|
|

 |
Note The information in this chapter applies to both UNIX workstations (Maps and SNA View) and Windows NT systems (SNA View). |
This chapter provides information on using the Process Manager on a UNIX workstation. The CiscoWorks Blue Process Manager provides an interface for starting, monitoring, and stopping the Maps and SNA View daemons and processes and the Process Manager services.
The Process Manager starts automatically when your system starts. When the Process Manager starts, it starts all the Maps and SNA View processes that are marked as Autostart, and it restarts any processes that have been stopped abnormally and are marked for Restart.
This chapter includes the following main sections:
This section describes how to start the Process Manager. The Process Manager consists of a server component that monitors and maintains the running processes and a client component that displays the results in a graphical user interface.
This section includes the following information:
UNIX Workstations
CiscoWorks Blue server processes are normally started automatically and kept running. Should you need to manually start them, use the following commands on a UNIX workstation:
From the command line, use the cwb start servers command to start all CiscoWorks Blue servers, including the database server and the Process Manager server. Because starting the database and naming servers requires root authority, you should always run cwb start servers as the root user:
/opt/CSCOcb/bin/cwb start serversFrom the command line, use the cwb start pm command to start the Process Manager server:
/opt/CSCOcb/bin/cwb start pm Windows NT
On a Windows NT system, you can select Start > Programs > CiscoWorks Blue > System Services > Start.
UNIX Workstations
You can start the Process Manager client from the Administration application or from the command line. From the command line, use the cwb start ProcMgrClient command:
/opt/CSCOcb/bin/cwb start ProcMgrClientFrom the Administration application, click Process Manager.
Windows NT
On a Windows NT system, you can use the following methods:
The Process Management Information window contains two tabs:
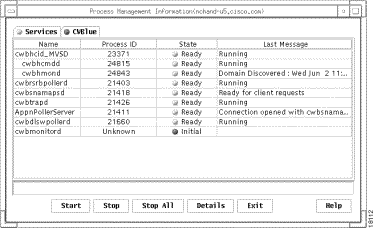
The CWBlue window displays a list of the Maps and SNA View processes in a single window, as shown in Figure 7-1. The host name of the connected workstation is displayed in the title bar of the window.
Fields
The CWBlue window contains the following fields:
Field
| Description
|
|---|---|
| |
| |
| |
| |
The buttons on the CWBlue window provide the following functions:
Button
| Description
|
|---|---|
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
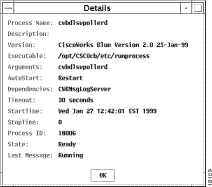
You can see detailed information about each process. Select a process and click Details in the CWBlue window to view the details of the selected process. The Details window is displayed, as shown in Figure 7-2.
Fields
The Details window contains the following fields:
Field
| Description
|
|---|---|
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
The following table shows the Maps and SNA View daemons and processes that can be monitored in the Process Manager:
Process Name
| Description
|
|---|---|
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
 |
Note The cwbhcmdd and cwbhmond TCP/IP processes are transient daemons. They are started by cwbhcid_domain_name, not by the Process Manager. Once started, their status is displayed by the Process Manager. When cwbhcid stops, these two stop as well, and disappear from the Process Manager window. |
Depending on the selections you make during configuration, some processes are set up to start automatically when the Process Manager starts, and some processes are dependent on others.
Depending on your configuration options, the following processes are started automatically:
Configuration Option
| Processes Autostarted
|
|---|---|
| |
| |
| |
| 1The cwbtrapd process is started only if an NMS was integrated during installation. |
The following processes start only after other processes are started:
Process
| Depends on
|
|---|---|
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
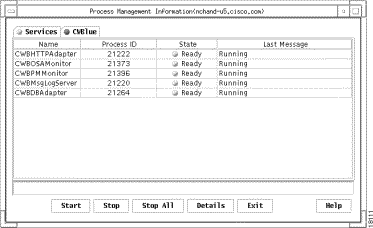
The Services window displays a list of all the Process Manager services, as shown in Figure 7-3.
Fields
The Services window contains the following fields:
Field
| Description
|
|---|---|
| |
| |
| |
| |
Buttons
The buttons on the Services window provide the following functions:
Button
| Description
|
|---|---|
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
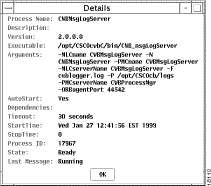
You can see detailed information about each service. From the Services window, select a service and click Details to view the Services Details window for the selected service, as shown in Figure 7-4.
