|
|

This chapter covers the following topics:
For general information about the Script Editor, see "Script Editor Overview".
After you save a script, you should check that all routes referenced have valid labels for the routing clients and dialed numbers for which you have scheduled the script.
 |
Note You must have saved the script to the ICM database before you can check the routes. |
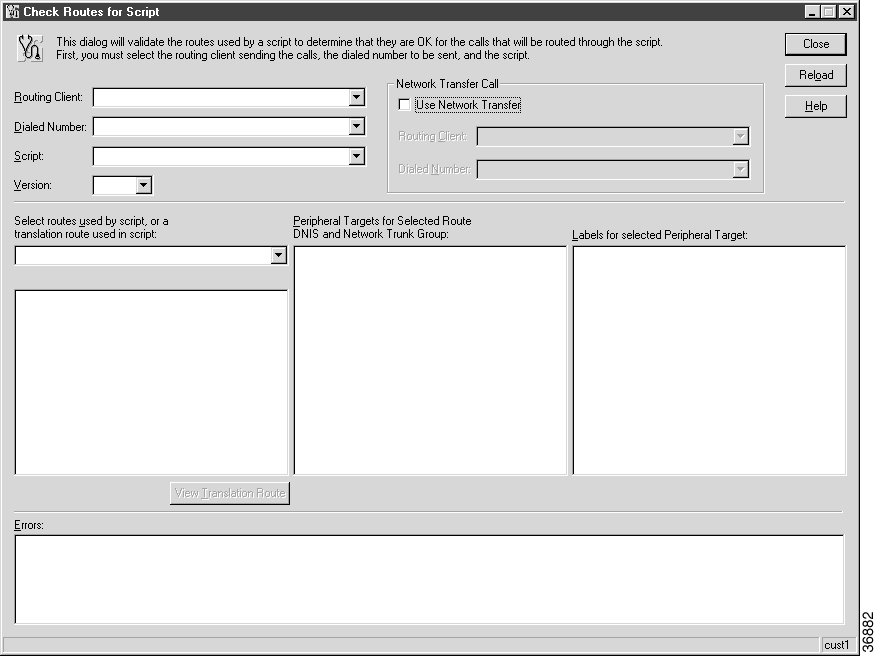
Step 2 Using the drop-down lists, select the following:
Step 3 To validate the route of a network transfer call target, select the Use Network Transfer check box and specify a routing client and a dialed number.
Step 4 Use the drop-down list to select Routes Used Directly by Script (the default) or Translation Route Used in Script. The routes referenced in the script appear in the left column. (If any of these routes do not have an associated label that is valid for the routing client and dialed number you have chosen, an error message appears in the Errors field.)
 |
Note To see the configuration details for a translation route, select the route name and click the View Translation Route button. (This button becomes enabled when you choose a specific translation route.) The Translation Route dialog box appears. |
Step 5 To see the specific peripheral targets associated with a route, select the route name in the left column. The associated peripheral targets appear in the center column.
The routes referenced in the script appear in the left column. If any of these routes does not have an associated label that is valid for the routing client and dialed number you have chosen, an error message appears in the Errors field at the bottom of the window.
Step 6 To see the specific labels associated with any of these peripheral targets, select the peripheral target. The associated peripheral targets appear in the right column.
The following symbols might appear next to a label:
 |
Note For more information about script version numbers, see the "General Script Administration" section. |
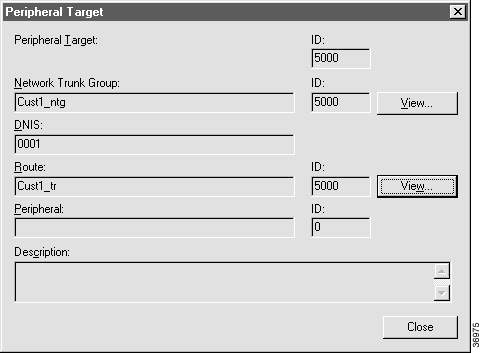
Step 7 To check configuration information for a route or peripheral target, double-click a route or peripheral target name. Check Routes displays the configuration information for that route or peripheral target.
 |
Note From the Peripheral Target dialog box, you can access information about the route by clicking the Route button. |
Step 8 To correct any problems you find through Check Routes, make changes within the Script Editor or the Configuration Manager.
 |
Note Remember to save any changes! |
Step 9 To see the effect of changes, click the Reload button in the Check Routes window. (If you have created a new version of the script, be sure to update the Version field.) Check Routes reads the latest version of scripts and configuration data from the local database.
