|
|

This chapter provides information about configuring your Cisco 626 ATM ADSL Modem. Your unit comes to you completely preconfigured for full operation. However, you may need to configure for management virtual connections (VC) and network timeouts. This chapter provides configuration procedures for management VCs and network timeouts.
The following table identifies the configuration procedures you may need. Please check with your service provider before proceeding with any configuration procedures.
| Configuration Procedures | Page Number |
|---|---|
3-2 | |
3-3 3-11 | |
3-12 | |
3-13 | |
3-13 3-14 |
After connecting all system cables, turning on the system, and starting the terminal access program, press the Enter key until the CBOS welcome screen appears. When you see the welcome screen, you can logon to the CBOS.
The CBOS also has two modes of operation: exec and enable. The CBOS defaults to exec mode when you log in. exec mode grants read-only (command execution) privileges to a user.
To write changes to NVRAM, you must work in enable mode. Follow the steps below to invoke enable mode:
1. Type enable at the command line:cpe626# enabled
2. Type another password when CBOS prompts you:cpe626# enabledPassword:
Your system comes preconfigured for full and immediate network operation. However, you may need to directly manage your Cisco 626 over the network. To do this you must establish and set management virtual connections (VC).
Each interface is expressed as atmx, where x is either 0 or 1. The atm0 interface is reserved for the local interface. The atm1 interface is used for the ADSL remote interface.
The valid ranges for the VPI and VCI addresses is shown in the following table.
| VPI Range | VCI Range |
|---|---|
0 to 255 | 0 to 65535 |
1. To set the VPI number to 2, enter:cpe626# set interface atm1 vpi 2
2. To begin using this connection with the new settings, enter:cpe626# set interface atm1 enable
To verify your setting do:
cpe626# set interface atm1
A display similar to the following will print to your screen:
atm1 RFC1483
IP address 192.168.1.100 Mask 255.255.255.0
MTU 1500 Metric 0
RX packets 0 errors 0
TX packets 0 errors 0
Port is currently enabled with no link status
VCI 32 VPI 2
3. Repeat steps 1 and 2 for every VPI assignment you want to make.
4. To save the new WAN port configuration, enter:cpe626# write
5. To exit the CBOS, enter:cpe626# quit
1. To set the VCI number to 4, enter:cpe626# set interface atm0 vci 32
To verify your setting do:
cpe626# set interface atm0
A display similar to the following will print to your screen:
atm1 RFC1483
IP address 192.168.1.100 Mask 255.255.255.0
MTU 1500 Metric 0
RX packets 0 errors 0
TX packets 0 errors 0
Port is currently enabled with no link status
VCI 32 VPI 2
2. To begin using this connection with the new settings, enter:cpe626# set interface atm0 open
3. Repeat steps 1 and 2 for every VCI assignment you want to make.
4. To save the new WAN port configuration, enter:cpe626# write
5. To exit the CBOS, enter:cpe626# quit
Telnet provides a command line interface and is used as a means of providing remote login connections between machines on many networks, including the Internet.
 | Caution Before closing a Telnet connection, always enter exit or quit at the cbos# prompt. |
1. Click on the Start button.
2. Select the Run... option.
3. When the Run box appears, enter telnet in the space provided.
4. Click the OK button. The Connect menu appears.
5. Select the Remote System... option from the Connect menu. The following window appears:
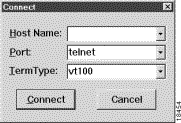
6. Enter the IP address of your modem in the Host Name box and press Connect. The system then initiates a connection session. When connection is initiated, information, similar to the following, is printed to your display:
Cisco Broadband Operating System V2.1.0 - Cisco 626 CPE
Copyright (c) 1999 Cisco Systems,Inc. All rights reserved.
12515 Research Blvd. Building 4 - Austin Texas USA - www.cisco.com
Login:
7. Provide the login and password information. Once the system authenticates your password, you have access to the CBOS.
Windows' Telnet client does not support NVT (Network Virtual Terminal) or any extra form of option negotiation. However, if you are going to use the Windows Telnet client, please read the following steps to set your terminal settings.
1. When the Telnet window appears, access the Preferences menu in Telnet by selecting Preferences from the Terminal drop down menu.
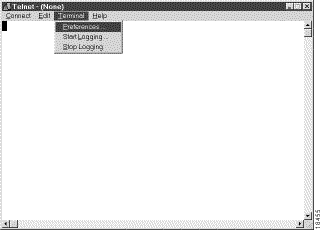
2. Set the terminal settings on the Terminal Preferences menu to the following values:
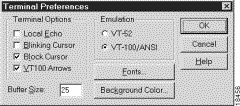
When you run Linux without installing the Term/Termcap database, the message BAD ADDRESS displays during a connection attempt. Use the original Linux installation disks to install the Term/Termcap database.
The following procedure describes how to log on to your ADSL DMT modem from a UNIX system.
1. Enter the following at your prompt:
telnet <IP address of your system >
Once you have connected, information similar to the following appears on your display:
Cisco Broadband Operating System V2.1.0 - Cisco 626 CPE
Copyright (c) 1999 Cisco Systems,Inc. All rights reserved.
