|
|

The Service Profile Configuration window has five tabbed sections: General, PPP-IP, PPP-L2TP, Bridged-Bridged, and Bridged-Routed.
The General tab (shown in Figure 7-1) appears by default and has a single frame.
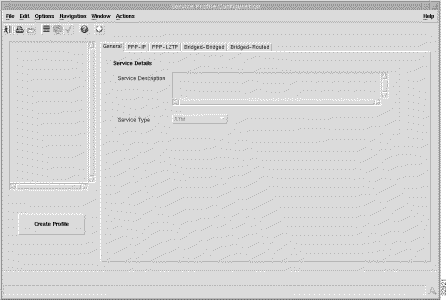
Service Description --- allows you to enter a description for the service.
Service Type --- allows you to select a service type from the available services. When a Service Type is selected the service tabs that do not relate to this service are greyed out and cannot be selected. For example, when the PPP-IP service is selected the PPP-IP tab can be selected and the PPP-L2TP, Bridged-Bridged and Bridged-Routed tabs are greyed out and cannot be selected.
Select Create Profile to create a new service profile with the parameters set in the service profile configuration tabs.
The PPP-IP tab (shown in Figure 7-2) has three frames.

A virtual template is a mechanism used by the 6400 UAC to establish or terminate subscriber PPP sessions.
The Virtual Template Parameters establish incoming subscriber PPP traffic information.
IP Address --- IP address of the virtual template.
Subnet Mask --- a 32 bit number used to separate the network and host sections of an IP address.
Authentication Type --- PPP authentication type for any subscribers wishing to connect to this service.
Peer DHCP --- when the Peer Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) option is enabled the Cisco 6400 UAC uses DHCP in place of IP pools.
Lower IP Address --- the lower limit on the IP address pool.
Higher IP Address --- the upper limit on the IP address pool.
No IP address pool is configured when the Higher IP Address and Lower IP Address parameter are left blank.
Encapsulation Type --- the IP over ATM encapsulation type used when forwarding traffic to the next hop.
Select Create Profile to create a new service profile with the parameters set in the service profile configuration tabs.
The PPP-L2TP tab (shown in Figure 7-3) has 5 frames.
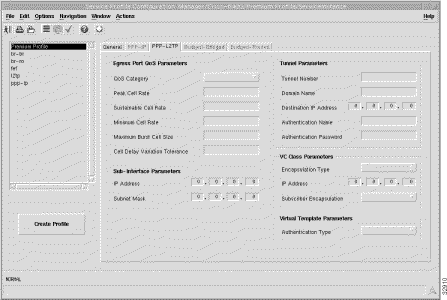
The ATM QoS parameters for the egress port are set according to the marketing offering of the carrier (wholesaler) to the upstream service provider.
QoS Category --- ATM Quality of Service.
Choose values appropriate to your selected QoS category for the following options:
Peak Cell Rate --- the maximum value that the cell rate will reach.
Sustainable Cell Rate --- the cell rate that the network must sustain.
Minimum Cell Rate --- the lowest value of the cell rate.
Maximum Burst Cell Size --- the maximum number of cells per burst.
Cell Delay Variation Tolerance --- the delay variation that the data can withstand without degradation.
The Sub-Interface Parameters define a local interface created (on the NRP) to communicate with the service network.
IP Address --- a local IP address that is used while communicating with the service.
Subnet Mask --- a 32 bit number used to separate the network and host sections of an IP address.
The Tunnel Parameters define the configuration of the tunnel that is created between the sub-interface and the tunnel destination (service).
Tunnel Number --- a unique identifier for the tunnel in the range 1 to 3000.
Domain Name --- the domain name to which the tunnel is mapped.
Destination IP Address --- the destination IP address of the tunnel.
Authentication Name --- the authentication name for the tunnel.
Authentication Password --- the authentication password for the tunnel.
The VC Class Parameters define the details of the next logical hop in the route to the service network.
Encapsulation Type --- the IP over ATM encapsulation type used when forwarding traffic to the next hop.
IP Address --- The IP address of the next hop. There should be a router at this address. This point may also be the tunnel termination point.
Subscriber Encapsulation --- The method of PPP over ATM encapsulation for any subscribers wishing to connect to this service.
The Virtual Template Parameters establish incoming subscriber PPP traffic information.
Authentication Type --- PPP authentication type for any subscribers wishing to connect to this service.
Select Create Profile to create a new service profile with the parameters set in the service profile configuration tabs.
The Bridged-Bridged tab (shown in Figure 7-3) appears by default and has four frames.
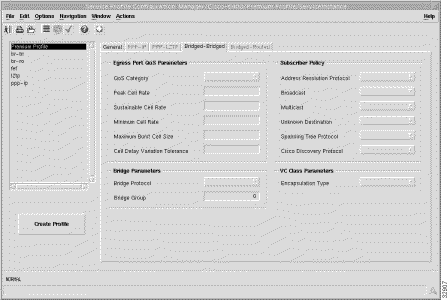
The ATM QoS parameters for the egress port are set according to the marketing offering for the carrier (wholesaler) to the upstream service provider.
QoS Category --- ATM Quality of Service.
Choose values appropriate to your selected QoS category for the following options:
Peak Cell Rate --- the maximum value that the cell rate will reach.
Sustainable Cell Rate --- the cell rate that the network must sustain.
