|
|

QPM includes a predefined database for IP telephony QoS. These topics describe how to configure QoS for IP telephony in an AVVID (Architecture for voice, video, and integrated data) network using the QPM templates:
In order to support an AVVID network, you need to maintain end-to-end Quality of Service for IP telephony traffic.
Voice quality is directly affected by packet loss, packet delay and delay variation. Packet loss causes voice clippings and skips. Packet delay can cause either voice quality degradation due to the end-to-end voice latency, or packet loss if the delay is variable. Because network congestion can occur at any time in any portion of the network—campus, branch office, or WAN—you must ensure end-to-end network quality for voice traffic.
End-to-end QoS configuration improves voice quality on AVVID networks by decreasing dropped voice packets during times of network congestion and by minimizing both the fixed and variable delays encountered in a given voice connection.
Figure 9-1 shows a typical IP telephony network model.
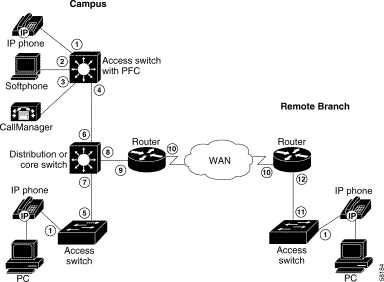
Table 9-1 lists the network points that require QoS configuration for IP telephony.
| Network Point in Figure 9-1 | Description |
|---|---|
1 | Access switch - IP phone port |
2 | Layer 3 QoS-aware access switch (with PFC) - SoftPhone port |
3 | Layer 3 QoS-aware access switch (with PFC) - CallManager port |
4 | Layer 3 QoS-aware access switch (with PFC) port to distribution or core switch |
5 | Layer 2 QoS-aware access switch port to distribution or core switch |
6 | Distribution or core switch port to Layer 3 QoS-aware access switch (with PFC) |
7 | Distribution or core switch port to Layer 2 QoS-aware access switch |
8 | Distribution or core switch port to router |
9 | Router interface to distribution or core switch |
10 | WAN interface |
11 | Layer 2 QoS-aware switch port to branch office router |
12 | Branch office router interface to Layer 2 QoS-aware switch |
QPM supports the QoS methods required to configure IP telephony QoS for:
To simplify the tasks of configuring QoS for IP telephony throughout the enterprise, QPM includes templates that contain predefined policies for each point in the IP telephony network.
The following topics describe the IP Telephony templates and how to use them:
QPM IP Telephony templates allow you to easily implement the end-to-end Quality of Service (QoS) that is required for successful deployment of IP telephony in an enterprise environment. QPM includes a special database that contains a template for each network point that needs QoS configuration for IP telephony, as shown in Figure 9-1.
Each template is a predefined device group with a set of QoS properties and policies for all points in the network that need QoS for IP telephony. To implement QoS for IP Telephony, you only need to add devices to the database, then add the appropriate interfaces to the device groups, and deploy the database.
Table 9-2 provides a summary of the templates included in the IP telephony database.
