|
|

February 16, 1998
This document describes what is new in this release, including a list of the new features and the fixed problems. It also lists the known (open) problems for this release and contains information about the Catalyst 3900 Token Ring Switch that was not included in the Catalyst 3900 Token Ring Switch User Guide. This document is available on the Cisco Connection Documentation CD-ROM or in print.
Sections in this document include the following:
This release includes support for larger frame sizes, up to 17800 bytes. The use of larger frame sizes in a stacked configuration requires revision B of the Stack Port module. The initial release of the Catalyst 3900 Stack Port module (which is identified as revision A) did not support MTUs greater than 4472. Revision B of the Catalyst 3900 Stack Port module supports MTUs of up to 17800.
When configuring MTUs, keep the following in mind:
If you attempt to create a stack that contains switches that have both revision A and revision B Stack Port modules, the stack will not completely form. If the controlling switch (the first switch in the stack to come up) contains a revision A Stack Port module, only the switches with revision A modules will be able to join the stack. Likewise, if the controlling switch contains a revision B Stack Port module, only the switches with revision B modules will be able to join the stack.
To verify the revision level of a Stack Port module on a Catalyst 3900, see the Module Information panel. This panel has been updated to include the revision level of the Stack Port module in the HW Rev field. A Stack Port module revision B will be displayed as 0.B.
Other console panels have been updated to allow you to configure larger MTUs for the physical ports, the TrBRFs, and the LECs (if an ATM module is installed).
You cannot configure a port MTU that is greater than the MTU configured for the TrBRF to which the port belongs. Likewise, you cannot configure an LEC MTU that is greater than the MTU configured for the TrBRF to which the LEC belongs.
If you reduce the MTU for a TrBRF to a value that is less than the MTU currently configured for the individual ports or LECs in the TrBRF, the MTU for the ports or LECs will automatically be reduced to a value (1500, 4472, 8144, or 17800) that is less than that specified for the TrBRF.
The following is a list of problems that have been resolved in this release.
| Problem Identifier | Problem Description |
|---|---|
| CSCdj57844 | TrCRFs are not removed from the list of monitored TrCRFs for SPAN after they are disassociated with an ATM port. |
| CSCdj57846 | The console allows user to specify VLAN 1003 for deletion then returns an error message. VLAN 1003 cannot be deleted. |
| CSCdj58703 | Setting the port to monitor for SPAN is not being preserved across a stack. |
| CSCdj62863 | Setting the monitored TrCRF for SPAN is not working through SNMP. |
| CSCdj63455 | The station information is not cleared when the port closes. |
| CSCdj63615 | The Port Status panel displays an incorrect status for ports (19 or 20) running in RI/RO mode. |
| CSCdj65350 | The label of Active Monitor Participate on the 802.5 State Information panel has been changed to Force Active Monitor Participate to more accurately reflect the information being displayed. |
| CSCdj64081 | You cannot delete MAC filters using SNMP if the switch is in a stack. |
| CSCdj66945 | An invalid warning is displayed on the secondary switch in a stack when you assign an ATM port to a TrCRF on the primary switch. |
| CSCdj69326 | The ATM module does not advertise the IP address of the parent TrBRF during ILMI exchanges. |
| CSCdj71567 | The RMON code does not support the correct the maximum number of stations (260). |
| CSCdj73281 | The MTU for ports is incorrectly reported through SNMP. |
| CSCdj73405 | An erroneous warning during the boot process may cause the ATM port to be disabled. |
| CSCdj75068 | The ATM port quits forwarding traffic after a change to the Spanning-Tree Protocol state. |
| CSCdj75861 | Source-routed frame sessions fail after the Catalyst 3900 has joined a stack. |
| CSCdj76365 | When using the hot stand-by router protocol (HSRP) on a router that is connected to an ATM Token Ring ELAN, it is possible for the Catalyst 3900 ATM module to have the wrong ATM address for the router in its LE-ARP cache. |
| CSCdj76615 | Heat-related DRAM problems on the ATM module. |
| CSCdj78819 | Catalyst 3900 is not responding to IP requests in certain network configurations that contain redundant source- route bridges. |
This section lists the currently known problems.