Minimum Cell Rate --- the lowest value of the cell rate.
Maximum Burst Cell Size --- the maximum number of cells per burst.
Cell Delay Variation Tolerance --- the delay variation that the data can withstand without degradation.
The Bridge Parameters define the details of the bridge group to be created, including the bridge virtual interface.
Bridge Protocol --- Defines the bridge spanning tree protocol.
Bridge Group --- unique identifier for the bridge group to be created in the range 1 to 255.
The Subscriber Policy defines the types of traffic allowed within the bridge group. Traffic types available are, Address Resolution Protocol, Broadcast, Multicast, Unknown Destination, Spanning Tree Protocol, and Cisco Discovery Protocol. Select Permit to allow the traffic type or Deny to disallow the traffic type.
The VC Class Parameters define the details of the next logical hop in the route to the service network.
Encapsulation Type --- the IP over ATM encapsulation type used when forwarding traffic to the next hop.
Select Create Profile to create a new service profile with the parameters set in the service profile configuration tabs.
The Bridged-Routed tab (shown in Figure 7-5) has 5 frames.
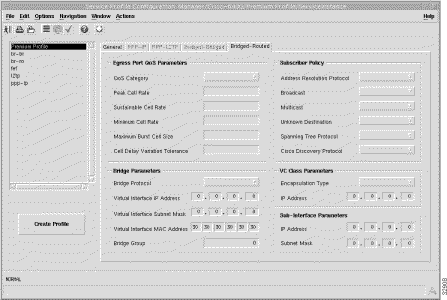
The ATM QoS parameters for the egress port are set according to the marketing offering for the carrier (wholesaler) to the upstream service provider.
QoS Category --- ATM Quality of Service.
Choose values appropriate to your selected QoS category for the following options:
Peak Cell Rate --- the maximum value that the cell rate will reach.
Sustainable Cell Rate --- the cell rate that the network must sustain.
Minimum Cell Rate --- the lowest value of the cell rate.
Maximum Burst Cell Size --- the maximum number of cells per burst.
Cell Delay Variation Tolerance --- the delay variation that the data can withstand without degradation.
The Bridge Parameters define the details of the bridge group to be created, including the bridge virtual interface.
Bridge Protocol --- Defines the bridge spanning tree protocol.
Virtual Interface IP Address --- the IP address of the virtual interface.
Virtual Interface Subnet Mask --- the subnet mask of the virtual interface. A subnet mask is a 32 bit number used to separate the network and host sections of an IP address.
Virtual Interface MAC Address --- The virtual interface Media Access Control (MAC) address.
Bridge Group --- unique identifier for the bridge group to be created in the range 1 to 255.
The Subscriber Policy defines the types of traffic allowed within the bridge group. Traffic types available are, Address Resolution Protocol, Broadcast, Multicast, Unknown Destination, Spanning Tree Protocol, and Cisco Discovery Protocol. Select Permit to allow the traffic type or Deny to disallow the traffic type.
The VC Class Parameters define the details of the next logical hop in the route to the service network.
Encapsulation Type --- the IP over ATM encapsulation type used when forwarding traffic to the next hop.
IP Address --- The IP address of the next hop. There should be a router at this address. This point may also be the tunnel termination point.
The Sub-Interface Parameters define a local interface created (on the NRP) to communicate with the service network.
IP Address --- a local IP address that is used while communicating with the service.
Subnet Mask --- a subnet mask is a 32 bit number used to separate the network and host sections of an IP address.
Select Create Profile to create a new service profile with the parameters set in the service profile configuration tabs.
Select the Cisco 6400 UAC, Profiles, Configure PTA-MD Profiles option from any card type (that is NSP, NRP or Line Card). to view the PTA-MD Service Profile Window (PTA-MD Tab).
The PTA-MD Service Profile window has two tabbed sections: PTA-MD and Local Service Profiles.
The PTA-MD tab (shown in Figure 7-6) appears by default and has two frames.
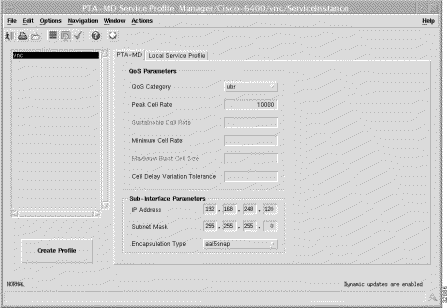
QoS Category --- ATM Quality of Service.
Choose values appropriate to your selected QoS category for the following options:
Peak Cell Rate --- the maximum value that the cell rate will reach.
Sustainable Cell Rate --- the cell rate that the network must sustain.
Minimum Cell Rate --- the lowest value of the cell rate.
Maximum Burst Cell Size --- the maximum number of cells per burst.
Cell Delay Variation Tolerance --- the delay variation that the data can withstand without degradation.
The Sub-Interface Parameters define a local interface created (on the NRP) to communicate with the service network.
IP Address --- a local IP address that is used while communicating with the service.
Subnet Mask --- a subnet mask is a 32 bit number used to separate the network and host sections of an IP address.
Encapsulation Type --- the IP over ATM encapsulation type used when forwarding traffic to the next hop.
Select Create Profile to create a new service profile with the parameters set in the service profile configuration tabs.
The Local Service Profile tab (shown in Figure 7-7) is divided into three frames.
