|
|

This chapter is targeted toward those tasked with understanding and deploying service provider scale Network Fault Management solutions for Cisco VoIP networks. These typically include service provider network operations center personnel, Cisco SE's, testing resources, and others (architects and designers) who require an understanding of the details of Cisco's service provider VoIP network management offering.
A complete Network Management System solution adheres to the Fault, Configuration, Accounting, Performance, and Security (FCAPS) model. The information discussed in this chapter relates to the Fault portion of the FCAPS model. It is intended to be referenced in conjunction with the companion chapters pertaining to provisioning and performance.
This chapter provides information about the following topics:
This Fault Management solution utilizes the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) and the Syslog logging facility. Some faults from non-Cisco devices are processed locally and then sent to the customer facing processing/reporting application. Fault event collection devices make use of the Tibco industry-standard (Cisco CNS Integration bus) method of data transfer. The Cisco CNS Integration bus follows the subscription/publish (sub/pub) technology model for communicating network events northbound to the NMS fault processing system, Cisco Info Center (CIC). Cisco CNS enabled applications can also be configured from the upstream side through the eXtended Markup Language (XML) protocol.
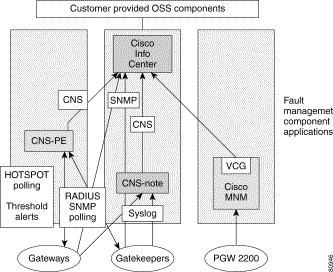
The Cisco VoIP: Infrastructure Manager Solution architecture of the Fault Management component is pictured by itself in Figure 4-1, which illustrates the main applications of the fault solution as well as the interconnection with other devices. The Cisco Media Gateway Controller Node Manager (CMNM) sends fault information directly to Cisco Info Center through the Voice Corba Gateway (VCG) pictured in Figure 4-1, utilizing the Cisco Element Management Framework (CEMF) probe (included in the Cisco Info Center distribution). The Cisco CNS Performance Engine (Cisco CNS PE) application sends threshold crossing alerts (TCA) to Cisco Info Center directly through the Cisco CNS Integration bus.
Cisco IOS network elements send SNMP traps to Cisco Info Center directly and transmit Syslog events to the Fault Collector, Cisco CNS Notification Engine. The lines indicating SNMP from network elements to Cisco Info Center are dashed to illustrate future development of the Cisco VoIP: Infrastructure Manager Solution where SNMP traps, (if configured on the IOS network elements), will also be sent to Cisco CNS Notification Engine along with Syslog events, as opposed to Cisco Info Center directly.

Cisco Info Center processes alarms and notifications from a number of different Collectors and Element Management Systems (EMSs). These include, but are not limited to:
Our discussion is centered on these three EMS applications in addition to Cisco Info Center and covers their functionality, inter connectivity, installation, initial configuration, and some troubleshooting tips. This chapter is meant to be an aid in the setup, operation and maintenance of the Cisco Internet OSS for VoIP: Infrastructure Manager Solution, as shown in Figure 4-1. Deeper discussion of any or all of the functional components of the solution is augmented by User and Administration guides that accompany the software. Each of the applications also has an account team responsible for technical details concerning each.
Because Cisco Info Center receives both SNMP v1 and v2c traps, version 3.4 of Cisco Info Center is required. Support for both SNMP versions is native in Cisco Info Center 3.4, whereas it may have to be customized into earlier versions.
The main functional areas of the fault solution are the collection device (Cisco CNS Notification Engine) and the Network Management System (Cisco Info Center with its accompanying Info Mediators). The
Cisco CNS Notification Engine application collects all Syslog information from the IOS devices and, after discarding duplicate and unnecessary messages, converts those messages to SNMP style traps and forwards them to the Cisco Info Center application. Cisco CNS Notification Engine parses the complicated and often inconsistent structure of syslog messages and converts the parsed data into structured, detailed SNMP style var binds, reducing the need for human interpretation.
The Cisco CNS Performance Engine sends threshold crossing alerts (TCA) to the Cisco Info Center over the Cisco CNS Integration bus and CMNM forwards SNMP v2c traps to Cisco Info Center through the CEMF probe.
Cisco Info Center provides the main display window for fault management. Customer OSS/BSS can interface to Cisco Info Center through gateway systems, Cisco Info Center is the management entry point, handling fault information from a large set of Cisco and non-Cisco components. Cisco Info Center is the MicroMuse NetCool product, OEM'ed and customized for Cisco. Cisco Info Center uses probes, created in Cisco Info Center software, to manage fault information from multiple mechanisms, including, but not limited to, XML, SNMP, Syslog, TL1, and CORBA (Voice CORBA). Cisco Info Center provides fault event de-duplication, correlation, and filtering (in addition to those functions performed by the Cisco CNS Notification Engine). Cisco Info Center can forward alarm data to external systems for value added processing. Cisco Info Center leverages the Cisco CNS Notification Engine to receive syslog generated fault information from IOS devices.
The Cisco CNS Performance Engine application is detailed in "Performance Monitoring." The Cisco Media Gateway Controller Node Manager (CMNM), along with the Voice Services Provisioning Tool (VSPT), Cisco Packet Telephony Center (Cisco PTC), Generic Dial Plan Manager (GDPM), and Cisco Element Management Framework (CEMF) are discussed in "Provisioning."
Referencing Figure 4-1, you can see Cisco Info Center as the Network Management System processing fault messages received from three different collection devices (EMSs). This list of EMSs is complete for the first phase of the Cisco VoIP: Infrastructure Manager Solution. This does not mean that Cisco Info Center is limited to collecting fault information from only the listed EMSs, but they are the main EMS components of the first phase of the Cisco VoIP: Infrastructure Manager Solution. Cisco Info Center is already deployed in many networks as a fault Network Management System for technologies and solutions other than VoIP.
The following sections focus on the individual devices and their hardware and software requirements. The hardware and software recommendations called out in this chapter are those that are used in the environment in which the solution is being tested.
Figure 4-2 is an illustration of many of the spheres of functionality that might require network management visibility in the Cisco VoIP: Infrastructure Manager Solution. The Fault Management solution must be able to detect fault and error conditions in the network elements pictured in Figure 4-2.
In addition, the solution must have some means of monitoring mission critical processes and applications present in a VoIP network.
Network Management System sizing can be calculated by considering the number of traps and messages received in a certain time period. As network size increases, scalability is achieved by increasing the capacity of the host Solaris machine and/or adding more Cisco CNS Notification Engine and/or Cisco Info Center instances.
Cisco Info Center can receive traps from multiple instances of the Cisco CNS Notification Engine. Multiple Cisco Info Center applications can be installed in a hierarchical manner where the top level Cisco Info Center receives network fault information from multiple second layer Cisco Info Center instances. Original deployment size requirements should be determined through consultation with the deployment team and by referencing existing deployments. This chapter attempts to provide a general rule of thumb for initial deployment parameters.
The eventual goal of the Cisco VoIP: Infrastructure Manager Solution is to have a fully integrated solution where a redundant, highly available, central database is created, maintained, and monitored with a consistent view of the entire network infrastructure. An overarching application, Cisco Packet Telephony Center (Cisco PTC), keeps track of and is alerted to changes in the underlying network, responding to these changes and alerts from the network devices.
In the 1.1 release of the Cisco VoIP: Infrastructure Manager Solution, minimal integration is achieved and some network elements are not completely supported by the described applications. The NMS is intended to be flexible enough to adapt to new devices and new technologies as they arise.
In this chapter the installation of the Cisco Info Center, Cisco CNS Notification Engine, Cisco CNS Performance Engine, and the associated probes for the Cisco Info Center that are used to communicate with the Cisco CNS Notification Engine, Cisco CNS Performance Engine, and CMNM applications, is detailed (the Cisco CNS Notification Engine Info Mediator probe on the Cisco CNS Notification Engine machine, the Cisco CNS Performance Engine Info Mediator probe on the Cisco CNS Performance Engine machine, and the CEMF probe on the CMNM machine.
In the deployment scenario described above, product installation should be in the following order:
1. The Cisco Info Center Server, Processing Control, MTTrapd and the MTTrapd Info Mediator, and the Licensing component on the Cisco Info Center host.
2. The Cisco CNS Notification Engine and the Cisco Info Center Info Mediator for the Cisco CNS Notification Engine on the Cisco CNS Notification Engine host.
3. The Cisco CNS Performance Engine Info Mediator on the Cisco CNS Performance Engine host (assuming that Cisco CNS Performance Engine is already installed, set up, running, and configured for sending threshold crossing alerts and application health notifications \on the Cisco CNS Performance Engine host).
4. The CEMF Info Mediator on the CMNM host (assuming that CMNM and CEMF are already installed on the CMNM host).
Configure and start the products in the following order:
1. Cisco Info Center and the Cisco Info Center License host.
2. Cisco CNS Notification Engine and the Cisco CNS Notification Engine Info Mediator for Cisco Info Center.
3. The Cisco CNS Performance Engine Info Mediator for the Cisco Info Center on the Cisco CNS Performance Engine host (assuming the Cisco CNS Performance Engine is set up, running, and configured for sending threshold crossing alerts and application health notifications.
4. The CEMF Info Mediator for the Cisco Info Center on the CMNM host (assuming CEMF and CMNM are already installed on the CMNM host).
 |
Note These directions refer to a particular deployment scenario. There are numerous possibilities for deploying various applications singly or co-resident with other applications. Both installation guides for the Cisco Info Center and Cisco CNS Notification Engine applications cover most of the potential deployment scenarios. This chapter describes one deployment model and provides the installation feedback associated with that particular model. The exact deployment model is described below and shown in Figure 4-2. |
This chapter describes a deployment model in which:
1. The Cisco Info Center occupies a Sun machine by itself.
2. The Cisco CNS Notification Engine is hosted on a separate Sun machine running Solaris 8 and communicates with Cisco Info Center over the Cisco CNS Integration bus.
3. The Cisco CNS Performance Engine is hosted on a separate Sun machine running Solaris 8 and communicates with Cisco Info Center over the Cisco CNS Integration bus.
4. The Cisco Media Gateway Controller Node Manager wit the h Cisco Element Management Framework are installed on a Sun machine and communicate faults received from the PGW2200 complex to Cisco Info Center through the CEMF probe.
This section describes what you must do to install the Cisco Info Center product.
Your machine may have other partitioning requirements, however, the example below of a partitioning with two 31GB hard drives is suitable for Cisco Info Center.
cic-tme# df -k
Filesystem kbytes used avail capacity Mounted on
/dev/dsk/c1t1d0s0 32488383 842895 31320605 3% /
/proc 0 0 0 0% /proc
fd 0 0 0 0% /dev/fd
mnttab 0 0 0 0% /etc/mnttab
/dev/dsk/c1t1d0s7 962573 8702 896117 1% /var
swap 3847384 24 3847360 1% /var/run
swap 3847688 328 3847360 1% /tmp
/dev/dsk/c1t2d0s7 33495974 2133 33158882 1% /opt
An example installation script of the Cisco Info Center host components follows using the options chosen for the deployment model as described above.
 |
Note Verify, prior to installing Cisco Info Center, that your server can ping the Cisco CNS Notification Engine, Cisco CNS Performance Engine, and CMNM servers, as you will be asked for their IP addresses during Cisco Info Center installation process. You can enter their machine names in the /etc/hosts file on the Cisco Info Center machine so that name resolution can occur without the requisite of DNS. |
Step 1 Login as root.
Step 2 On the Cisco Info Center host machine, create a directory under /opt for the image tar file:
cic-host# mkdir /opt/CIC34
cic341.EFT2.tar.Z is the image file for Cisco Info Center 3.4.1 found on the product CD, on the Cisco Connection Online (CCO), or delivered as a tar file by way of a down load.
Step 3 Change directory to /opt/CIC34:
cic-host# cd /opt/CIC34
Step 4 Copy the compressed tar file, (from either the product CD, the hard drive, or from CCO) into the directory you just created:
cic-host# cp /cdrom/cdrom0/cic341.EFT2.tar.Z /opt/CIC341
cic-host# ls -l
-rw-r--r-- 1 root other 272860672 Feb 13 10:03 cic341.EFT2.tar.Z
Step 5 Uncompress the tar file:
cic-host# uncompress cic341.EFT2.tar.Z
Step 6 Extract the files:
cic-host# tar -xvof cic341.EFT2.tar
If you see a "UDP checksum error!!" message at the end of the untarring operation feedback, you must repeat the operation or perhaps, gain access to a non-corrupted tar file. The checksum operation saves the deployment time should the tar file get corrupted. Trying to proceed after having a checksum error reported usually ends in failure.
Assuming the checksum is correct, continue.
The untarring operation creates a directory tree under /opt/CIC341 and an installation shell called OINSTALL. It takes approximately five minutes to complete. At this point, no Cisco Info Center packages are installed, you have only expanded the tar file.
cic-host# ls -l
total 533252
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root other 3989 Dec 21 14:57 OINSTALL
-rw-r--r-- 1 root other 1693 Dec 10 16:08 build-rel-note
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root other 272860672 Feb 13 10:03 cic341.EFT2.tar
drwxr-xr-x 3 root other 512 Dec 10 16:08 patches
drwxr-xr-x 3 root other 512 Dec 10 16:08 platform
drwxr-xr-x 13 root other 512 Feb 8 21:13 unix
Step 7 Prepare to execute the ./OINSTALL program to install Cisco Info Center 3.4.1, and follow the instructions. A Release Notes file called notes34.pdf or notes34.fm is also located in this directory.