Problem Identifier: CSCdj23476
Problem Description: If a device attached to a port begins to flood a given port with large frames (over 4Kb) addressed to the spanning-tree functional address, the message STP: Cpubuf_to_Netbuf No More Memory is displayed and a fatal error could occur.
Recommended Action: Identify the faulty device that is flooding the given port and remove it from the network.
Problem Identifier: CSCdj31691
Problem Description: The TrCRF hop counts for ARE and STE explorers displayed on the console can appear as 14, which is outside the valid range. This problem occurs if an SNMP manager is used to set the value to 14. This may cause explorers with 30 byte routing information fields to be dropped and not forwarded across a TrBRF.
Recommended Action: Users should only set hop counts to the values 1 through 13.
Problem Identifier: CSCdj33434
Problem Description: There are known problems associated with inserting Catalyst 3900 ports into the Transition Engineering, Inc. LAN Master TR 16 Retiming Hub.
Recommended Action: If you experience problems opening into this particular concentrator, do the following:
Step 1 Check the Operation Mode of the Catalyst 3900 port on the Port Configuration panel. If it is A-unknown, then configure it to be HDX station.
Step 2 Check the Media Speed of the Catalyst 3900 port on the Port Configuration panel. If it is A-unknown, then configure it to be the speed at which the Transition Engineering concentrator is currently running.
Step 3 Insert the Catalyst 3900 port into another MAU. Once the port opens, quickly move it out of that MAU and into the Transition Engineering hub.
Problem Identifier: CSCdj34650
Problem Description: A TFTP code download fails when the user tries to clear a message from a telnet or console screen. This problem occurs if a TFTP code download is in progress and an event occurs that causes a message to be displayed on the screen. The user presses the Esc key to clear the message and the download is aborted.
Recommended Action: Do not press Esc to clear the message until after the code has been downloaded and written to flash. The user will see the prompt to press the Return key below the message box. This problem will be corrected in a future code release.
Problem Identifier: CSCdj37544
Problem Description: The console cannot always be used to terminate telnet sessions to the switch.
Recommended Action: None
Problem Identifier: CSCdj37783
Problem Description: The following three MIB objects will return values with the incorrect magnitude. The values should be in 1/100's of a second, instead the values are actually in seconds.
Recommended Action: Multiply the returned number by 100 to get the value in 1/100's of a second.
Problem Identifier: CSCdj42684
Problem Description: If you have a community string "private" defined on the switch and send an SNMP set with "pri" it will not result in an authentication trap. Instead a "No Such Name" error will be returned. If you send a completely different string, such as "xxx" in a SNMP set, then it will time-out and send a trap.
Recommended Action: None.
Problem Identifier: CSCdj43071
Problem Description: Creating an entry in the unsupported RMON group alarm halts the SNMP agent in the box.
Recommended Action: Do not attempt to add entries to the RMON group alarms.
Problem Identifier: CSCdj43075
Problem Description: The values for the access protocol, individual address count, and phantom drive support are not correct when read from an SNMP agent.
Recommended Action: Read the information from the switch console.
Problem Identifier: CSCdj44177
Problem Description: After a period of time, the Current Spanning Tree Information panel may show incorrect information for the Root Port and for the Max Message Age. The display is wrong on both serial and Telnet consoles.
Recommended Action: None.
Problem Identifier: CSCdj49835
Problem Description: In some situations, selecting End on the Message Log Information panel does not scroll the message log display entirely to the end of the messages.
Recommended Action: If selecting End does not scroll to the bottom of the message log, select More.
Problem Identifier: CSCdj50465
Problem Description: The switch will not learn a new ring number after the ring number has been set back to "auto". For example, assume that the ring number for a TrCRF has been configured for "auto". When the switch learns the ring number (for example, 0x123) for this TrCRF, it will correctly reflect this in the Ring Number field by displaying "A-0x123". If you attempt to reset the learned ring number by entering a null value for the Ring Number field, the switch will display "auto" for the ring number, but it will not learn a different ring number until the switch is rebooted.
Recommended Action: One option is to reboot the switch. Alternatively, you can do the following:
Step 1 On the VTP VLAN Configuration panel, select Change and specify the VLAN ID of the TrCRF.