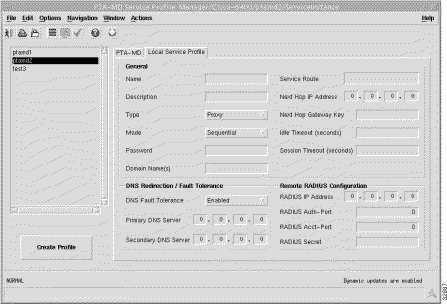
Name --- local service profile name.
Description --- allows you to enter a description to help identify the local service profile. The Description is optional.
Type --- allows you to select Passthrough or Proxy as the service Type. When Passthrough is selected, the NRP SSGs local RADIUS server will authenticate subscribers attempting to access the service. The IP Address of the local RADIUS server is configured in the Cisco 6400 NRP Management window (SSG Configuration tab). Refer to the "Cisco 6400 NRP Management Window" section for further details. When Proxy is selected the remote RADIUS server authenticates the user for access to the service (this is the RADIUS server at the service destination). The IP Address of the remote RADIUS server is configured in the Remote RADIUS Configuration frame (see the "Remote RADIUS Configuration" section for further details).
Mode --- allows you to select the service Mode parameter (Sequential or Concurrent).
The subscriber is prevented from simultaneously logging on to any other service when the Sequential option is selected. The subscriber can simultaneously log on to any other Concurrent service when the Concurrent option is selected.
Password --- required to access this service. The Password should be the same as the service password on Figure 5-16.
Domain Name(s) --- multiple Domain Names can be entered. each name must be separated by a semi-colon.
Service Route --- this defines the defines the destination network(s). You should enter the IP addresses and subnet mask(s) that make up the destination network(s) separated by a semi-colon.
Next Hop IP Address --- the IP Address of the next hop in the network.
Next Hop Gateway Key --- KEY string to bind next hop IP address to. When the Next Hop Gateway Key is not entered the 6400 SCM binds the next hop IP address to the service profile name.
Idle Timeout (seconds) --- allows you to set a timeout (in seconds) for the SSG connection object within the local Service profile that a connection object can remain idle. The Idle Timeout parameter is optional.
Session Timeout (seconds) --- allows you to set a session timeout (in seconds) for the SSG connection object within the local Service profile. The Session Timeout parameter is optional.
The DNS Redirection/Fault Tolerance parameters define the DNS configuration.
DNS Fault Tolerance --- can be set to Enabled or Disabled. When Enabled, both the Primary and Secondary DNS Server IP addresses are available. When Disabled only the Primary DNS Server IP address is available.
Primary DNS Server --- the IP address of the Primary DNS Server. No DNS commands are set onto the NRP when the Primary DNS Server IP Address is set to 0.0.0.0.
Secondary DNS Server (for failover) --- the IP Address of the failover DNS Server. Available only when the DNS Failover parameter is Enabled. When the DNS Failover parameter is Enabled the DNS Server at this IP Address is used when the Primary DNS Server fails.
The Remote RADIUS Configuration parameters are only valid for the Proxy service type.
RADIUS IP Address --- IP Address of the remote RADIUS Server.
RADIUS Auth-Port --- defines the port to be used for authentication. Defaults to 1645.
RADIUS Acct-Port --- defines the port to be used for accountancy. Defaults to 1646.
RADIUS Secret --- unique secret key for the RADIUS Server.
Select Create Profile to create a new service profile with the parameters set in the service profile configuration tabs.
Select the Cisco 6400 UAC, Profiles, Configure RBE Profiles option from any card type (that is NSP, NRP or Line Card). to view the RBE Service Profile Window (Route Bridge Encapsulation Tab).
The Route Bridge Encapsulation tab (shown in Figure 7-8) appears by default and has two frames: QoS Parameters and Sub-Interface Parameters.

QoS Category --- ATM Quality of Service.
Choose values appropriate to your selected QoS category for the following options:
Peak Cell Rate --- the maximum value that the cell rate will reach.
Sustainable Cell Rate --- the cell rate that the network must sustain.
Minimum Cell Rate --- the lowest value of the cell rate.
Maximum Burst Cell Size --- the maximum number of cells per burst.
Cell Delay Variation Tolerance --- the delay variation that the data can withstand without degradation.
The Sub-Interface Parameters define a local interface created (on the NRP) to communicate with the service network.
IP Address --- a local IP address that is used while communicating with the service.
Subnet Mask --- a subnet mask is a 32 bit number used to separate the network and host sections of an IP address.
Encapsulation Type --- the IP over ATM encapsulation type used when forwarding traffic to the next hop.
Select Create Profile to create a new service profile with the parameters set in the service profile configuration tabs.
Select the Cisco 6400 UAC, Profiles, Configure RFC1483 Routed Profiles option from any card type (that is NSP, NRP or Line Card) to view the PTA-MD Service Profile Window (RFC1483 Routed Tab).
The RFC1483 Service Profile Window has a single tabbed section: RFC1483 Routed. The RFC1483 Routed tab (shown in Figure 7-9) appears by default and has two frames: QoS Parameters and Sub-Interface Parameters.
