|
|

This chapter describes the steps required to configure the trunk and subtended interfaces on the Cisco DSLAM NI-2 card. It includes these sections:
Table 8-1 shows the NI-2 card and DSLAM chassis compatibility with regard to both trunk and subtending connections.
| NI-2 Card | Cisco 6015 | Cisco 6100 / Cisco 6130 | Cisco 6160 | Cisco 6260 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
DS3+T1/E1 IMA1
| Yes | No | Yes2 | Yes3 |
DS3/2DS3
| No | Yes | Yes | Yes4 |
OC-3c/OC-3c single-mode fiber (SMF)
| Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes5 |
OC-3c/OC-3c multimode fiber (MMF)
| Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes4 |
OC-3c/2DS3 single-mode fiber (SMF)
| No | No | Yes | No |
OC-3c/2DS3 multimode fiber (MMF)
| No | No | Yes | No |
NI-2 cards offer the same level of service and traffic fairness in subtending Cisco 6015, Cisco 6100, Cisco 6130, Cisco 6160, and Cisco 6260 DSLAMs. The level of service remains the same for both NI-1 and NI-2 based subtended nodes. (That is, you can mix NI-1 and NI-2 cards in the same subtending network for the Cisco 6100 and Cisco 6130 DSLAM.)
The following guidelines apply to subtending on an NI-2 supported DSLAM:
The NI-2 card supports system controller-type connectors.
Each port can be configured to support these clocking options:
The plug-and-play mechanisms of the DSLAM allow the interface to launch automatically. You can save all configuration information between hot swaps and reboots, while interface types are automatically discovered by the DSLAM, eliminating the need for mandatory manual configuration.
If Integrated Local Management Interface (ILMI) has been disabled or if the connecting end node does not support ILMI, these defaults are assigned to all 155 Mbps (OC-3c) interfaces:
The default subtend ID for each NI-2 DSLAM is 0 (zero).
To manually change any of the default configuration values, perform these tasks:
 |
Note Note that Steps 2 and 11 are alternatives; do not perform both steps. |
This example shows how to change the default ATM interface type to "private" using the atm uni type private command.
DSLAM# configure terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
DSLAM(config)# interface atm 0/1
DSLAM(config-if)# atm uni type private
This example shows how to change the clock source using the clock source network-derived command.
DSLAM# configure terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
DSLAM(config)# interface atm 0/1
DSLAM(config-if)# clock source network-derived
 |
Note See the "Interface Configuration Troubleshooting" section, to confirm your interface configuration. |
Use the 45 Mbps DS3 to accomplish the following tasks:
You can configure the NI-2 ports as redundant links using the switch routing protocols. You can also configure each port to support these clocking options:
Traffic pacing allows you to set the aggregate output traffic rate on any port to a rate below the line rate. This feature is useful when you are communicating with a slow receiver or when you are connected to public networks with peak-rate tariffs.
The plug-and-play mechanisms of the DSLAM allow the interface to launch automatically. You can save all configuration information between hot swaps and reboots, while interface types are automatically discovered by the DSLAM, eliminating the need for mandatory manual configuration.
If ILMI has been disabled or if the connecting end node does not support ILMI, these defaults are assigned to all DS3 interfaces:
These defaults are assigned to all DS3 interfaces:
These defaults are assigned to all E3 interfaces:
The default subtend ID for each NI-2 DSLAM is 0 (zero).
To manually change any of the DS3 or E3 default configuration values, perform these tasks:
 |
Note Note that Steps 2 and 14 are alternatives; do not perform both steps. |
This example shows how to change the default ATM interface type to "private" using the atm uni type private command.
DSLAM# configure terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
DSLAM(config)# interface atm 0/1
DSLAM(config-if)# atm uni type private
This example shows how to change the clock source using the clock source network-derived command.
DSLAM# configure terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
DSLAM(config)# interface atm 0/1
DSLAM(config-if)# clock source network-derived
 |
Note See the "Interface Configuration Troubleshooting" section, to confirm your interface configuration. |
Cisco IOS Inverse Multiplexing over ATM (IMA) is available for Cisco 6015 and Cisco 6160 DSLAMs with installed DS3+T1/E1 IMA NI-2 cards.
The T1/E1 inverse multiplexing over ATM uses IMA technology to aggregate multiple low-speed links (T1/E1) into one or more IMA groups at speeds between 1.5 Mbps and 12 Mbps for T1 and between 2 Mbps and 16 Mbps for E1. IMA breaks up the ATM cell stream and distributes the cells over the multiple physical links of an IMA group and then recombines the cells into a single stream at the other end of the connection. The multiple links of an IMA group increase the logical link bandwidth to approximately the sum of the individual link rates.