You can refer to the Cisco Info Center Installation and Configuration Guide to walk through the install from this point forward, however, due to the flexibility of installing in many different possible configuration scenarios, it is more generic than this section. This section helps you install components as they are needed for the particular scenario described herein.
 |
Note At a certain point of the install, the script is going to begin a session in which it needs to know the
terminal setting of the device from which you are running the install. If you are using a Sun machine
console or an Xwindows session, everything should be fine. If you are in a
terminal emulator program, you must let the application know before you begin. In the C shell, this is
accomplished with the following command: trapman# setenv TERM vt100 (or whatever terminal type you are using) Consult your UNIX administrator for help if you do not know how to set up terminal emulation. |
Step 8 Begin the Cisco Info Center installation:
cic-host# ./OINSTALL
Cisco Info Center Installation
Creating temporary directory /tmp/CICtemp and copying needed files.
Do you have a CIC distribution (i.e.: CDROM) (y/n)? [y] y
What directory is the distribution in? [/opt] /opt/CIC34
This is the Cisco Info Center installation and upgrade utility. It will allow
you to complete a new CIC installation, add/delete components on an existing
CIC installation, or upgrade a CIC installation to the current release, 3.4.1.
Do you want to proceed (y or n) [default y] y
A log file will be created to be able to review what the installation does.
The log file is: /tmp/cic_install.log
Press any key to continue....
Your system does not have an existing CIC installation.
Proceeding with an initial installation...
Do you want to change OMNIHOME(/opt/Omnibus) (y or n) [default n] n
Do you want to select components now (y or n) [default y] y
Cisco Information Center Install
Space bar to select, arrows to scroll, tabs for buttons
(+) Mediators
( ) Policy_Manager
(+) Desktop
( ) Wave
(+) InfoServer
(+) Licensing
( ) Gateways
( ) Java_Event_List
(+) Process_Control
<Help>
<Continue>
Step 9 Select the Mediators, Desktop, InfoServer, Licensing, and Process_Control options from the above list.
The script asks you to confirm several times.
Step 10 Check package dependencies and requirements. Hit any key to confirm the qualified components.
Step 11 Again, confirm the list it echoes back to you.
The selected components are installed (this takes less than two minutes):
Installing CIC packages for CIC 3.4.1
Installation of <CICcom> was successful.
Installation of <CICutl> was successful.
Installation of <CICpad> was successful.
Installation of <CICsrv> was successful.
Installation of <CICmed> was successful.
Installation of <CICdsk> was successful.
Installation of <CIClic> was successful.
Installed CIC packages for CIC 3.4.1
You have installed Process Control on Solaris8.
Installing nco_pad Patch. Please wait...
Solaris8 nco_pad patch has been installed.
Do you wish to configure now (y or n) [default y] y
###################################################################
Cisco Info Center Configuration Menu
###################################################################
1. Configure Info Server
2. Configure Mediators
3. Configure Info Admin Desktop
4. Configure All
5. Help
6. Quit
Select one of the above options: 4
You have selected the following:
Configure All
Do you want to continue (y/n)?: [y] y
You must first configure the Process Control Agent
The following questions will guide you through this procedure
Name for the Process Agent must be alphanumeric beginning with a letter, must NOT
exceed 11 characters and must end with _PA ***
This sample Cisco Info Center installation should use the default names and port numbers provided by the installation program.To do so, hit Return in response to the questions unless otherwise directed.
Name for the Process Agent [NCO_PA]:
Enter the Port Number for Process Agent [4200]:
Name for the Info Server must be alphanumeric beginning with a letter and up to 11
characters long ***
Name for the Info Server [INFOSERVER]:
Enter the Port Number for the Info Server [4100]:
Checking Port Availability Please Wait... done
Adding its entry to omni.dat.... done
Creating the new Info Server INFOSERVER
Generating the databases files... Info Server INFOSERVER created
Updating /etc/services file...
Do you wish to configure automatic startup upon system boot? (y/n)? [y] y
This above step sets a link from /etc/rcd.2/S81nco to /etc/init.d/nco.
Continuing:
************************************
Device configuration menu
************************************
1. MWFM
2. CW2K (include DFM and VHM)
3. CTM
4. CWM
5. CEMF
6. NNM
7. CNS-NOTE using SNMP
8. CNS-NOTE using CNS
9. Syslog
10. SNMP Generic Traps
11. CNS-PE using CNS
1-12. Toggle Component
S. Select All Components
U. Unselect All
I. Setup and Install Components
H. Help
Q. Quit
Option: 10
************************************
Device configuration menu
************************************
1. MWFM
2. CW2K (include DFM and VHM)
3. CTM
4. CWM
5. CEMF
6. NNM
7. CNS-NOTE using SNMP
8. CNS-NOTE using CNS
9. Syslog
10. SNMP Generic Traps SELECTED
11. CNS-PE using CNS
 |
Note At this point, you have selected only option 10. It is perhaps confusing to have not chosen some of the other options as you know you are going to be collecting data from Cisco CNS Notification Engine, Cisco CNS Performance Engine, and NNM. These options will be chosen when installing those applications on their own respective machines. Because the other applications are all installed on their own respective machines, this installation of the Cisco Info Center application requires only SNMP generic traps (option 10). |
1-12. Toggle Component
S. Select All Components
U. Unselect All
I. Setup and Install Components
H. Help
Q. Quit
Option: I
*** Configuring mttrapd Info Mediator ***
Info Mediator mttrapd Configured
Press <Return> when ready...
Creating the ncoadmin group for CIC...
Creating the cicpa user for CIC...
At this point, the executable is creating a password for the cicpa user. No input is required as it is done automatically.
New password:
Re-enter new password:
passwd (SYSTEM): passwd successfully changed for cicpa
Successfully created the cicpa user.
You have chosen to configure a stand alone InfoServer on the local host. This InfoServer will need to communicate with the remote InfoMediators via the Process Control Agent. It is necessary for the Process Control Agents to be aware of each other. The next set of prompts will configure the InfoServer to be aware of the remote InfoMediators.
Press <Return> when ready...
Is there a remote CWM InfoMediator? (y/n)? [y] n
Is there a remote CNS-NOTE InfoMediator? (y/n)? [y] n
Answer no to this question because when the installation program first asks about a Cisco CNS Notification Engine Info Mediator, it is referring to the Cisco CNS Notification Engine application sending SNMP traps to the Cisco Info Center using the SNMP protocol from a remote machine. In this sample installation, you want to configure the Cisco CNS Notification Engine to send messages over the Cisco CNS Integration bus using the XML protocol. This option is presented further on in this configuration portion of the installation program. You should configure the Cisco CNS Notification Engine to communicate with the Cisco Info Center in one of the two ways, but not both.
Is there a remote CEMF InfoMediator? (y/n)? [y] y
*** Configuring Process Control on Info Server Machine requires ***
*** Properties of the Process Control on the remote CEMF Info Mediator ***
Configuring local Process Control to talk to remote CEMF Info Mediator...
Enter the hostname where the remote Info Mediator is: cmnm-tme
If the machine has a DNS entry and/or the machine name is in the /etc/hosts file on the Cisco Info Center machine, you can use the machine's name, otherwise, use its IP address.
Trying to ping Host cmnm-tme... OK
If the above line does not return OK, there is a connectivity or name resolution problem to be overcome first.
 |
Note It is important to keep a record of the Process Control names used in the next section (that is, MED1_PA, MED2_PA, etc). The Process Control names and port numbers for the different Info Mediators must match the same on the individual Info Mediators installed on separately hosted collection/EMS applications, (Cisco CNS Notification Engine, Cisco CNS Performance Engine, and MNM). This is required for proper transport of messages between the applications. The port numbers can all be the same unless there are two different Info Mediators on the same host. For this sample installation, the port number upon which Cisco Info Center listens is 4200 for all the Info Mediators. |
Enter Process Control name on the remote Info Mediator [MED1_PA]:
Enter the Process Control port number on the remote Info Mediator [4200]:
Is there another remote CEMF InfoMediator? (y/n)? [n] n
Is there a remote CTM InfoMediator? (y/n)? [y] n
Is there a remote MWFM InfoMediator? (y/n)? [y] n
Is there a remote CW2K InfoMediator? (y/n)? [y] n
Is there a remote CNS InfoMediator? (y/n)? [y] y
This sequence of questions illustrates the variety of management applications with which Cisco Info Center is integrated. This step (question) is where the Info Mediators for both Cisco CNS Notification Engine and Cisco CNS Performance Engine are identified.
*** Configuring Process Control on Info Server Machine requires ***
*** Properties of the Process Control on the remote Info Mediator ***
Configuring local Process Control to talk to remote C-NOTE Info Mediator...
Enter the hostname where the remote Info Mediator is: cnote-tme
Trying to ping Host cnote-tme... OK
Enter Process Control name on the remote Info Mediator [MED2_PA]:
Enter the Process Control port number on the remote Info Mediator [4200]:
Is there another remote CEMF InfoMediator? (y/n)? [n] y
Enter the hostname where the remote Info Mediator is: perf-tme
Trying to ping Host perf-tme... OK
Enter Process Control name on the remote Info Mediator [MED3_PA]:
Enter the Process Control port number on the remote Info Mediator [4200]:
Is there another remote CNS InfoMediator? (y/n)? [n] n
The Process Control names for MNM, Cisco CNS Notification Engine, and Cisco CNS Performance Engine are MED1_PA, MED2_PA, and MED3_PA, respectively, which will be needed when those remote Info Mediators are installed. The port number for listening on the remote hosts is 4200 for both. If you forget to record these process control names, you can retrieve them from the /opt/Omnibus/etc/omni.dat file on the Cisco Info Center machine.
(+) CEMF.elc
( ) CTM.elc
( ) CW2K.elc
( ) CWM.elc
(+) PE.elc
(+) General_Traps.elc
( ) MWFM.elc
(+) C-NOTE.elc
( ) Syslog.elc
( ) VPNSC_MPLS.elc
Step 13 Continue to acknowledge the selections and confirm several times.
CIC has been successfully
Now you must prepare for license configuration. In order to complete this phase, you must have various license keys. These are provided by your Cisco account representative or the Micromuse Support organization. If you do not have license keys at this point, you can answer no and configure licensing when you obtain the keys.
 |
Note License keys are created using the machine ID and can only be used on the machine for which they were created. |
In your license e-mail request, include the following information:
1. Reason you need the license (for example, lab testing).
2. Primary contact information.
3. Physical location of the server.
4. Server code (shown above).
5. Duration requested (for example, 1 year).
 |
Note Customers must call Micromuse directly to request license keys. Micromuse issues keys according to Purchase Orders they have with a customer. Licenses cannot be moved from one machine to another, they are machine specific. This script runs through the licensing procedure for a certain machine. The license numbers listed will not work for any other machine. |
If you must wait for your license keys, you can finish the install now and run the licensing application later with the command:
trapman# /opt/Omnibus/bin/nco_license
The following script runs through the licensing procedure for a particular machine. The license numbers used in the following sample will not work for any other machine.
Step 14 Assuming you have your license keys, continue on:
Would you like to configure licensing now? (y/n)? [y] y
Cisco/InfoServer 3.4 License Installation
This machine is "trapman".
Is this correct machine to run the license server on (y/n)? [y] y
Starting License Management Daemon
How many license servers do you want to run? [1] 1
Code for "trapman" is: 194/1342 6215 8795 9806 9725
Please send the server and this code number to helpdesk@micromuse.com to get your license keys
 |
Note If you don't have a license for a particular function, you can skip that license request. It is recommended though that you read the entire section on licensing before starting the licensing application. You may have keys for licenses that are not prompted for. You can enter those licenses at the prompt for license strings that you don't have. This is explained more in the dialog feedback. |
Following is a typical license file received from Micromuse. Because the licenses are created with the host ID of the machine to which they are destined, you cannot use license files designated for one machine on any other machine. Therefore, the license keys listed below, while they are legitimate, will not work for any other machine other than trapman.
License file for trapman:
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
Server Code: 194/9070 8754 0503 9913 8537
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
Evaluation period: 180 days
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
ObjectServer Key [5]: 3908 0522 2377 0393 8249 0288 4
UNIX/Motif Desktop Key [5]: 9186 4110 3974 0938 4686 5494 8
Probe Band A (Special) Key [5]: 3131 8441 2589 4442 4712 9457 6
Probe Band B (NT) Key [5]: 9760 5239 7563 9459 9972 1087 6
Probe Band C (Standard) Key [5]: 4468 8537 3450 3101 1237 1491 1
Probe Band D (Custom) Key [5]: 1361 4825 9917 3224 2168 9291 8
Probe Band E (Bundled) Key [5]: 9345 1814 1917 6093 7840 0982 4
Internet Service Monitor (ISM) Key [5]: 0350 4013 8523 5947 9604 2853 5
Probe Band G (Generic) Key [5]: 1877 3242 6951 2269 2722 1675 9
Probe Band H (FireWallOne) Key [5]: 2972 7445 8637 4607 5712 4371 0
TelcoProbe (Telco Probe Band) Key [5]: 6630 8236 9481 7720 3167 7522 0
BMC Patrol Probe Key [5]: 6387 2492 6921 3217 9929 4120 5
Probe Band M (MultiHeaded) Key [5]: 4308 6092 6236 9289 8077 7923 4
Framework (EMS) Key [10]: 0750 1200 8549 8730 1150 8591 5
Gate Writer Key [5]: 3765 8934 7738 2861 6178 0021 0
Probe Proxy Server Key [5]: 2384 7370 5314 4434 4810 2721 0
NT Event List Key [5]: 3124 7059 5287 8988 7115 4929 5
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
Generation completed Wed May 22 18:26:19 2002
The point of listing this file is to compare it with the license setup script on the next few pages. For instance, the license file above has keys for Framework (EMS—this is the CEMF key) and Probe Bands G, H, and M. However, the script for entering the license keys never asks for those keys. Instead, it asks for several keys that are not available in the file.
The solution is that when the license program asks for a key you do not have, enter a key you do have, but will not get prompted for. How do you know if the program will eventually prompt you for the key or not? Let's try it and see.
