|
|

This chapter provides information about these topics:
The Catalyst 2950 switches are stackable Ethernet switches to which you can connect workstations and other network devices, such as servers, routers, and other switches. The switches can be deployed as backbone switches, aggregating 10BASE-T, 100BASE-TX, and Gigabit Ethernet traffic from other network devices. Refer to the Catalyst 2950 Desktop Switch Software Configuration Guide for examples showing how you might deploy the switches in your network.
Table 1-1 lists the switch features, and Figure 1-1 through Figure 1-8 show the Catalyst 2950 switches.
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
Hardware |
|
Configuration |
|
|
| 1GBIC = Gigabit Interface Converter 2DC = direct current 3AC = alternating current |
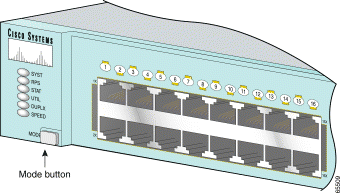
The switch front panel contains the ports, the LEDs, and the Mode button. Figure 1-1 to Figure 1-8 show the switches.

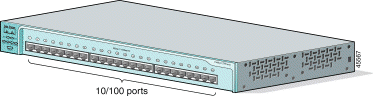
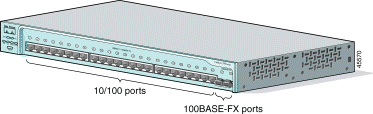
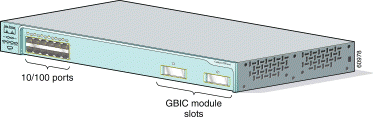


