|
|

This chapter describes how to use the setup command facility to configure your Cisco Catalyst 4000 Access Gateway Module (AGM).
 |
Note The setup command facility prompts you to enter information needed to quickly start the AGM functioning. The facility steps you through a basic configuration, including configuring LAN and WAN interfaces. |
This chapter contains these major sections:
This section contains information you need to be familiar with before you begin to configure your AGM for the first time, including interface numbering and steps to take before bringing your AGM online.
This section contains these subsections:
The factory configures the AGM to automatically load a Cisco IOS image the first time you insert the module into a Catalyst 4000 family switch. The software configuration register in the AGM determines where to find the image. The factory sets this register to load the IOS image into bootflash from configuration register 0x0101. This register enables autoboot at register 0x0103.
Table 3-1 shows the AGM default configuration.
| Feature | Default Value |
Host name | Gateway |
Interface configuration | None |
VLAN configuration | None |
Password encryption | Disabled |
Break to console | Ignore |
This section describes how to access the AGM from Catalyst Operating System on Supervisor Engine I and II, and from Cisco IOS on Supervisor Engine III and IV.
When the AGM finishes power-on self-test diagnostics, and the front panel status LED is green, you can access the module by entering the session mod/num command at the Switch> prompt. After you enter this command, the Gateway> prompt appears.
After booting the AGM for the first time, you can configure the interfaces, and then save the configuration to a file in NVRAM.
When the AGM finishes power-on self-test diagnostics, and the front panel status LED is green, you can access the module by entering the attach module mod/num command at the Switch# prompt. After you enter this command, the Gateway> prompt appears.
After booting the AGM for the first time, you can configure the interfaces, and then save the configuration to a file in NVRAM.
If you have already configured the AGM, you can download a runtime image from a TFTP server on the network. To download an image from a TFTP server, no supervisor engine interaction is required. TFTP downloads can take place over the out-of-band Ethernet management port, or over the internal Gigabit Ethernet connections. To perform a network download over the internal Gigabit Ethernet connections, you must first bring up these ports and configure them.
 |
Note Before you can download an image, you must first configure the management port. See the"Configuring the Management Port" section. |
To download an image to bootflash from Catalyst Operating System on Supervisor Engine I and II, access the AGM using the session command:
Console> (enable) session
To download an image to bootflash from Cisco IOS on supervisor engine III and IV, access the AGM using the attach command:
Switch# attach module module_number
Enter the following command in privileged mode:
copy tftp: [/directory] /filename [/directory] /filename
The console port mode switch allows you to connect a terminal to the AGM using either a Catalyst 5000 family supervisor engine III console cable or the console cable and adapters provided with a Catalyst 4000 family switch.
 |
Note Use a paper clip or a small, pointed object to access the console port mode switch. |
Use the console port mode switch as follows:
 |
Note You should not have to connect a terminal to the AGM console port. |
When your terminal is connected to the supervisor engine I or II console port, use the session command to access the Layer 3 services module for Gateway configuration.
When your terminal is connected to the supervisor engineIII or IV console port, use the attach module command to access the Layer 3 services module for Gateway configuration.
The console port allows you to access the AGM either locally (with a console terminal) or remotely (with a modem). The console port is an EIA/TIA-232 asynchronous, serial connection with an RJ-45 connector.
For complete console port cabling specifications and pinouts, refer to the Catalyst 4000 Family Installation Guide.
 |
Note The accessory kit that shipped with your Catalyst 4000 family switch contains the cable and adapters to connect a terminal or modem to the console port. These cables and adapters are the same as those shipped with the Cisco 2500 series routers and other Cisco products. |
To connect a terminal to the console port using the cable and adapters provided with the Catalyst 4000 family switch, ensure that the console port mode switch is in the in position (factory default). Connect to the port using the RJ-45-to-RJ-45 cable and RJ-45-to-DB-25 DTE adapter or RJ-45-to-DB-9 DTE adapter (labeled "Terminal").
To connect a terminal using a Catalyst 5000 Family supervisor engine III console cable, place the console port mode switch in the out position. Connect to the port using the Catalyst 4000 family supervisor engine III cable and the appropriate adapter for the terminal connection.
Check the documentation that came with your terminal to determine the baud rate. The baud rate of the terminal must match the default baud rate (9600 baud) of the console port.
Set up the terminal as follows:
To connect a modem to the console port, ensure that the console port mode switch is in the in position (factory default position). Connect the modem to the port using the RJ-45-to-RJ-45 cable and the RJ-45-to-DB-25 DCE adapter (labeled "Modem").