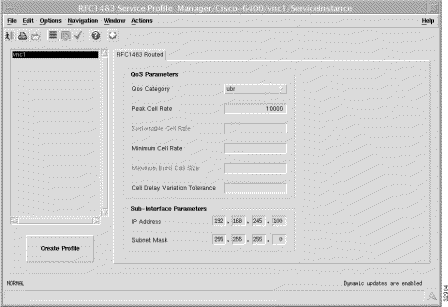
QoS Category --- ATM Quality of Service.
Choose values appropriate to your selected QoS category for the following options:
Peak Cell Rate --- the maximum value that the cell rate will reach.
Sustainable Cell Rate --- the cell rate that the network must sustain.
Minimum Cell Rate --- the lowest value of the cell rate.
Maximum Burst Cell Size --- the maximum number of cells per burst.
Cell Delay Variation Tolerance --- the delay variation that the data can withstand without degradation.
The Sub-Interface Parameters define a local interface created (on the NRP) to communicate with the service network.
IP Address --- a local IP address that is used while communicating with the service.
Subnet Mask --- a subnet mask is a 32 bit number used to separate the network and host sections of an IP address.
Select Create Profile to create a new service profile with the parameters set.
The Connect tab (shown in Figure 7-1) appears by default and has a six frames.

Lists the available DSLAM objects.
Lists the available subscribers.
Lists the available subscriber QoS.
Select Connect to connect the selected subscriber.
The RFC1483 Routed tab (shown in Figure 7-11) appears by default and has a single frame.
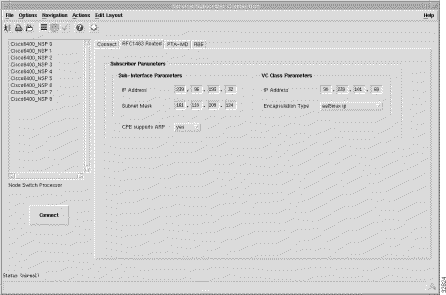
IP Address --- a local IP address that is used while communicating with the service.
Subnet Mask --- a subnet mask is a 32 bit number used to separate the network and host sections of an IP address.
Encapsulation Type --- the IP over ATM encapsulation type used when forwarding traffic to the next hop.
IP Address --- a local IP address that is used while communicating with the service.
Allows you the ability to switch on the address resolution protocol if the Customer Premises Equipment (CPE) supports ARP. When the CPE does not support ARP then the IP Address with the class parameters are assigned to the subscribers PVC residing within the sub-interface.
The PTA-MD tab (shown in Figure 7-12) appears by default and has a single frame.

Layer 2 Connection Type --- allows you to select the subscriber connection type (PPPoE or PPPoA).
Binding --- allows you to select the binding type (Static or Dynamic). Static binding is only valid when the subscriber connection type is PPPoA.
Encapsulation Type --- the IP over ATM encapsulation type used when forwarding traffic to the next hop. The following subscriber Encapsulation Types are available: aal5mux ppp (for PPPoE connection type), and aaal5mux ppp or aal5 ciscoppp for a PPPoA connection type.
Service Access Mode --- allows you to set the subscribers exclusivity to Non-Exclusive or Exclusive. Exclusivity is only a valid option when the subscriber connection type is PPPoA and the subscriber binding is Static.
The RBE tab (shown in Figure 7-13) appears by default and has a single frames.
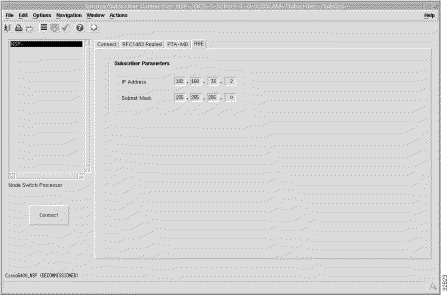
IP Address --- a local IP address that is used while communicating with the service.
Subnet Mask --- a subnet mask is a 32 bit number used to separate the network and host sections of an IP address.
The Cisco 6400 SCM has four Service Configuration windows: Service Instance Configuration window (for configuring ATM, PPP-IP, PPP-L2TP, Bridged-Bridged, and Bridged-Routed services), RFC1483 Routed Service Configuration window, PTA-MD Service Configuration window, and RBE Service Configuration window.
The Service Instance Configuration window (Figure 7-14) is divided into six tabbed sections: General, ATM, PPP-IP, PPP-L2TP, Bridged-Bridged, and Bridged-Routed.
The ATM tab displays a single Egress Port Parameters frame.

The physical line card and port details through which the service is accessed.
Egress VPI (0 - 255) --- outgoing port VPI value.
Egress VCI (32 - 16383) --- outgoing port VCI value.
Egress Port --- The location of the outgoing line card port. For example, 2/1/0, represents port 0 on the line card in subslot 1 contained in slot 2.
The PPP-IP tab displays three frames: Virtual Template Parameters, IP Address Pool, and VC Class Parameters.

The Virtual Template Parameters establish incoming subscriber PPP traffic information.
IP Address --- the virtual template IP address.
Subnet Mask --- a subnet mask is a 32 bit number used to separate the network and host sections of an IP address.
Authentication Type --- PPP authentication type for any subscribers wishing to connect to this service.
Peer DHCP --- when the Peer Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) option is enabled the Cisco 6400 UAC uses DHCP in place of IP pools.
Lower IP Address --- the lower limit on the IP address pool.
Higher IP Address --- the upper limit on the IP address pool.
No IP address pool is configured when the Higher IP Address and Lower IP Address parameter are left blank.
