|
|

Use the debug ipx ipxwan EXEC command to display debug information for interfaces configured to use IPXWAN. The no form of this command disables debugging output.
debug ipx ipxwanThis command has no arguments or keywords.
EXEC
The debug ipx ipxwan command is useful for verifying the startup negotiations between two routers running the IPX protocol through a WAN. This command produces output only during state changes or startup. During normal operations, no output is produced.
Figure 2-43 shows sample debug ipx ipxwan output during link startup.

Explanations for representative lines of output in Figure 2-43 follow.
The following line indicates that the interface has initialized:
%LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Serial1, changed state to up
The following lines indicate that the startup process failed to receive a timer response, brought the link down, then brought the link up and tried again with a new timer set:
IPXWAN: state (Sending Timer Requests -> Disconnect) [Serial1/6666:200 (IPX line
state brought down)]
IPXWAN: state (Disconnect -> Sending Timer Requests) [Serial1/6666:200 (IPX line
state brought up)]
The following lines indicate that the interface is sending timer requests and waiting on timer response:
IPXWAN: Send TIMER_REQ [seq 0] out Serial1/6666:200
IPXWAN: Send TIMER_REQ [seq 1] out Serial1/6666:200
The following lines indicate that the interface has received timer request from the other end of the link and has sent a timer response. The fourth line shows that the interface has come up as the master on the link.
IPXWAN: Rcv TIMER_REQ on Serial1/6666:200, NodeID 1234, Seq 1
IPXWAN: Send TIMER_REQ [seq 1] out Serial1/6666:200
IPXWAN: Rcv TIMER_RSP on Serial1/6666:200, NodeID 1234, Seq 1, Del 6
IPXWAN: state (Sending Timer Requests -> Master: Sent RIP/SAP) [Serial1/6666:200
(Received Timer Response as master)]
The following lines indicate that the interface is sending RIP/SAP requests:
IPXWAN: Send RIPSAP_INFO_REQ [seq 0] out Serial1/6666:200
IPXWAN: Rcv RIPSAP_INFO_RSP from Serial1/6666:200, NodeID 1234, Seq 0
IPXWAN: state (Master: Sent RIP/SAP -> Master: Connect) [Serial1/6666:200 (Received Router Info Rsp as Master)]
Use the debug ipx packet EXEC command to display information about packets received, transmitted, and forwarded. The no form of this command disables debugging output.
debug ipx packetThis command has no arguments or keywords.
EXEC
This command is useful for learning whether IPX packets are traveling over a router.
Figure 2-44 shows sample debug ipx packet output.

In Figure 2-43, the first line indicates that the router receives a packet from a Novell station (address 160.0260.8c4c.4f22); this trace does not indicate the address of the immediate router sending the packet to this router. In the second line, the router forwards the packet toward the Novell server (address 1.0000.0000.0001) through an immediate router (183.0000.0c01.5d85).
Table 2-26 describes significant fields shown in Figure 2-44.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
IPX
| Shows that this is a IPX packet. |
src = 160.0260.8c4c.4f22
| Source address of the IPX packet. The Novell network number is 160. Its MAC address is 0260.8c4c.4f22. |
| dst = 1.0000.0000.0001 | Destination address for the IPX packet. The address 0000.0000.0001 is an internal MAC address, and the network number 1 is the internal network number of a Novell 3.11 server. |
packet received
| The router received this packet from a Novell station, possibly through an intermediate router. |
| gw = 183.0000.0c01.5d85 | The router is sending the packet over to the next hop router; its address of 183.0000.0c01.5d85 was learned from the IPX routing table. |
| sending packet | The router is attempting to send this packet. |
Use the debug ipx routing EXEC command to display information on IPX routing packets that the router sends and receives. The no form of this command disables debugging output.
debug ipx routingThis command has no arguments or keywords.
EXEC
Normally, a router or server sends out one routing update per minute. Each routing update packet can include up to 50 entries. If many networks exist on the internetwork, the router sends out multiple packets per update. For example, if a router has 120 entries in the routing table, it would send three routing update packets per update. The first routing update packet would include the first 50 entries, the second packet would include the next 50 entries, and the last routing update packet would include the last 20 entries.
Figure 2-45 shows sample debug ipx routing output.

Table 2-27 describes significant fields shown in Figure 2-45.
debug ipx sap
Use the debug ipx sap EXEC command to display information about IPX Service Advertisement Protocol (SAP) packets. The no form of this command disables debugging output.
debug ipx sap [activity | events]| activity | (Optional) Provides more detailed output of SAP packets, including displays of services in SAP packets. |
| events | (Optional) Limits amount of detailed output for SAP packets to those that contain interesting events. |
EXEC
Normally, a router or server sends out one SAP update per minute. Each SAP packet can include up to seven entries. If many servers are advertising on the network, the router sends out multiple packets per update. For example, if a router has 20 entries in the SAP table, it would send three SAP packets per update. The first SAP would include the first seven entries, the second SAP would include the next seven entries, and the last update would include the last six entries.
The most meaningful detail is obtained by using both the debug ipx sap activity and the debug ipx sap events commands together.
 | Caution Because the debug ipx sap command can generate a lot of output, use it with caution on networks that have many interfaces and large service tables. |
Figure 2-46 shows sample debug ipx sap output.

As Figure 2-46 shows, the debug ipx sap command generates multiple lines of output for each SAP packet--a packet summary message and a service detail message.
Explanations for representative lines of output from Figure 2-46 follow.
The first line displays the internal router memory address of the packet. The technical support staff may use this information in problem debugging.
NovellSAP: at 0023F778:
Table 2-28 describes the fields shown in the second line of output in Figure 2-46.
Table 2-29 describes the fields shown in the third and fourth lines of output in Figure 2-46.
The fifth line of output indicates that the router sent a SAP update to network 160:
NovellSAP: sending update to 160
As Figure 2-46 shows, the format for debug ipx sap output describing a SAP update the router sends is similar to that describing a SAP update the router receives, except that the ssoc: field replaces the src: field, as the following line of output indicates:
O SAP Update type 0x2 len 96 ssoc:0x452 dest:160.ffff.ffff.ffff(452)
Table 2-30 describes possible values for the ssoc: field.
debug ipx routing
Use the debug isdn-event EXEC command to display ISDN events occurring on the user side (on the router) of the ISDN interface. The ISDN events that may display are Q.931 events (call setup and teardown of ISDN network connections). The no form of this command disables debugging output.
debug isdn-eventThis command has no arguments or keywords.
EXEC
Although the debug information provided through the debug isdn-event command is similar to the information provided in the debug isdn-q931 command, the information is displayed in a different format. If you want to see the information displayed in both formats, you can enable both of these commands at the same time. The displays will be intermingled.
Use the show dialer command to retrieve information about the status and configuration of the ISDN interface on the router.
Figure 2-47 shows sample debug isdn-event output of call setup events for an outgoing call.

Figure 2-48 shows sample debug isdn-event output of call setup events for an incoming call. The values used for internal purposes are unpacked information elements. The values that follow the ISDN specification are an interpretation of the unpacked information elements. Refer to the "ISDN Switch Types, Codes, and Values" appendix for information about these values.

Figure 2-49 shows sample debug isdn-event output of call teardown events for a call that has been hung up by the other side of the connection.
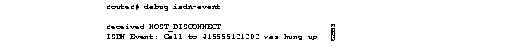
Figure 2-50 shows sample debug isdn-event output of a call teardown event for an outgoing or incoming call that has been hung up by the ISDN interface on the router side.

