 0: re-enable timeout Serial 0: wait for carrier timeout | One of these three messages is displayed when their corresponding dialer timer expires. They are mostly informational, but are useful when debugging a disconnected call or call failure. |
When DDR is enabled on the interface, information concerning the cause of any calls (called Dialing cause) may be displayed.
The following line of output for an IP packet lists the name of the DDR interface and the source and destination addresses of the packet:
Dialing cause: Serial0: ip (s=131.108.1.111 d=131.108.2.22)
The following line of output for a bridged packet lists the DDR interface and the type of packet (in hexadecimal). For information on these packet types, see the "Ethernet Type Codes," appendix of the Router Products Command Reference publication.
Dialing cause: Serial1: Bridge (0x6005)
Use the debug frame-relay EXEC command to display debugging information about the packets that have been received on a Frame Relay interface. The no form of this command disables debugging output.
debug frame-relayThis command has no arguments or keywords.
EXEC
This command helps you to analyze the packets that have been received. However, because the debug frame-relay command generates a lot of output, only use it when traffic on the Frame Relay network is less than 25 packets per second.
To analyze the packets that have been sent on a Frame Relay interface, use the debug frame-relay packets command.
Figure 2-28 shows sample debug frame-relay output.

Table 2-13 describes significant fields shown in Figure 2-28.
Use the debug frame-relay events EXEC command to display debugging information about Frame Relay ARP replies on networks that support a multicast channel and use dynamic addressing. The no form of this command disables debugging output.
debug frame-relay eventsThis command has no arguments or keywords.
EXEC
This command is useful for identifying the cause of end-to-end connection problems during the installation of a Frame Relay network or node.
Figure 2-29 shows sample debug frame-relay events output.

As Figure 2-29 shows, debug frame-relay events returns one specific message type. The first line, for example, indicates that IP address 131.108.170.26 sent a Frame Relay ARP reply; this packet was received as input on the Serial2 interface. The last field (126) is the DLCI to use when communicating with the responding router.
Use the debug frame-relay lmi EXEC command to display information on the local management interface (LMI) packets exchanged by the router and the Frame Relay service provider. The no form of this command disables debugging output.
debug frame-relay lmiThis command has no arguments or keywords.
EXEC
You can use this command to determine whether the router and the Frame Relay switch are sending and receiving LMI packets properly.
Figure 2-30 shows sample debug frame-relay lmi output.
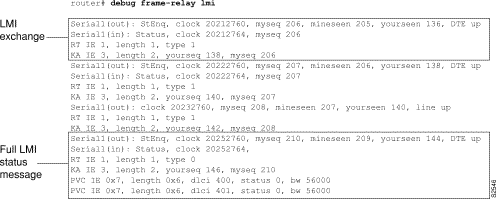
In Figure 2-30, the first four lines describe an LMI exchange. The first line describes the LMI request the router has sent to the switch. The second line describes the LMI reply the router has received from the switch. The third and fourth lines describe the response to this request from the switch. This LMI exchange is followed by two similar LMI exchanges. The last six lines in Figure 2-30 comprise a full LMI status message that includes a description of the router's two permanent virtual circuits (PVCs).
Table 2-14 describes significant fields in the first line of the debug frame-relay lmi output shown in Figure 2-30.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Serial1(out) | Indicates that the LMI request was sent out on the Serial1 interface. |
| StEnq | Command Mode of message:
StEnq--Status Enquiry Status--Status reply |
| clock 20212760 | System clock (in milliseconds). Useful for determining whether an appropriate amount of time has transpired between events. |
| myseq 206 | The myseq counter maps to the router's CURRENT SEQ counter. |
| yourseen 136 | The yourseen counter maps to the LAST RCVD SEQ counter of the switch. |
| DTE up | Indicates the line protocol up/down state for the DTE (user) port. |
Table 2-15 describes significant fields in the third and fourth lines of debug frame-relay lmi output shown in Figure 2-30.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| RT IE 1 | Value of the report type information element. |
| length 1 | Length of the report type information element (in bytes). |
| type 1 | Report type in RT IE. |
| KA IE 3 | Value of the keepalive information element. |
| length 2 | Length of the keepalive information element (in bytes). |
| yourseq 138 | The yourseq counter maps to the CURRENT SEQ counter of the switch. |
| myseq 206 | The myseq counter maps to the router's CURRENT SEQ counter. |
Table 2-16 describes significant fields in the last line of debug frame-relay lmi output shown in Figure 2-30.
