Who is using the network?
What are they using it for?
How much bandwidth is being used?
How much is it costing the company?
More than likely you have asked these questions because you are a network manager who is responsible for monitoring the network usage in your organization. By using the Cisco Enterprise Accounting (CEA) for ISDN application, you can now have answers to these questions and more.
CEA for ISDN can help you by providing information that allows you to do the following:
- Identify, monitor, and control the costs of ISDN network use in your organization.
- Better understand your network costs to ensure that your network is performing at optimum levels.
- Implement departmental billback.
- Lower the overall cost of network ownership.
- Determine end-user accountability with respect to network resource utilization.
- Manage enterprise-wide network budgeting.
- Determine trends for network capacity and growth planning.
- Identify network equipment problems.
- Provide the visibility necessary to meet service-level agreements.
You probably want to install CEA for ISDN and start using it right away. All you need is the CEA for ISDN installation CD-ROM, this guide, and about an hour to complete the installation and use the tutorial.
Before you begin, take a few minutes to read the rest of this chapter. It will answer these key questions:
At the core of the CEA for ISDN is usage, or call data. The raw call data is retrieved from Cisco IOS devices using the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP). CEA for ISDN then translates and filters this raw call data into standardized or flexible call data records (CDRs), which are stored in a relational database.
The database provides the foundation for a rich set of applications, including end-user accounting, cost allocation, traffic statistics, and exception reports.
In addition, network monitoring enables you, the network manager, to proactively watch for network usage patterns that are considered excessive or that violate your organization's policies.
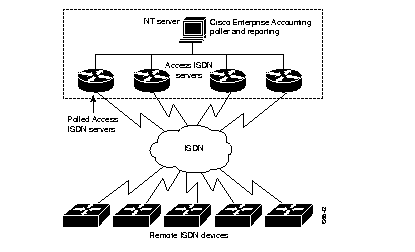
Only centralized routers and network access servers require polling because this is where the majority of calls are terminated (answered). See Figure 1-1.
Figure 1-1: Polled Devices
CEA for ISDN provides the following special features:
- CEA for ISDN continually collects, translates, and stores raw call data from your network devices. CEA for ISDN costs these "call records" on demand and stores the cost information in the call records. You can access the Call Records files to:
- View call records from various viewpoints (for example, you can view all calls from individuals in your Marketing department).
- Reprice specific calls by correcting individual call records and recosting the calls.
- Produce costing reports.
- CEA for ISDN allows you to charge back costs for calls to those individuals, organizational units, or locations responsible for them and to reconcile statements from the network service providers. Additional charges can be assigned to each account, such as one-time charges for installation or continuing charges for quality of service (QoS) or use of equipment. You set up and maintain the information needed for cost allocation in the Directory file. You will learn how to use the Directory in Chapter 3, "Getting Started."
- A query retrieves every current record that matches criteria you specify. The results of the search are displayed in a table on your screen. Queries allow you to focus on records with certain characteristics. From the query record set, you can update individual records.
- A report, like a query, searches for records that match your specified criteria. However, reports can include processed data, such as summaries, subtotals, and minimum and maximum values. The data is formatted for the printed page and cannot be changed. You can send a report to your screen to preview how it will look when printed. You can also send a report to an e-mail address, or you can save a report to a file.
- The Directory is a database containing information about individuals, locations, and equipment. You can access the Directory to:
- View Directory records from different viewpoints.
- Add, update, and delete Directory records.
- Generate Directory reports.
- Call Record Maintenance and Views
- Call Record report templates allow you to create reports to review call records, allocate call costs to the accounts that are responsible for them, and reconcile statements from the phone company. You can access the Call Records file to:
- View call records (for example, you can run a report of calls by Host ID).
- Reprice specific calls by correcting individual call records and recosting the calls.
- Produce costing reports.
- Traffic Statistics Reports
- Traffic Statistics reports show statistics related to the performance and cost effectiveness of your network. These statistics include packet and octet counts, maximum and minimum call duration, and call charges. You can search on different criteria such as date and time or type of call.
- Exception reports detect improper use of network resources or misconfigured network devices based on criteria you specify. For example, calls from a certain IP or ISDN address might be monitored to ensure proper use of network resources. Alternately, an excessive number of short calls with little or no packet transmission might indicate a router with the wrong configuration.
- CEA for ISDN reports are easily exported to other desktop applications, such as an Excel spreadsheet.
When you install CEA for ISDN, the following applications are available to you:
- Cisco Enterprise Accounting for ISDN
- This is the main application.
- This is a utility that allows you to specify (1) the routers from which you want to collect ISDN call history information and (2) the network management stations to which you want to be able to send SNMP alarms (traps).
- This application monitors the incoming application. You can view the raw data as it is recorded. In addition, it controls and monitors the scheduled events. As long as the Port Monitor application is running and the Scheduler is on, your scheduled events will run at the designated time.
Note You can enable or disable the Scheduler in the Port Monitor.
- You use the CEA for ISDN Utilities to maintain Raw Data and Calls tables. If calls were repolled, you can retranslate records, delete records by date range from the Calls and Raw Data files, and remove duplicates from the Calls table.
- PowerTCP is a tool kit used by the SNMP Proxy program; it must be loaded for CEA Proxy to run. PowerTCP is launched and closed by the CEA Proxy.
- You use this utility to rebuild the databases and restore corrupted files. This tool performs the following activities:
- Creates a folder named Recover in your Data folder.
- Copies all the files in the Data folder to the Recover folder.
- Creates a new database containing empty files in the Data folder.
- Copies the data from the files in the Recover folder to the empty files in the Data folder.
We'll get started with the installation in just a minute.
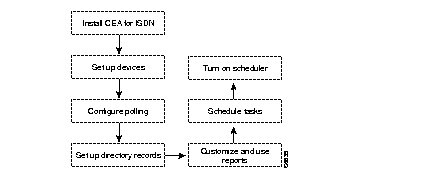
For your convenience, we've included an illustration (Figure 1-2) to show you the tasks you will accomplish by using this guide. You will learn how to install, configure, set up, and use CEA for ISDN.
Right now, you can see that the tasks have not been completed. We'll repeat this illustration in subsequent chapters and modify the task boxes to show you your progress.
Figure 1-2: High-Level Task Process Flow
We're ready. To install CEA for ISDN, turn to Chapter 2, "Installing and Configuring CEA for ISDN."
To start using CEA for ISDN, turn to Chapter 3, "Getting Started." It is a tutorial for learning the basics of CEA for ISDN.