Table 2-31 describes significant fields shown in Figure 2-47 through Figure 2-50.
Figure 2-51 shows sample debug isdn-event output of a call teardown event for a call that has passed call screening then has been hung up by the ISDN interface on the far end side.
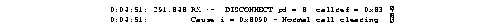
Figure 2-52 shows sample debug isdn-event output of a call teardown event for a call that has not passed call screening and has been rejected by the ISDN interface on the router side.
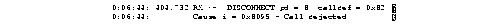
Figure 2-53 shows sample debug isdn-event output of a call teardown event for an outgoing call that uses a dialer subaddress.
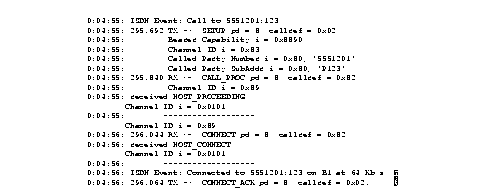
Use the debug isdn-q921 EXEC command to display data link layer (Layer 2) access procedures that are taking place at the router on the D-channel (LAPD) of its Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN) interface. The no form of this command disables debugging output.
debug isdn-q921This command has no arguments or keywords.
EXEC
The ISDN data link layer interface provided by the router conforms to the user interface specification defined by ITU-T recommendation Q.921. The display information provided when you enter the debug isdn-q921 command is limited to commands and responses exchanged during peer-to-peer communication carried over the D-channel. This debug information does not include data transmitted over the B-channels that are also part of the router's ISDN interface. The peers (data link layer entities and layer management entities on the routers) communicate with each other via an ISDN switch over the D-channel.
A router can be the calling or called party of the ISDN Q.921 data link layer access procedures. If the router is the calling party, the command displays information about an outgoing call. If the router is the called party, the command displays information about an incoming call and the keepalives (RRs).
The debug isdn-q921 command can be used with the debug isdn-event and the debug isdn-q931 commands at the same time. The displays will be intermingled. See debug isdn-event later in this chapter for samples of combination displays.
Sample Display
Figure 2-54 shows sample debug isdn-q921 output for an outgoing call.
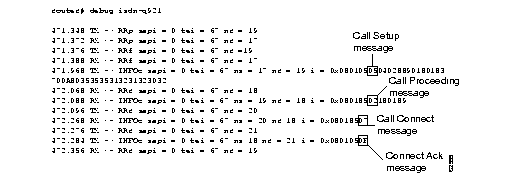
Figure 2-55 shows sample debug isdn-q921 output for a startup message on a DMS-100 switch.
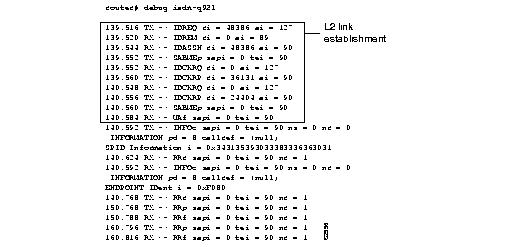
Figure 2-56 shows sample debug isdn-q921 output for an incoming call. It is an incoming SETUP message that assumes L2 link is already established to the other side.

Table 2-32 describes significant fields in Figure 2-54, Figure 2-55, and Figure 2-56.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| 139.516 | Indicates the time at which the frame was transmitted from or received by the data link layer entity on the router. The time is maintained by an internal clock. This internal clock is used for the various timers (such as T200, T202, and T201 that may expire while these access procedures are being processed) and for timestamping. Time is in seconds. |
| TX | Indicates that this frame is being transmitted from the ISDN interface on the local router (user side). |
| RX | Indicates that this frame is being received by the ISDN interface on the local router from the peer (network side). |
| IDREQ | Indicates the Identity Request message type sent from the local router to the network (assignment source point [ASP]) during the automatic terminal endpoint identifier (TEI) assignment procedure. This message is sent in a UI command frame. The service access point identifier (SAPI) value for this message type is always 63 (indicating that it is Layer 2 management procedure) but it is not displayed. The TEI value for this message type is 127 (indicating that it is a broadcast operation). |
| ri = 48386 | Indicates the Reference number used to differentiate between user devices requesting TEI assignment. This value is a randomly generated number between 0 and 65535. The same ri value sent in the IDREQ message should be returned in the corresponding IDASSN message. Note that a Reference number of 0 indicates that the message is sent from the network side management layer entity and a reference number has not been generated. |
| ai = 127 | Indicates the Action indicator used to request that the ASP assign any TEI value. It is always 127 for the broadcast TEI. Note that in some message types, such as IDREM, a specific TEI value is indicated. |
| IDREM | Indicates the Identity Remove message type sent from the ASP to the user side layer management entity during the TEI removal procedure. This message is sent in a UI command frame. The ASP sends the Identity Remove message twice to avoid message loss. |
| IDASSN | Indicates the Identity Assigned message type sent from the ISDN service provider on the network to the local router during the automatic TEI assignment procedure. This message is sent in a UI command frame. The SAPI value for this message type is always 63 (indicating that it is Layer 2 management procedure). The TEI value for this message type is 127 (indicating it is a broadcast operation). |
| ai = 90 | Indicates the TEI value automatically assigned by the ASP. This TEI value will be used by data link layer entities on the local router in subsequent communication with the network. The valid values are in the range 64 through 126. |
| SABME | Indicates the set asynchronous balanced mode extended command. This command places the recipient into modulo 128 multiple frame acknowledged operation. This command also indicates that all exception conditions have been cleared. The SABME command is sent once a second for N200 times (typically three times) until its acceptance is confirmed with a UA response. For a list and brief description of other commands and responses that can be exchanged between the data link layer entities on the local router and the network, see ITU-T Recommendation Q.921. |
| sapi = 0 | Identifies the service access point at which the data link layer entity provides services to Layer 3 or to the management layer. A SAPI with the value 0 indicates it is a call control procedure. Note that the Layer 2 management procedures such as TEI assignment, TEI removal, and TEI checking, which are tracked with the debug isdn-q921 command, do not display the corresponding SAPI value; it is implicit. If the SAPI value were displayed it would be 63. |
| tei = 90 | Indicates the TEI value automatically assigned by the ASP. This TEI value will be used by data link layer entities on the local router in subsequent communication with the network. The valid values are in the range 64 through 126. |
| IDCKRQ | Indicates the Identity Check Request message type sent from the ISDN service provider on the network to the local router during the TEI check procedure. This message is sent in a UI command frame. The ri field is always 0. The ai field for this message contains either a specific TEI value for the local router to check or 127, which indicates that the local router should check all TEI values. For a list and brief description of other message types that can be exchanged between the local router and the ISDN service provider on the network, see the "ISDN Switch Types, Codes, and Values" appendix. |
| IDCKRP | Indicates the Identity Check Response message type sent from the local router to the ISDN service provider on the network during the TEI check procedure. This message is sent in a UI command frame in response to the IDCKRQ message. The ri field is a randomly generated number between 0 and 65535. The ai field for this message contains the specific TEI value that has been checked. |
| UAf | Confirms that the network side has accepted the SABME command previously sent by the local router. The final bit is set to 1. |
| INFOc | Indicates that this is an Information command. It is used to transfer sequentially numbered frames containing information fields that are provided by Layer 3. The information is transferred across a data link connection. |
| INFORMATION pd = 8 callref = (null) | Indicates the information fields provided by Layer 3. The information is sent one frame at a time. If multiple frames need to be sent, several Information commands are sent. The pd value is the protocol discriminator. The value 8 indicates it is call control information. The call reference number is always null for SPID information, |
| SPID information i = 0x343135393033383336363031 | Indicates the service profile identifier (SPID). The local router sends this information to the ISDN switch to indicate the services to which it subscribes. SPIDs are assigned by the service provider and are usually 10-digit telephone numbers followed by optional numbers. Currently, only the DMS-100 switch supports SPIDs, one for each B-channel. If SPID information is sent to a switch type other than DMS-100, an error may be displayed in the debug information. |
| ns = 0 | Indicates the send sequence number of transmitted I frames. |
| nr = 0 | Indicates the expected send sequence number of the next received I frame. At time of transmission, this value should be equal to the value of ns. The value of nr is used to determine whether frames need to be retransmitted for recovery. |
| RRr | Indicates the Receive Ready response for unacknowledged information transfer. The RRr is a response to an INFOc. |
| RRp | Indicates the Receive Ready command with the poll bit set. The data link layer entity on the user side uses the poll bit in the frame to solicit a response from the peer on the network side. |
| RRf | Indicates the Receive Ready response with the final bit set. The data link layer entity on the network side uses the final bit in the frame to indicate a response to the poll. |
| sapi | Indicates the service access point identifier. The SAPI is the point at which data link services are provided to a network layer or management entity. Currently, this field can have the value 0 (for call control procedure) or 63 (for Layer 2 management procedures) |
| tei | Indicates the terminal endpoint identifier (TEI) that has been assigned automatically by the assignment source point (ASP) (also called the layer management entity on the network side). The valid range is 64 through 126. The value 127 indicates a broadcast. |
Explanations for individual lines of output from Figure 2-54 follow.
The following lines indicate the message exchanges between the data link entity on the local router (user side) and the assignment source point (ASP) on the network side during the TEI assignment procedure. This assumes that the link is down and no TEI currently exists.
139.516 TX -> IDREQ ri = 48386 ai = 127 139.544 RX <- IDASSN ri = 48386 ai = 90At 139.516, the local router data link layer entity sent an Identity Request message to the network data link layer entity to request a TEI value that can be used in subsequent communication between the peer data link layer entities. The request includes a randomly generated reference number (48386) to differentiate between user devices that may be simultaneously requesting automatic TEI assignment and an action indicator of 127 to indicate that the ASP can assign any TEI value available. The ISDN user interface on the router uses automatic TEI assignment.
At 139.544, the network data link entity responds to the Identity Request message with an Identity Assigned message. The response includes the reference number (48386) previously sent in the request and TEI value (90) assigned by the ASP.
The following line indicates a message exchange between the layer management entity on the network side and the layer management entity on the local router (user side) during the TEI removal procedure:
139.520 RX <- IDREM ri = 0 ai = 89At 139.520, the network layer management entity sends an Identity Remove message when it determines that removal is necessary. The message includes a reference number that is always 0, because it is not responding to a request from the local router. The message also includes the TEI value (89) that is being removed because it is an old value that is no longer used.
The following lines indicate the message exchanges between the layer management entity on the network and the layer management entity on the local router (user side) during the TEI check procedure:
139.552 RX <- IDCKRQ ri = 0 ai = 127 139.560 TX -> IDCKRP ri = 36131 ai = 90At 139.552, the layer management entity on the network sends the Identity Check Request message to the layer management entity on the local router to check whether a TEI is in use. The message includes a reference number that is always 0 and the TEI value to check. In this case, an ai value of 127 indicates that all TEI values should be checked. At 139.560, the layer management entity on the local router responds with an Identity Check Response message indicating that TEI value 90 is currently in use.
The following lines indicate the messages exchanged between the data link layer entity on the local router (user side) and the data link layer on the network side to place the network side into modulo 128 multiple frame acknowledged operation. Note that the data link layer entity on the network side also can initiate the exchange.
140.560 TX -> SABMEp sapi = 0 tei = 90140.584 RX <- UAf sapi = 0 tei = 90
At 140.560, the data link layer entity on the local router sends the SABME command with a SAPI of 0 (call control procedure) for TEI 90. At 140.584, the first opportunity, the data link layer entity on the network responds with a UA response. This response indicates acceptance of the command. The data link layer entity sending the SABME command may have to send it more than once before receiving a UA response.
The following lines indicate the status of the data link layer entities. Both are ready to receive I frames.
150.768 TX -> RRp sapi = 0 tei = 90 nr = 1
150.788 RX <- RRf sapi = 0 tei = 90 nr = 1
These I frames are typically exchanged every 10 seconds (T203 timer).
Use the debug isdn-q931 EXEC command to display information about call setup and teardown of ISDN network connections (Layer 3) between the local router (user side) and the network. The no form of this command disables debugging output.
debug isdn-q931This command has no arguments or keywords.
EXEC
The ISDN network layer interface provided by the router conforms to the user interface specification defined by ITU-T recommendation Q.931 supplemented by other specifications such as for switch types VN2 and VN3.The router tracks only activities that are occurring on the user side, not the network side, of the network connection. The display information provided when you enter the debug isdn-q931 command is limited to commands and responses exchanged during peer-to-peer communication carried over the D-channel. This debug information does not include data transmitted over the B-channels, which are also part of the router's ISDN interface. The peers (network layers) communicate with each other via an ISDN switch over the D-channel.
A router can be the calling or called party of the ISDN Q.931 network connection call setup and tear- down procedures. If the router is the calling party, the command displays information about an outgoing call. If the router is the called party, the command displays information about an incoming call.
The debug isdn-q931 command can be used with the debug isdn-event and the debug isdn-q921 commands at the same time. The displays will be intermingled. See debug isdn-event earlier in this chapter for samples of combination displays.
Figure 2-57 shows sample debug isdn-q931 output of a call setup procedure for an outgoing call.