Use the debug frame-relay packets EXEC command to display information on packets that have been sent on a Frame Relay interface. The no form of this command disables debugging output.
debug frame-relay packetsThis command has no arguments or keywords.
EXEC
This command helps you to analyze the packets that have been sent on a Frame Relay interface. Because the debug frame-relay packets command generates large amounts of output, only use it when traffic on the Frame Relay network is less than 25 packets per second.
To analyze the packets that have been received on a Frame Relay interface, use the debug frame-relay command.
Figure 2-31 shows sample debug frame-relay packets output.

As Figure 2-31 shows, debug frame-relay packets output comprises groups of output lines; each group describes a Frame Relay packet that has been sent. The number of lines in the group can vary, depending on the number of DLCIs on which the packet was sent. For example, the first two pairs of output lines describe two different packets, both of which were sent out on a single DLCI. The last three lines in Figure 2-31 describe a single Frame Relay packet that was sent out on two DLCIs.
Table 2-17 describes significant fields shown in the first pair of output lines in Figure 2-31.
Explanations for other lines of output shown in Figure 2-31 follow:
The following lines describe a Frame Relay packet sent to a particular address; in this case AppleTalk address 10.2:
Serial0: broadcast - 0, link 809B, addr 10.2
Serial0(o):DLCI 100 type 809B size 104
The following lines describe a Frame Relay packet that went out on two different DLCIs, because two Frame Relay map entries were found:
Serial0: broadcast search
Serial0(o):DLCI 300 type 809B size 24
Serial0(o):DLCI 400 type 809B size 24
The following lines do not appear in Figure 2-31. They describe a Frame Relay packet sent to a true broadcast address.
Serial1: broadcast search
Serial1(o):DLCI 400 type 800 size 288
Use the debug ip icmp EXEC command to display information on ICMP transactions. The no form of this command disables debugging output.
debug ip icmpThis command has no arguments or keywords.
EXEC
This command is useful for determining whether the router is sending and/or receiving ICMP messages; for example, when troubleshooting an end-to-end connection problem.
Figure 2-32 shows sample debug ip icmp output.

Table 2-18 describes significant fields shown in the first line of debug ip icmp output shown in Figure 2-32.
Table 2-19 describes significant fields shown in the second line of debug ip icmp output in
Figure 2-32.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| ICMP: | Indicates that this message describes an ICMP packet. |
| src 36.56.0.202 | The address of the sender of the echo. |
| dst 131.108.16.1 | The address of the receiving router. |
| echo reply | Indicates the router received an echo reply. |
Other messages that the debug ip icmp command can generate follow.
When an IP router or host sends out an ICMP mask request, the following message is generated when the router sends a mask reply:
ICMP: sending mask reply (255.255.255.0) to 160.89.80.23 via Ethernet0
The following two lines are examples of the two forms of this message. The first form is generated when a mask reply comes in after the router sends out a mask request. The second form occurs when the router receives a mask reply with a nonmatching sequence and ID. See Appendix I of RFC 950, "Internet Standard Subnetting Procedures," for details.
ICMP: mask reply 255.255.255.0 from 160.89.80.31
ICMP: unexpected mask reply 255.255.255.0 from 160.89.80.32
The following output indicates that the router sent a redirect packet to the host at address 160.89.80.31, instructing that host to use the gateway at address 160.89.80.23 in order to reach the host at destination address 131.108.1.111:
ICMP: redirect sent to 160.89.80.31 for dest 131.108.1.111 use gw 160.89.80.23
The following message indicates that the router received a redirect packet from the host at address 160.89.80.23, instructing the router to use the gateway at address 160.89.80.28 in order to reach the host at destination address 160.89.81.34:
ICMP: redirect rcvd from 160.89.80.23 -- for 160.89.81.34 use gw 160.89.80.28
The following message is displayed when the router sends an ICMP packet to the source address (160.89.94.31 in this case), indicating that the destination address (131.108.13.33 in this case) is unreachable:
ICMP: dst (131.108.13.33) host unreachable sent to 160.89.94.31
The following message is displayed when the router receives an ICMP packet from an intermediate address (160.89.98.32 in this case), indicating that the destination address (131.108.13.33 in this case) is unreachable:
ICMP: dst (131.108.13.33) host unreachable rcv from 160.89.98.32
Depending on the code received (as Table 2-18 describes), any of the unreachable messages can have any of the following "strings" instead of the "host" string in the message:
net
protocol
port
frag. needed and DF set
source route failed
prohibited
The following message is displayed when the TTL in the IP header reaches zero and a time exceed ICMP message is sent. The fields are self-explanatory.
