|
|

This appendix provides procedural and reference information that you can use to determine and resolve problems that you may be experiencing using NSP.
This appendix includes information on the following:
Sometimes a problem cannot be traced to a specific source. NSP provides three trace utility commands that you can use to isolate problems that NSP may be experiencing. The three utilities provided and their functions are:
| Trace Utility | Function |
|---|---|
| nspaid debug | Traces the internal data flow of NSP. |
| nspaid ctrace | Traces the internal commands being processed by NSP. |
| nspaid trflow | Traces the entries and exits of issued commands. |
The trace facilities that you enable using the nspaid command affect only the operator ID under which you issue the command. The following sections provide examples of the output received when operating NSP using the any of the trace utilities.
The NSP Internal Data Flow utility traces the internal data flow of the processes occurring in NSP. You turn on the NSP Internal Data Flow utility by issuing the following command:
nspaid debug onThe following is an example of the data that is returned to your console when you have turned on the NSP debug trace facility. The example provided is the internal tracing of the data flow that occurs when an operator has issued the nspcmda command.
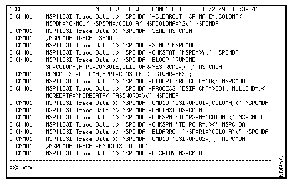
To turn off the trace of the NSP internal data flow, issue the following command:
nspaid debug offThe NSP CLIST Trace utility traces different NSP CLIST elements depending on the keyword you specify when turning on the trace utility.
| Specify | To |
|---|---|
| nspaid ctrace all | Trace the execution of all NSP CLISTs. |
| nspaid ctrace all_nnn | Trace the execution of only the CLIST nnn, where nnn is the number of the CLIST you want to trace. |
| nspaid ctrace err | Trace only CLIST errors. |
| nspaid ctrace cmd | Trace the commands issued from a CLIST. |
| nspaid ctrace off | Turn off CLIST tracing. |
The following is an example of the type of data that is returned to your console as NSP CLISTs are executed when the nspaid ctrace all command has been issued.
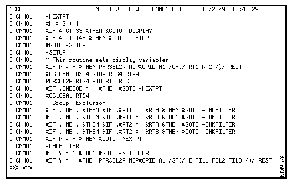
To turn off the tracing of NSP CLISTs, issue the following command:
nspaid ctrace offThe NSP Flow Trace utility traces the entries and exits of all the NSP routines issued by an NSP operator.
The following is an example of the type of data that is returned to your console as NSP routines are processed when the nspaid trflow on command has been issued:
To turn off the tracing of the entries and exits of NSP routines, issue the following command:
nspaid trflow offIf you have enabled all of the NSP trace utilities (debug, ctrace, and trflow), you can turn off each utility individually, or you can issue a command that turns off all tracing. For information on turning off a trace utility individually, see the command provided in the appropriate trace utility section.
To turn off all NSP trace utilities running, issue the following command:
nspaid offThe NSP User List utility enables you to view a list of all users defined to NSP. The NSP user list that includes the name of each user (if the name is specified in their profile), user ID, and their NSP user authority level.
To view a list of all the users defined to NSP, issue the following command:
nspulistThe following is a sample of the output that is displayed in response to the nspulist command.
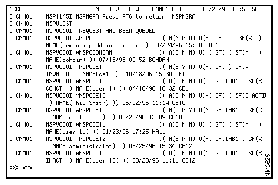
NSP provides a backup NSP administrator profile that can be used by a system administrator to recreate an NSP administrator profile if all existing NSP administrator profiles are accidentally deleted. If all NSP administrator profiles are deleted, there is not an NSP user capable of modifying the NSP management environment and assigning user authority levels for NSP users.
If the base NSP administrator profile is deleted:
Step 1 Add an NSPADMIN operator to NetView.
Step 2 Log on to NetView as the NSPADMIN operator.