Please enter each key at the prompt. Press RETURN to skip any key.
Key for Object Server: 3908 0522 2377 0393 8249 0288 4
Object Server key installed successfully
Key for Desktop: 9186 4110 3974 0938 4686 5494 8
Desktop key installed successfully
Key for Probe Band A: 3131 8441 2589 4442 4712 9457 6
Probe Band A key installed successfully
Key for Probe Band B: 9760 5239 7563 9459 9972 1087 6
Probe Band B key installed successfully
Key for Probe Band C: 4468 8537 3450 3101 1237 1491 1
Probe Band C key installed successfully
Key for Probe Band D: 1361 4825 9917 3224 2168 9291 8
Probe Band D key installed successfully
Key for Probe Band E: 9345 1814 1917 6093 7840 0982 4
Probe Band E key installed successfully
Key for Internet Service Monitor: 0350 4013 8523 5947 9604 2853 5
Internet Service Monitor key installed successfully
Key for Firewall-1 Monitor: 2972 7445 8637 4607 5712 4371 0
Firewall-1 Monitor key installed successfully
Key for Telco Probe Band: 6630 8236 9481 7720 3167 7522 0
Telco Probe Band key installed successfully
Key for Patrol Probe Band: 6387 2492 6921 3217 9929 4120 5
Patrol Probe Band key installed successfully
Key for Gate Writer: 3765 8934 7738 2861 6178 0021 0
Gate Writer key installed successfully
At this point, the application has skipped three of the keys that our file has. The next request is for a key we do not have. So, instead of pressing Return with no key entered, (as the application feedback instructs us), for this entry and the two entries after that (because we don't have those keys either), we can substitute the three keys we do have, and that have been skipped, namely: Probes B, G, H, and M.
Key for Reporter Gate Writer:1877 3242 6951 2269 2722 1675 9 (actually for Probe Band G)
Reporter Gate Writer key installed successfully
Key for ODBC Gate Writer: 2972 7445 8637 4607 5712 4371 0 (actually for Probe Band H)
Gate Writer key installed successfully
Key for Java Event List: 4308 6092 6236 9289 8077 7923 4 (actually for Probe Band M)
Java Event List key installed successfully
At this point the license dialog is asking for a key that we do have so we enter the proper key.
Key for Probe Proxy Server: 2384 7370 5314 4434 4810 2721 0
Probe Proxy Server key installed successfully
Key for NT Event List: 3124 7059 5287 8988 7115 4929 5
NT Event List key installed successfully
Once again, the next request is asking for a key we do not have. However, there is one license string (Framework EMS) that we have not yet entered, so we will enter it here:
Key for Service View: 0750 1200 8549 8730 1150 8591 5
Service View key installed successfully
This has worked well so far. There were four key strings for which we were not prompted, and four prompts for which we had no key (so it was a one to one substitution.) This may not work out so precisely according to the licenses you purchase. The main thing is to enter all of the keys you were issued and not worry if there are more prompts than you have keys.
 |
Note The CEMF probe requires a license, however, a prompt never appears asking for it. If you are expecting to install the CEMF Probe on your Cisco MNM host, be sure to substitute this key for one of the available prompts. The licensing application continues on. |
Do you want to list the installed licenses (y/n)? [y]
(you can also view this same data later with /opt/Omnibus/bin/elmadmin -l
Server trapman:
CID LID PACK User Feature Group Started
--- --- ---- -------------------------------- ---------- -------- ------------
7 1 00.0 root@trapman ObjectServ - Aug 23 17:17
ObjectServer [3201]: 5 licenses, 1 in use; installed Aug-22-02
Expires Nov-18-02.
Desktop [3202]: 5 licenses, 0 in use; installed Aug-22-02
Expires Nov-18-02.
Writer [3204]: 5 licenses, 0 in use; installed Aug-22-02
Expires Nov-18-02.
ProxyServer [3206]: 5 licenses, 0 in use; installed Aug-22-02
Expires Nov-18-02.
CID LID PACK User Feature Group Started
--- --- ---- -------------------------------- ---------- -------- ------------
2 5 00.0 root@perf-tme ProbeBandA - Aug 23 17:21
12 4 00.0 root@even20 ProbeBandA - Aug 23 17:18
ProbeBandA [3211]: 5 licenses, 2 in use; installed Aug-23-02
Expires Nov-18-02.
ProbeBandB [3212]: 5 licenses, 0 in use; installed Aug-22-02
Expires Nov-18-02.
CID LID PACK User Feature Group Started
--- --- ---- -------------------------------- ---------- -------- ------------
8 2 00.0 root@trapman ProbeBandC - Aug 23 17:17
ProbeBandC [3213]: 5 licenses, 1 in use; installed Aug-23-02
Expires Nov-18-02.
ProbeBandD [3214]: 5 licenses, 0 in use; installed Aug-22-02
Expires Nov-18-02.
ProbeBandE [3215]: 5 licenses, 0 in use; installed Aug-22-02
Expires Nov-18-02.
ISM [3216]: 5 licenses, 0 in use; installed Aug-22-02
Expires Nov-18-02.
3217: 5 licenses, 0 in use; installed Aug-22-02
Expires Nov-18-02.
FirewallOne [3218]: 5 licenses, 0 in use; installed Aug-22-02
Expires Nov-18-02.
TelcoProbe [3219]: 5 licenses, 0 in use; installed Aug-22-02
Expires Nov-18-02.
BMC [3220]: 5 licenses, 0 in use; installed Aug-22-02
Expires Nov-18-02.
3221: 5 licenses, 0 in use; installed Aug-22-02
Expires Nov-18-02.
3222: 10 licenses, 0 in use; installed Aug-22-02
Expires Nov-18-02.
NTEL [3250]: 5 licenses, 0 in use; installed Aug-22-02
Expires Nov-18-02.
CIC 3.4.1 has been installed.
The listing of the licenses shows the name of the license and the number of licenses supported for that function. You can run this at any point after the installation as well, with the command:
opt/Omnibus/bin/elmadmin -l
If you entered a license for one particular key at a prompt for another key, the name for that license will be a number instead of a name. Checking to make sure the CEMF (Framework EMS) key was properly entered we see the entry starting with the number:
3222: 10 licenses
Because all of the keys support only five licenses, except for the Framework key, which supports ten, we can be confident that the key for Framework has been installed and is labelled 3222.
Notice the licenses have an expiration date. It is prudent to anticipate this date and have an updated license file ready so you can re-run the licensing script before the license expires. Cisco Info Center warns you that your license is about to expire, days in advance of the actual expiration.
The installation process builds the directory tree under /opt/Omnibus and installs eleven Cisco Info Center packages in the /opt/CIC341/unix directory. The following output shows the directory structure after a successful install:
Step 15 Check which directory you are in:
trapman# pwd
/opt/CIC341/unix
Step 16 List the contents of the /opt/CIC341/unix directory:
trapman# ls -l
total 22
drwxr-xr-x 4 root other 512 Feb 8 21:10 CICcom
drwxr-xr-x 4 root other 512 Feb 8 21:10 CICdsk
drwxr-xr-x 4 root other 512 Feb 8 21:11 CICgtw
drwxr-xr-x 4 root other 512 Feb 8 21:11 CICjel
drwxr-xr-x 4 root other 512 Feb 8 21:11 CIClic
drwxr-xr-x 4 root other 512 Feb 8 21:11 CICmed
drwxr-xr-x 4 root other 512 Feb 8 21:11 CICpad
drwxr-xr-x 4 root other 512 Feb 8 21:13 CICpmr
drwxr-xr-x 4 root other 512 Feb 8 21:11 CICsrv
drwxr-xr-x 4 root other 512 Feb 8 21:12 CICutl
drwxr-xr-x 4 root other 512 Feb 8 21:12 CICwav
Step 17 Change directory to /opt/Omnibus:
trapman# cd /opt/Omnibus
Step 18 List the contents of the /opt/Omnibus directory:
trapman# ls -l
total 234
-r--r--r-- 1 root root 1030 Feb 7 16:52 RELEASE_ID
drwxr-xr-x 3 root root 1536 Feb 13 11:02 bin
-r--r--r-- 1 root root 2718 Feb 7 16:31 build-rel-note
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 1536 Feb 22 11:20 db
drwxr-xr-x 9 root root 512 Feb 14 15:57 desktop
drwxrwxr-x 2 root root 512 Feb 13 10:59 doc
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 1024 Feb 20 11:55 etc
drwxrwxr-x 4 root root 512 Feb 13 11:02 install
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 512 Feb 13 11:40 log
drwxr-xr-x 4 root root 512 Feb 13 11:02 man
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 96597 Jun 2 2000 mask
drwxrwxr-x 4 root root 512 Feb 13 11:00 patches
drwxr-xr-x 3 root root 512 Feb 13 10:59 platform
drwxr-xr-x 3 root root 2048 Feb 13 11:00 probes
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 512 Feb 13 11:01 tsm
drwxr-xr-x 21 root root 512 Feb 13 11:00 utils
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 512 Feb 13 11:40 var
Step 19 Start the Info Server. You must set the OMNIHOME environment variable. The following is for setting the environment variable in the C shell. If you are operating in a different shell, consult your UNIX administrator for instructions:
trapman# setenv OMNIHOME /opt/Omnibus
Step 20 Start the Cisco Info Center application with the startup script created during the installation process:
trapman# /etc/init.d/nco start
Cisco Info Center Process Agent Daemon - Version 3.4
Cisco Info Center PA API Library Version 1.2
Sybase Server-Library Release: 11.1.1
Server Settings:
Name of server : NCO_PA
Path of used log file : /opt/Omnibus/log/NCO_PA.log
Configuration File : /opt/Omnibus/etc/nco_pa.conf
Child Output File : /dev/null
Maximum logfile size : 1024
Thread stack size : 69632
Message Pool size : 45568
PID Message Pool size : 50
Rogue Process Timeout : 30
Truncate Log : False
Instantiate server to daemon : True
Internal API Checking : False
No Configuration File : False
Start Auto-start services : True
Authentication System : UNIX
Trace Net library : False
Trace message queues : False
Trace event queues : False
Trace TDS packets : False
Trace mutex locks : False
Forking to a Daemon Process.............
Step 21 Hit the Return key.
Cisco Info Center can be upgraded with bug fixes and code improvements with an upgrade utility in the /opt/Omnibus/bin directory.
Updater is available as /opt/Omnibus/bin/cic_update and the input to it is different tar files, bundled in the cic341patches/cic341patches.tar file. These tar file updates are available from CCO or through your Cisco engineering or account representative. When you receive the update file, place it in /opt/Omnibus/patches directory.
Use the tar xvf cic341patches.tar command to extract the individual tar files. Updater must be run on all machines that have Cisco Info Center components Updater overwrites the concerned files. If there are any customizations, it is better to back them up. Updater warns and proceeds whenever a minor issue that is common in deployments occurs. The cic341genpatch001patch must be the first update to the Cisco Info Center system.
Following is a session on a Cisco Info Center machine where the issued patches are installed:
Step 1 Login as user root.
Step 2 Change to the patches directory:
trapman# cd /opt/CIC34/patches
/opt/CIC34/patches
Step 3 List the contents of the /opt/CIC34/patches directory:
trapman# ls
cic341patches cic341patches.README cic341patches.tar solaris2
Step 4 Change to the cic341patches directory:
trapman# cd cic341patches
Step 5 List the contents of the /opt/CIC34/patches/cic341patches directory:
trapman# ls
cic341genpatch001.README cic341genpatch002.README cic341gldpatch001.README
cic341genpatch001.tar cic341genpatch002.tar cic341gldpatch001.tar
The README files have information and release notes about the individual patches. The README file in the cic341patches directory states that the first update to be run is the cic341genpatch001.tar patch.
Step 6 Set the OMNIHOME environment variable:
trapman# setenv OMNIHOME /opt/Omnibus
trapman# echo $OMNIHOME
/opt/Omnibus
Step 7 Update your existing Cisco Info Center installation:
trapman# /opt/Omnibus/bin/cic_update
OMNIHOME environment variable set: /opt/Omnibus
You must receive an update distribution and place it on the current host. This utility processes the update distribution and integrates it into your current Cisco Info Center installation.
Do you want to continue (y or n) [default y] y
Enter the name and directory where the update distribution is: /opt/CIC34/patches/cic341patches/cic341genpatch001.tar
Processing the CIC update distribution...
Cleaning up temporary files....
Your CIC system has been updated
Step 8 After the cic341genpatch001 patch is installed, you should install the latest of the rest of the available Cisco Info Center patches. In this case, it is the cic341genpatch003.tar patch file. You add it to the Cisco Info Center system the same way you added the cic341genpatch001 patch:
trapman# /opt/Omnibus/bin/cic_update
OMNIHOME environment variable set: /opt/Omnibus
This utility is used to update your existing CIC installation. You will need to have received an update distribution, and placed it on the current host. This utility will process the update distribution, and integrate it into your current CIC installation.
Do you want to continue (y or n) [default y] y
Enter the name and directory where the update distribution is:
/opt/CIC34/patches/cic341patches/cic341genpatch003.tar
Processing the CIC update distribution...
WARNING: Mediator nco_p_ssng was verified as not configured.
WARNING: Mediator nco_p_cwm was verified as not configured.
WARNING: Unable to restart the Mediator nco_p_cwm has not been verified as active
WARNING: Unable to restart the Mediator nco_p_ssng has not been verified as active
WARNING: Mediator nco_p_tibco was verified as not configured.
WARNING: Unable to restart the Mediator nco_p_tibco has not been verified as active
WARNING: Unable to restart the Mediator nco_p_mttrapd has not been verified as active
Cleaning up temporary files....
Your CIC system has been updated; however, 7 warnings were detected during the update. Please review the /opt/Omnibus/log/update.log file to determine if any require further action.