Fields
The Services Details window contains the following fields:
Field
| Description
|
|---|---|
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
The following Process Manager services can be monitored in the Services window:
Process Name
| Description
|
|---|---|
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
Depending on the selections you make during configuration, some services are set up to start automatically when the Process Manager starts, and some services are made to be dependent on others.
The following services are started automatically when the Process Manager server starts:
The following services start only after other processes are started:
Process
| Depends On
|
|---|---|
| |
| |
| |
This section provides information about the different ways you can configure how the Process Manager runs.
UNIX Workstations
The CWBPMMonitor process monitors the Process Manager to ensure that it remains active. If the Process Manager is not running, the CWBPMMonitor process stops all other CiscoWorks Blue processes. It then restarts the Process Manager server which in turn starts all the other servers.
Windows NT
On a Windows NT system, use the Configuration application. For more information, see "Using CiscoWorks Blue SNA View Configuration for Windows NT."
UNIX Workstations
On a UNIX workstation, use the CWBProcessMgrWaitTime parameter in the /opt/CSCOcb/etc/cwbinit file to specify how often, in minutes, the CWBPMMonitor process wakes up to check whether the Process Manager is running. The default value is 10 minutes.
**********************************************************
# This section is used by the Process Manager monitor process, which
# monitors the state of the CiscoWorks Blue Process Manager.
# This parameter controls how often, in minutes, the CWBPMMonitor
# process wakes up and makes sure that the Process Manager process is
# running on the system. If it is not running, this process stops
# all CWBlue processes and restarts Process Manager, which restart
# all servers.
CWBProcessMgrWaitTime = 10
On UNIX workstations, use the showWarnings parameter in the /opt/CSCOcb/etc/cwbinit file to specify whether the Verification program should issue warning messages.
*********************************************************************
# This section is used by the Verification Utility which validates
# the CiscoWorks Blue installation.
# Flag indicating whether or not the verification utility should issue
# warnings. If "true" warnings are issued, "false" otherwise.
showWarnings = true
Windows NT
On a Windows NT system, use the cwb config command. For more information, see "Commands and Processes for Windows NT."
The Process Manager is configured, during Maps or SNA View installation, to monitor the complete set of processes and to automatically start those processes that support the protocols (DLSw, APPN, and RSRB) that you want to manage. The settings that govern the Process Manager are stored in the following configuration files in /opt/CSCOcwbC/etc:
UNIX Workstations
Normally you would not need to make any changes in these configuration files. However, you might want to change selected default values (such as the Autostart value) or process dependencies.
The CWBlue.conf configuration file contains entries that describe the Maps and SNA View processes to be monitored and managed by the Process Manager. The Services.conf file contains entries that describe the Process Manager services to be monitored and managed by the Process Manager. Each file is made up of a series of entries, one for each process or service. Each entry is in the following format:
process_name autostart? dependencies executable arguments time_out
The entry contains the following fields:
Entry
| Description
|
|---|---|
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
The following sample CWBlue.conf file shows the file contents after you install CiscoWorks Blue:
# The Process Manager Configuration File for Maps/SNAView processes.
# Each line contains 6 tokens separated by spaces
# Format:
# process_name AutoStart Dependencies Executable Args TimeOut
# process_name :Name of the process
# autoStart :(Y/N) Whether ProcessManager should automatically
# [re]start this process
# Dependencies :(A list of process_name each separated by ',')
# Each process in the list has to be started before the particular # # # process can be started. If there are no dependencies, a single '-'