ICMP: time exceeded (time to live) send to 128.95.1.4 (dest was 131.108.1.111)
The following message is generated when parameters in the IP header are corrupted in some way and the parameter problem ICMP message is sent. The fields are self-explanatory.
ICMP: parameter problem sent to 128.121.1.50 (dest was 131.108.1.111)
Based on the preceding information, the remaining output can be easily understood.
ICMP: parameter problem rcvd 160.89.80.32
ICMP: source quench rcvd 160.89.80.32
ICMP: source quench sent to 128.121.1.50 (dest was 131.108.1.111)
ICMP: sending time stamp reply to 160.89.80.45
ICMP: sending info reply to 160.89.80.12
ICMP: rdp advert rcvd type 9, code 0, from 160.89.80.23
ICMP: rdp solicit rcvd type 10, code 0, from 160.89.80.43
Use the debug ip igrp events EXEC command to display information of IGRP routing messages that indicate the source and destination of each update, as well as the number of routes in each update. Messages are not generated for each route. The no form of this command disables debugging output.
debug ip igrp events [ip-address]| ip-address | (Optional) IP address of an IGRP neighbor |
EXEC
If the IP address of an IGRP neighbor is specified, the resulting debug ip igrp events output will include messages describing updates from that neighbor and updates that the router broadcasts toward that neighbor.
This command is particularly useful when there are many networks in your routing table. In this case, using debug ip igrp transaction could flood the console and make the router unusable. Use debug ip igrp events instead to display summary routing information.
Figure 2-33 shows sample debug ip igrp events output.
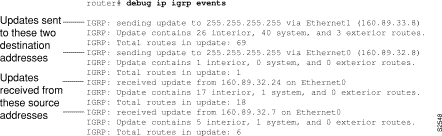
Figure 2-33 shows that the router has sent two updates to the broadcast address 255.255.255.255. The router also received two updates. Three lines of output describe each of these updates. Explanations for representative lines of output from Figure 2-33 follow.
The first line indicates whether the router sent or received the update packet, the source or destination address, and the interface through which the update was sent or received. If the update was sent, the IP address assigned to this interface is shown (in parentheses).
IGRP: sending update to 255.255.255.255 via Ethernet1 (160.89.33.8)
The second line summarizes the number and types of routes described in the update:
IGRP: Update contains 26 interior, 40 system, and 3 exterior routes.
The third line indicates the total number of routes described in the update.
IGRP: Total routes in update: 69
Use the debug ip igrp transaction EXEC command to display information on IGRP routing transactions. The no form of this command disables debugging output.
debug ip igrp transaction [ip-address]| ip-address | (Optional) IP address of an IGRP neighbor |
EXEC
If the IP address of an IGRP neighbor is specified, the resulting debug ip igrp transaction output will include messages describing updates from that neighbor and updates that the router broadcasts toward that neighbor.
When there are many networks in your routing table, debug ip igrp transaction can flood the console and make the router unusable. In this case, use debug ip igrp events instead to display summary routing information.
Figure 2-34 shows sample debug ip igrp transaction output.
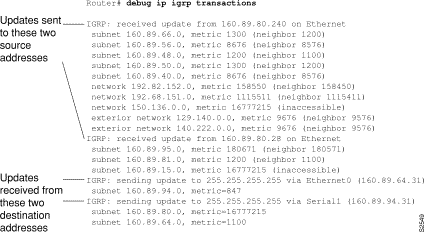
Figure 2-34 shows that the router being debugged has received updates from two other routers on the network. The router at source address 160.89.80.240 sent information about ten destinations in the update; the router at source address 160.89.80.28 sent information about three destinations in its update. The router being debugged also sent updates--in both cases to the broadcast address 255.255.255.255 as the destination address.