The T1/E1 IMA features for the Cisco 6015 and the Cisco 6160 DSLAMs offer the following benefits:
IMA links transmit IMA control protocol (ICP) cells, which enable the reconstruction of the original ATM cell stream. ICP cells define and separate IMA frames passing through each physical link in an IMA group. ICP cells also control the operation of IMA by accounting for cell delay variation (CDV), which is introduced by ICP cells, and the link differential delays on physical links to ensure the proper reassembly of IMA frames. If an IMA frame length of 128 cells is used, 1 out of every 128 cells on a physical link is an ICP cell. In this scenario, a frame containing fewer than 128 cells is injected with filler cells. The receiving end of an IMA group extracts the ICP and filler cells as the IMA stream is reconstructed into an ATM cell stream and passed to the ATM layer. IMA operation is transparent to ATM layer protocols. Therefore, the ATM layer operates as if a single physical interface were being used.
Figure 8-1 illustrates IMA with three bundled links.
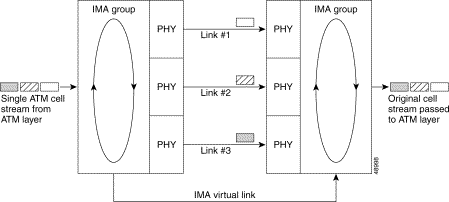
Depending upon the installed I/O module (1DS3+8T1 I/O or 8xE1 I/O), IMA can be configured by a grouping of the following physical links (see the "Supported Platforms" section):
 |
Note See the "Supported Platforms" section on page 8-9 for detailed information on platform-specific support of the network I/O modules. |
The DS3+T1/E1 IMA NI-2 supports three modes of operation:
 |
Note The type of network I/O module (1DS3+8T1 I/O or 8xE1 I/O) detected at system startup determines the mode of operation. |
The eight links on the DS3+T1/E1 IMA NI-2 can be independent ATM links or can be configured into one or more IMA groups. There are four static IMA groups. Each IMA group can contain from zero to eight T1/E1 links. Any combination of independent T1/E1 links and IMA groups is allowed, up to eight T1/E1 links total.
Some examples of allowed combinations are:
Table 8-2 show the supported platforms for the IMA feature.
Before you can configure a Cisco 6015 or Cisco 6160 DSLAM to provide T1/E1 IMA service, you must perform the following tasks:
Perform the following tasks to configure ATM interfaces for IMA:
Each link can be used as an independent T1/E1 ATM link with all the properties and functionality of ATM interfaces. When the link becomes part of an IMA group, its independent ATM functionality ceases; however, the IMA group can be configured like a single ATM port.
The DS3+T1/E1 IMA NI-2 card supports the trunk selection feature. This feature allows you to configure any WAN interface (the DS3, any T1 link, any E1 link, or any IMA group) as the trunk. When you configure a T1 link or an IMA group as the trunk, the DS3 port is disabled. When you select the DS3 port as the trunk, the T1 links and IMA groups are all treated as subtended ports.
Use the show running-config command to verify that the DSLAM running configuration contains the following statement:
atm ni2-switch trunk ATM 0/1
If the trunk interface is not the interface you meant to select, using the atm ni2-switch trunk command, repeat the procedure in the "Configuring a Trunk Interface" section.
To configure a T1 or E1 interface, use the following procedure:
After configuring your T1/E1 interfaces, use the following commands to verify their operational status:
| Command | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
Step 1 | DSLAM# show interface atm0/2
| Displays the interface configuration, status, and statistics of the ATM interface. |
Step 2 | DSLAM# show controllers
atm0/2
| Displays diagnostic information for the specified interface. |
If an interface is down and you configured it as up, or if the displays indicate that the hardware is not functioning properly, make sure that the T1/E1 interface is properly connected and configured.
To configure an IMA interface, you must use configuration mode (manual configuration). In this mode, you enter Cisco IOS commands at the DSLAM prompt.
| Command | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
Step 1 | DSLAM> enable
| Enter enable mode. |
Step 2 | DSLAM# configure terminal
| Enter global configuration mode, which has a prompt of |
Step 3 | DSLAM(config)# interface atm 0/2
| Enter interface configuration mode, which has a prompt of |
Step 4 | DSLAM(config-if)# ima-group 2
| Assign the ATM interface to an IMA group (numbered from 0 to 3). After the interface is assigned to an IMA group, individual ATM functionality is no longer available on the link. |
Step 5 | DSLAM(config-if)# no shutdown
| Enable the individual link by canceling the shutdownstate. Repeat Step 3 through Step 5 if your DSLAM has more than one interface that you need to configure. |
Step 6 | DSLAM(config-if)# exit
| Return to global configuration interface mode. |
Step 7 | DSLAM(config)# interface atm0/ima2
| Begin configuring the IMA interface. |
Step 8 | DSLAM(config-if)# ima clock-mode independent
| Select the transmit clock mode for the selected IMAgroup. |
Step 9 | DSLAM(config-if)# ima differential-delay-maximum | Enter the maximum differential delay in milliseconds for the selected IMA group. |
Step 10 | DSLAM(config-if)# ima active-links-minimum 2
| Enter the minimum number of links that need to be operational for the selected IMA group. |
Step 11 | DSLAM(config-if)# no shutdown
| Enable the IMA group by canceling the shutdownstate. |
Step 12 | DSLAM(config-if)# end
| When you finish configuring interfaces, return to enable mode. |
After configuring your IMA interfaces, use the following commands to verify their operational status.