Encapsulation Type --- the IP over ATM encapsulation type used when forwarding traffic to the next hop.
The PPP-L2TP tab displays seven frames: Egress Port Parameters, Egress Port QoS Parameters, Sub-Interface Parameters, NSP/NRP Interface PVC Parameters, Tunnel Parameters, VC Class Parameters, and Virtual Template Parameters.
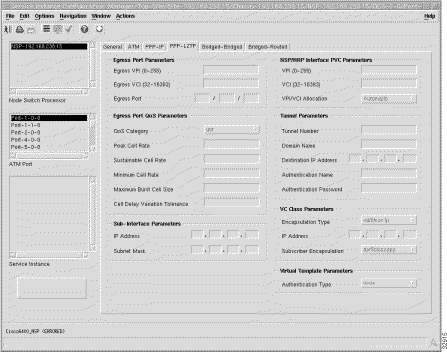
The physical line card and port details through which the service is accessed.
Egress VPI (0 - 255) --- outgoing port VPI value.
Egress VCI (32 - 16383) --- outgoing port VCI value.
Egress Port --- The location of the outgoing line card port. For example, 2/1/0, represents port 0 on the line card in subslot 1 contained in slot 2.
The ATM QoS parameters for the egress port are set according to the marketing offering of the carrier (wholesaler) to the upstream service provider.
QoS Category --- ATM Quality of Service.
Choose values appropriate to your selected QoS category for the following options:
Peak Cell Rate --- the maximum value that the cell rate will reach.
Sustainable Cell Rate --- the cell rate that the network must sustain.
Minimum Cell Rate --- the lowest value of the cell rate.
Maximum Burst Cell Size --- the maximum number of cells per burst.
Cell Delay Variation Tolerance --- the delay variation that the data can withstand without degradation.
The Sub-Interface Parameters define a local interface created (on the NRP) to communicate with the service network.
IP Address --- a local IP address that is used while communicating with the service.
Subnet Mask --- a subnet mask is a 32 bit number used to separate the network and host sections of an IP address.
The NSP/NRP Interface PVC Parameters define the internal PVCs between the NSP and NRP.
VPI (0-255) --- internal VPI value.
VCI (32-16383) --- internal VCI value.
VPI/VCI Allocation --- the NSP/NRP Interface PVC Parameters (VPI and VCI) can be completed either manually or automatically by selecting the appropriate option from the VPI/VCI Allocation list. When the Manual option is selected the VPI and VCI boxes must be completed by the operator. When the Automatic option is selected the values are selected automatically by the 6400 SCM and (the VPI and VCI boxes are greyed out). We recommend that you keep the Automatic option selected.
The Tunnel Parameters define the configuration of the tunnel that is created between the sub-interface and the tunnel destination (service).
Tunnel Number --- a unique identifier for the tunnel in the range 1 to 3000.
Domain Name --- the domain name to which the tunnel is mapped.
Destination IP Address --- the destination IP address of the tunnel.
Authentication Name --- the authentication name for the tunnel.
Authentication Password --- the authentication password for the tunnel.
The VC Class Parameters define the details of the next logical hop in the route to the service network.
Encapsulation Type --- the IP over ATM encapsulation type used when forwarding traffic to the next hop.
IP Address --- The IP address of the next hop. There should be a router at this address. This point may also be the tunnel termination point.
Subscriber Encapsulation --- The method of PPP over ATM encapsulation for any subscribers wishing to connect to this service.
The Virtual Template Parameters establish incoming subscriber PPP traffic information.
Authentication Type --- PPP authentication type for any subscribers wishing to connect to this service.
The Bridged-Bridged tab displays six frames: Egress Port Parameters, Egress Port QoS Parameters, Bridge Parameters, NSP/NRP Interface PVC Parameters, Subscriber Policy, and VC Class Parameters.

The physical line card and port details through which the service is accessed.
Egress VPI (0 - 255) --- outgoing port VPI value.
Egress VCI (32 - 16383) --- outgoing port VCI value.
Egress Port --- The location of the outgoing line card port. For example, 2/1/0, represents port 0 on the line card in subslot 1 contained in slot 2.
The ATM QoS parameters for the egress port are set according to the marketing offering from the carrier (wholesaler) to the upstream service provider.
QoS Category --- ATM Quality of Service.
Choose values appropriate to your selected QoS category for the following options:
Peak Cell Rate --- the maximum value that the cell rate will reach.
Sustainable Cell Rate --- the cell rate that the network must sustain.
Minimum Cell Rate --- the lowest value of the cell rate.
Maximum Burst Cell Size --- the maximum number of cells per burst.
Cell Delay Variation Tolerance --- the delay variation that the data can withstand without degradation.
The Bridge Parameters define the details of the bridge group to be created, including the bridge virtual interface.
Bridge Protocol --- Defines the bridge spanning tree protocol.
Bridge Group --- unique identifier for the bridge group to be created in the range 1 to 255.
VPI (0-255) --- internal VPI value.
VCI (32-16383) --- internal VCI value.
VPI/VCI Allocation --- the NSP/NRP Interface PVC Parameters (VPI and VCI) can be completed either manually or automatically by selecting the appropriate option from the VPI/VCI Allocation list. When the Manual option is selected the VPI and VCI boxes must be completed by the operator. When the Automatic option is selected the values are selected automatically by the 6400 SCM and (the VPI and VCI boxes are greyed out). We recommend that you keep the Automatic option selected.