The first line in Figure 2-34 is self-explanatory.
On the second line in Figure 2-34, the first field refers to the type of destination information: "subnet" (interior), "network" (system), or "exterior" (exterior). The second field is the Internet address of the destination network. The third field is the metric stored in the routing table and the metric advertised by the neighbor sending the information. "Metric ... inaccessible" usually means that the neighbor router has put the destination in holddown.
The entries in Figure 2-34 show that the router is sending updates that are similar, except that the numbers in parentheses are the source addresses used in the IP header. A metric of 16777215 is inaccessible.
Other examples of output that the debug ip igrp transaction command can produce follow.
The following entry indicates that the routing table was updated and shows the new edition number (97 in this case) to be used in the next IGRP update:
IGRP: edition is now 97
Entries such as the following occur on startup or when some event occurs such as an interface transitioning or a user manually clearing the routing table:
IGRP: broadcasting request on Ethernet0
IGRP: broadcasting request on Ethernet1
The following type of entry can result when routing updates become corrupted between sending and receiving routers:
IGRP: bad checksum from 160.89.64.43
An entry such as the following should never appear. If it does, the receiving router has a bug in the software or a problem with the hardware. In either case, contact your technical support representative.
IGRP: system 45 from 160.89.64.234, should be system 109
Use the debug ip ospf events EXEC command to display information on OSPF-related events, such as adjacencies, flooding information, designated router selection, and SPF calculation. The no form of this command disables debugging output.
debug ip ospf eventsThis command has no arguments or keywords.
EXEC
Figure 2-35 shows sample debug ip ospf events output.

The debug ip ospf events output shown in Figure 2-35 might appear if any of the following occurs:
If a router configured for OSPF routing is not seeing an OSPF neighbor on an attached network, do the following:
In the following example line, the neighbor and this router are not part of a stub area (that is, one is a part of transit area and the other is a part of a stub area, as explained in RFC 1247).
OSPF: hello packet with mismatched E bit
Use the debug ip packet EXEC command to display general IP debugging information and IPSO security transactions. The no form of this command disables debugging output.
debug ip packet [access-list-number]| access-list-number | (Optional) IP access list number that you can specify. If the datagram is not permitted by that access list, the related debugging output is suppressed. |
EXEC
If a communication session is closing when it should not be, an end-to-end connection problem can be the cause. The debug ip packet command is useful for analyzing the messages traveling between the local and remote hosts.
IP debugging information includes packets received, generated, and forwarded. Fast-switched packets do not generate messages.
IPSO security transactions include messages that describe the cause of failure each time a datagram fails a security test in the system. This information is also sent to the sending host when the router configuration allows it.
Figure 2-36 shows sample debug ip packet output.

Figure 2-36 shows two types of messages that the debug ip packet command can produce; the first line of output describes an IP packet that the router forwards, and the third line of output describes a packet that is destined for the router. In the third line of output, "rcvd 2" indicates that the router decided to receive the packet.
Table 2-20 describes the fields shown in the first line of Figure 2-36.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| IP: | Indicates that this is an IP packet. |
| s = 131.108.13.44 (Fddi0) | Indicates the source address of the packet and the name of the interface that received the packet. |
| d = 157.125.254.1 (Serial2) | Indicates the destination address of the packet and the name of the interface (in this case, S2) through which the packet is being sent out on the network. |
| g = 131.108.16.2 | Indicates the address of the next hop gateway. |
| forward | Indicates that the router is forwarding the packet. If a filter denies a packet, "access denied" replaces "forward," as shown in the last line of output in Figure 2-36. |
The calculation on whether to send a security error message can be somewhat confusing. It depends upon both the security label in the datagram and the label of the incoming interface. First, the label contained in the datagram is examined for anything obviously wrong. If nothing is wrong, assume it to be correct. If there is something wrong, the datagram is treated as unclassified genser. Then the label is compared with the interface range, and the appropriate action is taken as Table 2-21 describes.
| Classification | Authorities | Action Taken |
|---|---|---|
| Too low | Too low
Good Too high | No Response
No Response No Response |
| In range | Too low
Good Too high | No Response
Accept Send Error |
| Too high | Too low
In range Too high | No Response
Send Error Send Error |
The security code can only generate a few types of ICMP error messages. The only possible error messages and their meanings follow:
When an IP packet is rejected due to an IP security failure, an audit message is sent via DNSIX NAT. Also, any debug ip packet output is appended to include a description of the reason. These reasons can be any of the following:
Use the debug ip rip EXEC command to display information on RIP routing transactions. The no form of this command disables debugging output.
debug ip ripThis command has no arguments or keywords.