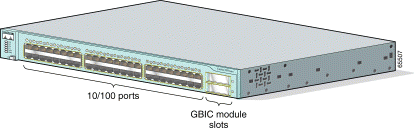

The 10/100 ports use RJ-45 connectors and twisted-pair cabling. The ports can connect to these devices:
 |
Note When connecting the switch to workstations, servers, and routers, be sure that the cable is a twisted-pair straight-through cable. When connecting the switch to hubs or other switches, use a twisted-pair crossover cable. Pinouts for the cables are described in "Connectors and Cables." |
The 10/100 ports can be explicitly set to operate in any combination of half duplex, full duplex, 10 Mbps, or 100 Mbps. They can also be set for speed and duplex autonegotiation, compliant with IEEE 802.3U. In all cases, the cable length from a switch to an attached device cannot exceed 328 feet (100 meters).
When set for autonegotiation, a port senses the speed and duplex settings of the attached device and advertises its own capabilities. If the attached device supports autonegotiation, the port negotiates the best connection (that is, the fastest line speed that both devices support and full-duplex transmission, if the attached device supports it) and configures itself accordingly.
The 100BASE-FX ports use 50/125- or 62.5/125-micron multimode fiber-optic cabling. These ports only operate at 100 Mbps in full-duplex mode.
In full-duplex mode (the default), the cable length from a switch to an attached device cannot exceed 6562 feet (2 kilometers).
You can connect a 100BASE-FX port to an SC or ST port on a target device by using one of the MT-RJ fiber-optic patch cables listed in Table 1-2. Use the Cisco part numbers in Table 1-2 to order the patch cables that you need.
| Type | Cisco Part Number |
|---|---|
1-meter, MT-RJ-to-SC multimode cable | CAB-MTRJ-SC-MM-1M |
3-meter, MT-RJ-to-SC multimode cable | CAB-MTRJ-SC-MM-3M |
5-meter, MT-RJ-to-SC multimode cable | CAB-MTRJ-SC-MM-5M |
1-meter, MT-RJ-to-ST multimode cable | CAB-MTRJ-ST-MM-1M |
3-meter, MT-RJ-to-ST multimode cable | CAB-MTRJ-ST-MM-3M |
5-meter, MT-RJ-to-ST multimode cable | CAB-MTRJ-ST-MM-5M |
The 10/100/1000 ports on Catalyst 2950T-24 switches use RJ-45 connectors and twisted-pair cabling. The ports can connect to these devices:
 |
Note When connecting to a 1000BASE-T-compatible device, be sure to use a four twisted-pair, Category 5 cable. |
 |
Note When connecting the switch to workstations, servers, and routers, be sure that the cable is a twisted-pair straight-through cable. When connecting the switch to hubs or other switches, use a twisted-pair crossover cable. Pinouts for the cables are described in "Connectors and Cables." |
The 10/100/1000 ports on Catalyst 2950T-24 switches can be explicitly set to operate at 10 or 100 Mbps in half- or full-duplex mode or at 1000 Mbps in full-duplex mode. The default duplex setting is full duplex. They can also be set for speed and duplex autonegotiation, compliant with IEEE 802.3AB. In all cases, the cable length from a switch to an attached device cannot exceed 328 feet (100 meters).
The GBIC module slots support these modules:
For more information about these GBICs, refer to your GBIC documentation.
You can use the LEDs to monitor switch activity and performance. Figure 1-9, Figure 1-10, and Figure 1-11 show the location of the LEDs and the Mode button that you use to select the port mode. Changing the port mode changes the information provided by each port status LED.
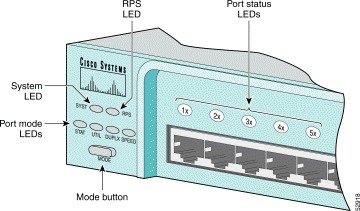
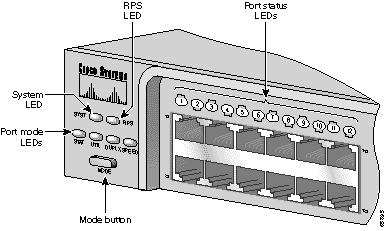
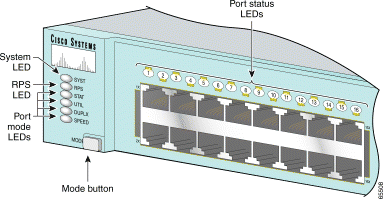
The system LED shows whether the system is receiving power and functioning properly. Table 1-3 lists the LED colors and meanings.
| Color | System Status |
|---|---|
Off | System is not powered up. |
Green | System is operating normally. |
Amber | System is receiving power but is not functioning properly. |
For information about the system LED colors during the power-on self-test (POST), see the "Running POST" section.
The RPS LED shows the RPS status. Table 1-4 lists the LED colors and meanings.
| Color | RPS Status |
|---|---|
Off | RPS is off or is not installed. |
Solid green | RPS is connected and ready to provide back-up power. |
Flashing green | RPS is connected but is unavailable because it is providing power to another device (redundancy has been allocated to a neighboring device). |
Solid amber | RPS is in standby mode or in a fault condition. Press the Standby/Active button on the RPS, and the LED should turn green. If it does not, the RPS fan could have failed. Contact Cisco Systems. |
Flashing amber | The internal power supply in a switch has failed, and the RPS is providing power to the switch (redundancy has been allocated to this device). |
For more information about the Cisco RPS 300, refer to the Cisco RPS 300 Redundant Power System Hardware Installation Guide.
Each port has a port status LED, also called a port LED. These LEDs, as a group or individually, display information about the switch and the individual ports. The port modes (see Table 1-5) determine the type of information displayed.
| Mode LED | Port Mode | Description |
|---|---|---|
STAT | Port status | The port status. This is the default mode. |
UTIL | Switch utilization | The current bandwidth in use by the switch. |
DUPLX | Port duplex mode | The port duplex mode: half duplex or full duplex. |
SPEED | Port speed | The port operating speed: 10 or 100 Mbps for 10/100 ports and 10, 100, or 1000 Mbps for 10/100/1000 ports. |
To select or change the port mode, press the Mode button (see Figure 1-12, Figure 1-13, and Figure 1-14) to highlight the mode that you want. Release the button to enable the highlighted mode.
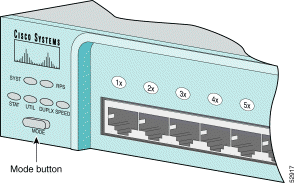