Figure 2-58 shows sample debug isdn-q931 output of a call setup procedure for an incoming call.
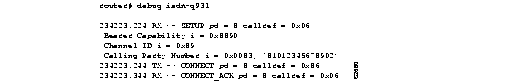
Figure 2-58 shows sample debug isdn-q931 output of a call teardown procedure from the network.
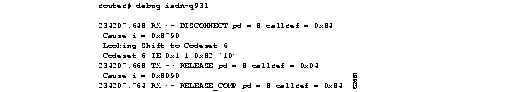
Figure 2-60 shows sample debug isdn-q931 output of a call teardown procedure from the router.

Table 2-33 describes significant fields in Figure 2-57 through Figure 2-60.
Use the debug isis adj packets EXEC command to display information on all adjacency-related activity such as hello packets sent and received and IS-IS adjacencies going up and down. The no form of this command disables debugging output.
debug isis adj packetsThis command has no arguments or keywords.
EXEC
Figure 2-61 shows sample debug isis adj packets output.

Explanations for individual lines of output from Figure 2-61 follow.
The following line indicates that the router received an IS-IS hello packet (IIH) on Ethernet0 from the Level 1 router (L1) at MAC address 0000.0c00.40af. The circuit type is the interface type: 1--Level 1 only; 2--Level 2 only; 3--Level 1/2.
The circuit ID is what the neighbor thinks is the designated router for the interface.
ISIS-Adj: Rec L1 IIH from 0000.0c00.40af (Ethernet0), cir type 3, cir id BBBB.BBBB.BBBB.01
The following line indicates that the router (configured as a Level 1 router) received on Ethernet1 an IS-IS hello packet from a Level 1 router in another area, thereby declaring an area mismatch:
ISIS-Adj: Area mismatch, level 1 IIH on Ethernet1
The following lines indicates that the router (configured as a Level 1/Level 2 router) sent on Ethernet1 a Level 1 IS-IS hello packet, and then a Level 2 IS-IS packet:
ISIS-Adj: Sending L1 IIH on Ethernet1
ISIS-Adj: Sending L2 IIH on Ethernet1
Use the debug isis spf statistics EXEC command to display statistical information about building routes between intermediate systems (ISs). The no form of this command disables debugging output.
debug isis spf statisticsThis command has no arguments or keywords.
EXEC
The Intermediate System to Intermediate System (IS-IS) Intra-Domain Routing Exchange Protocol (IDRP) provides routing between ISs by flooding the network with link-state information. IS-IS provides routing at two Levels, intra-area (Level 1) and intra-domain (Level 2.) Level 1 routing allows Level 1 ISs to communicate with other Level 1 ISs in the same area. Level 2 routing allows Level 2 ISs to build an interdomain backbone between Level 1 areas by traversing only Level 2 ISs. Level 1 ISs only need to know the path to the nearest Level 2 IS in order to take advantage of the interdomain backbone created by the Level 2 ISs.
The IS-IS protocol uses the Shortest Path First (SPF) routing algorithm to build Level 1 and Level 2 routes. The debug isis spf statistics command will provide information for determining the length of time it takes to place a Level 1 IS or Level 2 IS on the shortest path tree (SPT) using the IS-IS protocol.
Figure 2-62 shows sample debug isis spf statistics output.