Cisco Info Center was updated successfully with seven warnings, as shown in the above output. The first four warnings are about Info Mediators that were not installed and therefore, are moot. The last three warnings are also non critical and can be ignored.
Cisco Info Center begins collecting data as soon as it is installed and devices are pointed at it. Out of the box, Cisco Info Center is configured with de-duplication and intelligent processing options. Automation, filters, and views are the three main attributes of Cisco Info Center you can customize.
Filters are the vehicle for configuring what actual events are seen in any particular window of the Cisco Info Center Graphical User Interface (GUI). The Event List window is where the different filters are built. Any of the filters can be customized and new filters can be built. Events can be filtered by one or more of the many device attributes built into Cisco Info Center. Examples of these attributes are NEName, NEAddress, Summary, Manager, and Last Occurrence. The Cisco Info Center GUI allows you to build simple or complex binary logical expressions upon which to filter.
Views are the arrangement and format of the device attribute columns visible in the Filter Event list. The default views that come configured with Cisco Info Center, as well as the view in any filter, including the all events filter, can be customized.
For a demonstration of filter and view building and a quick start guide, see the Cisco Info Center Installation and Configuration Guide at:
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/rtrmgmt/info_ctr/3_4_1/install/install.htm
The Cisco CNS Notification Engine application is deployed in one of four configurations:
1. Standalone.
2. With Cisco WAN Manager (CWM).
3. With Cisco Info Center.
4. With Hewlett Packard Open View (HPOV).
Engineering resources have determined that the optimal test configuration is as a standalone application. Test resources will install Cisco CNS Notification Engine on the same machine as Cisco CNS Performance Engine. This is covered under the standalone deployment option because they do not share any processes and can be partitioned so as to be totally independent while on the same machine. The options listed above are listed for the benefit of the reader, should they wish to deploy Cisco CNS Notification Engine in another manner.
In this chapter's scenario, the Cisco CNS Notification Engine application is installed on a Sun Solaris8 machine by itself. The installation script is described in the following sections.
The Cisco CNS Notification Engine application has gone through a series of name changes to best reflect its technology and its relationship to other NMS component applications. The original name for the Cisco CNS Notification Engine application was the Syslog to SNMP Notification Generator (SSNG). The code was written with this name in mind and therefore, many of the installation directives and file directories refer to ssng. Any reference to ssng in the installation script or directory structure should be understood to be a reference to Cisco CNS Notification Engine.
In this sample installation, the Cisco CNS Notification Engine application is installed on a Sun Blade with a two 770 MHz processors, 1GB RAM, and two 31GB hard drives (this is a standard configuration). The Operating System is Solaris, version 8. Other options are possible with the above being the recommended minimum.
There are two components to the installation and operation of the Cisco CNS Notification Engine application:
1. Installation of the Cisco CNS Notification Engine application.
2. Installation of the Cisco Info Center probe that facilitates communication between the Cisco CNS Notification Engine and the Cisco Info Center. The Cisco CNS Notification Engine itself is a Collector. It requires an upstream device to process the output it generates.
The Cisco CNS Notification Engine can communicate with the Cisco Info Center in two ways:
1. SNMP using Robust/Reliable Transport Mode (RTM) over UDP.
2. Cisco CNS Integration bus (Cisco CNS Rendezvous technology).
This chapter describes an installation of the Cisco CNS Notification Engine application using the Cisco CNS Integration bus as the means of communication between the Cisco CNS Notification Engine and Cisco Info Center applications.
For information on upgrading and data backup and restore, refer to the "Installing Patches for Cisco Info Center Using the cic_update Utility" and "Upgrading Cisco CNS Notification Engine with Patches" sections.
Step 1 Login as root on the Cisco CNS Notification Engine machine.
Step 2 Create the /opt/ssng directory and then copy the Cisco CNS Notification Engine tar file into it.
cnote-tme# mkdir /opt/ssng
cnote-tme# cp /tmp/cnote.2.0-ga.tar /opt/ssng
Step 3 Change to the /opt/ssng directory:
cnote-tme# cd /opt/ssng
Step 4 Untar the file:
cnote-tme# tar -xvf cnote.2.0-ga.tar
Step 5 You are now ready to install the Cisco CNS Notification Engine 2.0 software. The session below is a remote Xwindows session and the DISPLAY environment variable is set in order to display the GUI window towards the end of the setup procedure. This is not a prerequisite. If you are installing remotely using something other than Xwindows emulation, you will not see the GUI window. You will see an error message about the DISPLAY variable. If you are installing from the console of the machine upon which Cisco CNS Notification Engine is installed, you are not required to set the DISPLAY environment variable.
cnote-tme# setenv DISPLAY 171.71.66.156:0
Step 6 Start installing the Cisco CNS Notification Engine application:
cnote-tme# cd /opt/ssng/bin
even20# setenv DISPLAY 171.71.66.156:0
even20# ./setup
SSNGHOME not set .... Setting it to "/opt/ssng"
SSNGHOME is /opt/ssng
Activate the auto-sense new node feature? (yes/no) y
Enter y to use the auto-sense new node feature
Enter n if you do not want to use auto-sense new node feature
y
The Autosense feature is where the Cisco CNS Notification Engine detects the network elements that are sending it Syslog messages and automatically adds them to the /opt/ssng/log/nodeinfo.dat file.
Typically you would want to enable the Autosense feature. This feature automatically adds a host entry to the nodeinfo.dat file. This eliminates the need to manually enter the hosts into the nodeinfo.dat file, a very useful feature for large networks. If however, you wish to restrict the number of hosts sending to your instance of the Cisco CNS Notification Engine application, you should disable this feature and manually create the nodeinfo.dat file, listing only the hosts with which you wish your instance of the Cisco CNS Notification Engine to communicate. A yes response was entered above.
Please specify the setup environment:
1) To install C-NOTE standalone, enter 1
2) To install C-NOTE to support CWM, enter 2
3) To install C-NOTE to support Solaris, enter 3
1
The is considered a standalone installation.
Specify the transport protocol you are using:
1) To generate SNMPV1 traps, enter 1
2) To generate SNMPV2C traps, enter 2
3) To use Tibco/Rendezvous daemon, enter 3
4) To use CNS daemon, enter 4
4
Specify the type of CNS/Rendezvous Daemon:
1) CNS/Rendezvous daemon, enter 1
2) CNS/Rendezvous routing daemon, enter 2
3) Do not need to start, enter 3
1
RVD Daemon already running
root 25666 1 0 16:46:45 ? 0:00/opt/ssng/bin/rvd -listen 7500
Continue to launch other related processes(yes/no) y
***Starting ssngBurstLog***
***Starting Filter***
 |
Note At this point, if your DISPLAY environment variable is set up correctly and if you are remote and using Xhost+ (the Configuration GUI needs X-windows), the window shown in Figure 4-3 appears. |
Basic setup for C-NOTE 2.0 is finished.
Step 8 Add the following entry to the end of the crontab file:
cnote-tme# crontab -e
In vi user insert mode, at the end of the file (Gi) the following and save to file (ZZ).
0 * * * * /opt/ssng/bin/ssng_health -b
Step 9 That completes the installation of the Cisco CNS Notification Engine. Check for Cisco CNS Notification Engine processes by searching for ssng:
cnote-tme# ps -ef | grep ssng
root 20129 10385 0 16:44:18 ? 0:00 sh -c /usr/bin/ps -ef | grep -v grep | grep ssngPing
root 430 1 0 May 21 ? 40:45 /opt/ssng/bin/rvd -listen 7500
root 10416 1 0 13:40:23 ? 0:01 /opt/ssng/bin/perl /opt/ssng/bin/ssngPing
root 10411 1 0 13:40:21 ? 0:00 /opt/ssng/bin/perl /opt/ssng/bin/solFilter
root 10461 1 0 13:40:25 ? 0:00 /opt/ssng/bin/ssngBurstLog
root 10402 1 0 13:40:20 ? 0:03 /opt/ssng/bin/perl /opt/ssng/bin/ssngFilter -cns=tib
root 10385 1 4 13:40:18 ? 8:22 /opt/ssng/bin/perl /opt/ssng/bin/ssngWatchDog -rvd_exist
start
Look for the above processes to insure that everything is running. Don't be confused by the name ssng, as it is coded into the binary file. It is the previous name for the product (Syslog to SNMP Notification Generator.)
The version of the Cisco CNS Notification Engine referred to in this document is version 2.0, general availability (ga). Upgrades to version 2.0 are available and use the following naming convention:
cnote.2.0-ga.00<x>.tar
where <x> in the distribution name is a placeholder. The distribution files are numbered consecutively as new patches become available, (that is, cnote.2.0-ga.001, cnote.2.0-ga.002, cnote.2.0-ga.003, etc.). You should install the latest patch available. The most recent, as of August 15, 2002, is cnote.2.0-ga.003. Patching or updating the release is similar to the installation of the main distribution package.
An upgrade to patch cnote.2.0-ga.004 is detailed below where the patch distribution file is stored in the /tmp directory.
Step 1 Login as root.
Step 2 Create a patch directory in the SSNGHOME directory:
cnote-tme# mkdir /opt/ssng/patch
Step 3 Copy the tar file to the patch directory:
cnote-tme# cp /tmp/cnote.2.0-ga.004.tar /opt/ssng/patch
Step 4 Change to the $SSNGHOME directory:
cnote-tme# cd /opt/ssng
Step 5 Untar the file from the $SSNGHOME directory:
cnote-tme# tar -xvf patch/cnote.2.0-ga.004.tar
x ., 0 bytes, 0 tape blocks
x ./config, 0 bytes, 0 tape blocks
x ./config/trap_filter.conf, 23616 bytes, 47 tape blocks
x ./config/fac.dat, 245321 bytes, 480 tape blocks
x ./config/ssng.conf, 2602 bytes, 6 tape blocks
x ./config/151.fac.dat, 52972 bytes, 104 tape blocks
x ./bin, 0 bytes, 0 tape blocks
x ./bin/keepalive, 414468 bytes, 810 tape blocks
x ./bin/setup.ov, 798 bytes, 2 tape blocks
x ./bin/setup.oss, 2221 bytes, 5 tape blocks
x ./bin/setup, 10981 bytes, 22 tape blocks
x ./bin/ssng, 17026 bytes, 34 tape blocks
x ./bin/ssngStg, 4445024 bytes, 8682 tape blocks
x ./bin/ssngrlog, 413 bytes, 1 tape blocks
x ./bin/solFilter, 5589 bytes, 11 tape blocks
x ./bin/ssngFilter, 90002 bytes, 176 tape blocks
x ./bin/ssngWatchDog, 31873 bytes, 63 tape blocks
x ./bin/ssng_health, 25357 bytes, 50 tape blocks
x ./bin/ssngPing, 4395 bytes, 9 tape blocks
x ./bin/setup.auto, 939 bytes, 2 tape blocks
x ./bin/ssng_backup, 335 bytes, 1 tape blocks
x ./bin/ssng_restore, 4266 bytes, 9 tape blocks
x ./bin/ssng_start, 1413 bytes, 3 tape blocks
x ./bin/simbasic, 9808 bytes, 20 tape blocks
x ./bin/ssng_register, 7037 bytes, 14 tape blocks
x ./bin/deregmgr, 827 bytes, 2 tape blocks
x ./bin/ssng_register2, 7342 bytes, 15 tape blocks
x ./bin/ssngBurstLog, 41334 bytes, 81 tape blocks
x ./bin/check_cwm_restart, 1460 bytes, 3 tape blocks
x ./bin/cwm_register, 1123 bytes, 3 tape blocks
x ./mib, 0 bytes, 0 tape blocks
x ./mib/ssng-syslog-mib, 762564 bytes, 1490 tape blocks
x ./mib/HPOV_install.script, 1023 bytes, 2 tape blocks
x ./mib/recommended_action.lst, 622110 bytes, 1216 tape blocks
x ./mib/explanation.lst, 700627 bytes, 1369 tape blocks
x ./mib/Ssng_trapd.conf, 523399 bytes, 1023 tape blocks
x ./mib/151.Ssng_trapd.conf, 233156 bytes, 456 tape blocks
x ./mib/151.ssng-syslog-mib, 335853 bytes, 656 tape blocks
x ./cnote.2.0-ga.003, 29 bytes, 1 tape blocks
x ./lib, 0 bytes, 0 tape blocks
x ./lib/site_perl, 0 bytes, 0 tape blocks
x ./lib/site_perl/5.6.1, 0 bytes, 0 tape blocks
x ./lib/site_perl/5.6.1/Logfile, 0 bytes, 0 tape blocks
x ./lib/site_perl/5.6.1/Logfile/Rotate.pm, 14146 bytes, 28 tape blocks
x ./lib/site_perl/5.6.1/sun4-solaris-thread, 0 bytes, 0 tape blocks
x ./lib/site_perl/5.6.1/sun4-solaris-thread/auto, 0 bytes, 0 tape blocks
x ./lib/site_perl/5.6.1/sun4-solaris-thread/auto/Logfile, 0 bytes, 0 tape blocks
x ./lib/site_perl/5.6.1/sun4-solaris-thread/auto/Logfile/Rotate, 0 bytes, 0 tape blocks
x ./readme, 13400 bytes, 27 tape blocks
x ./FAQ, 11738 bytes, 23 tape blocks
Step 6 Rerun the Cisco CNS Notification Engine setup script:
cnote-tme# bin/setup
SSNGHOME not set .... Setting it to "/opt/ssng"
SSNGHOME is /opt/ssng
DISPLAY not set ... setting it to cnote-tme:0.0
DISPLAY is cnote-tme:0.0
Activate the auto-sense new node feature? (yes/no)
Enter y to use the auto-sense new node feature
Enter n if you do not want to use auto-sense new node feature
y
Please specify the setup environment:
1) To install C-NOTE standalone, enter 1
2) To install C-NOTE to support CWM, enter 2
3) To install C-NOTE to support Solaris, enter 3
1
Once again standalone mode was chosen. Just because it is running on a Solaris machine does not mean you must choose option 3. Cisco CNS Notification Engine is running on Solaris, not supporting it.