| Use this Template: | At Network Point: | On these Devices: | Minimum OS version: | QoS Techniques: |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Acc3500=>IP-Phones | IP phone ports | Catalyst 3500 and 2900 XL | IOS 12.0E | trust-ext |
Acc6000=>IP-Phones | IP phone ports | Catalyst 6000 family with PFC | CatOS 5.5 | trust-ext, trust-cos, port-base/vlan-base |
Acc6000=>SoftPhones | SoftPhone ports | Catalyst 6000 family with PFC | CatOS 5.5 | marking DSCP, port-base/vlan-base |
Acc6000=>VoIPControl | CallManager and Voice Gateway ports | Catalyst 6000 family with PFC | CatOS 5.5 | marking DSCP, port-base/vlan-base |
AccDist6K-VoiceVLAN | Voice VLAN on access and distribution switch | Catalyst 6000 family | CatOS 5.5 | marking DSCP |
Acc6000_GE=>Dist | Access switch port to distribution or core switch | Catalyst 6000 family | CatOS 5.5 | trust-cos, marking DSCP, port-base/vlan-base |
Dist(IOS)-VoiceVLAN | Voice VLAN on distribution switch | Catalyst 6000 with Supervisor IOS | IOS 12.1(6)E | trust DSCP |
Dist(IOS)=>6K-PFC | Distribution or core switch port to Layer 3 QoS-aware access switch | Catalyst 6000 with Supervisor IOS | IOS 12.1(6)E | trust-dscp, cos to queue mapping |
Dist(IOS)=>Non6KPFC | Distribution or core switch port to Layer 2 QoS-aware access switch | Catalyst 6000 with Supervisor IOS | IOS 12.1(6)E | trust-cos, cos to queue mapping |
Dist(IOS)=>RouterWAN | Distribution or core switch port to WAN router | Catalyst 6000 with Supervisor IOS | IOS 12.1(6)E | trust-dscp, cos to queue mapping |
Dist=>Acc6K-PFC | Distribution or core switch port to Layer 3 QoS-aware access switch | Catalyst 6000 family with PFC | CatOS 5.5 | trust-cos, port-base/vlan-base |
Dist=>AccNon6KPFC | Distribution or core switch port to Layer 2 QoS-aware access switch | Catalyst 6000 family with PFC | CatOS 5.5 | trust-cos, marking DSCP, port-base/vlan-base |
Dist=>RouterWAN or Dist_GE=>RouterWAN | Distribution or core switch port to WAN router | Catalyst 6000 family with PFC | CatOS 5.5 | trust-dscp, port-base/vlan-base |
RouterWAN=>Non6KPFC | WAN router interface to branch office Layer 2 QoS-aware switch | Router 7200, 7100, 7500, 3600, 2600, 1750 | IOS 12.2 | DSCP marking, IP precedence |
WAN-MLP-Slow(<768K) | Slow serial point to point WAN links | Router 7200, 7100, 7500, 3600, 2600, 1750 | IOS 12.2 | LFI, cRTP, LLQ+CBWFQ |
WAN-MLP-High(>768K) or WAN-PPP-High(>768K) | High-speed serial point to point WAN links | Router 7200, 7100, 7500, 3600, 2600, 1750 | IOS 12.2 | cRTP, LLQ+CBWFQ |
WAN-FR-Interface | Frame relay links | Router 7200, 7100, 7500, 3600, 2600, 1750 | IOS 12.2 | FRTS |
WAN-FR-64K-DLCI | Frame relay DLCI subinterfaces | Router 7200, 7100, 7500, 3600, 2600, 1750 | IOS 12.2 | cRTP, FRTS, FRF, per DLCI CBWFQ |
WAN-FR-128K-DLCI | Frame relay DLCI subinterfaces | Router 7200, 7100, 7500, 3600, 2600, 1750 | IOS 12.2 | cRTP, FRTS, FRF, per DLCI CBWFQ |
WAN-FR-256K-DLCI | Frame relay DLCI subinterfaces | Router 7200, 7100, 7500, 3600, 2600, 1750 | IOS 12.2 | cRTP, FRTS, FRF, per DLCI CBWFQ |
WAN-FR-512K-DLCI | Frame relay DLCI subinterfaces | Router 7200, 7100, 7500, 3600, 2600, 1750 | IOS 12.2 | cRTP, FRTS, FRF, per DLCI CBWFQ |
WAN-FR-768K-DLCI | Frame relay DLCI subinterfaces | Router 7200, 7100, 7500, 3600, 2600, 1750 | IOS 12.2 | cRTP, FRTS, FRF, per DLCI CBWFQ |
WAN-FR-1.5M-DLCI | Frame relay DLCI subinterfaces | Router 7200, 7100, 7500, 3600, 2600, 1750 | IOS 12.2 | cRTP, FRTS, per DLCI CBWFQ |
WAN-ATM-VirtualTempl | ATM virtual templates | Router 7200, 7100, 7500, 3600, 2600, 1750 | IOS 12.2 | LFI, LLQ+CBWFQ |
 |
Note For details of the policies and properties in each device group, see QPM IP Telephony Template Reference. |
This section describes how to configure QoS for IP telephony using the QPM templates:
You create a new IP telephony database from the predefined IP Telephony Template database that is included with QPM. After you open the QPM IP Telephony database, you must save it with a new name because it is read-only.