Although the Script Editor may contain several versions of a script, only one version of a particular script can be active at one time: this is the version that ICM software runs if the script is currently scheduled.
There are three methods for setting the active version of a script:
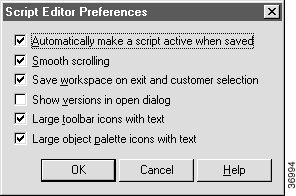
Step 2 Choose a checkbox setting for the Automatically Make a Script Active When Saved checkbox:
In an open script in edit mode, select Script > Make Active Version or click the Make Active Version button. ICM software makes the open script version the current active version.
Step 2 Select a script version and click the Activate button. ICM software makes that version the active version.
Once a script has been saved and scheduled, it is considered enabled. Use the Enabled Scripts dialog box to examine all scripts currently enabled in the system.
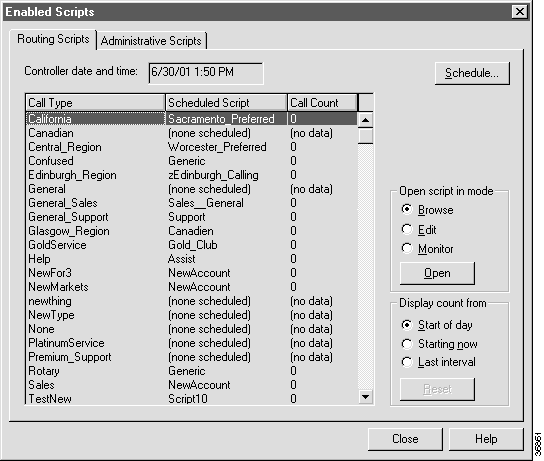
The dialog box lists all call types and the script that is currently scheduled for each. The Call Count column lists the number of calls the script has processed.
Step 2 Optionally, use the Display Count From section of the dialog box to choose how to display the number of calls processed. Whichever option you choose, the counts are updated every 15 seconds. This allows you to see which scripts are currently handling calls.
 |
Note The Call Count values are associated with scripts, not necessarily with call types. If the script has been scheduled for more than one call type, the Call Count value includes all calls processed by the script regardless of call type. |
Step 3 To see all administrative scripts scheduled for the current date and time, click the Administrative Scripts tab. This lists all administrative scripts.
After you create the script, you have to specify under what conditions you want ICM software to use it. For example, once you associate a script with a specific call type, you can instruct ICM software when the script should be active for the call type.
 |
Note The procedure for scheduling a script depends on whether it is a routing script or an administrative script. |
Step 2 Click the Schedules tab.
Step 3 Choose the call type you want to associate with the script and click the Add button. The Add Call Type Schedule dialog box appears.
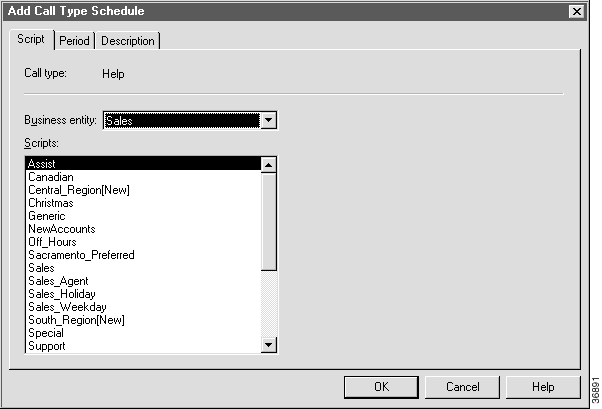
Step 4 Select the script you want to schedule and click the Period tab. Initially, this shows the default schedule. The default is to activate the script all day, every day.