Step 2 On the VTP VLAN Parameter Configuration for TrCRF panel, select the Ring Number field and temporarily configure the ring number using the value that should have been learned.
Step 3 Select Return to exit the VTP VLAN Parameter Configuration for TrCRF panel.
Step 4 On the VTP VLAN Configuration panel, select Change again and specify the VLAN ID of the TrCRF.
Step 5 On the VTP VLAN Parameter Configuration for TrCRF panel, select the Ring Number field and enter a null value to set the ring number back to auto, which will enable the switch to relearn a new ring number.
Problem Identifier: CSCdj53766
Problem Description: The current version of the switching ASIC in the Catalyst 3900 does not reduce STE frames. The ASIC could forward a frame back onto a ring that it has already traversed.
Recommended Action: To prevent this situation, do one of the following:
Problem Identifier: CSCdj68288
Problem Description: When using two switches in a back-to-back stack configuration, one of the switches may hang during heavy traffic (when there are 2000 or more addresses to be learned at 50% ring utilization).
Recommended Action: None. This problem does not occur under normal traffic conditions.
Problem Identifier: CSCdj75021
Problem Description: The source address of a beaconing station is not being reported on the DTR MAC TXI Information panel or through SNMP.
Recommended Action: None.
Problem Identifier: CSCdj78821
Problem Description: It is possible to lose IP connectivity to the switch via the ATM port. This condition can occur under heavy address management loads, which can be caused by Spanning- Tree state changes, reboot and reconfiguration of ATM module, switch congestion, or by having multiple TrCRFs assigned to the ATM module.
Recommended Action: Using the Local VLAN Port Configuration panel, unassigned one of the TrCRFs from the ATM port and then reassign it. Do this for each TrCRF, one at a time.
Problem Identifier: CSCdj84923
Problem Description: When upgrading the Catalyst 3900 main code from 1.0(x) to 2.1(1), the MTU for Token Ring ports is set to 1500 bytes. This problem occurs only when you upgrade from 1.0(x) to 2.1.1. It does not occur when you upgrade from 2.0(1) to 2.1(1).
Recommended Action: If you haven't upgraded to 2.1(1), you can avoid this problem. If you have already upgraded to 2.1(1), you can correct this problem.
This section contains information that was not included in the Catalyst 3900 Token Ring Switch User Guide. The headings in this section correspond with the applicable section titles in the documentation.
The Switch Information and Stack Information options have been renamed to Switch Configuration and Stack Configuration.
The MAC address (burned in or locally administered) displayed on the Switch Configuration panel is used as the basis for the MAC addresses of the ports and VLANs of the switch. For more information about how MAC addresses are assigned, refer to the "Codes and IDs" appendix.
The Module Information panel has been enhanced. The Revision field as documented in the Catalyst 3900 Token Ring Switch User Guide has been replaced with two fields:
The module numbers displayed on the Module Information panel have the following meaning:
The possible statuses of a module are up, down, and empty. Up indicates that the module is properly installed. It does not imply that any ports on the module are connected and operational.
The VLAN with the VLAN name of "default" is an Ethernet VLAN and is the VLAN that will be used to transmit information for Cisco proprietary protocols, such as VTP and CDP.
A management domain is a logical grouping of VLANs used by the VLAN Trunking Protocol (VTP) for the purpose of administration and management. VTP parameters are propagated throughout the VLANs within a single management domain. While you can have duplicate VLAN names in a network, each VLAN name within a management domain must be unique. A management domain is not device specific. Different devices may belong to the same management domain if the VLANs defined for the devices belong to the same management domain. Likewise, a device may belong to multiple management domains if the VLANs defined for the device belong to different management domains.
The possible values for the State of a VLAN are Operational and Suspended. By default, all VLANs are Operational. You can change the states for TrBRFs and TrCRFs only. Consider the following when changing the states of a TrBRF or TrCRF:
For TrCRFs, you can configure the ring number or allow the Catalyst 3900 to learn the ring number. To enable ring number learning, the Local Mode (on the VTP Administrative Configuration panel) must be set to Transparent (which is the default) and the Ring Number (on the VTP VLAN Parameter Configuration for the TrCRF) must be set to auto (which is the default). If you have set the Local Mode to Client or Server, you cannot set the Ring Number to auto. Also, if you have previously set the Local Mode to Transparent and the Ring Number to auto, you cannot change the Local Mode while ring number learning is in progress.