Specify the transport protocol you are using:
1) To generate SNMPV1 traps, enter 1
2) To generate SNMPV2C traps, enter 2
3) To use Tibco/Rendezvous daemon, enter 3
4) To use CNS daemon, enter 4
4
Choose option 4 to specify Cisco CNS as the transport technology.
Specify the type of CNS Daemon
1) CNS daemon, enter 1
2) CNS routing daemon, enter 2
3) Do not need to start, enter 3
1
RVD Daemon already running
root 430 1 0 May 21 ? 40:44 /opt/ssng/bin/rvd -listen 7500
Continue to launch other related processes...(yes/no) y
***Starting ssngBurstLog ***
cannot bind port 514
***Starting Filter ***
***Starting ssngPing ***
Stopping syslogd
Starting ssngBurstLog
The following message is left in the test in order to illustrate what was discussed in the "Installing the Cisco CNS Notification Engine" section. Namely, that an error message is displayed if you are installing the Cisco CNS Notification Engine remotely and not using an Xwindows emulator. As can be seen from the error message, there is a problem with the display. This is a non fatal error and can be ignored.
You can view the SSNG NODE ADMINISTRATION window, shown in Figure 4-3, if you desire.
Application initialization failed: couldn't connect to display "cnote-tme:0.0"
Error in startup script: invalid command name "wm"
while executing
"wm title . "SSNG NODE ADMINISTRATION""
(procedure "_main_proc" line 8)
invoked from within
"_main_proc"
(file "/opt/ssng/bin/node.tk" line 382)
Basic setup for C-NOTE 2.0 is finished.
One can add the following to crontab by:
crontab -e
In vi user insert mode at end of the file (Gi) the following and save to file (ZZ)
0 * * * * /opt/ssng/bin/ssng_health -b
cnote-tme# Starting syslogd
Step 7 Because you already entered the SSNG health check in the crontab file, the last message is a repeat. If, however, you did not modify the crontab command, it is wise to do so now.
Step 8 Check for the ssng processes again:
cnote-tme# ps -ef | grep ssng
root 12631 10385 0 13:41:04 pts/2 0:00 /opt/ssng/bin/perl /opt/ssng/bin/ ssngWatchDog -rvd_exist
start
root 430 1 0 May 21 ? 40:44 /opt/ssng/bin/rvd -listen 7500
root 10416 1 1 13:40:23 pts/2 0:01 /opt/ssng/bin/perl /opt/ssng/bin/ssngPing
root 10411 1 0 13:40:21 pts/2 0:00 /opt/ssng/bin/perl /opt/ssng/bin/solFilter
root 10461 1 0 13:40:25 pts/2 0:00 /opt/ssng/bin/ssngBurstLog
root 10402 1 1 13:40:20 pts/2 0:02 /opt/ssng/bin/perl /opt/ssng/bin/ssngFilter -cns=tib
root 10385 1 4 13:40:18 pts/2 0:02 /opt/ssng/bin/perl /opt/ssng/bin/ssngWatchDog -rvd_exist
start
Refer to the "Starting the Cisco CNS Notification Engine Application" section for instructions on how to start the Cisco CNS Notification Engine application.
Installing the Cisco CNS probe on the Cisco CNS Notification Engine machine is very much like installing Cisco Info Center itself. A Cisco CNS probe that handles the transport of the Cisco CNS Notification Engine traps is installed in this section.
The previous section detailed the installation of the Cisco CNS Notification Engine application.
The Info Mediator is installed in a manner similar to the installation of the Cisco Info Center application on the Cisco CNS Notification Engine machine. You need access to the same Cisco Info Center tar file that was used to install the Cisco Info Center application on its own machine. This can be accomplished by either untarring the Cisco Info Center image file on the Cisco CNS Notification Engine machine or by remotely mounting the Cisco Info Center tar file directory from the Cisco CNS Notification Engine machine. Remote mounting saves the space required for the Cisco Info Center image as you will have it loaded on only one machine.
It is assumed you have a sufficient degree of familiarity with UNIX and Solaris in order to accomplish this remote mount procedure. For help in configuring remote mounting, consult the application note at:
http://von.cisco.com/Netman/tempo/docs/remote-mounting.doc
Step 1 Mount the /opt/CIC34 /mnt directory:
cnote-tme# mount trapman:/opt/CIC34 /mnt
Step 2 Go to the home directory for Cisco Info Center through the remote mount:
cnote-tme# cd /mnt
Step 3 List the contents of the /mnt directory:
cnote-tme# ls
ISM OINSTALL build-rel-note cic341.EFT2.tar patches
platform unix
Step 4 Run the OINSTALL program:
cnote-tme# ./OINSTALL
Cisco Info Center Installation
Creating temporary directory /tmp/CICtemp and copying needed files.
Do you have a CIC distribution (i.e.: CDROM) (y/n)? [y] y
What directory is the distribution in? [/mnt]
Copying files from CIC distribution in /mnt...
This is the Cisco Info Center installation and upgrade utility. It will allow
you to complete a new CIC installation, add/delete components on an existing
CIC installation, or upgrade a CIC installation to the current release, 3.4.1.
Do you want to proceed (y or n) [default y] y
A log file will be created to be able to review what the installation does.
The log file is: /tmp/cic_install.log
Press <Return> to continue....
The following several lines appear when Cisco Info Center was previously installed. The following directions are for installing the probes to overwrite an existing installation. It is essentially the same as a new install except for the prompts that ask you to confirm that you want to overwrite the existing installation.
Your system has an existing CIC 3.4.1 installation.
Do you want to use the existing installation (y or n) [default y] n
You have chosen not to use the existing CIC installation. An initial installation will be performed instead. This will OVERWRITE the existing CIC installation!
Are you sure you want to do this (y or n) [default y] y
Your existing CIC installation will be overwritten.
Proceeding with an initial installation...
Do you want to change the OMNIHOME directory (/opt/Omnibus) (y or n)
[default n] n
Backing up the existing CIC installation.
The backup directory /opt/Omnibus3.4.1 already exists.
Do you want to overwrite it (y or n) [default y] y
Moving existing CIC to /opt/Omnibus3.4.1
Removing InfoCenter 3.4.1 packages...
Removal of <CICcom> was successful.
Removal of <CICmed> was successful.
Removal of <CICpad> was successful.
Removal of <CICutl> was successful.
Removed InfoCenter 3.4.1 packages.
Do you want to select components now (y or n) [default y] y
Cisco Information Center Install
Press any key to continue....
Select Mediators and Process Control
Mediators (+)
Policy_Manager ( )
Desktop ( )
Wave ( )
InfoServer ( )
Licensing ( )
Gateways ( )
Java_Event_List ( )
Process_Control (+)
It may have been necessary to adjust the selected components due to Cisco Info Center dependencies. Required components may have been added for Cisco Info Center to be properly configured. This next list shows what components are going to be installed. You are given the opportunity to modify this list.
Press <Return> to view and confirm the CIC components...
Step 5 Confirm this a few times.
Installing CIC packages for CIC 3.4.1
Installation of <CICcom> was successful.
Installation of <CICutl> was successful.
Installation of <CICpad> was successful.
Installation of <CICmed> was successful.
Installed CIC packages for CIC 3.4.1
You have installed Process Control on Solaris8.
Installing nco_pad Patch. Please wait...
Solaris8 nco_pad patch has been installed.
Do you wish to configure now (y or n) [default y] y
###################################################################
Cisco Info Center Configuration Menu
###################################################################
1. Configure Mediators
2. Help
3. Quit
Select one of the above options: 1
You have selected the following:
Configure Mediators
Do you want to continue (y/n)?: [y] y
Step 6 You must first configure the Process Control Agent. The following text guides you through this procedure.
*** Name for the Process Agent must be alphanumeric beginning with ***
*** a letter, must NOT exceed 11 characters and must end with _PA ***
Step 7 This is the point where you refer to the process control name (and port number) that was used when installing Cisco CNS Notification Engine. The following process control number and port must match the ones you specified previously.
Name for the Process Agent [MED1_PA]: MED2_PA
Enter the Port Number for Process Agent [4200]: 4200
You must now define the location of the CIC InfoServer
*** Name for the Info Server must be alphanumeric beginning ***
*** with a letter and up to 11 characters long ***
Name for the Info Server [INFOSERVER]:
Hostname of the Machine running the Info Server: trapman
Trying to ping Host trapman... OK
Enter the InfoServer Port Number [4100]:
InfoServer comms could not be verified
InfoServer (hostname): trapman
InfoServer (port number): 4100
InfoServer (server name}: INFOSERVER
Are you sure the above information is correct? (y/n)? [y]: y
Adding its entry to omni.dat.... done
Press <Return> when ready...
Step 8 Cisco Info Center now installs a startup script to allow you to start and stop the Cisco Info Center. You have the option of having the Cisco Info Center application start up automatically or not. If you chose not to configure automatic start up, you must start and stop Cisco Info Center manually with the /etc/init.d/nco {start | stop} command.
Do you wish to configure automatic startup upon system boot? (y/n)? [y] y
Automatic Startup Scripts installed
Step 9 The next few steps configure the device and method of transport. Choose option 8 for Cisco CNS Notification Engine (SSNG) over Cisco CNS.
************************************
Device configuration menu
************************************
1. MWFM
2. CW2K (include DFM and VHM)
3. CTM
4. CWM
5. CEMF
6. NNM
7. SSNG using SNMP
8. SSNG using CNS
9. Syslog
10. SNMP Generic Traps
11. PE using CNS
1-11. Toggle Component
S. Select All Components
U. Unselect All
I. Setup and Install Components
H. Help
Q. Quit
Option: 8
************************************
Device configuration menu
************************************
1. MWFM
2. CW2K (include DFM and VHM)
3. CTM
4. CWM
5. CEMF
6. NNM
7. SSNG using SNMP
8. SSNG using CNS SELECTED
9. Syslog
10. SNMP Generic Traps
11. PE using CNS
1-11. Toggle Component
S. Select All Components
U. Unselect All
I. Setup and Install Components
H. Help
Q. Quit
Option: i
*** Configuring CNS Mediator ***
Step 10 The following steps require you to know the path to the Cisco CNS Rendezvous daemon and the subjects of the Cisco CNS Notification Engine (Syslog to SNMP Notification Generator) modifier. If you are not sure where it is, use the UNIX find command:
cnote-tme# find / -name tibrv -print
/opt/ssng/include/tibrv
On this machine, you can see the tibrv directory (containing the Cisco CNS Rendezvous daemon) was installed.
*** Configuring CNS Mediator ***
Enter the path for the Tib/rendezvous daemon [e.g. /opt/ssng/bin or /opt/PE/tools/tibrv/bin or /usr/tibco/tibrv/bin]: /opt/ssng/include/tibrv
Step 11 The Notifier subjects must be entered.
Enter the subject, SSNG notifier is configured for [e.g. cisco.mgmt.ssng]: cisco.mgmt.ssng
..............................................................................................................................
Info Mediator CNS Configured
Press <Return> when ready...
Creating the ncoadmin group for CIC...
The ncoadmin group already exists in the /etc/group file.
Creating the cicpa user for CIC...
The cicpa user already exists.
Press <Return> when ready...
CIC has been successfully configured
Step 12 The licensing component has not been installed on this host. A license server is needed to start any of the Cisco Info Center applications. If a license server is needed on this host, re-run the install script and include the licensing component. If a license server is not needed, ensure the NCO_ELMHOST environment variable is set with the name of the host where the license server is located (refer to the Cisco Info Center Installation and Configuration Guide document at the following URL: http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/rtrmgmt/info_ctr/3_4_1/install/index.htm).
Step 13 Refer to the "Starting the Cisco CNS Info Mediator on the Cisco CNS Notification Engine Host" for instructions on how to start the Cisco CNS Notification Engine Info Mediator.
Installing the Cisco CNS probe on the Cisco CNS Performance Engine machine is very much like installing Cisco Info Center itself. A Cisco CNS probe that handles the transport of the Cisco CNS Performance Engine TCAs is installed in this section.
A prerequisite to installing the Cisco CNS Performance Engine Info Mediator probe is a complete installation of the Cisco CNS Performance Engine application. The Cisco CNS Performance Engine application installation is described in "Performance Monitoring."
 |
Note If the Cisco CNS Performance Engine is not installed, refer to "Performance Monitoring" and complete the installation and startup of the Cisco CNS Performance Engine before continuing here. If installation of the Cisco CNS Performance Engine is not required, do not choose to enable the Cisco CNS Performance Engine probe during the Device Configuration Menu stage of the installation process. |
The Info Mediators are installed in a manner similar to the installation of the Cisco Info Center application on the Cisco CNS Performance Engine machine. You need access to the same Cisco Info Center tar file that was used to install the Cisco Info Center application on its own machine. This can be accomplished by either untarring the Cisco Info Center image file on the Cisco CNS Performance Engine machine or by remotely mounting the Cisco Info Center tar file directory from the Cisco CNS Performance Engine machine. Remote mounting saves the space required for the Cisco Info Center image as you will have it loaded on only one machine.
It is assumed you have a sufficient degree of familiarity with UNIX and Solaris in order to accomplish this remote mount procedure.
Step 1 Mount the /opt/CIC34 /mnt directory:
perf-tme# mount trapman:/opt/CIC34 /mnt
Step 2 Go to the home directory for Cisco Info Center through the remote mount:
perf-tme# cd /mnt
Step 3 List the contents of the /mnt directory:
perf-tme# ls
ISM OINSTALL build-rel-note cic341.EFT2.tar patches
platform unix
Step 4 Run the OINSTALL program:
perf-tme# ./OINSTALL
Cisco Info Center Installation
Creating temporary directory /tmp/CICtemp and copying needed files.
