|
|

CiscoWorks Blue SNA View, together with CiscoWorks Blue Maps, provides the SNA control and correlation needed to manage SNA devices from a UNIX platform, allowing the network administrator to see beyond the routers and into the SNA resources.
By interacting with the mainframe, SNA View adds vital PU and LU information to the maps created by CiscoWorks Blue Maps. By correlating SNA resource names to router ports, the network administrator can more easily solve and identify problems in the network or in the SNA environment. Resource information is dynamically updated to provide a snapshot of the network as it appears at any given time. This allows the administrator to display a single map that depicts details from the host down to the PU name, providing information such as:
This chapter:
Table 1-1 lists and describes the features that are provided by CiscoWorks Blue SNA View (in addition to those provided by CiscoWorks Blue Maps).
| Feature | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Map Enhancements |
|
|
|
SNA Control |
|
|
The trend in network management is to reduce the need for separate disparate element managers by providing direct management of heterogeneous multivendor networks from a single network management system. In keeping with this strategy, CiscoWorks Blue SNA View uses information from VTAM, and MVS to enable network administrators to monitor and manage SNA resources. To further simplify and enhance network management, this information is provided to the network administrator through a logical map graphical interface, CiscoWorks Blue Maps.
CiscoWorks Blue SNA View requires the mapping capability of CiscoWorks Blue Maps. By adding onto the logical maps of the SNA-related protocols, SNA View augments the information that is already presented. MAC addresses are correlated with the corresponding SNA PU data and displayed on the specific protocol map. For large networks, a global map is displayed, and the user can easily navigate through the network using the graphical user interface (GUI).
Virtual Telecommunication Access Method (VTAM) SNA resource information is gathered from the mainframe, correlated and associated with the MAC address information, and displayed at the UNIX workstation. PU and LU status, as well as LU dependencies are listed in the pull-down menus of the CiscoWorks Blue Maps application. By bringing this information together, a clearer picture of the network is presented.
The network operator can then manage SNA devices (activate and deactivate PUs and LUs) and SNMP devices from a single console. And, by leveraging the consolidated protocol information with the vital SNA resource information, problem determination and isolation are accomplished more quickly.
The following components comprise CiscoWorks Blue SNA View:
The Host Connection Interface (HCI) is the primary server for the SNA View workstation application. The HCI establishes LU6.2 or TCP/IP communications with the SNA View mainframe application. The HCI also manages LU6.2 and TCP/IP mainframe communications for the SNA View secondary servers. All SNA data received by the HCI is routed to the appropriate server based on the message type (VTAM, MVS, etc.).
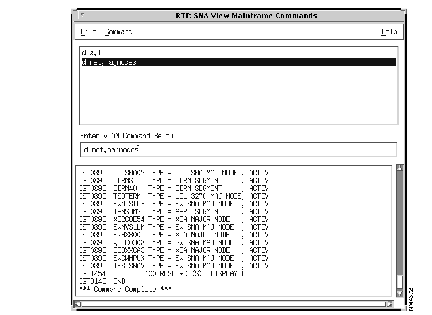
The Command Server sends commands to the mainframe and receives the responses. The Command Server opens and bonds a UDP socket or LU6.2 connection over which clients can register and issue commands to the mainframe. It also establishes connections with the Host Connection Interface over which it receives the mainframe command responses. Commands can be sent to VTAM, to the MVS operating system, and, if present, to NetView or SOLVE:Netmaster.
The user sends commands and views the responses using the Command Client window, as shown in Figure 1-1.
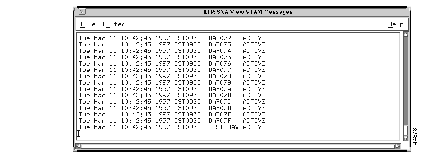
The VTAM Message Server allows clients to receive solicited and unsolicited VTAM messages from the mainframe as they are generated. The VTAM Message Server establishes a socket connection with the HCI and initializes a socket connection over which clients can register for services.
The messages received are displayed in the VTAM Message Client's window, as shown in Figure 1-2. From this window, you can also define filters to eliminate unwanted messages (Refer to "Filtering Mainframe Messages"). Messages can be saved in a VTAM Message Log file.
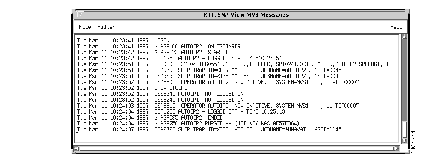
The MVS Message Server allows clients to receive solicited and unsolicited MVS messages from the mainframe as they are generated. The MVS Message Server establishes a socket connection with the HCI and initializes a socket connection over which clients can register for services.
The messages received are displayed in the MVS Message Client's window, as shown in Figure 1-3. From this window, you can also define filters to eliminate unwanted messages (Refer to "Filtering Mainframe Messages"). Messages can be saved in an MVS Message Log file.
The Status Manager keeps the CiscoWorks Blue Maps application up-to-date with the existence and status of resources. The Status Manager updates the CiscoWorks Blue Maps database when previously unknown resources are discovered. Also, when the status of an SNA PU or LU changes, the Status Manager receives a notification from the mainframe via the HCI, which, in turn, drives the state of the PU/LU objects managed within CiscoWorks Blue Maps.
The SNA PU Discovery discovers VTAM information about the SNA PUs and LUs.
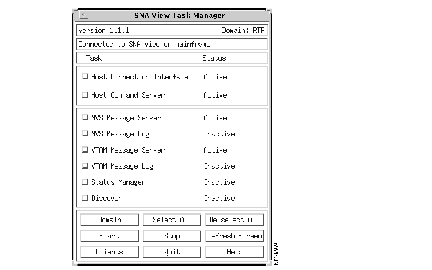
The Task Manager allows users to monitor and manage the SNA View workstation tasks for each managed SNA domain. Using the Task Manager, users can start and stop the:
The Task Manager also provides an interface for accessing the following SNA View client windows:
Figure 1-4 shows the SNA View Task Manager window.
CiscoWorks Blue includes a sophisticated online help system that allows users to access different levels of help information by selecting underlined text to open additional windows.
The online help system provides overviews, related information, procedures, and glossary information on the CiscoWorks Blue applications and features. It contains both keyword and full-text search capabilities to enable users to search for specific text within the online help.
For more information, refer to the CiscoWorks Blue online help menu located on the main maps window.
|
|