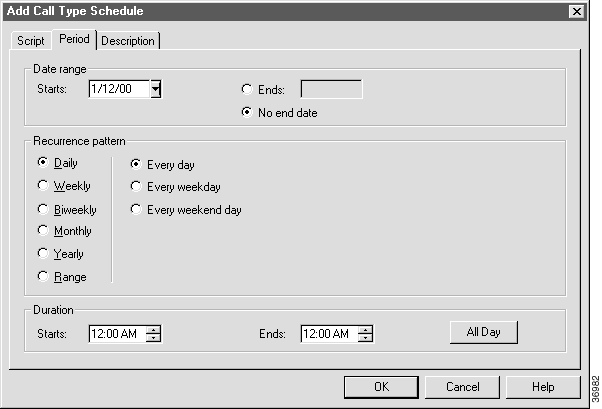
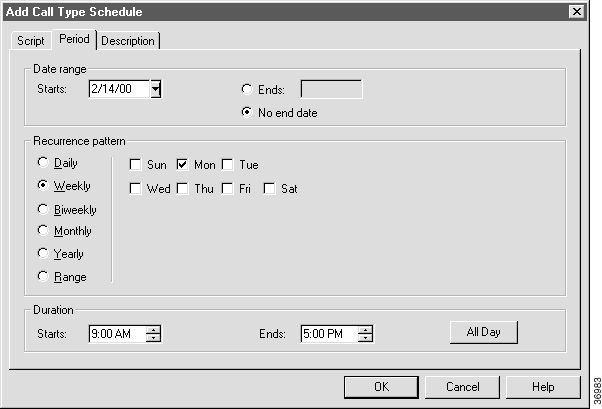
Step 5 In the Date Range, Recurrence Pattern, and Duration sections, specify the range of times when this script may run.
For example, you might define a schedule that runs the script from 9:00 AM through 5:00 PM every Monday, starting after February 14, 2000.
 |
Note For more information about setting the Date Range, Recurrence Pattern, and Duration fields for a schedule, see "Call Types". Optionally, click the Description tab and add some descriptive text about this schedule. |
Step 6 Click OK to submit the entry to the schedule and return to the Call Type Manager.
Step 7 Click OK to close the Call Type Manager and save your changes to the ICM database.
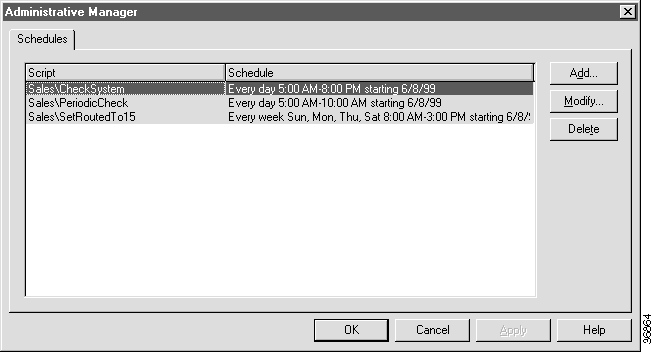
Step 2 Click the Add button. The Add Administrative Schedule dialog box appears, opening at the Script tab.
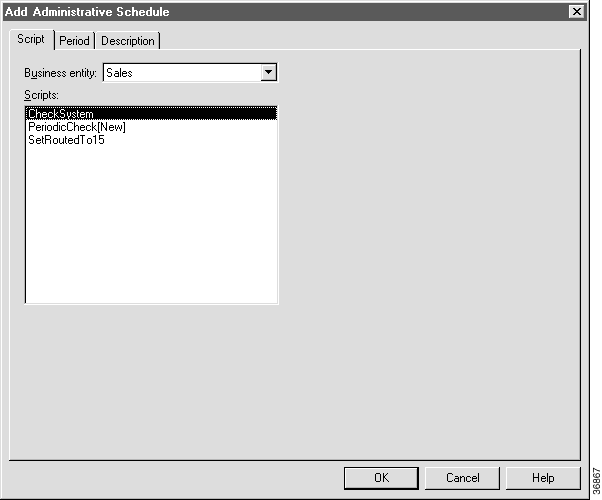
Step 3 Select the script you want to schedule and click the Period tab.