You can manage the AGM through the 10/100 management port by assigning it an IP address.
 |
Caution By default, the Fast Ethernet interface does not route data traffic. We do not recommend that you override this default configuration. |
The supervisor engine reports one IP address assigned to the AGM that can be used for network management through the Cisco Stack MIB.
If the Ethernet 10/100 management port is up and an IP address has been configured, the AGM selects the IP address assigned to the 10/100 Ethernet management port. If the management port is down or an IP address has not been configured, the AGM randomly selects an IP address that has been assigned to one of the Gigabit Ethernet ports or port channels as the network management IP address, provided the interface or subinterface associated with this IP address is up at the time of selection.
If the selected network management IP address is removed or the interface or subinterface associated with this IP address is shut down, the AGM selects another IP address as a replacement.
If all the interfaces are down or no IP address has been assigned to any interface or subinterface that is up, the IP address for network management is 0.0.0.0.
After each IP address selection or change of the IP address, the AGM sends an unsolicited message to the supervisor engine, which then populates the IP address attribute of the Cisco Stack MIB entry of the AGM.
The AGM has three slots in which you can install interface cards:
Each individual interface is identified by a slot number and a port number. The slots are numbered as follows:
 |
Note On the WIC-2A/S, the top slot is 0 and the bottom slot is 1. |
When you configure an interface, identify the interface name before the slot and port numbers. For example, if you install a serial T1 VWIC interface in slot 2, port 0 would be labeled as serial 2/0.
The Gigabit Ethernet port interface name, slot, and port number are gigabit-ethernet 0/0:S. The S represents the possible subinterfaces, which could be one of six VLAN connections.
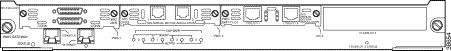
Figure 3-1 shows the AGM front panel.
Cisco voice gateways run versions of the Cisco IOS software that includes specialized adaptations for Voice over IP (VoIP) and Media Gateway Control Protocol (MGCP). If you are familiar with other versions of Cisco IOS, you will find configuring Cisco voice gateways straightforward because you will use the Cisco IOS CLI, with which you are familiar.
If you have never used the Cisco IOS CLI, you should still be able to perform the configuration required using the instructions and examples provided in this guide. To help get you started, this section provides a brief overview of some of the main features of the CLI. For more information, refer to the Cisco IOS configuration guides and command references.
This section contains these topics:
Use the question mark (?) and arrow keys to help you enter commands, as follows:
Gateway> ?
Gateway> s?
Gateway> show ?
The Cisco IOS interface is divided into different modes. Each command mode permits you to configure different components on your gateway. The commands available at any given time depend on which mode you are currently using. Entering a question mark (?) at the prompt displays a list of commands available for each command mode. Table 3-2 lists the most common command modes.
 |
TimeSaver Each command mode restricts you to a subset of commands. If you are having trouble entering a command, check the prompt and enter the question mark (?) for a list of available commands. You might be in the wrong command mode or using the wrong syntax. |
In the following example, which uses the default prompt (Gateway>), notice how the prompt changes after each command to indicate a new command mode:
Gateway> enable
Password: <enable password>
Gateway#configure terminal
Gateway(config-if)# line 0
Gateway(config-line)# controller t1 1/0
Gateway(config-controller)# exit
Gateway(config)# exit
Gateway#
%SYS-5-CONFIG_I: Configured from console by console
The last message is normal and does not indicate an error. Press Return to return to the prompt.
 |
Note You can press Ctrl-Z in any mode to return immediately to privileged EXEC mode (Gateway#), instead of entering exit, which returns you to the previous mode. |
If you want to undo a command you entered or disable a feature, enter the keyword no before most commands; for example, no mgcp.
You need to enter the copy running-config startup-config command to save your configuration changes to nonvolatile random-access memory (NVRAM), so the changes are not lost if there is a system reload or power outage. For example:
Gateway# copy running-config startup-config
Building configuration...
 |
Note It might take a minute or two to save the configuration to NVRAM. After the configuration has been saved, the privileged EXEC mode prompt (Gateway#) reappears. |
To configure the AGM interfaces, you can use the setup command facility and automate the process. If you need interface configuration examples for using the setup command facility, go to the following url:
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Posted: Thu Dec 19 10:06:07 PST 2002
All contents are Copyright © 1992--2002 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Important Notices and Privacy Statement.