Table 2-34 describes significant fields shown in Figure 2-62.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Compute L1 SPT | Indicates that Level 1 ISs are to be added to a Level 1 area. |
| Timestamp | Indicates the time at which the SPF algorithm was applied. The time indicates the number of seconds that have elapsed since the system has been up and configured. |
| Complete L1 SPT | Indicates that the algorithm has completed for Level 1 routing. |
| Compute time | Indicates the time it took to place the ISs on the shortest path tree (SPT). |
| nodes on SPT | Indicates the number of ISs that have been added. |
| Compute L2 SPT | Indicates that Level 2 ISs are to be added to domain. |
| Complete L2 SPT | Indicates that the algorithm has completed for Level 2 routing. |
Explanations for individual lines of output from Figure 2-62 follow.
The following lines show the statistical information available for Level 1 ISs:
ISIS-Stats: Compute L1 SPT, Timestamp 2780.328 seconds ISIS-Stats: Complete L1 SPT, Compute time 0.004, 1 nodes on SPTThe output indicates that the SPF algorithm was applied 2780.328 seconds after the system was up and configured. Given the existing intra-area topology, it took 4 milliseconds to place one Level 1 IS on the SPT.
The following lines show the statistical information available for Level 2 ISs:
ISIS-Stats: Compute L2 SPT, Timestamp 2780.3336 seconds ISIS-Stats: Complete L2 SPT, Compute time 0.056, 12 nodes on SPT
This output indicates that the SPF algorithm was applied 2780.3336 seconds after the system was up and configured. Given the existing intra-domain topology, it took 56 milliseconds to place 12 Level 2 ISs on the SPT.
Use the debug isis update-packets EXEC command to display various sequence number protocol data units (PDUs) and link state packets that are seen by the router. This router has been configured for IS-IS routing. The no form of this command disables debugging output.
debug isis update-packetsThis command has no arguments or keywords.
EXEC
Figure 2-63 shows sample debug isis update-packets output.

Explanations for individual lines of output from Figure 2-63 follow.
The following lines indicate that the router has sent a periodic Level 1 and Level 2 complete sequence number PDU on Ethernet 0:
ISIS-Update: Sending L1 CSNP on Ethernet0
ISIS-Update: Sending L2 CSNP on Ethernet0
The following lines indicate that the network service access point (NSAP) identified as 8888.8800.0181.00 has been deleted from the Level 2 LSP 1600.8906.4022.00-00. The sequence number associated with this LSP is 0xE.
ISIS-Update: Updating L2 LSP
ISIS-Update: Delete link 888.8800.0181.00 from L2 LSP 1600.8906.4022.00-00, seq E
The following lines indicate that the NSAP identified as 8888.8800.0181.00 has been added to the Level 2 LSP 1600.8906.4022.00-00. The new sequence number associated with this LSP is 0x10.
ISIS-Update: Updating L1 LSP
ISIS-Update: Sending L1 CSNP on Ethernet0
ISIS-Update: Sending L2 CSNP on Ethernet0
ISIS-Update: Add link 8888.8800.0181.00 to L2 LSP 1600.8906.4022.00-00, new seq 10,
len 91
The following line indicates that the router has sent Level 2 LSP 1600.8906.4022.00-00 with sequence number 0x10 on Tunnel0:
ISIS-Update: Sending L2 LSP 1600.8906.4022.00-00, seq 10, ht 1198 on Tunnel0
The following lines indicates that a Level 2 LSP could not be transmitted because it was recently transmitted:
ISIS-Update: Sending L2 CSNP on Tunnel0
ISIS-Update: Updating L2 LSP
ISIS-Update: Rate limiting L2 LSP 1600.8906.4022.00-00, seq 11 (Tunnel0)
The following lines indicate that a Level 2 partial sequence number PDU (PSNP) has been received on Tunnel0:
ISIS-Update: Updating L1 LSP
ISIS-Update: Rec L2 PSNP from 8888.8800.0181.00 (Tunnel0)
The following line indicates that a Level 2 PSNP with an entry for Level 2 LSP 1600.8906.4022.00-00 has been received. This output is an acknowledgment that a previously sent LSP was received without an error.
ISIS-Update: PSNP entry 1600.8906.4022.00-00, seq 10, ht 1196
Use the debug lapb EXEC command to display all traffic for interfaces using LAPB encapsulation. The no form of this command disables debugging output.
debug lapbThis command has no arguments or keywords.
EXEC
This command displays information on the X.25 Layer 2 protocol. It is useful to users who are familiar with the LAPB protocol.
You can use the debug lapb command to determine why X.25 virtual circuits or LAPB connections are going up and down. It is also useful for identifying link problems, as evidenced when show interfaces command displays a high number of rejects or frame errors over the X.25 link.
 | Caution Because the debug lapb command generates a lot of output, use it when the aggregate of all LAPB traffic on X.25 and LAPB interfaces is fewer than five frames per second. |
Figure 2-64 shows sample debug lapb output. (The numbers 1 through 6 at the top of the display have been added in order to aid documentation.)

In Figure 2-64 each line of output describes a LAPB event. There are two types of LAPB events: frame events (when a frame enters or exits the router) and timer events. In Figure 2-64, the last line describes a timer event; all of the other lines describe frame events. Table 2-35 describes the first six fields shown in Figure 2-64.
As Figure 2-64 shows, a timer event only displays the first six fields of debug lapb output. For frame events, however, the fields that follow the sixth field document the LAPB control information present in the frame. Depending on the value of the frame type name shown in the sixth field, these fields may or may not appear. Descriptions of the fields following the first six fields shown in Figure 2-64 follow.
If the frame's Poll/Final bit is set, an indicator will be printed after the frame type name. Possible values follow:
After the Poll/Final indicator, depending on the frame type, three different types of LAPB control information can be printed.
For information frames, the value of the N(S) field and the N(R) field will be printed. The N(S) field of an information frame is the sequence number of that frame, so this field will rotate between 0 and 7 for successive outgoing information frames and (under normal circumstances) also will rotate for incoming information frame streams. The N(R) field is a "piggybacked" acknowledgment for the incoming information frame stream; it informs the other end of the link what sequence number is expected next.
RR, RNR, and REJ frames have an N(R) field, so the value of that field is printed. This field has exactly the same significance that it does in an information frame.
For the FRMR frame, the frame's three bytes of error information is printed (in hexadecimal notation).
The remaining frames do not have this data, so nothing will be printed.
For incoming frames, the last field will indicate whether the received frame was a command (C) or a response (R).
Use the debug lat packet EXEC command to display information on all LAT events. The no form of this command disables debugging output.
debug lat packetThis command has no arguments or keywords.
EXEC
For each datagram (packet) received or transmitted, a message is logged to the console.
Figure 2-65 shows sample debug lat packet output.

The second line of output in Figure 2-65 describes a packet that is input to the router. Table 2-36 describes the fields in this line.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| LAT: | Indicates that this display shows LAT debugging output. |
| I | Indicates that this line of output describes a packet that is input to the router (I) or output from the router (O). |
| int = Ethernet0 | Indicates the interface on which the packet event took place. |
| src = 0800.2b11.2d13 | Indicates the source address of the packet. |
| dst = 0000.0c01.7876 | Indicates the destination address of the packet. |
| type = A | Indicates the message type (in hex). Possible values are as follows:
0 = Run Circuit 1 = Start Circuit 2 = Stop Circuit A = Service Announcement C = Command D = Status E = Solicit Information F = Response Information |
The third line of output in Figure 2-65 describes a packet that is output from the router. Table 2-37 describes the last three fields in this line.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| len= 20 | Indicates the length (hex) of the packet in bytes. |
| next 0 | Indicates the link on transmit queue. |
| ref 1 | Indicates the count of packet users. |
Use the debug lnm events EXEC command to display any unusual events that occur on a Token Ring network. These events include stations reporting errors or error thresholds being exceeded. The no form of this command disables debugging output.
debug lnm eventsThis command has no arguments or keywords.
EXEC
Figure 2-66 shows sample debug lnm events output.