Step 1  In the Policy Manager window, click the New IP Telephony Database button.
In the Policy Manager window, click the New IP Telephony Database button.
The IP_TELEPHONY_TEMPLATE database is displayed in the Tree View of the Policy Manager window.
Step 2 Choose File>Save As. The Save Database dialog box opens.
Step 3 Enter a name in the Database Name field. Enter a description in the Database Description field. Click OK.
You must add or import all the devices and interfaces that require QoS configuration for IP telephony.
 |
Note Do not use the Upload function when adding devices to the IP telephony QoS database. This database changes specific QoS properties on certain devices, and these will be overwritten if you upload the current device configuration. |
For information about adding and importing devices, see the following topics:
After you have added the devices and interfaces to the IP telephony database, you add interfaces to the appropriate predefined device groups. See Table 9-2 for a summary of the device groups in the IP telephony database. For details of the policies and properties in each device group, see QPM IP Telephony Template Reference.
For details about how to add interfaces to a device group, see the Procedure.
Step 1 Select the device group to which you want to add interfaces.
Step 2 Choose Devices>Device Group>Add/Remove Members. The Add/Remove Members dialog box opens.
Step 3 Select the interfaces you want to add from the Available Interfaces list, and click >>. The selected interfaces are added to the Group Members list.
Step 4 Click OK.
After you have added all the required interfaces to the relevant device groups, you can deploy the IP telephony database from the Distribution Manager.
 |
Note You can preview the CLI commands that will be downloaded to the devices, using the Devices>View Commands option in the Distribution Manager. See Viewing the Configuration Commands for a Device for details. |
Step 1 To open the Distribution Manager from the Policy Manager, choose Tools>Distribution Manager.
Step 2 Distribute the policies. See "Distributing Policies to Network Devices" for more information.
The QPM IP telephony templates are based on the Cisco IP Telephony QoS Design Guide. This template reference describes the QoS properties and policies in each of the templates.
In general, the CLI commands generated by the templates on deployment are compliant with those defined in the QoS Design Guide. You can preview the CLI commands that will be generated on deployment, using the Devices>View Commands menu option in the Distribution Manager. See Viewing the Configuration Commands for a Device for details.
The template reference is organized according to the network points that require QoS configuration for IP telephony:
When connected by a single cable, the IP phone is the edge of the managed network. An integral part of the Cisco network design architecture has always been the classification, or coloring, of traffic as close to the edge of the network as possible. As such, the IP phone can and should classify traffic flows.
By default, Cisco IP phones mark all VoIP traffic with CoS=5 and DSCP=46. However, it is critical to make sure that the PC connected to the access port of the IP phone is not also classifying traffic. The recommended method for ensuring this is to extend the trust boundary of the Ethernet switch to the IP phone and not beyond, meaning the IP phone will re-classify all traffic coming from the PC with CoS=0. The switch port is set to trust the CoS value and copy it to the DSCP field according to the CoS to DSCP mapping table. To overcome a configuration limitation on the line card ASIC, the switch port is also configured to trust the IP phones. VLAN-based QoS configuration is used to trust all CoS classification on the IP phone ports in the voice VLAN. The VLAN-based configuration is deployed to all ports in the VLAN that have been added to QPM.
This template is for IP phone ports on Catalyst 6000 switches with CatOS 5.5 and higher.
The following device group properties are configured for this template:
The following QoS policies are configured for this template:
This template is for the voice VLAN on Catalyst 6000 switches with CatOS 5.5 and higher. This template is required to configure specific policies because the QoS style on the IP phone ports is set to VLAN based, which means that only the VLAN-based policies (not the individual port's policies) will be deployed to the ports on the VLAN.