EXEC
Figure 2-37 shows sample debug ip rip output.

Figure 2-37 shows that the router being debugged has received updates from one router at source address 160.89.80.28. That router sent information about five destinations in the routing table update. Notice that the fourth destination address in the update--131.108.0.0--is inaccessible because it is more than 15 hops away from the router sending the update. The router being debugged also sent updates, in both cases to broadcast address 255.255.255.255 as the destination.
The first line in Figure 2-37 is self-explanatory.
The second line in Figure 2-37 is an example of a routing table update. It shows how many hops a given Internet address is from the router.
The entries in Figure 2-37 show that the router is sending updates that are similar, except that the number in parentheses is the source address encapsulated into the IP header.
Examples of additional output that the debug ip rip command can generate follow.
Entries such as the following appear at startup or when some event occurs such as an interface transitioning or the user manually clearing the routing table:
RIP: broadcasting general request on Ethernet0
RIP: broadcasting general request on Ethernet1
The following line is self-explanatory:
RIP: received request from 160.89.80.207 on Ethernet0
An entry such as the following is most likely caused by a malformed packet from the transmitter:
RIP: bad version 128 from 160.89.80.43
Use the debug ip routing EXEC command to display information on RIP routing table updates and route-cache updates. The no form of this command disables debugging output.
debug ip routingThis command has no arguments or keywords.
EXEC
Figure 2-38 shows sample debug ip routing output.
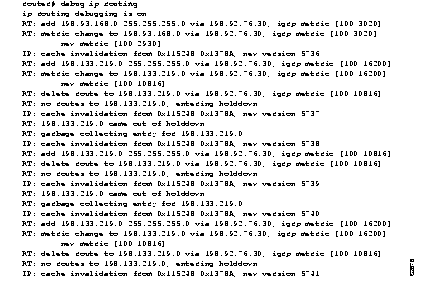
Explanations for representative lines of output in Figure 2-38 follow.
In the following lines, a newly created entry has been added to the IP routing table. The metric change indicates this entry existed previously, but its metric changed and that the metric was reported by means of IGRP. The metric could also be reported via RIP, OSPF, or another IP routing protocol. The numbers inside the brackets report the administrative distance and the actual metric. Cache invalidation means that the fast switching cache was invalidated due to a routing table change. New version is the version number of the routing table. When the routing table changes, this number is incremented. The hexadecimal numbers are internal number that vary from version to version and software load to software load.
RT: add 198.93.168.0 255.255.255.0 via 198.92.76.30, igrp metric [100/3020]
RT: metric change to 198.93.168.0 via 198.92.76.30, igrp metric [100/3020]
new metric [100/2930]
IP: cache invalidation from 0x115248 0x1378A, new version 5736
In the following output, the holddown and invalid lines are displayed. Most of the distance vector routing protocols use holddown to avoid typical problems like counting to infinity and routing loops. If you look at the output of show ip protocols you will see what the timer values are for holddown and invalid. Invalid corresponds to came out of holddown. Delete route is triggered when a better path comes along. It gets rid of the old worse path.
RT: delete route to 198.133.219.0 via 198.92.76.30, igrp metric [100/10816]
RT: no routes to 198.133.219.0, entering holddown
IP: cache invalidation from 0x115248 0x1378A, new version 5737
RT: 198.133.219.0 came out of holddown
Use the debug ip security EXEC command to display IP security option processing. The no form of this command disables debugging output.
debug ip securityThis command has no arguments or keywords.
EXEC
The debug ip security command displays information for both basic and extended IP security options. For interfaces where ip security is configured, each IP packet processed for that interface results in debugging output whether or not the packet contains IP security options. IP packets processed for other interfaces that also contain IP security information also trigger debugging output. Some additional IP security debugging information is also controlled by the debug ip packet EXEC command.
Figure 2-39 shows sample debug ip security output.