Explanations for the messages shown in Figure 2-66 follow.
The following message indicates that station 0000.3001.1166 reported errors and has been added to the list of stations reporting errors. This station is located on Ring 3.
IBMNM3: Adding 0000.3001.1166 to error list
The following message indicates that station 0000.3001.1166 has passed the "early warning" threshold for error counts:
IBMNM3: Station 0000.3001.1166 going into preweight condition
The following message indicates that station 0000.3001.1166 is experiencing a severe number of errors:
IBMNM3: Station 0000.3001.1166 going into weight condition
The following message indicates that the error counts for station 0000.3001.1166 have all decayed to zero, so this station is being removed from the list of stations that have reported errors:
IBMNM3: Removing 0000.3001.1166 from error list
The following message indicates that Ring 0 has entered failure mode. This ring number is assigned internally.
LANMGR0: Beaconing is present on the ring
The following message indicates that Ring 0 is no longer in failure mode. This ring number is assigned internally.
LANMGR0: Ring is no longer beaconing
The following message indicates that the router is beginning its attempt to determine whether or not any stations left the ring during the automatic recovery process for the last beaconing failure. The router attempts to contact stations that were part of the fault domain to see if they are still operating on the ring.
IBMNM3: Beaconing, Postmortem Started
The following message indicates that the router is attempting to determine whether or not any stations left the ring during the automatic recovery process for the last beaconing failure. It heard back from station 0000.3000.1234, one of the two stations in the fault domain.
IBMNM3: Beaconing, heard from 0000.3000.1234
The following message indicates that the router is attempting to determine whether or not any stations left the ring during the automatic recovery process for the last beaconing failure. It is initiating another attempt to contact the two stations in the fault domain.
IBMNM3: Beaconing, Postmortem Next Stage
The following message indicates that the router has attempted to determine whether or not any stations left the ring during the automatic recovery process for the last beaconing failure. It has successfully heard back from both stations that were part of the fault domain.
IBMNM3: Beaconing, Postmortem Finished
Explanations for other messages that the debug lnm events command can generate follow.
The following message indicates that the router is out of memory:
LANMGR: memory request failed, find_or_build_station()
The following message indicates that Ring 3 is experiencing a large number of errors that cannot be attributed to any individual station:
IBMNM3: Non-isolating error threshold exceeded
The following message indicates that a station (or stations) on Ring 3 are receiving frames faster than they can be processed.
IBMNM3: Adapters experiencing congestion
The following message indicates that the beaconing has lasted for over 1 minute and is considered to be a "permanent" error:
IBMNM3: Beaconing, permanent
The following message indicates that the beaconing lasted for less than 1 minute. The router is attempting to determine whether either of the stations in the fault domain left the ring.
IBMNM: Beaconing, Destination Started
In the preceding line of output, the following can replace Started: Next State, Finished, Timed out, and Cannot find station 0000.0301.4876.
Use the debug lnm llc EXEC command to display all communication between the router/bridge and the LNMs that have connections to it. The no form of this command disables debugging output.
debug lnm llcThis command has no arguments or keywords.
EXEC
One line is displayed for each message sent or received.
Figure 2-67 shows sample debug lnm llc output.
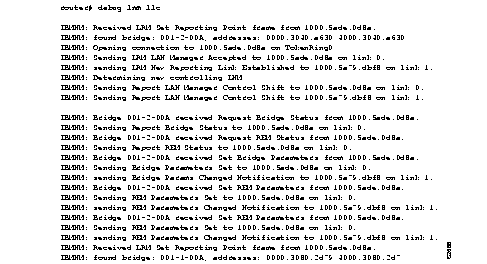
As Figure 2-67 indicates, debug lnm llc output can vary somewhat in format. Table 2-38 describes significant fields shown in the first line of output in Figure 2-67.
Explanations for other types of messages shown in Figure 2-67 follow.
The following message indicates that the lookup for the bridge with which the LAN Manager was requesting to communicate was successful:
IBMNM: found bridge: 001-2-00A, addresses: 0000.3040.a630 4000.3040.a630
The following message is self-explanatory:
IBMNM: Opening connection to 1000.5ade.0d8a on TokenRing0
The following message indicates that a LAN Manager has connected or disconnected from an internal bridge and that the router computes which LAN Manager is allowed to change parameters:
IBMNM: Determining new controlling LNM
The following line of output indicates which bridge in the router is the destination for the frame:
IBMNM: Bridge 001-2-00A received Request Bridge Status from 1000.5ade.0d8a.
Use the debug lnm mac EXEC command to display all management communication between the router/bridge and all stations on the local Token Rings. The no form of this command disables debugging output.
debug lnm macThis command has no arguments or keywords.
EXEC
One line is displayed for each message sent or received.
Figure 2-68 shows sample debug lnm mac output.

Table 2-39 describes significant fields shown in the first line of output in Figure 2-68.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| LANMGR0: | LANMGR indicates that this line of output displays MAC-level debugging information. 0 indicates the number of the Token Ring interface associated with this line of debugging output. |
| RS | Indicates which function of the MAC-level software is communicating:
CRS--Configuration Report Server REM--Ring Error Monitor RPS--Ring Parameter Server RS--Ring Station |
| received | Indicates that the router received a frame. The other possible value is sending, to indicate that the router is sending a frame. |
| request address | Name of the specific frame that the router sent or received. Possible values include the following:
AMP initialize station report address report attachments report NAUN change report soft error report state request address request attachments request initialization request state ring purge SMP |
| from 4000.3040.a670 | If the router has received the frame, this address is the source address of the frame. If the router is sending the frame, this address is the destination address of the frame. |
As Figure 2-68 indicates, all debug lnm mac messages follow the format described in Table 2-39 except the following:
LANMGR2: RS start watching ring poll
LANMGR2: RS stop watching ring poll
These messages indicate that the router starts and stops receiving AMP and SMP frames. These frames are used to build a current picture of which stations are on the ring.
Use the debug local-ack state EXEC command to display the new and the old state conditions whenever there is a state change in the Local Acknowledgment state machine. The no form of this command disables debugging output.
debug local-ack stateThis command has no arguments or keywords.
EXEC
Figure 2-69 shows sample debug local-ack state output.
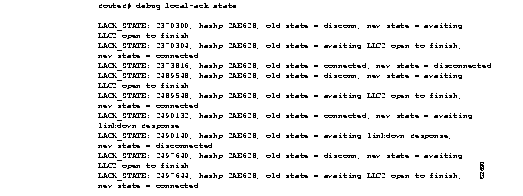
Table 2-40 describes significant fields shown in Figure 2-69.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| LACK_STATE: | Indicates that this packet describes a state change in the Local Acknowledgment state machine. |
| 2370300 | System clock. |
| hashp 2AE628 | Internal control block pointer used by technical support staff for debugging purposes. |
| old state = disconn | Indicates the old state condition in the Local Acknowledgment state machine. Possible values include the following:
Disconn (disconnected) awaiting LLC2 open to finish connected awaiting linkdown response |
| new state = awaiting LLC2 open to finish | Indicates the new state condition in the Local Acknowledgment state machine. Possible values include the following:
Disconn (disconnected) awaiting LLC2 open to finish connected awaiting linkdown response |
Use the debug netbios-name-cache EXEC command to display name caching activities on a router. The no form of this command disables debugging output.
debug netbios-name-cacheThis command has no arguments or keywords.
EXEC
Examine the display to diagnose problems in NetBIOS name caching.
Figure 2-70 illustrates a collection of sample debug netbios-name-cache output listings.