The Subscriber Policy defines the types of traffic allowed within the bridge group. Traffic types available are, Address Resolution Protocol, Broadcast, Multicast, Unknown Destination, Spanning Tree Protocol, and Cisco Discovery Protocol. Select Permit to allow the traffic type or Deny to disallow the traffic type.
Encapsulation Type --- the IP over ATM encapsulation type used when forwarding traffic to the next hop.
The Bridged-Routed tab displays seven frames: Egress Port Parameters, Egress Port QoS Parameters, Bridge Parameters, NSP/NRP Interface PVC Parameters, Subscriber Policy, VC Class Parameters, and Sub-Interface Parameters.
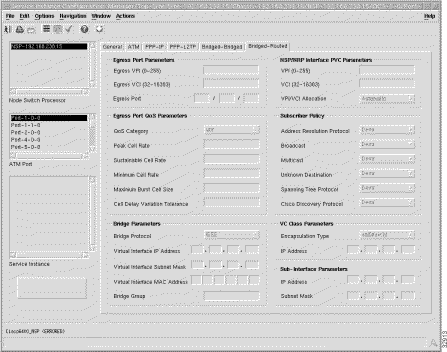
The physical line card and port details through which the service is accessed.
Egress VPI (0 - 255) --- outgoing port Virtual Path Identifier (VPI) value.
Egress VCI (32 - 16383) --- outgoing port Virtual Circuit Identifier (VCI) value.
Egress Port --- The location of the outgoing line card port. For example, 2/1/0, where 2 represents the slot number in the 6400 chassis where the line card is located, 1 is the subslot (lower row) and 0 is the port number.
The ATM QoS parameters for the egress port are set according to the marketing offering of the carrier (wholesaler) to the upstream service provider.
QoS Category --- ATM Quality of Service.
Choose values appropriate to your selected QoS category for the following options:
Peak Cell Rate --- the maximum value that the cell rate will reach.
Sustainable Cell Rate --- the cell rate that the network must sustain.
Minimum Cell Rate --- the lowest value of the cell rate.
Maximum Burst Cell Size --- the maximum number of cells per burst.
Cell Delay Variation Tolerance --- the delay variation that the data can withstand without degradation.
The Bridge Parameters define the details of the bridge group to be created, including the bridge virtual interface.
Bridge Protocol --- Defines the bridge spanning tree protocol.
Virtual Interface IP Address --- the IP address of the virtual interface.
Virtual Interface Subnet Mask --- the subnet mask of the virtual interface. A subnet mask is a 32 bit number used to separate the network and host sections of an IP address.
Virtual Interface MAC Address --- The virtual interface Media Access Control (MAC) address.
Bridge Group --- unique identifier for the bridge group to be created in the range 1 to 255.
The NSP/NRP Interface PVC Parameters define the
VPI (0-255) --- internal VPI value.
VCI (32-16383) --- internal VCI value.
VPI/VCI Allocation --- the NSP/NRP Interface PVC Parameters (VPI and VCI) can be completed either manually or automatically by selecting the appropriate option from the VPI/VCI Allocation list. When the Manual option is selected the VPI and VCI boxes must be completed by the operator. When the Automatic option is selected the values are selected automatically by the 6400 SCM and (the VPI and VCI boxes are greyed out). We recommend that you keep the Automatic option selected.
The Subscriber Policy defines the types of traffic allowed within the bridge group. Traffic types available are, Address Resolution Protocol, Broadcast, Multicast, Unknown Destination, Spanning Tree Protocol, and Cisco Discovery Protocol. Select Permit to allow the traffic type or Deny to disallow the traffic type.
The VC Class Parameters define the details of the next logical hop in the route to the service network.
Encapsulation Type --- the IP over ATM encapsulation type to be used when forwarding traffic to the next hop.
IP Address --- The IP address of the next hop.
The Sub-Interface Parameters define a local interface created (on the NRP) to communicate with the service network.
IP Address --- a local IP address that is used while communicating with the service.
Subnet Mask --- a subnet mask is a 32 bit number used to separate the network and host sections of an IP address.
The PTA-MD tab (Figure 7-19) displays four frames: QoS Parameters, Sub-Interface Parameters, Egress Port Parameters, and PVC Configuration.
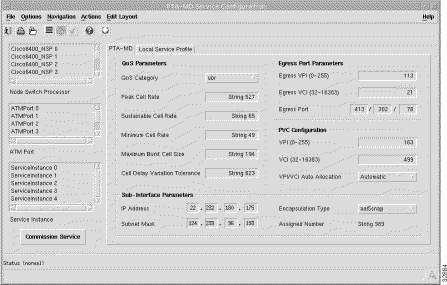
QoS Category --- ATM Quality of Service.
Choose values appropriate to your selected QoS category for the following options:
Peak Cell Rate --- the maximum value that the cell rate will reach.
Sustainable Cell Rate --- the cell rate that the network must sustain.
Minimum Cell Rate --- the lowest value of the cell rate.
Maximum Burst Cell Size --- the maximum number of cells per burst.
Cell Delay Variation Tolerance --- the delay variation that the data can withstand without degradation.
The Sub-Interface Parameters define a local interface created (on the NRP) to communicate with the service network.