12515 Research Blvd. Building 4 - Austin Texas USA - www.cisco.com
Login:
2. Provide the login and password information. Once the system authenticates your password, you have access to the CBOS.
Telnet sessions time out after a period of inactivity. Enter the following commands to keep the Telnet client from timing out.
cpe626# set telnet timeout off
cpe626# write
The set telnet timeout off setting is not saved in NVRAM after a reboot. You must explicitly set it for every session.
The Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP) enables you to transfer files to and from your ADSL DMT modem. Your system runs a tftp daemon that enables remote users who have TFTP client software, to transfer files to and from the system. The TFTP client is enabled and disabled from the CBOS or the Web Management Interface.
 | Caution For security reasons, Cisco recommends that you disable the TFTP application, except when uploading or downloading a file. |
Use the TFTP utility to transfer a new software image from Cisco to your system, where the file name equals nsrouter.ima.626.
Use the TFTP utility to backup a copy of your configuration file before changing it so you can easily recover the old file if necessary. The naming conventions for the configuration file are:
nscfg.cfg.
For information on the UNIX TFTP client, access the online manual on your UNIX system, by entering:
man tftp
At your command line prompt and the manual page for TFTP appears. The TFTP UNIX man page contains all the information you need to establish and invoke a remote TFTP session.
Follow these steps:
1. Set the IP address for the remote TFTP host computer by entering:
cpe626# set tftp remote <TFTP Host Computer IP Address >
This command instructs the system to accept TFTP transfers from that specific IP address.
2. Start a DOS session and enter one of the following commands:C:>tftp -i <IP address > get/put <nsrouter software image file name >tftp -i
C:> <IP address> get/put <system configuration config file name >
Where necessary, implement the following options:
-i - Sets the transfer mode to binary mode.
get - Downloads a file to a specified IP address.
put - Uploads a file onto that IP address.
3. Be sure that you reboot the device to activate the new image. When you log back onto your system after the reboot, use the following command to verify the version of the firmware that is active:
cbos# show version
Windows 95 does not have a TFTP client. If you want to utilize TFTP on a Windows 95 system, you must install a TFTP client from a third-party vendor on your system. One way to locate a TFTP client is to use an Internet search engine to locate a vendor who sells a TFTP client. Some TFTP clients are provided as share or freeware on the Internet. By request, Cisco will provide a TFTP client.
Your system supports a session timeout value. The session timeout is based on the total uptime of the session. The expiration of the session timeout will end the session. However, since authentication is invisible, only the training delay is perceived by the user (approximately seven to fifteen seconds) when the connection is re-established.
Use the set timeout command to configure the session timeout value in seconds.
1. To set the session timeout rate to 300, enter:cpe626# set timeout session 300
2. To save your changes, enter:cpe626# write
3. To exit the CBOS, enter:cpe626# quit
The default Cisco 626 system prompt is cpe626#. The command prompt is limited to 8 characters. You can change this prompt to a unique subscriber identifier as shown in the following example.
1. Logon to the CBOS using either the serial or Telnet interfaces. Refer to the "Using Telnet" section in this chapter for more information on how to use Telnet to logon to the CBOS.
2. To change the default prompt to 4412883 as the subscriber identifier, enter:cpe626# set prompt cbos626#
cbos626#
3. To save your changes, enter: cpe626# write
4. To exit the CBOS, enter: cpe626# quit
After you have configured your sstem, you should pick new passwords for both the enable and exec modes. Keep in mind that the enable mode provides all the functionality of a system administrator for the ADSL DMT modem. Examples of good and bad passwords are:
Use the set password command to change both the root and user passwords as in the following:
1. To change the password enter:cpe626# set password <mode > <new password >Example: set password enable 33Low44PassMe
2. To save your changes, enter:cpe626# write
3. To exit the CBOS, enter:cpe626# quit
Use the write command to save any changes you have made during provisioning to the NVRAM configuration file.
cpe626# write
 | Caution If you do not use the write command after changes, all the changes you made during your current session will be lost when you reboot the Cisco 626. |
The following table describes the LEDs and their status.
| LED Label | Full Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
WAN-LNK | WAN Link | When this light is ON, it indicates that a link has been established on the WAN port. The WAN-LNK light blinks steadily during ADSL line training activities. When the light is solid, the system is connected and trained. If the light blinks in a number of times and then stops blinking, this indicates that the Central Office equipment is unavailable. |
WAN-ACT | WAN Activity | When this light blinks ON, indicates that the WAN port is transmitting or receiving data. |
LAN-LNK | ATM25 LAN Link | When this light is ON, it indicates that a link has been established on the ATM25 port. |
LAN-ACT | ATM25 LAN Activity | When this light blinks ON, it indicates activity on the ATM25 port. |
PWR | Power Light | When this two-color light is Green, the system is ON and working correctly. |
ALARM | Alarm Light | When the light is Red, the system is ON but indicates a problem or that needs to be resolved. |
The stats command shows information about the number of packets transmitted and received and activity information about general applications.
To retrieve statistics:
1. To see a list of variables, enter:cpe626# stats
2. To display specific statistics, enter:cpe626# stats <variable from list >
3. To exit the CBOS, enter:cpe626# quit
Use the stats command to retrieve key statistics regarding ADSL performance. These statistics are:
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Posted: Tue Mar 16 08:34:01 PST 1999
Copyright 1989-1999©Cisco Systems Inc.