Descriptions of selected debug netbios-name-cache output fields are provided in Table 2-41.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| NETBIOS | Indicates that this is a NetBIOS name caching debugging output. |
| L, U | L means lookup; U means update. |
| vrn=0 | Router determined that the packet comes from virtual ring number 0; this packet actually comes from a real Token Ring interface, because virtual ring number 0 is not valid. |
| addr=1000.4444.5555 | MAC address 1000.4444.5555 of machine being looked up in NetBIOS name cache. |
| idb=TR1 | Indicates that name of machine was learned from Token Ring interface number 1; idb translates into interface data block |
| type=1 | The type field indicates the way that the router learned about the specified machine. The possible values for type are as follows:
1 = Learned from traffic 2 = Learned from a remote peer 4, 8 = Statically entered via the router's configuration |
The following discussion briefly outlines each line shown in the example provided in Figure 2-70.
With the first line of output, the router declares that it has examined the NetBIOS name cache table for the machine name ORINDA and that the packet that prompted the lookup came from virtual ring 0. In this case, this packet comes from a real interface--virtual ring number 0 is not valid.
NETBIOS: L checking name ORINDA, vrn=0
The following two lines indicate that there is a invalid NetBIOS entry and that the corrupted memory was detected. The invalid memory will be removed from the table; no action is needed.
NetBIOS name cache table corrupted at offset 13
NetBIOS name cache table corrupted at later offset, at location 13
The following line indicates that the router has attempted to check the NetBIOS cache table for the name ORINDA with MAC address 1000.4444.5555. This name was obtained from Token Ring interface 1. The type field indicates that the name was learned from traffic.
NETBIOS: U chk name=ORINDA, addr=1000.4444.5555, idb=TR1, vrn=0, type=1
The following line indicates that the NetBIOS name ORINDA is in the name cache table and has been updated to the current value:
NETBIOS: U upd name=ORINDA,addr=1000.4444.5555,idb=TR1,vrn=0,type=1
The following line indicates that the NetBIOS name ORINDA is not in the table and must be added to the table:
NETBIOS: U add name=ORINDA,addr=1000.4444.5555,idb=TR1,vrn=0,type=1
The following line indicates that there was insufficient cache buffer space when the router tried to add this name:
NETBIOS: U no memory to add cache entry. name=ORINDA,addr=1000.4444.5555
The following line indicates that the NetBIOS ager detects an invalid memory in the cache. The router clears the entry; no action is needed.
NETBIOS: Invalid structure detected in netbios_name_cache_ager
The following line indicates that the entry for ORINDA has been flushed from the cache table:
NETBIOS: flushed name=ORINDA, addr=1000.4444.5555
The following line indicates that the entry for ORINDA has timed out and has been flushed from the cache table:
NETBIOS: expired name=ORINDA, addr=1000.4444.5555
The following line indicates that the router has removed the ORINDA entry from its cache table:
NETBIOS: removing entry. name=ORINDA,addr=1000.4444.5555,idb=TR1,vrn=0
The following line indicates that the router discarded a NetBIOS packet of type ADD_NAME, STATUS, NAME_QUERY, or ADD_GROUP. These packets are discarded when multiple copies of one of these packet types are detected during a certain period of time.
NETBIOS: Tossing ADD_NAME/STATUS/NAME/ADD_GROUP frame
The following line indicates that the system was unable to find a NetBIOS name in the cache:
NETBIOS: Lookup Failed -- not in cache
The following line indicates that the destination NetBIOS name was found in the cache but was determined to be located on the same ring from which the packet came. The router would drop this packet because it should not leave this ring.
NETBIOS: Lookup Worked, but split horizon failed
The following line indicates that the NetBIOS name was found in the cache but the router could not find the corresponding RIF. The packet will be sent as a broadcast frame.
NETBIOS: Could not find RIF entry
The following line indicates that no buffer was available to create a NetBIOS name-cache proxy. A proxy will not be created for the packet, which will be forwarded as a broadcast frame.
NETBIOS: Cannot duplicate packet in netbios_name_cache_proxy
Use the debug packet EXEC command to display information on packets that the network is unable to classify. The no form of this command disables debugging output.
debug packetThis command has no arguments or keywords.
EXEC
Figure 2-71 shows sample debug packet output. Notice how similar it is to debug broadcast output.

Table 2-42 describes significant fields shown in Figure 2-71.
Use the debug ppp EXEC command to display information on traffic and exchanges in an internetwork implementing the Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP). The no form of this command disables debugging output.
debug ppp {packet | negotiation | error | chap}EXEC
Use the debug ppp commands when trying to find the following:
Refer to Internet RFCs 1331, 1332, and 1333 for details concerning PPP-related nomenclature and protocol information.
Figure 2-72 shows sample debug ppp packet output as seen from the Link Quality Monitor (LQM) side of the connection. This display example depicts packet exchanges under normal PPP operation.

Table 2-43 describes significant fields shown in Figure 2-72.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| PPP | Indicates that this is PPP debugging output. |
| Serial4 | Interface number associated with this debugging information. |
| (o), O | Both indicate that this packet was detected as an output packet. |
| (i) I | Both indicate that this packet was detected as an input packet. |
| lcp_slqr() | Procedure name; running LQM, send a Link Quality Report (LQR). |
| lcp_rlqr() | Procedure name; running LQM, received an LQR. |
| input (C025) | Indicates that the router received a packet of the specified packet type (in hex). A value of C025 indicates packet of type LQM. |
| state = OPEN | PPP state; normal state is OPEN. |
| magic = D21B4 | Magic Number for indicated node; when output is indicated, this is the Magic Number of the node on which debugging is enabled. The actual Magic Number depends on whether the packet detected is indicated as I or O. |
| datagramsize = 52 | Packet length including header. |
| code = ECHOREQ(9) | Code identifies the type of packet received. Both forms of the packet, string and hexadecimal, are presented. |
| len = 48 | Packet length without header. |
| id = 3 | ID number per Link Control Protocol (LCP) packet format. |
| pkt type 0xC025 | Packet type in hexadecimal; typical packet types are C025 for LQM and C021 for LCP. |
| LCP ECHOREQ (9) | Specifies Echo Request; value in parentheses is the hexadecimal representation of the LCP type. |
| LCP ECHOREP (A) | Specifies Echo Reply; value in parentheses is the hexadecimal representation of the LCP type. |
To elaborate on what the router is displaying here, consider the partial exchange in Figure 2-73. This sequence shows that one side is using ECHO for its keepalives and the other side is using LQRs.