Step 3 Create several NSP administrator profiles as described in the "Defining Operator Profiles" section in the "Installing and Configuring Native Service Point" chapter to ensure that there will be additional NSP administrator level profiles available for backups if needed.
 | Caution This backup procedure can be performed only one time. Please ensure that several administrator level profiles are created to serve as backups in case this situation ever occurs again. |
If you are experiencing problems in establishing communication with a router, service point configuration problems may exist. To verify the configuration of a router using a RUNCMD, issue the following from a NetView or VTAM command line before starting NSP:
RUNCMD SP=ROUTER_NAME,APPL=CONLOSE, SHOW ?
Where ROUTER_NAME is the name of the router you are verifying.
The possible responses may indicate that the router is one of the following:
If the router is not defined to VTAM, a response similar to the following is displayed:
* CNM01 RUNCMD SP=LIBERTY,APPL=CONSOLE, SHOW ? - CNM01 DSI358I RUNCMD FAILED. ID 'LIBERTY' IS INVALID, SENSE CODES = X'08060000' ------------------------------------------------------------------------- * CNM01 D NET,ID=LIBERTY CNM01 IST453I ID PARAMETER VALUE INVALID ------------------------------------------------------------------------- Sense=08060000The explanation of the sense code returned displays the following:
SENSE DATA:
CATEGORY - (08) Resource unknown: For example, the request contained a
MODIFIER - (06) name or address not identifying a PU, LU, SSCP, link, or
BYTE 2 - (00) link station known to the receiver or the sender.
BYTE 3 - (00) Note: In an interconnected network environment, this sense code may be set by an SSCP in whose subnetwork and domain the LU was expected to reside; it is not set by an SSCP that is only an intermediary on the session-setup path. A gateway SSCP examines the resource identifier control vector in a session setup request (for example, CDINIT), to determine whether the LU is in the SSCP's subnetwork and domain. Bytes 2 and 3 following the sense code contain sense code-specific information.
No specific code applies.
VTAM Information: When VTAM receives this sense code for a session initiation, it continues searching through the adjacent SSCP table until the destination LU is found or routing is exhausted.
VTAM Hint: A possible cause of this error is that uservarname has been specified on the ID operand of the DISPLAY NCPSTOR command.
This response indicates that an SSCP-to-PU session has not been established between VTAM and the router. This also means that the connection has failed because the router has not been defined to VTAM.
If the router is defined to VTAM, but a connection has never been established, a response similar to the following may be displayed when you verify the router from NetView:
* CNM01 RUNCMD SP=CWBC03,APPL=CONSOLE, SHOW ? - CNM01 DSI264I RUNCMD FAILED FOR CWBC03 - RTNCD = X'04', FDBK2 = X'04', SYSTEM SENSE = X'0807', USER SENSE = X'0000' ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- * CNM01 D NET,ID=CWBC03 CNM01 IST097I DISPLAY ACCEPTED ' CNM01 IST075I NAME = CWBC03 , TYPE = PU_T2 IST486I STATUS= CONCT , DESIRED STATE= CONCT IST1043I CP NAME = ***NA***, CP NETID = NETA , DYNAMIC LU = YES IST136I SWITCHED SNA MAJOR NODE = SWDRTRS IST654I I/O TRACE = OFF, BUFFER TRACE = OFF IST1500I STATE TRACE = OFF IST314I END -------------------------------------------------------------------------------The explanation of the sense code returned displays the following:
Sense=0807
SENSE DATA:
CATEGORY - (08) Resource not available--LUSTAT forthcoming: A subsidiary
MODIFIER - (07) device will be unavailable for an indeterminate period of
BYTE 2 - (00) time. LUSTAT will be sent when the device becomes
BYTE 3 - (00) available.