The following device group properties are configured for this template:
The following QoS policies are configured for this template:
This template is for IP phone ports on Catalyst 3500XL and 2900XL switches with IOS 12.0E and higher.
The following device group properties are configured for this template:
The following QoS policies are configured for this template:
The Cisco SoftPhone application marks voice traffic only at the Layer 3 IP header. This means that the access switch to which it is connected must be Layer 3 aware in order to prioritize voice traffic before the first uplink to the distribution layer. This limits the choice of wiring closet switches with multiple queues to the Catalyst 6000 with a PFC installed.
This template is for SoftPhone ports on Catalyst 6000 switches with CatOS 5.5 and higher, and with a PFC installed.
The following device group properties are configured for this template:
The following QoS policies are configured for this template:
In networks with high traffic loads, timely transmission of control traffic is critical to ensure a positive user experience with VoIP, for example, maintaining Delay to Dial-Tone (DTT) time at acceptable levels. When a Cisco IP Phone goes off hook, it uses Skinny Station Protocol to communicate with Cisco CallManager. Cisco CallManager then instructs the Cisco IP Phone to play dial-tone. If this Skinny Client Protocol management and control traffic is dropped or delayed within the network, the user experience is adversely affected. This same logic applies to all signaling traffic for gateways and phones.
To ensure that this control and management traffic is marked as important (but not as important as the actual RTP stream), Access Control Lists (ACLs) are used to classify these streams on Catalyst 6000 switches that are enabled for Layer 3 and Layer 4.
This template is for CallManager and Voice Gateway ready ports on Catalyst 6000 switches with CatOS 5.5 and higher.
The following device group properties are configured for this template:
The following QoS policies are configured for this template:
 |
Note To mark packets destined to CallManager and packets originating from CallManager, the policy also filters all the above ports as source ports. |
After QoS configuration of the access interfaces, QoS must be configured throughout the LAN.
These templates are for uplink ports on a Catalyst 6000 access switch to the distribution or core switch.
This template is for access ports on a Catalyst 6000 with CatOS 5.5 and higher, and with a PFC installed.
The following device group properties are configured for this template:
The following QoS policies are configured for this template:
These templates are for downlink ports on a Catalyst 6000 distribution or core switch to the access layer Catalyst 6000 switch with a PFC installed.
Because classification is set on the access switch, a switch can trust traffic from a neighboring switch. The level of trust depends on the neighboring switch's capabilities. For switches with layer 3 capabilities, trust layer 3 is sufficient.
This template is for distribution or core switch ports on a Catalyst 6000 with CatOS 5.5 and higher, and with a PFC installed.
The following device group properties are configured for this template:
The following QoS policies are configured for this template:
This template is for distribution or core switch ports on a Catalyst 6000 with Supervisor IOS 12.1(6)E.
The following device group properties are configured for this template:
 |
Note There is currently no corresponding template for 2Q2T interfaces. |
The following QoS policies are configured for this template:
These templates are for downlink ports on a Catalyst 6000 distribution or core switch to Layer 2 QoS-aware access switches, such as Catalyst 3500 or Catalyst 4000.
Because classification is set on the access switch, a switch can trust traffic from a neighboring switch. The level of trust depends on the neighboring switch's capabilities. For switches with layer 2 capabilities, trust of layer 2 is required with the addition of layer 3 and 4 classification statements.
This template is for distribution or core switch ports on a Catalyst 6000 with CatOS 5.5 and higher, and with a PFC installed.
The following device group properties are configured for this template:
The following QoS policies are configured for this template:
 |
Note Because the QoS style in this template is VLAN based, you should also use the AccDist6K-VoiceVLAN template described in AccDist6K-VoiceV LAN. |
This template is for distribution or core switch ports on a Catalyst 6000 with Supervisor IOS 12.1(6)E.
The following device group properties are configured for this template:
 |
Note There is currently no corresponding template for 2Q2T interfaces. |
The following QoS policies are configured for this template:
This template is for the voice VLAN on Catalyst switches with Supervisor IOS 12.1(6)E. This template is required to configure specific policies because the QoS style on the ports is set to VLAN based.