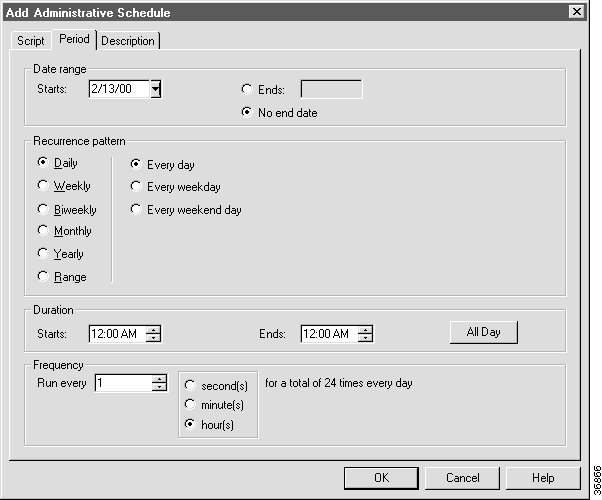
Step 4 Specify when you want the script to be active:
 |
Note You can use this field to override the default system setting for the Minimum Script Schedule Time, set through the System Information dialog box. ICM software will schedule the script based on which has the larger time interval: the Administrative Schedule or the system limit. (For complete information about the System Information dialog box, see the Cisco ICM Software Configuration Guide.) |
Step 5 Optionally, click the Description tab and add some descriptive text about this schedule.
Step 6 When you have finished your changes, click OK to submit the schedule and return to the Administration Manager.
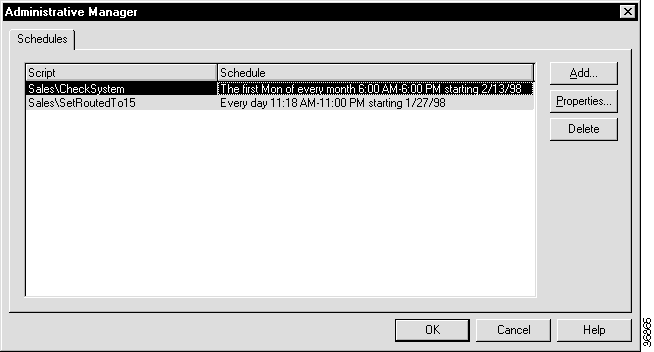
Step 7 Click OK to save your changes to the ICM database and close the Administrative Manager.
Note several points about administrative script schedules:
After a routing or administrative script has been saved, you can observe how it runs. Watching routing requests moving through a script in real-time helps ensure that the routing script is operating as expected.
When you monitor a script, that is, view the script in Monitor mode, labels appear on each connection in the script, as shown in Figure 7-1.
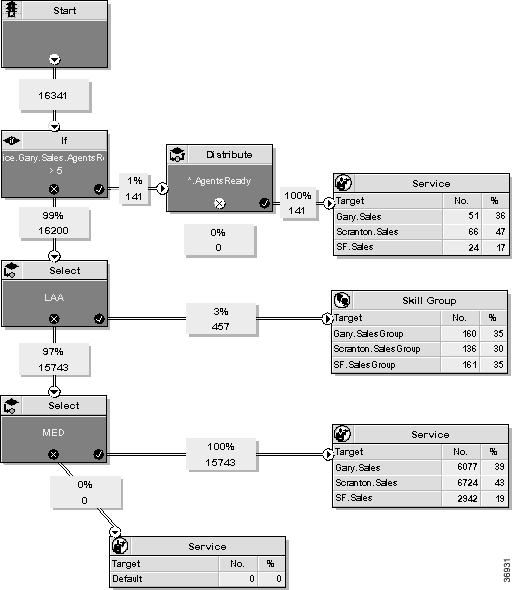
Most monitor labels display the raw number and percentage of call requests that have passed through the connection since the start of the monitoring period. Several monitor labels have been modified to display new meters (see Modified Monitor Labels).
Each target set also lists the number and percentage of calls routed to each of the targets in that set. Each statistic is updated automatically as new real-time data become available about every 15 seconds.
 |
Note When you edit a script, you should be careful to position nodes so that there is enough space for the monitor labels to display. (Since you cannot make any changes to a script while in Monitor mode, you cannot rearrange the nodes at that time.) Use the Script > Display Monitor Labels command while in edit mode to display blank monitor labels on each connection of the script. |
Most of the node Properties dialog boxes include a Labels tab that lets you adjust the location of labels on a node's connections. How to adjust Monitor label location describes how to do this.