Do you have a CIC distribution (i.e.: CDROM) (y/n)? [y] y
What directory is the distribution in? [/mnt]
Copying files from CIC distribution in /mnt...
This is the Cisco Info Center installation and upgrade utility. It will allow
you to complete a new CIC installation, add/delete components on an existing
CIC installation, or upgrade a CIC installation to the current release, 3.4.1.
Do you want to proceed (y or n) [default y] y
A log file will be created to be able to review what the installation does.
The log file is: /tmp/cic_install.log
Press <Return> to continue....
The following several lines appear when Cisco Info Center was previously installed. The following directions are for installing the probes to overwrite an existing installation. It is essentially the same as a new install except for the prompts that ask you to confirm that you want to overwrite the existing installation.
Your system has an existing CIC 3.4.1 installation.
Do you want to use the existing installation (y or n) [default y] n
You have chosen not to use the existing CIC installation. An initial installation will be performed instead. This will OVERWRITE the existing CIC installation!
Are you sure you want to do this (y or n) [default y] y
Your existing CIC installation will be overwritten.
Proceeding with an initial installation...
Do you want to change the OMNIHOME directory (/opt/Omnibus) (y or n)
[default n] n
Backing up the existing CIC installation.
The backup directory /opt/Omnibus3.4.1 already exists.
Do you want to overwrite it (y or n) [default y] y
Moving existing CIC to /opt/Omnibus3.4.1
Removing InfoCenter 3.4.1 packages...
Removal of <CICcom> was successful.
Removal of <CICmed> was successful.
Removal of <CICpad> was successful.
Removal of <CICutl> was successful.
Removed InfoCenter 3.4.1 packages.
Do you want to select components now (y or n) [default y] y
Cisco Information Center Install
Press any key to continue....
Select Mediators and Process Control
Mediators (+)
Policy_Manager ( )
Desktop ( )
Wave ( )
InfoServer ( )
Licensing ( )
Gateways ( )
Java_Event_List ( )
Process_Control (+)
It may have been necessary to adjust the selected components due to Cisco Info Center dependencies. Required components may have been added for Cisco Info Center to be properly configured. This next list shows what components are going to be installed. You are given the opportunity to modify this list.
Press <Return> to view and confirm the CIC components...
Step 5 Confirm this a few times.
Installing CIC packages for CIC 3.4.1
Installation of <CICcom> was successful.
Installation of <CICutl> was successful.
Installation of <CICpad> was successful.
Installation of <CICmed> was successful.
Installed CIC packages for CIC 3.4.1
You have installed Process Control on Solaris8.
Installing nco_pad Patch. Please wait...
Solaris8 nco_pad patch has been installed.
Do you wish to configure now (y or n) [default y] y
###################################################################
Cisco Info Center Configuration Menu
###################################################################
1. Configure Mediators
2. Help
3. Quit
Select one of the above options: 1
You have selected the following:
Configure Mediators
Do you want to continue (y/n)?: [y] y
Step 6 You must first configure the Process Control Agent. The following text guides you through this procedure.
*** Name for the Process Agent must be alphanumeric beginning with ***
*** a letter, must NOT exceed 11 characters and must end with _PA ***
Step 7 This is the point where you refer to the process control name (and port number) that was used when installing Cisco CNS Performance Engine. The following process control number and port must match the ones you specified previously in the Cisco Info Center installation procedure.
Name for the Process Agent [MED1_PA]: MED3_PA
Enter the Port Number for Process Agent [4200]: 4200
You must now define the location of the CIC InfoServer
*** Name for the Info Server must be alphanumeric beginning ***
*** with a letter and up to 11 characters long ***
Name for the Info Server [INFOSERVER]:
Hostname of the Machine running the Info Server: trapman
Trying to ping Host trapman... OK
Enter the InfoServer Port Number [4100]:
InfoServer comms could not be verified
InfoServer (hostname): trapman
InfoServer (port number): 4100
InfoServer (server name}: INFOSERVER
Are you sure the above information is correct? (y/n)? [y]: y
Adding its entry to omni.dat.... done
Press <Return> when ready...
Step 8 Cisco Info Center now installs a startup script to allow you to start and stop the Cisco Info Center. You have the option of having the Cisco Info Center application start up automatically or not. If you chose not to configure automatic start up, you must start and stop Cisco Info Center manually with the /etc/init.d/nco {start | stop} command.
Do you wish to configure automatic startup upon system boot? (y/n)? [y] y
Automatic Startup Scripts installed
Step 9 The next few steps configure the device and method of transport. Choose option 11 for Cisco CNS Performance Engine over Cisco CNS.
************************************
Device configuration menu
************************************
1. MWFM
2. CW2K (include DFM and VHM)
3. CTM
4. CWM
5. CEMF
6. NNM
7. SSNG using SNMP
8. SSNG using CNS
9. Syslog
10. SNMP Generic Traps
11. PE using CNS
1-11. Toggle Component
S. Select All Components
U. Unselect All
I. Setup and Install Components
H. Help
Q. Quit
Option: 11
************************************
Device configuration menu
************************************
1. MWFM
2. CW2K (include DFM and VHM)
3. CTM
4. CWM
5. CEMF
6. NNM
7. SSNG using SNMP
8. SSNG using CNS
9. Syslog
10. SNMP Generic Traps
11. PE using CNS SELECTED
1-11. Toggle Component
S. Select All Components
U. Unselect All
I. Setup and Install Components
H. Help
Q. Quit
Option: i
*** Configuring CNS Mediator ***
Step 10 The following steps require you to know the path to the Cisco CNS Rendezvous daemon and the subjects of the Cisco CNS Notification Engine (Syslog to SNMP Notification Generator) modifier. If you are not sure where it is, use the UNIX find command:
cnote-tme# find / -name tibrv -print
/opt/ssng/include/tibrv
On this machine, you can see the tibrv directory (containing the Cisco CNS Rendezvous daemon) was installed.
*** Configuring CNS Mediator ***
Enter the path for the CNS/rendezvous daemon [e.g. /opt/ssng/bin or /opt/PE/tools/tibrv/bin or /usr/CNS/tibrv/bin]: /opt/CSCOdas/tools/tibrv/bin
Step 11 The Notifier subjects must be entered.
Enter the subject, SSNG notifier is configured for [e.g. cisco.mgmt.ssng]: cisco.mgmt.ssng
..............................................................................................................................
Info Mediator CNS Configured
Press <Return> when ready...
Creating the ncoadmin group for CIC...
The ncoadmin group already exists in the /etc/group file.
Creating the cicpa user for CIC...
The cicpa user already exists.
Press <Return> when ready...
CIC has been successfully configured
Step 12 The licensing component has not been installed on this host. A license server is needed to start any of the Cisco Info Center applications. If a license server is needed on this host, re-run the install script and include the licensing component. If a license server is not needed, ensure the NCO_ELMHOST environment variable is set with the name of the host where the license server is located (refer to the Cisco Info Center Installation and Configuration Guide document at the following URL: http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/rtrmgmt/info_ctr/3_4_1/install/index.htm).
Step 13 Refer to the "Starting the Cisco CNS Performance Engine Application" for instructions on how to start the Cisco CNS Performance Engine Info Mediator.
The Cisco Media Gateway Controller Node Manager (CMNM) application is installed as an Element Management System (EMS) for the PGW2200 component. CMNM provides fault monitoring as a component application in a suite of EMS functionality. CMNM is fully described in "Provisioning." If you have not already installed CMNM to monitor the SS7 complex components in your network, you must do that first, then return here for complete installation instructions on installing the CEMF Info Mediator on the CMNM machine.
This section describes the elements that facilitate communication of fault information generated in the SS7 complex to the Cisco Info Center application. Faults can be monitored on the CMNM GUI which provides fault information and the traps generated by the PGW2200 and Signaling Link Termination (SLT) components. In order for those traps and fault event messages to be communicated to the Cisco Info Center application, you must configure CEMF and the CEMF probe on the CMNM machine. The CEMF Info Mediator probe on the CEMF machine does not have additional hardware requirements above those of CMNM and CEMF.
A prerequisite for installing the CEMF Probe is that CEMF and CMNM are already installed, as detailed in "Provisioning."
Step 1 Login as root.
Step 2 List the current directory contents:
cmnm-tme# ls
Backup ECSntp SUNWdtpcv cemf lost+found perl
CSCOvsp16 ECSossh SUNWits cmnm nsite transact.log
cmnm-tme# /etc/init.d/nco stop
cmnm-tme# /opt/cemf/bin/cemf stop
cmnm-tme# ps -ef | grep nco
cmnm-tme# mount cic-tme:/opt/CIC34 /mnt
cmnm-tme# cd /mnt
cmnm-tme# ls
ISM OINSTALL build-rel-note cic341.EFT2.tar patches platform unix
Step 5 Run the OINSTALL program:
cmnm-tme# ./OINSTALL
Cisco Info Center Installation
Creating temporary directory /tmp/CICtemp and copying needed files.
Do you have a CIC distribution (i.e.: CDROM) (y/n)? [y] y
What directory is the distribution in? [/mnt]
Copying files from CIC distribution in /mnt...
This is the Cisco Info Center installation and upgrade utility. It will allow you to complete a new CIC installation, add/delete components on an existing CIC installation, or upgrade a CIC installation to the current release, 3.4.1.
Do you want to proceed (y or n) [default y] y
A log file will be created to be able to review what the installation does.
The log file is: /tmp/cic_install.log
Press <Return> to continue....
Your system has an existing CIC 3.0 installation.
Do you want to use the existing installation (y or n) [default y] n
You have chosen not to use the existing CIC installation. An initial
installation will be performed instead. This will OVERWRITE the existing
CIC installation!
Are you sure you want to do this (y or n) [default y] y
Your existing CIC installation will be overwritten.
Proceeding with an initial installation...
Backing up the existing CIC installation.
Moving existing CIC to /opt/Omnibus3.0
Removing InfoCenter 3.0 packages...
Removal of <CICcom> was successful.
Removal of <CICdsk> was successful.
Removal of <CICmed> was successful.
Removal of <CICpad> was successful.
Removal of <CICutl> was successful.
Removed InfoCenter 3.0 packages.
Do you want to change the OMNIHOME directory (/opt/Omnibus) (y or n)
[default n] n
Do you want to select components now (y or n) [default y] y
Step 6 Select the Mediators and Process Control options. This is the same process used to install the Cisco CNS probes on the Cisco CNS Notification Engine and Cisco CNS Performance Engine machines.
Mediators (+)
Policy_Manager ( )
Desktop ( )
Wave ( )
InfoServer ( )
Licensing ( )
Gateways ( )
Java_Event_Lis ( )
Process_Control (+)
Checking package dependencies and requirements...
Step 7 It may have been necessary to adjust the selected components due to Cisco Info Center dependencies. Required components may have been added for Cisco Info Center to be properly configured. This next list shows what components are going to be installed. You are given the opportunity to modify this list.
Press <Return> to view and confirm the CIC components...
Step 8 After confirming this several times:
Installing CIC packages for CIC 3.4.1
Installation of <CICcom> was successful.
Installation of <CICutl> was successful.
Installation of <CICpad> was successful.
Installation of <CICmed> was successful.
Installed CIC packages for CIC 3.4.1
You have installed Process Control on Solaris8.
Installing nco_pad Patch. Please wait...
Solaris8 nco_pad patch has been installed.
Do you wish to configure now (y or n) [default y] y
###################################################################
Cisco Info Center Configuration Menu
###################################################################
1. Configure Mediators
2. Help
3. Quit
Select one of the above options: 1
You have selected the following:
Configure Mediators
Do you want to continue (y/n)?: [y] y
Step 9 You must first configure the Process Control Agent.
*** Name for the Process Agent must be alphanumeric beginning with ***
*** a letter, must NOT exceed 11 characters and must end with _PA ***
Name for the Process Agent [MED1_PA]: MED1_PA
Enter the Port Number for Process Agent [4200]: 4200
You must now define the location of the CIC InfoServer
*** Name for the Info Server must be alphanumeric beginning ***
*** with a letter and up to 11 characters long ***
Name for the Info Server [INFOSERVER]:
Hostname of the Machine running the Info Server [cic-tme]: cic-tme
Trying to ping Host cic-tme... OK
Enter the InfoServer Port Number [4100]:
InfoServer comms could not be verified
InfoServer (hostname): cic-tme
InfoServer (port number): 4100
InfoServer (server name}: INFOSERVER
Are you sure the above information is correct? (y/n)? [y]: y
Adding its entry to omni.dat.... done
Press <Return> when ready...
Step 10 Cisco Info Center now installs a startup script to allow for the starting and stopping of Cisco Info Center. You have the option of having Cisco Info Center start up automatically or not. If you choose not to configure automatic start up, you must start and stop Cisco Info Center manually with the
/etc/init.d/nco {start | stop} command.
Press <Return> when ready...
Do you wish to configure automatic startup upon system boot? (y/n)? [y] y
Automatic Startup Scripts installed
Device configuration menu
1. MWFM
2. CW2K (include DFM and VHM)
3. CTM
4. CWM
5. CEMF
6. NNM
7. C-NOTE using SNMP
8. C-NOTE using CNS
9. Syslog
10. SNMP Generic Traps
11. Global Long Distance (TV)
12. PE using CNS
1-12. Toggle Component
S. Select All Components
U. Unselect All
I. Setup and Install Components
H. Help
Q. Quit
Option: 5
1. MWFM
2. CW2K (include DFM and VHM)
3. CTM
4. CWM
5. CEMF SELECTED
6. NNM
7. C-NOTE using SNMP
8. C-NOTE using CNS
9. Syslog
10. SNMP Generic Traps
11. Global Long Distance (TV)
12. PE using CNS
1-12. Toggle Component
S. Select All Components
U. Unselect All
I. Setup and Install Components
H. Help
Q. Quit
Option: I
*** Configuring cemf Mediator ***
Where is cemf installed? Default: [/opt/cemf]
Info Mediator cemf Configured
Press <Return> when ready...