IP Address --- a local IP address that is used while communicating with the service.
Subnet Mask --- a subnet mask is a 32 bit number used to separate the network and host sections of an IP address.
Encapsulation Type --- the IP over ATM encapsulation type used when forwarding traffic to the next hop.
Assigned Number --- uniquely identifies the sub-interface for the service uplink.
The physical line card and port details through which the service is accessed.
Egress VPI (0 - 255) --- outgoing port VPI value.
Egress VCI (32 - 16383) --- outgoing port VCI value.
Egress Port --- The location of the outgoing line card port. For example, 2/1/0, where 2 represents the slot number in the 6400 chassis where the line card is located, 1 is the subslot (lower row) and 0 is the port number.
VPI (0 - 255) --- internal VPI value.
VCI (32 - 16383) --- internal VCI value.
VPI/VCI Auto Allocation --- the NSP/NRP Interface PVC Parameters (VPI and VCI) can be completed either manually or automatically by selecting the appropriate option from the VPI/VCI Allocation list. When the Manual option is selected the VPI and VCI boxes must be completed by the operator. When the Automatic option is selected the values are selected automatically by the 6400 SCM and (the VPI and VCI boxes are greyed out). We recommend that you keep the Automatic option selected.
The Local Service Profile tab (shown in Figure 7-20) displays the attributes that need to be configured to set up the PTA-MD local service profile on the NRP-Service Selection Gateway (SSG).
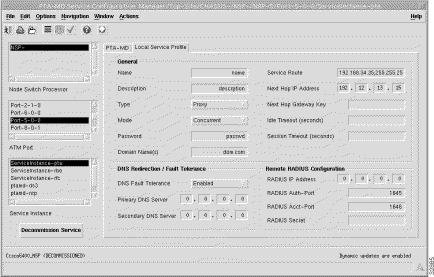
The Local Service Profile tab displays three frames: General, DNS Configuration, and Remote RADIUS Configuration.
Name --- local service profile name.
Description --- allows you to enter a description to help identify the local service profile. The Description is optional.
Type --- allows you to select Passthrough or Proxy as the service Type. When Passthrough is selected, the NRP SSGs local RADIUS server authenticates the service. The IP Address of the local RADIUS server is configured in the Cisco 6400 NRP Management window (SSG Configuration tab). Refer to the "Cisco 6400 NRP Management Window" section for further details. When Proxy is selected the remote RADIUS server authenticates the user for access to the service (this is the RADIUS server at the service destination). The IP Address of the remote RADIUS server is configured in the Remote RADIUS Configuration frame (see the "Remote RADIUS Configuration" section for further details).
Mode --- allows you to select the service Mode parameter. The service Mode is configurable within the local service profile for security reasons (that is, from the service provider's point of view if a subscriber is logged on to this service).
The SCM allows the ability to specify whether the service can be accessed concurrently with other services or not by configuring a Service Profile's Service Mode as Sequential or Concurrent. The subscriber is prevented from simultaneously logging on to any other service when the Sequential option is selected. The subscriber can simultaneously log on to any other Concurrent service when the Concurrent option is selected.
The SCM allows the ability to specify whether the service can be accessed concurrently with other services or not by configuring a Service Profile's Service Mode as Sequential or Concurrent. The subscriber is prevented from simultaneously logging on to any other service when the Sequential option is selected. The subscriber can simultaneously log on to any other Concurrent service when the Concurrent option is selected.
Password --- required to access this service. The Password should be the same as the service password on Figure 5-16.
Domain Name(s) --- multiple Domain Names can be entered. each name must be separated by a semi-colon.
Service Route --- The SCM provides the ability to configure the networks that make up the service by defining Service Routes. The SCM allows multiple service routes to be specified.
Next Hop IP Address --- the IP Address of the next hop in the network. The SCM allows you to configure the next hop gateway IP address for the service. The SCM binds the local service profile to the next hop gateway IP address or will bind the NHG key to the next hop gateway IP address depending upon the selection made.
Next Hop Gateway Key --- KEY string to bind next hop IP address to. When the Next Hop Gateway Key is not entered the 6400 SCM binds the next hop IP address to the service profile name.
Idle Timeout (seconds) --- allows you to set a timeout (in seconds) for the SSG connection object within the local Service profile that a connection object can remain idle. The Idle Timeout parameter is optional.
Session Timeout (seconds) --- allows you to set a session timeout (in seconds) for the SSG connection object within the local Service profile. The Session Timeout parameter is optional.
The DNS Redirection/Fault Tolerance parameters define the DNS configuration.
DNS Fault Tolerance --- can be set to Enabled or Disabled. When Enabled, both the Primary and Secondary DNS Server IP addresses are available. When Disabled only the Primary DNS Server IP address is available.
Primary DNS Server --- the IP address of the Primary DNS Server. No DNS commands are set onto the NRP when the Primary DNS Server IP Address is set to 0.0.0.0.
Secondary DNS Server (for failover) --- the IP Address of the failover DNS Server. Available only when the DNS Failover parameter is Enabled. When the DNS Failover parameter is Enabled the DNS Server at this IP Address is used when the Primary DNS Server fails.
The Remote RADIUS Configuration parameters are only valid for the Proxy service type.
RADIUS IP Address --- IP Address of the remote RADIUS Server.