The monitor labels have been modified for the following seven nodes.
The modified monitor labels can display two of the following three meters:
The InProgress meter is displayed in the top row of all the monitor labels for all the listed nodes except the Queue node. The top row of the Queue node monitor label displays the InQueue meter.
The second row of the monitor label for all of the listed nodes displays the Abort meter.
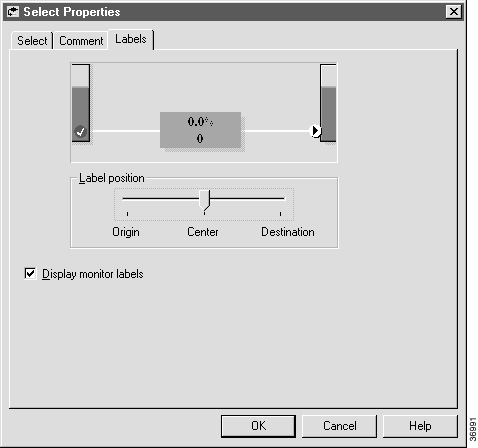
Step 2 Specify the following:
Step 3 Click OK to apply changes and to close the Select Properties dialog box.
There are several options for accessing Monitor mode,
The script displays in Monitor mode in the Script Editor workspace.
You can set different monitoring periods. For example, you can choose to see information about all requests handled by the script since midnight; from this point forward; or for the most recent 15-second interval.
You can also have options on how the connection display percentages are calculated.
 |
Note You can reset these options at any time. |
A drop-down menu appears.
Step 2 Choose among the following options:
In viewing the number of calls that pass through each branch of the script, you can also view real-time information about activity at the call centers, such as statistics for each skill group or service referenced in the script.
 |
Note For specific information about the real-time data, see the descriptions of the Service_Real_Time and Skill_Group_Real_Time tables in the Cisco ICM Software Database Schema Handbook. For information on other ways to monitor call center activity, see the Cisco ICM Software Supervisor Guide. |
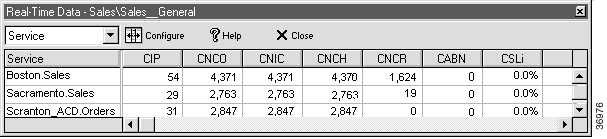
By default, the Real-Time Data window displays information about the Services referenced in the current script. (Scroll to the right to see additional columns.) The values in the screen are updated continuously as new real-time data arrives at the Admin Workstation.
Step 2 To display information about skill groups or scheduled targets, rather than services, change the value in the field in the upper-left corner of the Real-Time Data window. The window contents automatically change to show skill group data.
Step 3 When done using the window, click Close.
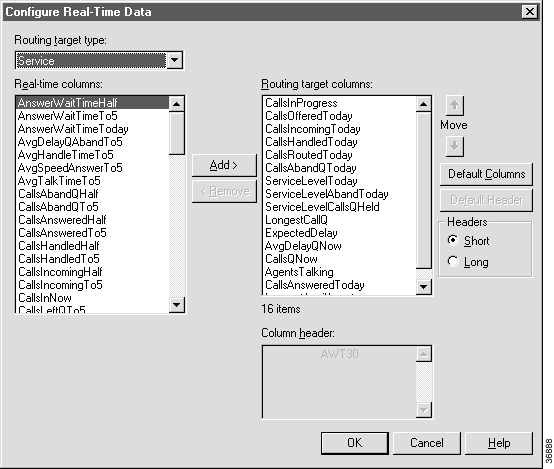
Use this dialog box to add new columns, remove existing columns, reorder the columns, or change the column labels.
Step 2 Select a Routing target type (Service, Scheduled Target, or Skill groups). This updates the other fields:
Step 3 Use the Add and Remove buttons to move columns between the lists. Use the Move buttons to change the order of the selected columns. (To change back to the default column order, click the Default Columns button.)
Step 4 Optionally, to edit a Routing Target Columns heading, make changes within the Column Header field. (To change back to the default header, highlight the Routing Target Column name and click the Default Header button.)