The VTP VLAN Configuration panel (Figure 1) has been redesigned. The panel now lists the VLANs with respect to their parent-child relationships. Each TrBRF is followed by an indented list of the TrCRFs for which it is a parent. You can also sort the entries on the panel by VLAN ID. This is particularly useful when you are searching for a particular VLAN or when you want to add a VLAN and need to see the IDs that have already been assigned.
The panel also displays additional information about the VLANs.
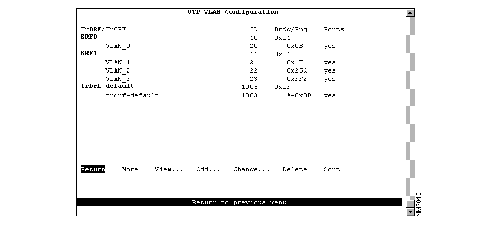
The following information is displayed on this panel:
| To | Select | Then |
|---|---|---|
| View the current configuration of a VLAN, including a list of associated ports for a TrCRF... | View | Specify the VLAN ID. |
| Add a new TrBRF VLAN configuration... | Add | Specify the VLAN ID. Select TrBRF. Refer to the "Adding or Changing TrBRF VLAN Parameters" section of the Catalyst 3900 Token Ring Switch User Guide. |
| Add a new TrCRF VLAN configuration... | Add | Specify the VLAN ID. Select TrCRF. Refer to the "Adding or Changing TrCRF VLAN Parameters" section of the Catalyst 3900 Token Ring Switch User Guide. |
| Change an existing TrBRF VLAN configuration... | Change | Specify the VLAN ID and refer to the "Adding or Changing TrBRF VLAN Parameters" section of the Catalyst 3900 Token Ring Switch User Guide. |
| Change an existing TrCRF VLAN configuration... | Change | Specify the VLAN ID and refer to the "Adding or Changing TrCRF VLAN Parameters" section of the Catalyst 3900 Token Ring Switch User Guide. |
| Delete a VLAN... | Delete | Specify the VLAN ID. |
| Display a list of VLANs sorted by VLAN ID... | Sort | Select Sort_by_VLAN_ID. |
| Save your changes... | Return |
If you have a Stack Port module revision B or later installed in your Catalyst 3900, you can configure MTUs larger than 4472. Possible values for the MTU are 1500 through 18190. The default is 4472.
If you reduce the MTU for a TrBRF to a value that is less than the MTU currently configured for the individual ports in the TrBRF, the MTU for the ports will automatically be reduced to a value (1500, 4472, 8144, or 17800) that is less than that specified for the TrBRF.
The IP information that you can configure is associated with a TrBRF. Therefore, if the ports of the Catalyst 3900 are assigned to more than one TrBRF, when you select IP configuration you will be presented with a list of possible TrBRFs from which to choose.
The SNMP Trap Receivers information that you can configure is associated with a TrBRF. Therefore, if the ports of the Catalyst 3900 are assigned to more than one TrBRF and you select Trap Receivers on the SNMP Configuration panel, you will be presented with a list of possible TrBRFs from which to choose.
When you configure spanning-tree parameters for a TrBRF, you:
Likewise, when you configure the spanning-tree parameters for a TrCRF, you:
You can create your own spanning tree by setting the STP Participation to No and manually controlling the forwarding state of each logical and physical port using the STP Mode fields. However, if you then decide to use one of the standard Spanning-Tree Protocols and change the STP Participation to a value other than no, you must set the STP Mode for each port to auto. The Catalyst 3900 will not automatically change the forwarding mode of related ports when you change the STP Participation from No to one of the Spanning-Tree Protocols.
To further distinguish between the spanning-tree parameters configured at the TrBRF level from those configured at the TrCRF level, the following field labels have been changed on the Spanning Tree for TrBRF panel.
| Old Field Label | New Field Label |
|---|---|
| Switch Priority | Bridge Priority |
| Switch Hello Time | Bridge Hello Time |
| Switch Maximum Message Age | Bridge Maximum Message Age |
| Switch Forward Delay | Bridge Forward Delay |
Two fields on the Spanning Tree for TrCRF panel warrant further explanation.