The following discussion briefly outlines each line of this exchange.
The first line states that the router with debugging enabled has sent an LQR to the other side of the PPP connection:
PPP Serial4(o): lcp_slqr() state = OPEN magic = D21B4, len = 48
The next two lines indicate that the router has received a packet of type C025 (LQM) and provides details about the packet:
PPP Serial4(i): pkt type 0xC025, datagramsize 52
PPP Serial4(i): lcp_rlqr() state = OPEN magic = D3454, len = 48
The next two lines indicate that the router received an ECHOREQ of type C021 (LCP). The other side is sending ECHOs. The router on which debugging is configured for LQM but also responds to ECHOs.
PPP Serial4(i): pkt type 0xC021, datagramsize 16
PPP Serial4: I LCP ECHOREQ(9) id 3 (C) magic D3454
Next the router is detected to have responded to the ECHOREQ with an ECHOREP and is preparing to send out an LQR:
PPP Serial4: O LCP ECHOREP(A) id 3 (C) magic D21B4
PPP Serial4(o): lcp_slqr() state = OPEN magic = D21B4, len = 48
Figure 2-74 shows sample debug ppp negotiation output. This is a normal negotiation, where both sides agree on NCP parameters. In this case, protocol type IP is proposed and acknowledged.
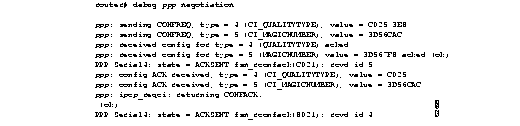
Table 2-44 describes significant fields shown in Figure 2-74.
The following discussion briefly outlines each line shown in the example provided in Figure 2-74.
The first two lines in Figure 2-74 indicate that the router is trying to bring up LCP and intends to use the indicated negotiation options (Quality Protocol and Magic Number). The value fields are the values of the options themselves. C025/3E8 translates to Quality Protocol LQM. 3E8 is the reporting period (in hundredths of a second). 3D56CAC is the value of the Magic Number for the router.
ppp: sending CONFREQ, type = 4 (CI_QUALITYTYPE), value = C025/3E8
ppp: sending CONFREQ, type = 5 (CI_MAGICNUMBER), value = 3D56CAC
The next two lines indicate that the other side negotiated for options 4 and 5 as requested and acknowledged both. If the responding end does not support the options, a CONFREJ is sent by the responding node. If the responding end does not like the value of the option, a CONFNAK is sent with the value field modified.
ppp: received config for type = 4 (QUALITYTYPE) acked
ppp: received config for type = 5 (MAGICNUMBER) value = 3D567F8 acked (ok)
The next three lines indicate that the router received a CONFACK from the responding side and displays accepted option values. Use the rcvd id field to verify the CONFREQ and CONFACK have the same id field.
PPP Serial4: state = ACKSENT fsm_rconfack(C021): rcvd id 5
ppp: config ACK received, type = 4 (CI_QUALITYTYPE), value = C025
ppp: config ACK received, type = 5 (CI_MAGICNUMBER), value = 3D56CAC
The next line indicates that the router has IP routing enabled on this interface and that the IPCP NCP negotiated successfully:
ppp: ipcp_reqci: returning CONFACK.
In the last line, the router's state is listed as ACKSENT.
PPP Serial4: state = ACKSENT fsm_rconfack(C021): rcvd id 5\
Figure 2-75 shows sample output when both debug ppp packet and debug ppp negotiation output are enabled at the same time.

Figure 2-76 shows sample debug ppp negotiation output when the remote side of the connection is unable to respond to LQM requests.
Figure 2-77 shows sample output when no response is detected for configuration requests (with both debug ppp negotiation and debug ppp packet enabled).
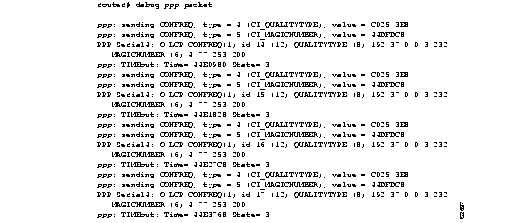
Figure 2-78 shows sample debug ppp error output. These messages might appear when the Quality Protocol option is enabled on an interface that is already running PPP.

Table 2-45 describes significant fields shonw in Figure 2-78.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| PPP | Indicates that this is PPP debugging output. |
| Serial3(i) | Interface number associated with this debugging information; indicates that this is an input packet. |
| rlqr receive failure | Indicates that the request to negotiate the Quality Protocol option is not accepted. |
| myrcvdiffp = 159 | Number of packets received over the time period. |
| peerxmitdiffp = 41091 | Number of packets sent by the remote node over this period. |
| myrcvdiffo = 2183 | Number of octets received over this period. |
| peerxmitdiffo = 1714439 | Number of octets sent by the remote node over this period. |
| threshold = 25 | The maximum error percentage acceptable on this interface. This percentage is calculated by the threshold value entered in the ppp quality number interface configuration command. A value of 100-number (100 minus number) is the maximum error percentage. In this case, a number of 75 was entered. This means that the local router must maintain a minimum 75 percent non-error percentage, or the PPP link will be considered down. |
| OutLQRs = 1 | Local router's current send LQR sequence number. |
| LastOutLQRs = 1 | The last sequence number that the remote node side has seen from the local node. |
Figure 2-79 shows sample debug ppp chap output. When doing CHAP authentication, use this debug command to determine why an authentication fails. This command is also useful when doing PAP authentication.