Step 5 Optionally, click the Short Headers / Long Headers radio buttons to change between the full and abbreviated forms of the default column headers. The abbreviated forms are typically three to four letters. (For example, AHT is used for Average Handle Time.)
Step 6 When done making configuration changes, click OK. The settings apply to the current and future Script Editor sessions.
You can examine router log messages to determine how calls have been routed and to see any errors ICM software has encountered in processing routing requests.
Start Router Log Viewer from the ICM Admin Workstation group. The Router Log Viewer window appears.
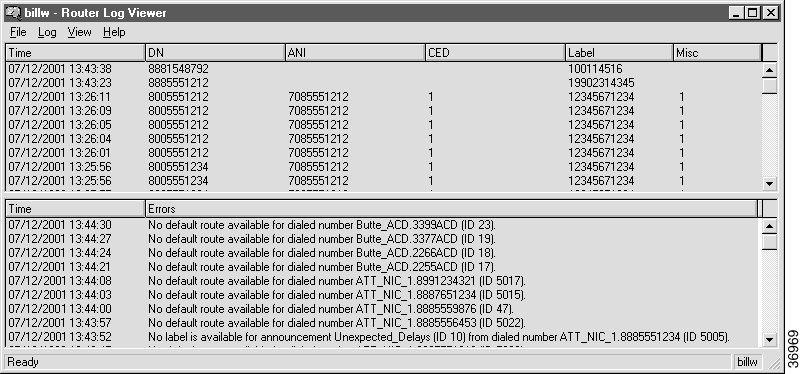
The top field of the Router Log Viewer window displays information about each call ICM software has routed, including:
The bottom field of the window displays any errors that ICM software has encountered in routing calls, including:
When you save a script, the Script Editor attaches a version number to the name. If you make changes to a script that was previously saved, the Script Editor generates a new version number before saving the script. ICM software saves older versions of the script in the database so that you have an audit trail of changes and can revert to a previous version of a script, if needed. The Script Explorer command provides access to script versions so you can perform "housekeeping" tasks, such as:
Step 2 Select File > Script Explorer or click the Script Explorer button on the main toolbar. The Script Explorer dialog box appears, listing scripts by customer and business entity.
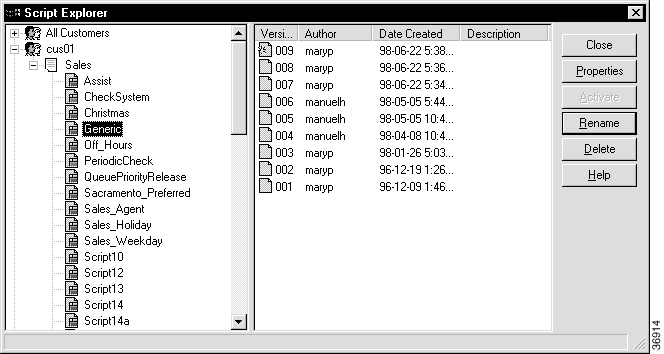
Step 3 Select a script and do one of the following:
Step 4 When finished, click Close.
It is often useful to copy a script created on one system to another system. Some possible reasons for doing so include:
The sections that follow describe how to import and export scripts.
Step 2 Optionally, change the File Name.
 |
Note You cannot change the file type; the script can only be saved in .ICMS format. |
Step 3 Click Save. If the file name already exists, the system prompts you to confirm the save.
Step 4 If prompted, click OK.
Step 2 Choose a file name with an ICM Script extension (.ICMS) and click Open. The Script Editor performs automapping and the following happens:
The Object Mapping dialog box contains three columns:
Step 3 Optionally, click an Imported Object value. The Mapped To column's drop-down list shows all the valid objects on the target system. (The Script Editor window also highlights the script nodes that refer to this object.)
Step 4 Optionally, select an object from the Mapped To drop-down list on the target system that you want to map the imported object to.
 |
Note Multiple objects may be mapped to the same target. Objects may be left unmapped; however, the resulting script will not be valid until the script elements referencing these objects are edited. |
Step 5 When the mapping is complete, click Apply and Finish.
You can use the System Information dialog box to modify settings for:
Step 2 Enter the Minimum Script Schedule Time.