If a port has been disabled by the Catalyst 3900 software, the Enabled field on the Port Configuration panel will display No (auto-disabled). To manually enable the port, move to the Enabled field and select Yes.
If you have a Stack Port module revision B or later installed in your Catalyst 3900, you can configure MTUs larger than 4472. Possible values for the port MTU are 1500, 4472, 8144, and 17800. The default is 4472. You cannot configure a port MTU that is greater than the MTU configured for the TrBRF to which the port belongs.
On the CDP Configuration panel, the field labeled Trans Frequency Time has been renamed to Message Interval.
A Switched Port Analyzer (SPAN) port performs the function of port mirroring. Traffic on the monitored port is copied to the monitoring port.
Before you use a SPAN port to monitor traffic, make sure that the SPAN port is isolated by assigning it to its own TrCRF and TrBRF. See "Configuring VLANs and VTP" for more information about how to define a TrBRF and a TrCRF, and how to assign a port to a TrCRF.
You cannot specify a port that is a member of a TokenChannel as a monitoring port. Likewise, you cannot add a port that has been specified as a monitoring port to a TokenChannel.
The Running TokenChannel Information option has been renamed to Current Token Channel Information.
The Catalyst 3900 Token Ring Switch User Guide incorrectly states that you can change the names assigned to protocol classes. You cannot change the names.
When configuring MAC address filters for a port, you cannot configure multiple filters for a port that include the same MAC address. For example, you cannot specify the same MAC address in both a 'Block Destination Address' filter and a 'Block Source Address' filter for the same port. Also, you cannot specify the same MAC address in both an 'Allow Destination Address' filter and an 'Allow Source Address' filter for the same port.
The Message Log Information panel has been enhanced. The log can now maintain a list of up to 200 messages. Once 200 messages have been logged, new messages received will be added to the end of the log and the oldest message will be deleted from the panel. The log entry numbers continue to increment, indicating the total number of messages received.
To view the message log, select Message Log Information from the Statistics panel. The first (oldest) seven messages are displayed. You can use the options at the bottom of the panel to move through the message log.
To delete all messages from the message log, select Clear. You will be prompted to confirm your request to clear the log.
The Active Monitor Participate field has been changed to Force Active Monitor Participate. This field indicates whether the switch will seek to become the active monitor. Possible values are Enabled (yes) and Disable (no). Disable does not prevent the switch from becoming the active monitor, it only means that the switch will not seek to become the active monitor.
When changes are made to the Catalyst 3900 software, the new image is posted to CCO. You can then obtain a copy of the image and download it to your switch.
For service and support for a product purchased from a reseller, contact the reseller. Resellers offer a wide variety of Cisco service and support programs, which are described in the section "Service and Support" in the information packet that shipped with your product.
For service and support for a product purchased directly from Cisco, use CCO.
Cisco Connection Online (CCO) is Cisco Systems' primary, real-time support channel. Maintenance customers and partners can self-register on CCO to obtain additional information and services.
Available 24 hours a day, 7 days a week, CCO provides a wealth of standard and value-added services to Cisco's customers and business partners. CCO services include product information, product documentation, software updates, release notes, technical tips, the Bug Navigator, configuration notes, brochures, descriptions of service offerings, and download access to public and authorized files.
CCO serves a wide variety of users through two interfaces that are updated and enhanced simultaneously: a character-based version and a multimedia version that resides on the World Wide Web (WWW). The character-based CCO supports Zmodem, Kermit, Xmodem, FTP, and Internet e-mail, and it is excellent for quick access to information over lower bandwidths. The WWW version of CCO provides richly formatted documents with photographs, figures, graphics, and video, as well as hyperlinks to related information.
You can access CCO in the following ways:
For a copy of CCO's Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ), contact cco-help@cisco.com. For additional information, contact cco-team@cisco.com.
Documentation for Cisco products is available in three forms: in a CD-ROM package, printed books, and on the World Wide Web. You have the option of subscribing to the CD ROM package through an update service. Or you can order printed documentation at an additional cost. Refer to the information packet included with the router for detailed ordering information. You can also access Cisco documentation on the World Wide Web URL http://www.cisco.com.

|
|