RADIUS Auth-Port --- defines the port to be used for authentication. Defaults to 1645.
RADIUS Acct-Port --- defines the port to be used for accountancy. Defaults to 1646.
RADIUS Secret --- unique secret key for the RADIUS Server.
The Route Bridge Encapsulation tab (Figure 7-21) displays four frames: QoS Parameters, Sub Interface Parameters, Egress Port Parameters, and PVC Configuration.

QoS Category --- ATM Quality of Service.
Choose values appropriate to your selected QoS category for the following options:
Peak Cell Rate --- the maximum value that the cell rate will reach.
Sustainable Cell Rate --- the cell rate that the network must sustain.
Mean Cell Rate --- the mean cell rate value.
Maximum Burst Cell Size --- the maximum number of cells per burst.
Cell Delay Variation Tolerance --- the delay variation that the data can withstand without degradation.
The Sub-Interface Parameters define a local interface created (on the NRP) to communicate with the service network.
IP Address --- a local IP address that is used while communicating with the service.
Subnet Mask --- a subnet mask is a 32 bit number used to separate the network and host sections of an IP address.
Encapsulation Type --- the IP over ATM encapsulation type used when forwarding traffic to the next hop.
Assigned Number --- uniquely identifies the sub-interface for the service uplink.
The physical line card and port details through which the service is accessed.
Egress VPI (0 - 255) --- outgoing port Virtual Path Identifier (VPI) value.
Egress VCI (32 - 16383) --- outgoing port Virtual Circuit Identifier (VCI) value.
Egress Port --- The location of the outgoing line card port. For example, 2/1/0, where 2 represents the slot number in the 6400 chassis where the line card is located, 1 is the subslot (lower row) and 0 is the port number.
VPI (0 - 255) --- internal VPI value.
VCI (32 - 16383) --- internal VCI value.
VPI/VCI Auto Allocation --- the NSP/NRP Interface PVC Parameters (VPI and VCI) can be completed either manually or automatically by selecting the appropriate option from the VPI/VCI Allocation list. When the Manual option is selected the VPI and VCI boxes must be completed by the operator. When the Automatic option is selected the values are selected automatically by the 6400 SCM and (the VPI and VCI boxes are greyed out). We recommend that you keep the Automatic option selected.
Next Hop IP Address --- the IP Address of the next hop in the network. The SCM allows you to configure the next hop gateway IP address for the service. The SCM binds the local service profile to the next hop gateway IP address or will bind the NHG key to the next hop gateway IP address depending upon the selection made.
Next Hop Gateway Key --- KEY string to bind next hop IP address to. When the Next Hop Gateway Key is not entered the 6400 SCM binds the next hop IP address to the service profile name.
The RFC1483 tab (Figure 7-22) displays three frames: QoS Parameters, Sub Interface Parameters, and Uplink PVC Configuration.

QoS Category --- ATM Quality of Service.
Choose values appropriate to your selected QoS category for the following options:
Peak Cell Rate --- the maximum value that the cell rate will reach.
Sustainable Cell Rate --- the cell rate that the network must sustain.
Minimum Cell Rate --- the lowest value of the cell rate.
Maximum Burst Cell Size --- the maximum number of cells per burst.
Cell Delay Variation Tolerance --- the delay variation that the data can withstand without degradation.
The Sub-Interface Parameters define a local interface created (on the NRP) to communicate with the service network.
IP Address --- a local IP address that is used while communicating with the service.
Subnet Mask --- a subnet mask is a 32 bit number used to separate the network and host sections of an IP address.
Assigned Number --- uniquely identifies the sub-interface for the service uplink.
Uplink PVCs --- the Uplink PVCs configuration frame allows you to view all PVCs that reside within the uplink sub-interface.
The VC Class Parameters define the details of the next logical hop in the route to the service network.
CPE Supports ARP --- select Yes to disable the IP Address (in the VC Class Parameters frame) or select No to enable the IP Address (in the VC Class Parameters frame).
Encapsulation Type --- the IP over ATM encapsulation type used when forwarding traffic to the next hop.
IP Address --- The IP address of the PVC.
The physical line card and port details through which the service is accessed.
Egress VPI (0 - 255) --- outgoing port VPI value.
Egress VCI (32 - 16383) --- outgoing port VCI value.
Egress Port --- The location of the outgoing line card port. For example, 2/1/0, represents port 0 on the line card in subslot 1 contained in slot 2.
VPI (0 - 255) --- internal VPI value.
VCI (32 - 16383) --- internal VCI value.
VPI/VCI Auto Allocation --- the NSP/NRP Interface PVC Parameters (VPI and VCI) can be completed manually or automatically by selecting the appropriate option from the VPI/VCI Allocation list. When the Manual option is selected the VPI and VCI boxes must be completed by the operator. When the Automatic option is selected the values are selected automatically by the 6400 SCM and (the VPI and VCI boxes are greyed out). We recommend that you keep the Automatic option selected.
Select the Add button to add the Uplink PVC Configuration parameters to the Uplink PVCs list. Enter an UPlink PVC Object name in the pop-up window the appears. Select the OK button. The new UPlink PVC Object appears in the Uplink PVCs list.
Select Commission to commission the service.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Posted: Wed Feb 2 12:56:37 PST 2000
Copyright 1989 - 2000©Cisco Systems Inc.