The following device group properties are configured for this template:
The following QoS policies are configured for this template:
These templates are for the interfaces from the distribution and core switches to the WAN router.
This template is for the ethernet interfaces to the WAN router from a Catalyst 6000 with CatOS 5.5 or higher.
The following device group properties are configured for this template:
The following QoS policies are configured for this template:
This template is for the gigabit ethernet interfaces to the WAN router from a Catalyst 6000 with CatOS 5.5 or higher.
The following device group properties are configured for this template:
The following QoS policies are configured for this template:
The following device group properties are configured for this template:
 |
Note There is currently no corresponding template for 2Q2T interfaces. |
The following QoS policies are configured for this template:
The following QoS properties are set for the Catalyst 6000:
The following QoS properties are set for the Catalyst 6000 with Supervisor IOS.
 |
Note On the Catalyst 6000 with Supervisor IOS the scheduling is configured per interface and not per device. |
Link speed in the WAN is much slower than in the LAN, therefore QoS configuration for WAN links is most important to prevent delay.
The templates for Point-to-Point (PPP) and Multilink PPP (MLP) WAN interfaces use the following QoS techniques:
This template is for low-speed Multilink PPP (MLP) WAN links (<= 768kbs) running IOS 12.1(3)T and later.
The following QoS properties are set:
The following QoS policies are configured for this template:
This template is for high-speed Multilink PPP (MLP) WAN links (> 768kbs) running IOS 12.1(3)T and later. It uses the same QoS techniques as in the low-speed point-to-point template, but without LFI.
The following QoS properties are set:
The following QoS policies are configured for this template:
This template is for high-speed PPP WAN links without Multilink (> 768kbs) running IOS 12.1(3)T and later. It uses the same configuration as for the WAN-MLP-High(>768k) template except for the interface type, which is defined as propPointToPointSerial.
The templates for Frame Relay WAN interfaces use the following QoS techniques:
This template is for a main, Frame Relay interface that has DLCI interfaces for voice traffic, running IOS 12.1(3)T and later. (There are separate templates for the DLCI subinterfaces.)
The following QoS properties are set:
This set of templates is for low-speed Frame Relay subinterfaces. The QoS configuration for these subinterfaces use FRTS with CIR, and because a different configuration is required for each speed, there are five templates: WAN-FR-64K-DLCI, WAN-FR-128K-DLCI, WAN-FR-256K-DLCI, WAN-FR-512K-DLCI and WAN-FR-768K-DLCI.
When you use these templates, you should also use the WAN-FR-Interface described in WAN-FR-Interface for the main interfaces.
The following information is for the WAN-FR-256K-DLCI template.
The following QoS properties are set:
The following QoS policies are configured for this template:
This template is for high-speed (> 768kbs) Frame Relay subinterfaces running IOS 12.1(3)T and later. It uses the same QoS techniques as in the low-speed Frame Relay templates, but without FRF.
When you use this template, you should also use the WAN-FR-Interface described in WAN-FR-Interface for the main interfaces.
The following QoS properties are set:
The following QoS policies are configured for this template:
This template implements QoS over ATM using one PVC with CBWFQ and LLQ.
This template implements QoS over ATM using a virtual template.
The following QoS properties are set:
The following QoS policies are configured for this template:
 |
Note This template does not configure the TX-ring buffer size. You must adjust the TX-ring buffer size using CLI commands. See the Cisco IP Telephony QoS Design Guide for more details at http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/voice/ip_tele//index.htm. |
The traditional branch office design for up to 100 users consists of a branch router and an Ethernet switch. The router handles all IP routing and WAN connectivity.
This template is for the interfaces on a router running IOS 12.2 or higher, to a layer 2 switch.
The following QoS properties are set:
The following QoS policies are configured for this template:
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Posted: Tue Nov 12 12:28:09 PST 2002
All contents are Copyright © 1992--2002 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Important Notices and Privacy Statement.