# is used.
# Executable :Complete path to the executable representing the process
# Args :Arguments to the process, separated by ',' ; If no arguments # # are required, a '-' should be specified.
# TimeOut :(timeout value) The time in seconds, until which the PM
# waits for a 'InitializationComplete' notification from the
# started process). Once it receives the notification, the state of
# the process is moved from starting->Ready.
UNIX Workstations
cwbmonitord N CWBMsgLogServer,CWBDBAdapter /opt/CSCOcb/etc/runprocess cwbmonitord 30
cwbhcid_MVSD R CWBMsgLogServer,CWBDBAdapter /opt/CSCOcb/etc/runprocess cwbhcid_MVSD,MVSD 30
cwbsnamapsd R CWBMsgLogServer,CWBDBAdapter /opt/CSCOcb/etc/runprocess cwbsnamapsd 30
cwbdlswpollerd R CWBMsgLogServer,CWBDBAdapter /opt/CSCOcb/etc/runprocess cwbdlswpollerd 30
cwbrsrbpollerd R CWBMsgLogServer,CWBDBAdapter /opt/CSCOcb/etc/runprocess cwbrsrbpollerd 30
Windows NT
cwbmonitord N CWBMsgLogServer,CWBDBAdapter c:/PROGRA~1/CISCOW~1.0/CSCOcb/etc/runprocess cwbmonitord 30
cwbhcid_MVSD R CWBMsgLogServer,CWBDBAdapter c:/PROGRA~1/CISCOW~1.0/CSCOcb/etc/runprocess cwbhcid_MVSD,MVSD 30
cwbsnamapsd R CWBMsgLogServer,CWBDBAdapter c:/PROGRA~1/CISCOW~1.0/CSCOcb/etc/runprocess cwbsnamapsd 30
cwbdlswpollerd R CWBMsgLogServer,CWBDBAdapter c:/PROGRA~1/CISCOW~1.0/CSCOcb/etc/runprocess cwbdlswpollerd 30
cwbrsrbpollerd R CWBMsgLogServer,CWBDBAdapter c:/PROGRA~1/CISCOW~1.0/CSCOcb/etc/runprocess cwbrsrbpollerd 30
The following sample Services.conf file shows the file contents after you install CiscoWorks Blue:
CWBMsgLogServer R - /opt/CSCOcwbC/bin/CWB_msgLogServer -MLCname,CWBMsgLogServer,-N,CWBMsgLogServer,-PMCname,CWBMsgLogServer,-
MLCserverName,CWBMsgLogServer,-F,cwblogger.log,-P,/opt/CSCOcb/logs,-PMCserverName,CWBProcessMgr,-ORBagentPort,44542
UNIX Workstations
CWBDBAdapter R CWBMsgLogServer /opt/CSCOcb/etc/runprocess
CWBDBAdapter 100
CWBHTTPAdapter R CWBMsgLogServer /opt/CSCOcb/etc/runprocess CWBHTTPAdapter 70
CWBOSAMonitor R CWBMsgLogServer /opt/CSCOcb/etc/runprocess CWBOSAMonitor 50
CWBPMMonitor Y CWBMsgLogServer /opt/CSCOcb/etc/runprocess
CWBPMMonitor 50
Windows NT
CWBDBAdapter R CWBMsgLogServer c:/PROGRA~1/CISCOW~1.0/CSCOcb/etc/runprocess CWBDBAdapter 100
CWBHTTPAdapter R CWBMsgLogServer c:/PROGRA~1/CISCOW~1.0/CSCOcb/etc/runprocess CWBHTTPAdapter 70
CWBOSAMonitor R CWBMsgLogServer c:/PROGRA~1/CISCOW~1.0/CSCOcb/etc/runprocess CWBOSAMonitor 50
CWBPMMonitor Y CWBMsgLogServer c:/PROGRA~1/CISCOW~1.0/CSCOcb/etc/runprocess CWBPMMonitor 50
After you make changes to the Services.conf or CWBlue.conf configuration file, you must activate those changes by stopping and restarting the Process Manager server, as described in "Starting the Process Manager." The Process Manager restarts, starting any processes specified as autostart in the changed configuration file.
Use the following information for the different ways you can start the Process Manager servers and client on Unix Workstations and windows NT systems.
UNIX Workstations
After you stop the Process Manager server, you can restart it from the command line using the following commands:
/opt/CSCOcb/bin/cwb start pm Windows NT
UNIX Workstations
Restart the Process Manager client from the command line using the following command:
/opt/CSCOcb/bin/cwb start ProcMgrClient Windows NT
In Windows NT systems, you can also restart the Process Manager server or client from the start menu and from the CiscoWorks Blue taskbar icon.
You can edit the Process Manager properties file to change Process Manager properties.
Unix Workstations
The file is /opt/CSCOcwbC/classes/com/cisco/AM/conf/kubit/process/
displayMain.properties.
Windows NT
The file is install_directory\CSCOcwbC\classes\com\cisco\AM\conf\kubit\process\
displayMain.properties
Where:
install_directory is the directory in which you installed the product.
You can change the following values:
Value
| Meaning
|
|---|---|
| |
| |
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Posted: Mon Sep 4 10:54:16 PDT 2000
Copyright 1989-2000©Cisco Systems Inc.