If an interface is down and you configured it as up, or if the displays indicate that the hardware is not functioning properly, make sure that the new interface is properly connected and configured.
Use the following general guidelines to troubleshoot IMA groups and the individual links of an IMA group.
| Command | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
Step 1 | DSLAM# show interface atm 0/2
| Use the show interface atm command to verify the status of a T1 or E1 link. Verify that the administrative status and protocol status are both up. Also, check for CRC errors and loopback status. |
Step 2 | DSLAM# show running-config
interface atm 0/2
| Verify that the interface is not shut down. Also, compare the interface configuration with the far end interface to ensure that there are no configuration mismatches. |
Step 3 | DSLAM# show controllers
| Use the show controllers command to verify the port status and view any active alarms states. |
| Command | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
Step 1 | DSLAM# show ima interface
atm0/ima0
| Verify that the IMA group status is up. Also, use the command output to verify the IMA configuration at the near and far end. |
Step 2 | DSLAM# show ima interface
atm0/2
| Verify that the member links of the IMA group are up. |
Step 3 | DSLAM# show ima counters
| The show ima counters command reports IMA statistics in 15-minute intervals with 24 hour totals. |
See http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/dsl_prod/6015/user/hig/index.htm for troubleshooting information.
This section describes commands that you can use to monitor and maintain IMA configurations. Table 8-3 lists the commands.
This section contains sample configurations that show how to configure the following trunks:
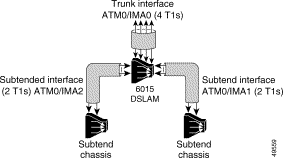
The following sample configuration shows how to configure the following groups:
Figure 8-2 illustrates the network topology being configured in the following configuration sample.
 |
Note Comments are written in boldface type and encapsulated with exclamation points. |
...
atm ni2-switch trunk ATM0/IMA0 !Configures interface ATM0/IMA0 as the trunk!
!
!
!
interface ATM0/0
no ip address
no ip route-cache
atm maxvp-number 0
atm maxvc-number 4096
atm maxvci-bits 12
!
interface Ethernet0/0
ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
no ip route-cache
!
interface ATM0/1
no ip address
no ip route-cache
shutdown
no atm ilmi-keepalive
!
interface ATM0/2
no ip address
no ip route-cache
no ip mroute-cache
no atm ilmi-keepalive
clock source loop-timed
scrambling cell-payload
linecode ami
lbo short 133
ima-group 0 !Adds this interface to IMA group 0!
!
interface ATM0/3
no ip address
no ip route-cache
no ip mroute-cache
no atm ilmi-keepalive
clock source loop-timed
scrambling cell-payload
linecode ami
lbo short 133
ima-group 0 !Adds this interface to IMA group 0!
!
interface ATM0/4
no ip address
no ip route-cache
no ip mroute-cache
no atm ilmi-keepalive
clock source loop-timed
scrambling cell-payload
linecode ami
lbo short 133
ima-group 0 !Adds this interface to IMA group 0!
!
interface ATM0/5
no ip address
no ip route-cache
no ip mroute-cache
no atm ilmi-keepalive
clock source loop-timed
scrambling cell-payload
linecode ami
lbo short 133
ima-group 0 !Adds this interface to IMA group 0!
!
interface ATM0/6
no ip address
no ip route-cache
no ip mroute-cache
no atm ilmi-keepalive
clock source loop-timed
scrambling cell-payload
linecode ami
lbo short 133
ima-group 1 !Adds this interface to IMA group 1!
!
interface ATM0/7
no ip address
no ip route-cache
no ip mroute-cache
no atm ilmi-keepalive
clock source loop-timed
scrambling cell-payload
linecode ami
lbo short 133
ima-group 1 !Adds this interface to IMA group 1!
!
interface ATM0/8
no ip address
no ip route-cache
no ip mroute-cache
no atm ilmi-keepalive
clock source loop-timed
scrambling cell-payload
linecode ami
lbo short 133
ima-group 2 !Adds this interface to IMA group 2!
!
interface ATM0/9
no ip address
no ip route-cache
no ip mroute-cache
no atm ilmi-keepalive
clock source loop-timed
scrambling cell-payload
linecode ami
lbo short 133
ima-group 2 !Adds this interface to IMA group 2!