When you change the port mode, the meanings of the port LED colors change. Table 1-6 explains how to interpret these colors.
| Port Mode | Color | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
STAT (port status) | Off | No link. |
| Solid green | Link present. |
| Flashing green | Activity. Port is transmitting or receiving data. |
Alternating green-amber | Link fault. Error frames can affect connectivity, and errors such as excessive collisions, CRC errors, and alignment and jabber errors are monitored for a link-fault indication. | |
Solid amber | Port is not forwarding. Port was disabled by management, an address violation, or Spanning Tree Protocol (STP). Note After a port is reconfigured, the port LED can remain amber for up to 30 seconds while STP checks the switch for possible loops. | |
UTIL (utilization) | Green | The current backplane utilization that is displayed over the amber LED background on a logarithmic scale. |
| Amber | The maximum backplane utilization since the switch was powered on. |
| Green and amber | See Figure 1-15 to Figure 1-18 for details. Note If the current utilization exceeds the maximum utilization, the maximum utilization is automatically updated. |
Off | Port is operating in half duplex. | |
(half or full duplex) | Green | Port is operating in full duplex. |
SPEED (speed) | 10/100 ports | |
Off | Port is operating at 10 Mbps. | |
Green | Port is operating at 100 Mbps. | |
10/100/1000 ports | ||
Off | Port is operating at 10 Mbps. | |
Green | Port is operating at 100 Mbps. | |
Flashing green | Port is operating at 1000 Mbps. | |
1000BASE-X GBIC module ports | ||
Off | Port is not operating. | |
Port is operating at 1000 Mbps. | ||
For more information about GBIC LEDs, refer to your GBIC documentation.
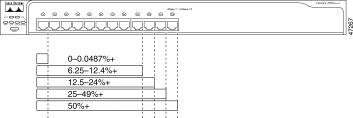
Figure 1-15 to Figure 1-18 show the bandwidth utilization percentages displayed by the right-most LEDs.
If all LEDs on Catalyst 2950-12, 2950-24, 2950C-24, and 2950T-24 switches are green (no amber showing), the switch is using 50 percent or more of the total bandwidth. If the far-right LED is off, the switch is using more than 25 but less than 50 percent of the total bandwidth, and so on. If only the far-left LED is green, the switch is using less than 0.0488 percent of the total bandwidth. (See Figure 1-15.)
If all LEDs on Catalyst 2950G-12-EI switches are green (no amber showing), the switch is using 50 percent or more of the total bandwidth. If the LED for GBIC module slot 2 is off, the switch is using more than 25 but less than 50 percent of the total bandwidth. If LEDs for both GBIC module slots are off, the switch is using less than 25 percent of the total bandwidth, and so on. (See Figure 1-16.)
If all LEDs on Catalyst 2950G-24-EI and 2950G-24-EI-DC switches are green (no amber showing), the switch is using 50 percent or more of the total bandwidth. If the LED for GBIC module slot 2 is off, the switch is using more than 25 but less than 50 percent of the total bandwidth. If LEDs for both GBIC module slots are off, the switch is using less than 25 percent of the total bandwidth, and so on. (See Figure 1-17.)
If all LEDs on Catalyst 2950G-48-EI switches are green (no amber showing), the switch is using 50 percent or more of the total bandwidth. If the LED for the upper GBIC module slot is off, the switch is using more than 25 but less than 50 percent of the total bandwidth. If LEDs for both GBIC module slots are off, the switch is using less than 25 percent of the total bandwidth, and so on. (See Figure 1-18.)



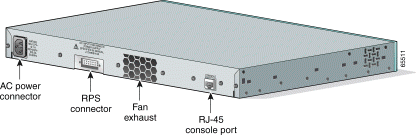
Other than the Catalyst 2950G-24-EI-DC switch, the rear panel of a Catalyst 2950 switch has an AC power connector, an RPS connector, and an RJ-45 console port. (See Figure 1-19 and Figure 1-20.)
The rear panel of the Catalyst 2950G-24-EI-DC switch has a DC power connector (also referred to as the terminal block header), a DC ground lug, an RPS connector, and an RJ-45 console port. (See Figure 1-21.)

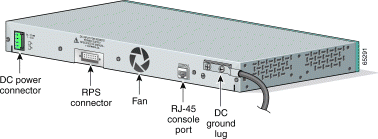
The Catalyst 2950G-24-EI-DC switch has an internal DC-power converter. It has dual feeds (A and B) that are diode-OR-ed into a single power block. For installation instructions, see the "Connecting to DC Power" section.
 |
Caution You must connect the Catalyst 2950G-24-EI-DC switch only to a DC-input power source that has an input supply voltage from -36 to -72 VDC. If the supply voltage is not in this range, the switch might not operate properly or might be damaged. |
The RPS is a 300W redundant power system that can support six external network devices and provides DC power to one failed device at a time. It automatically senses when the internal power supply of a connected device fails and provides power to that device, preventing loss of network traffic.
 |
Warning Attach only the Cisco RPS 300 (model PWR300-AC-RPS-N1) to the RPS receptacle. |
For more information about the Cisco RPS 300, refer to the Cisco RPS 300 Redundant Power System Hardware Installation Guide.
You can connect a switch to a PC through the console port and the supplied rollover cable and DB-9 adapter. If you want to connect a switch to a terminal, you need to provide an RJ-45-to-DB-25 female DTE adapter. You can order a kit (part number ACS-DSBUASYN=) with that adapter from Cisco. For console-port and adapter-pinout information, see the "Cable and Adapter Specifications" section.
Catalyst 2950 switches offer these management options:
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Posted: Mon Dec 17 18:28:05 PST 2001
All contents are Copyright © 1992--2001 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Important Notices and Privacy Statement.