If information similar to the following is displayed when you verify the router from NetView, the router is active, but the service point in not enabled:
CNM01 RUNCMD SP=BULLDOG,APPL=CONSOLE, SHOW ? - CNM01 DWO614E RUNCMD REQUEST NOT PERFORMED BY ID BULLDOG FOR APPL = 'CONSOLE', SENSE CODE = X'080C0005' FUNCTION INACTIVE ----------------------------------------------------------------------------- * CNM01 D NET,ID=BULLDOG CNM01 IST097I DISPLAY ACCEPTED ' CNM01 IST075I NAME = BULLDOG , TYPE = PU_T2.1 IST486I STATUS= ACTIV , DESIRED STATE= ACTIV IST1043I CP NAME = BULLDOG , CP NETID = NETA , DYNAMIC LU = YES IST1354I DLUR NAME = BEAST MAJNODE = SWDLURSJ IST136I SWITCHED SNA MAJOR NODE = SWDLURSJ IST654I I/O TRACE = OFF, BUFFER TRACE = OFF IST1500I STATE TRACE = OFF IST314I END -----------------------------------------------------------------------------The explanation of the sense code returned displays the following:
Sense=080c0005
SENSE DATA:
CATEGORY - (08) Procedure not supported: A procedure (Test, Trace, IPL,
MODIFIER - (0C) REQMS type, MS major vector key) specified in an RU is
BYTE 2 - (00) not supported by the receiver. Bytes 2 and 3 following
BYTE 3 - (05) the sense code contain sense-code-specific information.
The MS major vector key is not supported by the receiver.
4. Service Point active and correct operation.
* CNM01 RUNCMD SP=CWBC02,APPL=CONSOLE, SHOW ?
- appn APPN show commands
- boot Boot and related environment variable
- calendar Display the hardware calendar
- clock Display the system clock
- history Display the session command history
- hosts IP domain-name, lookup style, nameservers, and
host table
- ipc Interprocess communications commands
- kerberos Show Kerberos Values
- location Display the system location
- modemcap Show Modem Capabilities database
- ncia Native Client Interface Architecture
- ppp PPP parameters and statistics
- rmon rmon statistics
- rtr Response Time Reporter (RTR)
- sessions Information about Telnet connections
- sgbp SGBP group information
- snmp snmp statistics
- tacacs Shows tacacs+ server statistics
- terminal Display terminal configuration parameters
- traffic-shape traffic rate shaping information
- users Display information a bout terminal lines
- version System hardware and software status
- vpdn VPDN information
- cwb-c2>
If you determine that the service point has not been enabled or correctly defined in the router, refer to the Cisco IOS software Bridging and IBM Networking Configuration Guide and Bridging and IBM Networking Command Reference publications for detailed information on configuring the service point.
This section provides a list of the operator task globals available with NSP:
| Task Global | Description |
|---|---|
| DEBUG | Saved values of the NSPAID DEBUG. |
| CTRACE | Saved value(s) of the NSPAID CTRACE operand(s). |
| TRFLOW | Saved value(s) of the NSPAID TRFLOW. |
This following two tables provide a list of the common globals used for the NSP management environment and the common globals used by NSP to monitor a specific router.
| Common Global | Description |
|---|---|
| NSPINITS | When NSP was initialized. |
| NSPAPPL | NSP application status. |
| NSPINITM | Interfaces being monitored. |
| NSPMGR | Autotask managing NSP. |
| NSPOPNUM | Additional autotasks managing NSP. |
| NSPMINTV | Router monitoring interval. |
| NSPMINTVI | Interface monitoring interval. |
| NSPNTHPU | Router CPU performance threshold. |
| NSPMTHMU | Router memory level threshold. |
| NSPMOPER | NSP security indicator. |
| NSPRTRHDB | Router database values. |
| NSPINTHDB | Interface database values. |
| NSPRIFHDB | SNA View RIF database values. |
| NSPCONHDB | Router configuration database values. |
| NSPNVM | Number of routers being managed by NSP. |
| Common Global | Description |
|---|---|
| NSPspname | Index pointer to the router information. |
| NSP&n | Router service point name. |
| RTA&n | When router became active. |
| RTB&n | Router busy with operator. |
| RTC&n | Configuration status/control. |
| RTD&n | Domain in which router is located. |
| RTE&n | Router description. |
| RTF&n | Last failure or alert generated for or by a router. |
| RTG&n | Operation groups to which the router belongs. |
| RTH&n | Router host name (IP name). |
| RTI&n | Router IP address. |
| RTL&n | Last related alert. |
| RTM&n | The NSP autotask managing the router. |
| RTO&n | Operator enabled to the router. |
| RTO&n | Pointer to performance history. |
| RTS&n | Current NSP to router status. |
| RTX&n | Extended status indicators. |
|
|