!
interface ATM0/IMA0 !IMA group 0 configuration!
no ip address
no ip route-cache
no ip mroute-cache
no atm ilmi-keepalive
ima active-links-minimum 2
ima clock-mode independent
ima differential-delay-maximum 68
!
interface ATM0/IMA1 !IMA group 1 configuration!
no ip address
no ip route-cache
no ip mroute-cache
no atm ilmi-keepalive
ima active-links-minimum 2
ima clock-mode independent
ima differential-delay-maximum 68
!
interface ATM0/IMA2 !IMA group 2 configuration!
no ip address
no ip route-cache
no ip mroute-cache
no atm ilmi-keepalive
ima active-links-minimum 2
ima clock-mode independent
ima differential-delay-maximum 68
!
interface ATM0/IMA3
no ip address
no ip route-cache
shutdown
no atm ilmi-keepalive
...
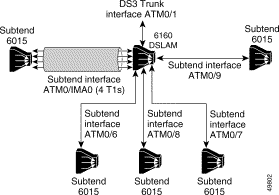
The following sample configuration involves a network topology containing a mixture of IMA, T1, and DS3 interfaces. It is relevant only to IMA on platforms with the 1DS3+8xT1 I/O module installed.
Figure 8-3 illustrates the network topology being configured in the following configuration sample.
...
atm ni2-switch trunk ATM0/1 !DS3 is the default trunk!
!
!
!
interface ATM0/0
no ip address
no ip route-cache
atm maxvp-number 0
atm maxvc-number 4096
atm maxvci-bits 12
!
interface Ethernet0/0
ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
no ip route-cache
!
interface ATM0/1
no ip address
no ip route-cache
no atm ilmi-keepalive
!
interface ATM0/2
no ip address
no ip route-cache
no atm ilmi-keepalive
ima-group 0 !Adds this interface to IMA group 0!
!
interface ATM0/3
no ip address
no ip route-cache
no atm ilmi-keepalive
ima-group 0 !Adds this interface to IMA group 0!
!
interface ATM0/4
no ip address
no ip route-cache
no atm ilmi-keepalive
ima-group 0 !Adds this interface to IMA group 0!
!
interface ATM0/5
no ip address
no ip route-cache
no atm ilmi-keepalive
ima-group 0 !Adds this interface to IMA group 0!
!
interface ATM0/6 !T1 configuration!
no ip address
no ip route-cache
no ip mroute-cache
no atm ilmi-keepalive
clock source loop-timed
scrambling cell-payload
linecode ami
lbo short 133
!
interface ATM0/7 !T1 configuration!
no ip address
no ip route-cache
no ip mroute-cache
no atm ilmi-keepalive
clock source loop-timed
scrambling cell-payload
linecode ami
lbo short 133
!
interface ATM0/8 !T1 configuration!
no ip address
no ip route-cache
no ip mroute-cache
no atm ilmi-keepalive
clock source loop-timed
scrambling cell-payload
linecode ami
lbo short 133
!
interface ATM0/9 !T1 configuration!
no ip address
no ip route-cache
no ip mroute-cache
no atm ilmi-keepalive
clock source loop-timed
scrambling cell-payload
linecode ami
lbo short 133
!
interface ATM0/IMA0 !IMA group 0 configuration!
no ip address
no ip route-cache
no ip mroute-cache
no atm ilmi-keepalive
ima active-links-minimum 4
ima clock-mode independent
ima differential-delay-maximum 68
!
interface ATM0/IMA1
no ip address
no ip route-cache
shutdown
no atm ilmi-keepalive
!
interface ATM0/IMA2
no ip address
no ip route-cache
shutdown
no atm ilmi-keepalive
!
interface ATM0/IMA3
no ip address
no ip route-cache
shutdown
no atm ilmi-keepalive
...
You can use the following privileged EXEC mode commands to confirm that the hardware, software, and interfaces for the DSLAM are configured as intended.
You can also view an ATM layer fault state and loss of cell delineation using the CLI and MIB. The default alarm level for this fault state is Major.
You can use the following privileged EXEC mode commands to initiate line loopbacks.
| Command | Purpose |
|---|---|
DSLAM# loopback diagnostic
| Diagnostic loopback. The outgoing cells are looped back toward the switch. This command is available on all ports. |
DSLAM# loopback line
| Line loopback. The incoming line is looped back toward the coax. This command is available only on trunk and subtending ports. |
DSLAM# loopback payload
| Payload loopback. The incoming payload is looped back toward the coax. This command is available only on DS3 trunk and subtendingports. |
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Posted: Mon Dec 9 15:07:21 PST 2002
All contents are Copyright © 1992--2002 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Important Notices and Privacy Statement.