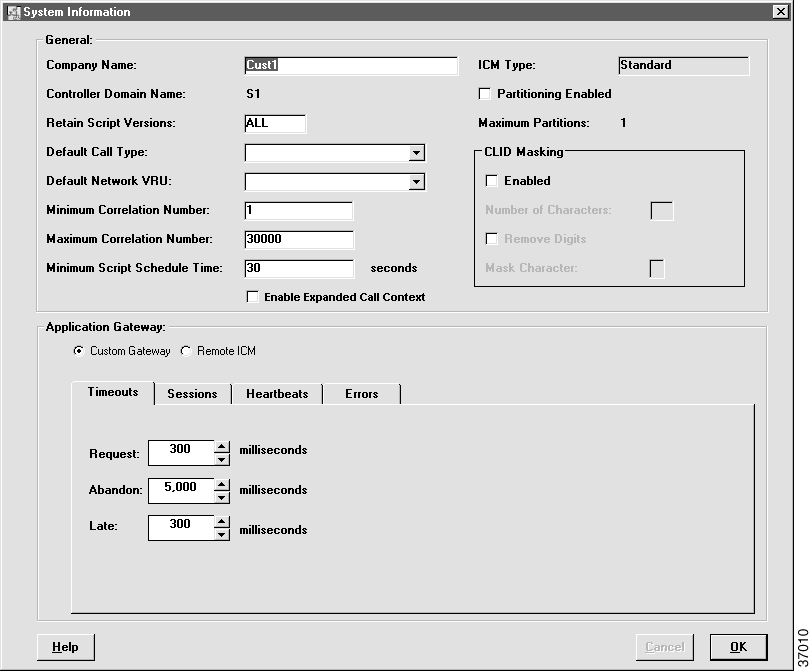
Step 3 Set the number of script versions to be retained in the Retain Script Versions field.
 |
Note You can override this setting through the Script Editor. When executing a script, ICM software will schedule the script based on which has the larger interval: the script schedule or the system limit. For additional information refer to the online Help. For more information on the System Information window, see the Cisco ICM Software Configuration Guide. |
Step 4 Click Save to apply your changes.
Feature Control addresses the need of restricting users, or classes of users, from all functionality of the ICM software. In a possible deployment scenario, an ICM software administrator can restrict certain people from doing specific types of script editing or from using certain applications.
Similar functionality is available in the ICM software in both the "Limited AWs" and Web View "Quick Edit" feature control.
A distinction should be made between object level control and feature customizing. Feature control, like the Limited AW, is a method of security for prohibiting access to ICM software features. Object control, like the ICM software partitioning feature, is a method of security for prohibiting access to configuration data in the ICM database.
Script node control allows an administrator to create feature sets that can be assigned to users. The feature set controls which script nodes are accessible to the user. There are two possible presentation effects:
If a script is imported that contains a disabled node, you can browse or monitor the script but you cannot put the script into edit mode. If you attempt to put this script into edit mode a message indicating you are not authorized to enter edit mode is displayed.
Configuring a feature control set consists of:
The system administrator can create a feature control set using the ICM Configuration Manager on the ICM distributor.
Step 2 Start the Configuration Manager by selecting:
Start > Programs > ICM Admin Workstation > Configuration Manager
The Configuration Manager dialog opens.
Step 3 Select Tools > List Tools > Feature Control Set List.
Step 4 In the Feature Control Set section (on the left), click Add.
Step 5 Select the Attributes tab.
Step 6 Enter the name of the feature control set. The name appears in the left section when Enter or Tab is pressed.
Step 7 Enter a description (optional).
Step 2 Select Show only unassigned users.
Step 3 Select the user(s) to whom feature control set is to be assigned.
 |
Note If no users appear, exit Feature Control and configure the user(s) using the User List Tool. |
Step 4 Click OK.
Step 5 Click Save when the user(s) have been selected.
Step 2 Select the Attributes tab.
Step 3 Select Advanced (under Script Editor).
Step 4 In the Script Editor Feature Control dialog, select the nodes for this feature control set.
Step 5 Click OK.
Step 6 Click Save.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Posted: Tue Jun 25 08:38:36 PDT 2002
All contents are Copyright © 1992--2002 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Important Notices and Privacy Statement.