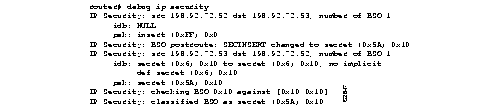
Table 2-22 describes significant fields shown in Figure 2-39.
Explanations for representative lines of output in Figure 2-39 follow.
The following line indicates that the packet was locally generated, and it has been classified with the internally significant security level "insert" (0xff) and authority 0x0:
idb: NULL
pak: insert (0xff) 0x0
The following line indicates that the packet was received via an interface with dedicated IP security configured. Specifically, the interface is configured at security level "secret" and with authority information of 0x0. The packet itself was classified at level "secret" (0x5a) and authority 0x10.
idb: secret (0x6) 0x10 to secret (0x6) 0x10, no implicit
def secret (0x6) 0x10
pak: secret (0x5A) 0x10
Use the debug ip tcp driver EXEC command to display information on TCP driver events; for example, connections opening or closing, or packets being dropped because of full queues. The no form of this command disables debugging output.
debug ip tcp driverThis command has no arguments or keywords.
EXEC
The TCP driver is the process that the router software uses to send packet data over a TCP connection. Remote source-route bridging, STUN, and X.25 switching currently use the TCP driver.
Using the debug ip tcp driver command together with the debug ip tcp driver-pak command provides the most verbose debugging output concerning TCP driver activity.
Figure 2-40 shows sample debug ip tcp driver output.
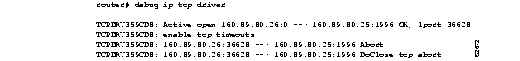
Explanations for individual lines of output from Figure 2-40 follow.
Table 2-23 describes the fields in the first line of output.
The following line indicates that the TCP driver user (remote source-route bridging, in this case) will allow TCP to drop the connection if excessive retransmissions occur:
TCPDRV359CD8: enable tcp timeouts
The following line indicates that the TCP driver user (in this case, remote source-route bridging) at IP address 160.89.80.26 (and using TCP port number 36628) is requesting that the connection to IP address 160.89.80.25 using TCP port number 1996 be aborted:
TCPDRV359CD8: 160.89.80.26:36628 --> 160.89.80.25:1996 Abort
The following line indicates that this connection was in fact closed due to an abort:
TCPDRV359CD8: 160.89.80.26:36628 --> 160.89.80.25:1996 DoClose tcp abort
Use the debug ip tcp driver-pak EXEC command to display information on every operation that the TCP driver performs. The no form of this command disables debugging output.
debug ip tcp driver-pakThis command has no arguments or keywords.
EXEC
This command turns on a verbose debugging by logging at least one debugging message for every packet sent or received on the TCP driver connection.
The TCP driver is the process that the router software uses to send packet data over a TCP connection. Remote source-route bridging, STUN, and X.25 switching currently use the TCP driver.
To observe the context within which certain debug ip tcp driver-pak messages occur, turn this command on in conjunction with the debug ip tcp driver command.
Figure 2-41 shows sample debug ip tcp driver-pak output.

Explanations for individual lines of output from Figure 2-40 follow.
Table 2-24 describes the fields shown in the first line of output.
The following line indicates that the TCP driver has sent the data that it had received from the TCP driver user, as shown in the previous line of output. The last field in the line (26) indicates that the 26 bytes of data were sent out as a single unit.
TCPDRV359CD8: output pak 2E8CD8 (len 26) (26)
The following line indicates that the TCP driver has received 42 bytes of data from the remote IP address. The TCP driver user (in this case, remote source-route bridging) has established an input threshold of 16 bytes for this connection. (The input threshold instructs the TCP driver to transfer data to the TCP driver user only when at least 16 bytes are present.)
TCPDRV359CD8: readf 42 bytes (Thresh 16)
Use the debug ip tcp transactions EXEC command to display information on significant TCP transactions such as state changes, retransmissions, and duplicate packets. The no form of this command disables debugging output.
debug ip tcp transactionsThis command has no arguments or keywords.
EXEC
This command is particularly useful for debugging a performance problem on a TCP/IP network that you have isolated above the data link layer.
The debug ip tcp command displays output for packets the router sends and receives, but does not display output for packets it forwards.
Figure 2-41 shows sample debug ip tcp transactions output.

Table 2-25 describes significant fields shown in Figure 2-41.
|
|