Creating the ncoadmin group for CIC...
The ncoadmin group already exists in the /etc/group file.
Creating the cicpa user for CIC...
New password:<password>
Re-enter new password:<password>
passwd (SYSTEM): passwd successfully changed for cicpa
Successfully created the cicpa user.
Press <Return> when ready...
CIC has been successfully configured
CIC 3.4.1 has been installed.
Step 11 The licensing component has not been installed on this host. A license server is needed to start any of the Cisco Info Center applications. If a license server is needed on this host, re-run the installation script and include the licensing component. If a license server is not needed, ensure that the NCO_ELMHOST environment variable is set with the name of the host where the license server is located (refer to the Cisco Info Center Installation and Configuration Guide document at the following URL: http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/rtrmgmt/info_ctr/3_4_1/install/index.htm)
Step 12 The licensing component has not been installed on this host. A license server is needed to start any of the Cisco Info Center applications. If a license server is needed on this host, re-run the install script and include the licensing component. If a license server is not needed, ensure the NCO_ELMHOST environment variable is set with the name of the host where the license server is located (refer to the Cisco Info Center Installation and Configuration Guide document at the following URL: http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/rtrmgmt/info_ctr/3_4_1/install/index.htm).
Step 13 Refer to the "Starting the Cisco Element Management Framework" for instructions on how to start the CEMF Info Mediator.
Step 1 Cisco Info Center was started at the end of the installation directions in the "Cisco Info Center Installation Script" section. If you did not do that, start Cisco Info Center now, as root, on the Cisco Info Center machine. Refer to the "Cisco Info Center Installation Script" section for the expected feedback from this install script.
trapman# /etc/init.d/nco start
Step 2 Check the processes to insure the Cisco Info Center application started:
trapman# ps -ef | grep nco_
root 16890 16889 0 13:13:34 ? 0:07 /opt/Omnibus/bin/solaris2/nco_objserv -name
INFOSERVER -pa NCO_PA -paaware 10 -
root 16949 16922 0 13:13:46 pts/4 0:04 /opt/Omnibus/bin/solaris2/nco_event_2.6 -display
171.71.150.203:0.0 -server INF
root 16904 16889 0 13:13:35 ? 0:02 /opt/Omnibus/probes/solaris2/nco_p_mttrapd
root 16922 21984 0 13:13:40 pts/4 0:02 /opt/Omnibus/bin/solaris2/nco_2.6
root 16889 1 0 13:13:34 ? 0:18 /opt/Omnibus/bin/solaris2/nco_pad_2.6 -name NCO_PA
Step 1 As root, start the Cisco CNS Notification Engine (Syslog Collector) on the Cisco CNS Notification Engine machine:
cnote-tme# /opt/ssng/bin/ssng start
Enter the choice (1-4):
1) v1
2) v2c
3) SSNG with CWM (use v1)
4) SSNG with CIC (use v1)
5) SSNG with OpenView (use v1)
6) SSNG with Tibco/Rendezvous daemon
6
Specify the type of Tibco/Rendezvous Daemon:
1) Tibco/Rendezvous daemon (rvd), enter 1
2) Tibco/Rendezvous routing daemon (rvrd), enter 2
3) Do not need to start, enter 3
1
Continue to launch other related processes...(yes/no) y
Enter y as opposed to yes.
cnote-tme# syslog service starting
***Re Starting Filter ***
cnote-tme#
Step 2 Check to see if the Cisco CNS Notification Engine application is running (search for ssng, not c-note):
cnote-tme # ps -ef | grep ssng
root 27189 1 0 18:16:22 pts/4 0:01 /opt/ssng/bin/perl /opt/ssng/bin/ssngFilter -cns=tib
root 2222 27167 0 18:17:46 pts/4 0:00 sh -c /usr/bin/ps -ef | grep -v grep | grep ssngFilter
root 27167 1 4 18:16:21 pts/4 0:04 /opt/ssng/bin/perl /opt/ssng/bin/ssngWatchDog -none start
Step 1 If you haven't started the Cisco CNS Performance Engine as part of the installation procedures described in "Performance Monitoring," navigate to the $PE HOME/bin directory on the Cisco CNS Performance Engine machine and run the executable start.sh:
cnote-tme # cd /opt/das/CSCOdas/bin
cnote-tme # ls
backup.sh env.sh restore.sh start.sh stop.sh sysProperties_sparc
cnote-tme # ./start.sh
start.sh: Thu Mar 28 16:44:44 PST 2002
start.sh: Guessing DAS_HOME from start.sh to /opt/das/CSCOdas
Step 2 Check to see if any Cisco CNS Performance Engine processes are running:
cnote-tme # ps -ef | grep das
root 1148 1 0 16:44:46 pts/2 0:02 /opt/das/CSCOdas/tools/java1.3.1/bin/../bin/sparc/native_threads/java -Dtomcat.
cnote-tme # ps -ef | grep DAS
root 1182 1 0 16:44:47 pts/2 0:01 dbeng7 -n DASDBServer -ti 0 -m -ch 50P DASmain.db -hn 7
Step 1 If you have not already, during the installation of CEMF and CMNM, start CEMF and then CMNM:
cmnm-tme# /opt/cemf/bin/cemf start
ATL license manager daemon already running.
Copyright 2000 Cisco Systems, Inc.
Copyright 1996 - 2000 Atlantech Technologies, Ltd.
CEMF Manager uses software technology from the following organizations,
Copyright respectfully acknowledged:
ObjectStore 5.1p2, Copyright (C) 1989-1999 by Object Design, Inc.
FLEXlm 6.0g, Copyright (C) 1988-1998 by Globetrotter Software, Inc.
SNMP v15.2.1.7 patch Copyright (C) 1989-2000 by SNMP Research, Incorporated.
ILOG Views 3.0.2, Copyright (C) 1990-1998 by ILOG.
ILOG TGO 1.0.3, Copyright (C) 1997-1998 by ILOG.
Starting CEMF Manager system.
CEMF Manager startup complete.
Step 1 Start the CMNM application:
cmnm-tme# cd /opt/cemf/bin
cmnm-tme#./cemf session
Starting CEMF Manager Applications.
ILOG Views 3.0.2
ILOG TGO 1.0.3
ObjectStore Release 5.1 SP4
 |
Note This is an Xwindows session so it must be started from a UNIX machine or through an Xwindows or VNC application. |
Cisco Info Center Info Mediators require a license in order to operate. The license server that verifies the Cisco Info Center application can be used to verify the Info Mediators as well. You can install a license server on the Cisco CNS Notification Engine host (which would require a new set of license keys that correspond to that machine) or set the NCO_ELMHOST environment variable that points to the license server on the Cisco Info Center host (the preferred method). The Cisco Info Center host is used as the license host by setting the license host environment variable. All Info Mediators must be started on their respective machines (that is, the CEMF probe, the Cisco CNS Performance Engine probe, and the Cisco CNS Notification Engine probe).
This section details the starting of the Cisco CNS Notification Engine probe on the Cisco CNS Notification Engine machine. The process is identical on the other host machines as well.
The Info Mediator for the Cisco CNS Notification Engine application starts when the nco process is started.
Step 1 To set the license host environment variable, configure the following on the Cisco CNS Notification Engine host:
cnote-tme# setenv NCO_ELMHOST @trapman.cisco.com
where trapman.cisco.com is the actual Cisco Info Center host.
Step 2 Start the Cisco Info Center Info Mediator on the Cisco CNS Notification Engine machine. It has a link to a startup script the same as Cisco Info Center:
cnote-tme# /etc/init.d/nco start
Checking CIC Process Control Agent
Starting CIC Process Control Agent...
Cisco Info Center Process Agent Daemon - Version 3.4.1
Cisco Info Center PA API Library Version 1.56
Sybase Server-Library Release: 11.1.1
Server Settings:
Name of server : MED2_PA
Path of used log file : /opt/Omnibus/log/MED2_PA.log
Configuration File : /opt/Omnibus/etc/nco_pa.conf
Child Output File : /dev/null
Maximum logfile size : 1024
Thread stack size : 69632
Message Pool size : 45568
PID Message Pool size : 50
Rogue Process Timeout : 30
Truncate Log : False
Instantiate server to daemon : True
Internal API Checking : False
No Configuration File : False
Start Auto-start services : True
Authentication System : UNIX
Trace Net library : False
Trace message queues : False
Trace event queues : False
Trace TDS packets : False
Trace mutex locks : False
Forking to a Daemon Process.............
Step 3 Check to see if the processes started:
cnote-tme # ps -ef | grep nco
root 6555 1 0 16:34:59 ? 0:00 /opt/Omnibus/bin/solaris2/nco_pad_2.6 -name MED2_PA
root 6558 6555 0 16:34:59 ? 0:01 /opt/Omnibus/probes/solaris2/nco_p_CNS
Step 4 On the Cisco Info Center Server machine, look for the following line in the /opt/Omnibus/log/elmd.log file:
02-Mar-21 16:37:58: root@cnote-tme [8], ProbeBandA (3211): LID 4 issued, 1 in use.
Cisco Info Center Info Mediators require a license in order to operate. The license server that verifies the Cisco Info Center application can be used to verify the Info Mediators as well. You can install a license server on the Cisco CNS Performance Engine host (which would require a new set of license keys that correspond to that machine) or set the NCO_ELMHOST environment variable that points to the license server on the Cisco Info Center host (the preferred method). The Cisco Info Center host is used as the license host by setting the license host environment variable. All Info Mediators must be started on their respective machines (that is, the CEMF probe, the Cisco CNS Performance Engine probe, and the Cisco CNS Notification Engine probe).
This section details the starting of the Cisco CNS Performance Engine probe on the Cisco CNS Performance Engine machine. The process is identical on the other host machines as well.
The Info Mediator for the Cisco CNS Performance Engine application starts when the nco process is started.
Step 1 To set the license host environment variable, configure the following on the Cisco CNS Performance Engine host:
perf-tme# setenv NCO_ELMHOST @trapman.cisco.com
where trapman.cisco.com is the actual Cisco Info Center host.
Step 2 Start the Cisco Info Center Info Mediator on the Cisco CNS Performance Engine machine. It has a link to a startup script the same as Cisco Info Center:
perf-tme# /etc/init.d/nco start
Checking CIC Process Control Agent
Starting CIC Process Control Agent...
Cisco Info Center Process Agent Daemon - Version 3.4.1
Cisco Info Center PA API Library Version 1.56
Sybase Server-Library Release: 11.1.1
Server Settings:
Name of server : MED3_PA
Path of used log file : /opt/Omnibus/log/MED3_PA.log
Configuration File : /opt/Omnibus/etc/nco_pa.conf
Child Output File : /dev/null
Maximum logfile size : 1024
Thread stack size : 69632
Message Pool size : 45568
PID Message Pool size : 50
Rogue Process Timeout : 30
Truncate Log : False
Instantiate server to daemon : True
Internal API Checking : False
No Configuration File : False
Start Auto-start services : True
Authentication System : UNIX
Trace Net library : False
Trace message queues : False
Trace event queues : False
Trace TDS packets : False
Trace mutex locks : False
Forking to a Daemon Process.............
Step 3 Check to see if the processes started:
cnote-tme # ps -ef | grep nco
root 6555 1 0 16:34:59 ? 0:00 /opt/Omnibus/bin/solaris2/nco_pad_2.6 -name MED3_PA
root 6558 6555 0 16:34:59 ? 0:01 /opt/Omnibus/probes/solaris2/nco_p_CNS
Step 4 On the Cisco Info Center Server machine, look for the following line in the /opt/Omnibus/log/elmd.log file:
02-Mar-21 16:37:58: root@perf-tme [6], ProbeBandA (3211): LID 5 issued, 2 in use.
Step 1 Login as root, then set the environment variable for the licensing host. The licensing host for this installation is on the cic-tme machine.
cmnm-tme# setenv NCO_ELMHOST @cic-tme
cmnm-tme# echo $NCO_ELMHOST
@cic-tme
Step 2 Start the probe:
cmnm-tme# /etc/init.d/nco start
Checking CIC Process Control Agent
Starting CIC Process Control Agent...
Cisco Info Center Process Agent Daemon - Version 3.4.1
Cisco Info Center PA API Library Version 1.56
Sybase Server-Library Release: 11.1.1
Server Settings:
Name of server : MED1_PA
Path of used log file : /opt/Omnibus/log/MED1_PA.log
Configuration File : /opt/Omnibus/etc/nco_pa.conf
Child Output File : /dev/null
Maximum logfile size : 1024
Thread stack size : 69632
Message Pool size : 45568
PID Message Pool size : 50
Rogue Process Timeout : 30
Truncate Log : False
Instantiate server to daemon : True
Internal API Checking : False
No Configuration File : False
Start Auto-start services : True
Authentication System : UNIX
Trace Net library : False
Trace message queues : False
Trace event queues : False
Trace TDS packets : False
Trace mutex locks : False
Forking to a Daemon Process.............
(hit ENTER)
Step 3 Check the health of the system:
cmnm-tme# ps -ef | grep nco
root 6555 1 0 16:34:59 ? 0:00 /opt/Omnibus/bin/solaris2/nco_pad_2.6 -name MED1_PA
root 6558 6555 0 16:34:59 ? 0:01 /opt/Omnibus/probes/solaris2/nco_p_CNS
Step 4 On the Cisco Info Center Server machine, look for the following line in the /opt/Omnibus/log/elmd.log file:
02-Mar-21 16:37:58: root@cic-tme [6], ProbeBandA (3211): LID 6 issued, 3 in use.