In general, these messages are self-explanatory. Fields that appear in debug ppp chap displays that can show optional output are outlined in Table 2-46.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Serial0 | Interface number associated with this debugging information and CHAP access session in question. |
| USERNAME pioneer not found. | The name pioneer in this example is the name received in the CHAP response. The router looks up this name in the list of usernames that are configured for the router. |
| Remote message is Unknown name | Messages that can appear are the following: No name received to authenticate Unknown name No secret for given name Short MD5 response received MD compare failed |
| code = 4 | Specific CHAP type packet detected. Possible values are as follows:
1 = Challenge 2 = Response 3 = Success 4 = Failure |
| len = 48 | Packet length without header. |
| id = 3 | ID number per Link Control Protocol (LCP) packet format. |
Use the debug rif EXEC command to display information on entries entering and leaving the RIF cache. The no form of this command disables debugging output.
debug rifThis command has no arguments or keywords.
EXEC
In order to use the debug rif command to display traffic source-routed through an interface, fast switching of SRB frames must first be disabled with the no source-bridge route-cache interface interface configuration command.
Figure 2-80 shows sample debug rif output.
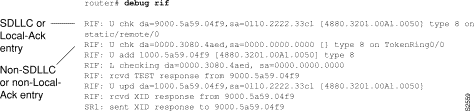
Explanations for representative lines of debug rif output in Figure 2-80 follow.
The first line of output is an example of a RIF entry for an interface configured for SDLLC or Local-Ack. Table 2-47 describes significant fields shown in this line of debug rif output.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| RIF: | Indicates that this message describes RIF debugging output. |
| U chk | Update checking. The entry is being updated; the timer is set to zero (0). |
| da = 9000.5a59.04f9 | Destination MAC address. |
| sa = 0110.2222.33c1 | Source MAC address. This field contains values of zero (0000.0000.0000) in a non-SDLLC or non-Local-ack entry. |
| [4880.3201.00A1.0050] | RIF string. This field is blank (null RIF) in a non-SDLLC or non-Local-ack entry. |
| type 8 | Possible values follow:
0--Null entry 1--This entry was learned from a particular Token Ring port (interface) 2--Statically configured 4--Statically configured for a remote interface 8--This entry is to be aged 16--This entry (which has been learned from a remote interface) is to be aged 32--This entry is not to be aged 64 --This interface is to be used by LAN Network Manager (and is not to be aged) |
| on static/remote/0 | Indicates that this route was learned from a real Token Ring port, in contrast to a virtual ring. |
The following line of output is an example of a RIF entry for an interface that is not configured for SDLLC or Local-Ack:
RIF: U chk da=0000.3080.4aed,sa=0000.0000.0000 [] type 8 on TokenRing0/0
Notice that the source address contains only zero values (0000.0000.0000), and that the RIF string is null ([ ]). The last element in the entry indicates that this route was learned from a virtual ring, rather than a real Token Ring port.
The following line shows that a new entry has been added to the RIF cache:
RIF: U add 1000.5a59.04f9 [4880.3201.00A1.0050] type 8
The following line shows that a RIF cache lookup operation has taken place:
RIF: L checking da=0000.3080.4aed, sa=0000.0000.0000
The following line shows that a TEST response from address 9000.5a59.04f9 was inserted into the RIF cache:
RIF: rcvd TEST response from 9000.5a59.04f9
The following line shows that the RIF entry for this route has been found and updated:
RIF: U upd da=1000.5a59.04f9,sa=0110.2222.33c1 [4880.3201.00A1.0050]
The following line shows that an XID response from this address was inserted into the RIF cache:
RIF: rcvd XID response from 9000.5a59.04f9
The following line shows that the router sent an XID response to this address:
SR1: sent XID response to 9000.5a59.04f9
Table 2-48 explains the other possible lines of debug rif output.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| RIF: L Sending XID for address | The router/bridge wanted to send a packet to address but did not find it in the RIF cache. It sent an XID explorer packet to determine which RIF it should use. The attempted packet is dropped. |
| RIF: L No buffer for XID to address | Similar to the previous description; however, a buffer in which to build the XID packet could not be obtained. |
| RIF: U remote rif too small [rif] | A packet's RIF was too short to be valid. |
| RIF: U rej address too big [rif] | A packet's RIF exceeded the maximum size allowed and was rejected. The maximum size is 18 bytes. |
| RIF: U upd interface address | The RIF entry for this router/bridge's interface has been updated. |
| RIF: U ign address interface update | A RIF entry that would have updated an interface corresponding to one of this router's interfaces. |
| RIF: U add address[rif] | The RIF entry for address has been added to the RIF cache. |
| RIF: U no memory to add rif for address | No memory to add a RIF entry for address. |
| RIF: removing rif entry for address, type code | The RIF entry for address has been forcibly removed. |
| RIF: flushed address | The RIF entry for address has been removed because of a RIF cache flush. |
| RIF: expired address | The RIF entry for address has been aged out of the RIF cache. |
Use the debug sdlc EXEC command to display information on SDLC frames received and sent by any router serial interface involved in supporting SDLC end station functions. The no form of this command disables debugging output.
debug sdlcThis command has no arguments or keywords.
EXEC
Because using this command is processor intensive, it is best to use it after hours, rather than in a production environment. It is also best to turn this command on by itself, rather than use it in conjunction with other debug commands.
Figure 2-81 shows sample debug sdlc output.
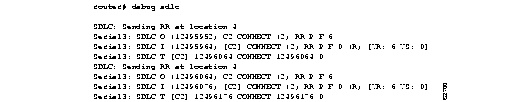
Explanations for individual lines of output from Figure 2-81 follow.
The following line of output indicates that the router is sending a Receiver Ready packet at location 4 in the code:
SDLC: Sending RR at location 4
The following line of output describes a frame input event:
Serial3: SDLC O (12495952) C2 CONNECT (2) RR P/F 6
Table 2-49 describes the fields in this line of output.
The following line of output describes a frame input event:
Serial3: SDLC I (12495964) [C2] CONNECT (2) RR P/F 0 (R) [VR: 6 VS: 0] rfp: P
In addition to the fields described in Table 2-49, output for a frame input event also includes two additional fields, as described in Table 2-50.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| (R) | Frame Type:
C--Command R--Response |
| VR: 6 | Receive count; range: 0-7. |
| VS: 0 | Send count; range: 0-7. |
| rfp: P | Ready for poll;
P --Idle poll (keepalive) timer is on. T--Data acknowledgment timer is on. These timers are based on the T1 timer. |
| VS: 0 | Send count; range: 0-7. |
The following line of output describes a frame timer event:
Serial3: SDLC T [C2] 12496064 CONNECT 12496064 0
Table 2-51 describes the fields in this line of output.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Serial3: | Interface type and unit number reporting the frame event. |
| SDLC | Protocol providing the information. |
| T | Indicates that the timer has expired. |
| [C2] | SDLC address of this SDLC connection. |
| 12496064 | System clock. |
| CONNECT | State of the protocol when the frame event occurred. Possible values follow:
BOTHBUSY CONNECT DISCONNECT DISCSENT (disconnect sent) ERROR (FRMR frame sent) REJSENT (reject frame sent) SNRMSENT (SNRM frame sent) THEMBUSY BOTHBUSY |
| 12496064 | Top timer. |
| 0 | Retry count; default: 0. |
Use the debug sdlc local-ack EXEC command to display information on the Local Acknowledgment feature. The no form of this command disables debugging output.
debug sdlc local-ack [number]| number | (Optional) Frame type that you want to monitor. Refer to the "Usage Guidelines" section. |
This command has no arguments or keywords.
EXEC
You can select the frame types you want to monitor; the frame types correspond to bit flags. You can select 1, 2, 4, or 7, which is the decimal value of the bit flag settings. If you select 1, the octet is set to 00000001. If you select 2, the octet is set to 0000010. If you select 4, the octet is set to 00000100. If you want to select all frame types, select 7; the octet is 00000111. The default is 7 for all events. Table 2-52 defines these bit flags.
| Debug Command | Meaning |
|---|---|
| debug sdlc local-ack 1 | Only U-Frame events |
| debug sdlc local-ack 2 | Only I-Frame events |
| debug sdlc local-ack 4 | Only S-Frame events |
| debug sdlc local-ack 7 | All SDLC Local-Ack events (default setting) |
 | Caution Because using this command is processor intensive, it is best to use it after hours, rather than in a production environment. It is also best to turn this command on by itself, rather than use it in conjunction with other debug commands. |
Figure 2-82 shows sample debug sdlc local-ack output.
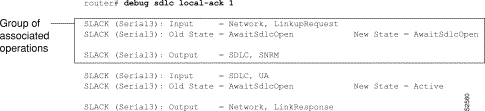
Explanations for individual lines of output from Figure 2-82 follow.
The first line shows the input to the SDLC Local Acknowledgment state machine:
SLACK (Serial3): Input = Network, LinkupRequest
Table 2-53 describes the fields in this line of output.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| SLACK | Indicates that the SDLC Local-Acknowledgment feature is providing the information. |
| (Serial3): | Interface type and unit number reporting the event. |
| Input = Network | Indicates that the source of the input. |
| LinkupRequest | Indicates the op code. A LinkupRequest is an example of possible values. |
The second line shows the change in the SDLC Local Acknowledgment state machine. In this case the AwaitSdlcOpen state is an internal state that has not changed while this display was captured.
SLACK (Serial3): Old State = AwaitSdlcOpen New State = AwaitSdlcOpen
The third line shows the output from the SDLC Local Acknowledgment state machine:
SLACK (Serial3): Input = Network, LinkupRequest
Use the debug sdllc EXEC command to display information about data link layer frames transferred between a device on a Token Ring and a device on a serial line via a router configured with the SDLLC feature. The no form of this command disables debugging output.
debug sdllcThis command has no arguments or keywords.
EXEC
The SDLLC feature translates between the SDLC link layer protocol used to communicate with devices on a serial line and the LLC2 link layer protocol used to communicate with devices on a Token Ring.
The router configured with the SDLLC feature must be attached to the serial line. The router sends and receives frames on behalf of the serial device on the attached serial line but acts as an SDLC station.
The topology between the router configured with the SDLLC feature and the Token Ring is network dependent and is not limited by the SDLLC feature.
Figure 2-83 shows sample debug sdllc output between link layer peers from the perspective of the SDLLC-configured router.

Table 2-54 describes significant fields shown in Figure 2-83:
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| rx | Router receives message from the FEP. |
| explr rsp | Response to an explorer (TEST) frame previously sent by the router to FEP. |
| da | Destination address. This is the address of the router receiving the response. |
| sa | Source address. This is the address of the FEP sending the response to the router. |
| rif | Routing information field. |
| tx | Router sent message to the FEP. |
| short xid | Router sent the null XID to the FEP. |
| dsap | Destination service access point |
| ssap | Source service access point. |
| tx long xid | Router sent the XID type 2 to the FEP. |
| Rcvd | Router received Layer 2 message from the FEP |
| SABME/LINKUP_REQ | Set asynchronous Balanced Mode Extended command. |
The following line indicates that an explorer frame response has been received by the router at address 4000.2000.1001 from the FEP at address C000.1020.1000 with the specified RIF. The original explorer sent to the FEP from the router is not monitored as part of the debug sdllc command.
SDLLC: rx explorer rsp, da 4000.2000.1001, sa C000.1020.1000, rif
8840.0011.00A1.0050
The following line indicates that the router sent the null XID (Type 0) to the FEP. The debugging information does not include the response to the XID message sent by the FEP to the router.
SDLLC: tx short xid, sa 4000.2000.1001, da C000.1020.1000, rif
88C0.0011.00A1.0050, dsap 4 ssap 4
The following line indicates that the router sent the XID command (Format 0 Type 2) to the FEP:
SDLLC: tx long xid, sa 4000.2000.1001, da C000.1020.1000, rif
88C0.0011.00A1.0050, dsap 4 ssap 4
The following line is the SABME response to the XID command previously sent by the router to the FEP:
Rcvd SABME/LINKUP_REQ pak from TR host
|
|