This completes the installation, initial configuration, and startup of the Cisco CNS Notification Engine application (the Syslog Event Collector), Cisco CNS Performance Engine (the TCA and system health notifier), CEMF and CMNM (the FCAPS monitoring tool for the SS7 interconnect node (SC2200, SLT, and accompanying gateways)), the Cisco Info Center application (the network SNMP Trap Monitor and upstream NMS Collector for all of the above applications), and all of their associated Info Mediator probes that facilitate communication between the network elements and collectors and the Cisco Info Center application.
Checking the processes running on the various machines is the first step in confirming proper operation. This has been done step by step at the end of the installation procedures for each application. It is done again here, both to keep the directions in one place and to check that nothing has stopped in the interim.
Step 1 On the Cisco Info Center machine:
trapman# ps -ef | grep nco
root 6834 1 3 12:42:58 ? 5:38 /opt/Omnibus/bin/solaris2/nco_pad_2.6 -name NCO_PA
root 6835 6834 1 12:42:58 ? 1:53 /opt/Omnibus/bin/solaris2/nco_objserv -name INFOSERVER -pa NCO_PA - paaware 10 -
root 4770 4635 0 14:33:26 pts/6 0:07 /opt/Omnibus/bin/solaris2/nco_event_2.6 -display 171.71.66.135:0.0 -server INFO
root 6849 6834 0 12:42:59 ? 0:03 /opt/Omnibus/probes/solaris2/nco_p_mttrapd
root 4635 4610 0 14:32:56 pts/6 0:01 /opt/Omnibus/bin/solaris2/nco_2.6
The first search is for ssng (the old name), not Cisco CNS Notification Engine. On the Cisco CNS Notification Engine machine, search for the three strings having to do with the Cisco CNS Notification Engine and its associated probe. Then we search for DAS and das on the same machine to check for Cisco CNS Performance Engine processes. The Cisco CNS probe that serves the Cisco CNS Notification Engine is the same one that serves the Cisco CNS Performance Engine.
Step 2 Search for the Cisco CNS Notification Engine process on the Cisco CNS Notification Engine machine:
cnote-tme # ps -ef | grep ssng
root 21848 1 4 Apr 01 ? 551:44 /opt/ssng/bin/perl /opt/ssng/bin/ssngWatchDog -none start
root 13595 21848 0 16:18:21 ? 0:00 sh -c /usr/bin/ps -ef | grep -v grep | grep ssngFilter
root 13599 12710 0 16:18:21 pts/2 0:00 grep ssng
root 21870 1 0 Apr 01 ? 0:48 /opt/ssng/bin/perl /opt/ssng/bin/ssngFilter -cns=tib
root 13596 13595 0 16:18:21 ? 0:00 sh -c /usr/bin/ps -ef | grep -v grep | grep ssngFilter
Step 3 Search for the Syslog process:
cnote-tme # ps -ef | grep syslog
root 27002 1 0 16:29:32 ? 0:00 /usr/sbin/syslogd
On the Cisco CNS Performance Engine machine, search for the three strings having to do with the Cisco CNS Performance Engine and its associated probe: java, dbeng, and nco_.
Step 4 Search for the Cisco CNS Performance Engine process on the Cisco CNS Performance Engine machine:
perf-tme# ps -ef | grep java
root 29038 1 0 Jun 28 ? 55:42
/opt/CSCOdas/tools/java1.3.1/bin/../bin/sparc/native_threads/java -Dorg.omg.COR
root 390 1 0 Jun 12 ? 1:47
/opt/CSCOdas/tools/java1.3.1/bin/../bin/sparc/native_threads/java -Dtomcat.home
perf-tme# ps -ef | grep dbeng
root 29033 1 0 Jun 28 ? 14:53 dbeng7 -n DASDBServer -ti 0 -m -ch
50P DASmain.db -hn 7
perf-tme# ps -ef | grep nco_
root 25796 1 0 Jul 10 ? 0:00 /opt/Omnibus/bin/solaris2/nco_pad_2.6
-name MED4_PA
root 25801 25796 0 Jul 10 ? 0:36
/opt/Omnibus/probes/solaris2/nco_p_CNS
Step 5 Search for the CEMF processes:
cmnm-tme # ps -ef | grep cemf
root 266 1 0 Apr 01 ? 0:00 /opt/cemf/flexlm/lmgrd -c /opt/cemf/config/licenses
root 201 1 0 Apr 01 ? 6:42 /opt/cemf/ODI/OS5.1/ostore/lib/osserver
root 18582 18556 0 14:51:15 ? 0:00 /opt/cemf/tools/bin/perl -I/opt/cemf/tools/lib/perl5/5.00502/sun4-solaris:/opt/
root 270 266 0 Apr 01 ? 0:00 ATL -T magic 6.0 4 -c /opt/cemf/config/licenses -lmgrd_port 6978 -path /opt/cemf
root 323 1 0 Apr 01 ? 0:08 /opt/cemf/ODI/OS5.1/ostore/lib/oscmgr4 7
root 18594 18556 0 14:51:39 ? 0:11 /opt/cemf/snmp15.2.1.7/md5nodes/solaris_sun4.bin/brassagt -nosubagent -d
root 18604 18556 0 14:52:56 ? 0:00 /opt/cemf/Orbix/bin/orbixd -s
root 18655 18556 0 14:56:36 ? 0:01 /opt/cemf/bin/corbaMetadata
root 18664 18556 0 14:56:44 ? 0:01 /opt/cemf/bin/corbaActionLauncher
root 18653 18556 0 14:56:35 ? 0:01 /opt/cemf/bin/corbaGatewayManager
root 18666 18556 0 14:56:47 ? 0:01 /opt/cemf/bin/corbaParticipation
root 18657 18604 0 14:56:39 ? 0:05 /opt/cemf/Orbix/tools/jre/bin/../bin/sparc/green_threads/jre -classpath /opt/ce
root 18662 18556 0 14:56:42 ? 0:01 /opt/cemf/bin/corbaDataAbstractor
root 18668 18556 0 14:56:49 ? 0:01 /opt/cemf/bin/corbaObjectGroups
root 18670 18556 0 14:56:51 ? 0:22 /opt/cemf/bin/corbaEventChannelManager
root 18561 1 0 14:49:48 ? 0:00 /bin/ksh /opt/cemf/config/scripts/watchDog 18556
root 18673 18604 0 14:57:27 ? 0:02 /opt/cemf/bin/EventChannel_svr NOTIFYS -f
/opt/cemf/config/init/corbaNotificati
root 18556 1 0 14:49:48 ? 0:07 /opt/cemf/bin/sysmgr
root 22913 22908 0 19:29:12 pts/4 0:00 grep cemf
Step 6 Search for NCO processes:
cmnm-tme # ps -ef | grep nco
root 22915 22908 0 19:29:31 pts/4 0:00 grep nco
root 21217 1 0 17:42:32 ? 0:00 /opt/Omnibus/bin/solaris2/nco_pad_2.6 -name MED1_PA
Once all of the required applications are installed and started and the gateways configured, verification of operations can be done using the Cisco Info Center GUI. It is based on Xwindows, so you must use a UNIX terminal (or the console of the Cisco Info Center machine) or be using a PC based XWindows or VNC application. Starting Cisco Info Center is described in this section.
Step 1 As root user, from the console or in an XWindows or VNC session with the Cisco Info Center machine, type the following to start the Cisco Info Center GUI in the background:
cic-tme# nco &
[1] 4368
The Login window, shown in Figure 4-4, appears.
Step 2 Click OK. The default password is blank (no password required).
After the Cisco Info Center Welcome window, shown in Figure 4-5, appears, the Cisco Info Center Conductor window, shown in Figure 4-6, appears.
Step 3 You can change or configure the password by selecting the File -> Change Password menu option in the Conductor window, as shown in Figure 4-7.
Step 4 Click the Event List button in the Conductor window. The Event List window, shown in Figure 4-8, appears.
The Event List window, for the options that are installed, has Event Lists (pre-configured filters and views) for all events, Cisco CNS Notification Engine (ssng), Cisco CNS Performance Engine (DAS), SNMP traps (generic), as well as several Event Lists corresponding to potential CEMF-based EMS systems (CEMF:CMNM is the one you installed).
The All Events window presents a graphical display of all events received by Cisco Info Center. The other Event Lists are subsets of the All Events window and have filters that look for events associated with particular applications.
Step 5 Select the View -> All Events menu option in the Event List window.
The Cisco Info Center Event List - All Events window, shown in Figure 4-9 appears. You can check to see if events are being receiving by monitoring this window while creating an event in a downstream device.
Contained in the Cisco CNS Notification Engine application, when utilizing the Cisco CNS Integration bus technology, is a Listener process (cisco.mgmt.ssng)that can be monitored on the Cisco CNS Notification Engine machine to verify events that are sent north bound to Cisco Info Center. This Listener process is activated, in the background, on the Cisco CNS Notification Engine machine with the tibrvlisten command.
Step 1 Go to the /opt/ssng/bin directory on the Cisco CNS Notification Engine machine:
cnote-tme# cd /opt/ssng/bin
Step 2 List the contents of any tib directories:
cnote-tme # ls -l tib*
-r--r--r-- 1 root bin 254 Feb 7 20:48 tibrv.tkt
-r-xr-xr-x 1 root bin 369596 Feb 7 20:48 tibrvlisten
-r-xr-xr-x 1 root bin 369084 Feb 7 20:48 tibrvsend
-r--r--r-- 1 root bin 765 Feb 7 20:48 tibrvtkt.smp
Step 3 Activate the Listener process in the background:
cnote-tme # ./tibrvlisten cisco.mgmt.ssng &
[1] 2964
cnote-tme # tibrvlisten: Listening to subject cisco.mgmt.ssng
Some configuration lines are required in downstream devices to enable them to send SNMP traps and Syslog event messages to the Cisco CNS Notification Engine and the Cisco Info Center. Following is an example of the configuration required on an AS5400.
Step 1 For Syslog events to be sent to the Cisco CNS Notification Engine Collector, three logging configuration lines are of concern. As root, invoke the following command:
gwh-5400# wr t
Building configuration...
Current configuration: 9894 bytes
!
! Last configuration change at 17:22:14 PST Tue Apr 23 2002
! NVRAM config last updated at 17:20:57 PST Tue Apr 23 2002
!
?------------------output suppressed ------------------?
logging source-interface FastEthernet0/0
logging 172.19.49.10
logging trap information
?------------------output suppressed ------------------?
The logging source-interface line is optional on most platforms and can be used to configure a specific management interface, if so desired.
The logging <IP address> line is required and tells the device where to send the Syslog events.
The logging trap <severity level> line has eight degrees of severity from which to choose:
gwh-5400(config)# logging trap?
<0-7> Logging severity level
alerts Immediate action needed (severity=1)
critical Critical conditions (severity=2)
debugging Debugging messages (severity=7)
emergencies System is unusable (severity=0)
errors Error conditions (severity=3)
informational Informational messages (severity=6)
notifications Normal but significant conditions (severity=5)
warnings Warning conditions (severity=4)
<cr>
The default level is informational (severity 6) and does not show up in the configuration file. It sends all events other than debugging events. If traffic control is a cause of concern, manipulating the severity level of Syslog events can be significant.
Step 1 Assuming the configuration options detailed above and that the device is pointed to the Cisco CNS Notification Engine Collector, and that the Listener is being monitored, go to the device and, in Enable mode, do the following:
gwh-5400# terminal monitor
gwh-5400# conf t
Enter the configuration commands, one per line. End with Ctrl Z:
5400(config)# logging console
gwh-5400(config)# end
%SYS-5-CONFIG_I: Configured from console by vty0 (171.71.66.156)
gwh-5400#
The above routine generates a Syslog event (displayed at the console or terminal monitor of the device) that should be sent to the Cisco CNS Notification Engine Collector and then appears in the Cisco Info Center Console window. It should also be recorded in the Cisco CNS Rendezvous Listener and you should observe the following on the Cisco CNS Notification Engine Listener machine:
cnote-tme# [2002-04-24 09:58:24]: subject=cisco.mgmt.ssng, message={DATA="<lastSequenceNumber>149</lastSequenceNumber><NodeName>172.19.49.6</NodeName><RouterIpAddr>172.19.49.6</RouterIpAddr><TrapReason>0</TrapReason><TrapFacility>18</TrapFacility><TrapSeverity>5</TrapSeverity><TrapMnemonic>CONFIG_I</TrapMnemonic><TrapRepeatCount>1</TrapRepeatCount><TrapTimeStamp>Apr23</TrapTimeStamp><ParentDeviceName></ParentDeviceName><ParentDeviceIp></ParentDeviceIp><ParentDeviceSlotNo></ParentDeviceSlotNo><TrapNumber>26010</TrapNumber><ssngRouterConfigFrom>console</ssngRouterConfigFrom><ssngRouterConfigBy>vty0</ssngRouterConfigBy><ssngRouterConfigByIpAddr>171.71.150.105</ssngRouterConfigByI pAddr><ssngTrapMessage> Configured from console by vty0 (171.71.150.105)</ssngTrapMessage><ssngActionRequest>4198,1888</ssngActionRequest>"}
Step 2 You are now monitoring for faults from all devices that are pointed at the Cisco CNS Notification Engine Collector, as shown in Figure 4-10. To collect SNMP traps, further configuration is required in network elements. Collection of the PGW2200 complex faults should also be operational. It is beyond the scope of this chapter to detail all of the possibilities. Consult with a Cisco technical resource to obtain application technical notes that further detail IOS and non-IOS configuration requirements.

![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Posted: Thu Oct 17 03:02:32 PDT 2002
All contents are Copyright © 1992--2002 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Important Notices and Privacy Statement.