|
|

The Cisco AS5200 universal access servers support Microcom or MICA modem carrier cards. For details on the carrier cards, refer to the Cisco AS5200 Universal Access Server Hardware Installation Guide.
You can manage your modems using monitoring, polling, and troubleshooting commands. For both Microcom and MICA modems, most of the modem management functions are identical. This appendix discusses procedures and commands common to both types of modems as well as procedures and commands that apply to only one type of modem. Sections or commands that apply to only one type of modem are clearly indicated.
This appendix includes the following sections:
This section describes how to send AT commands to Microcom and MICA modems.
For a list and description of AT commands, refer to the AT Command Set and Register Summary for MICA Six-Port Modules or AT Command Set and Register Summary for V.34 and 56K 12-Port Modules publications.
To monitor Microcom (V.34 and 56K) modems you must perform two main configuration tasks:
Table B-1 describes all the steps necessary to enter AT command mode on the access server.
To send AT commands to a MICA modem involves a reverse Telnet procedure. Table B-2 shows how to enter AT command mode from EXEC mode using reverse Telnet.
Note MICA modems do not support the modem at-mode commands available in Cisco IOS line configuration mode.
You can view modem statistics and configure modem events using the Cisco IOS software with the Cisco AS5200 access server. To view performance statistics for the Microcom and MICA modems, enter one or more of the following commands in enable mode (the prompt is displayed as 5200#):
To view additional performance statistics for MICA modems only, enter one or more of the following commands in EXEC mode:
Note The first three channels displayed for each board are the DC session (#60), Status polling (#61), and the control (#62) channel.
This section describes how to manage modems by checking the type of modem connected to the access server, removing inoperable modems from service, disabling a modem from dial-up service, and setting modem recovery times and event buffers. For details on disabling a modem from dial-up services, see the section, "Troubleshooting Modems," later in this appendix.
To check the type of modem connected to the access server and to configure the modem automatically, enter the following command in global configuration mode [the prompt is displayed as 5200(config)#]:
The modem is identified each time the line is reset. If a modem cannot be detected, the line continues retrying for 10 seconds. After the modem type is determined, this information remains stored until the modem is recycled or disconnected. Discovery mode is much slower than configuring a line directly.
Each time the modem is reset (every time a chat reset script is executed), a string of commands is sent to the modem, the first one being "return to factory-defaults."
This section applies to Microcom modems only. To configure the size of the history event queue buffer for manageable modems in the access server, enter the following command in global configuration mode [the prompt is displayed as 5200(config)#]:
This section applies to Microcom modems only. To set the maximum amount of time the call-switching module waits for a local modem to respond to a request before it is considered locked in a suspended state, enter the following command in global configuration mode [the prompt is displayed as 5200(config)#]:
After the call-switching module resets a suspended modem, the module recovers to a default call-switching module state.
To remove modems from service and indicate them as suspected or proven to be inoperable, enter the following command in line configuration mode [the prompt is displayed as 5200(config-line)#]:
If you mark a single modem as inoperable using this command, it appears as Bad—without the asterisk (*)—in the Status column of the show modem command's output for that particular modem. A modem marked inoperable by the modem startup-test command appears as Bad* in the show modem command output for that particular modem. Use the no modem bad command to unmark a modem as Bad* or Bad and restore it for dial-up connection services.
This section describes polling modems for statistics, including setting the time interval between polls and the maximum number of polling attempts.
To set the maximum number of polling attempts used to retrieve a local modem's status or statistics, enter the following command in global configuration mode [the prompt is displayed as 5200(config)#]:
If the number of attempts to retrieve modem status or statistics exceeds the number you define, the out-of-band port is removed from operation. In this case, you must reset the modem hardware using the clear modem command.
To set the time interval between the polls that are sent to the local modems for reporting modem status and statistics, enter the following command in global configuration mode [the prompt is displayed as 5200(config)#]:
To poll for a modem's status and statistics through its out-of-band port, enter the following command in line configuration mode [the prompt is displayed as 5200(config-line)#]:
The no modem status-poll command disables status polling through the out-of-band port for a specified modem.
This section describes how to perform diagnostic testing on installed modems, test two modems back-to-back, disable modems from service, reset a modem, and debug a modem.
To perform diagnostic testing on all the installed modems during the system's initial startup or rebooting process, enter the following command in global configuration mode [the prompt is displayed as 5200(config)#]:
The results of the modem startup test are displayed in the Status column of the show modem command's output. Modems that pass the diagnostic test are marked as Idle, Busy, Downloading, and Reset. Modems that fail the diagnostic test are marked as Bad*. These modems cannot be used for call connections. Depending on how many modems are installed, this diagnostic test may take from 5 to 15 minutes to complete. Perform additional testing on an inoperative modem by executing the test modem back-to-back command. The no modem startup-test command disables startup testing.
Perform additional testing on a modem suspected of being inoperable by conducting a series of internal back-to-back connections and data transfers between two modems. All modem test connections occur inside the access server. For example, if mobile users cannot dial into modem 2/5 (which is the sixth modem port on the modem board in the second chassis slot), attempt a back-to-back test with modem 2/5 and a known-functioning modem such as modem 2/6. Enter the following command in enable mode (the prompt is displayed as 5200#) to perform internal back-to-back modem tests between two modems:
You might need to enable this command on several different combinations of modems to determine which one is not functioning properly. A pair of operable modems successfully connect and complete transmitting data in both directions. An operable modem and an inoperable modem do not successfully connect with each other.
This section applies to Microcom modems only. To reset and isolate the modem hardware for extensive troubleshooting, enter the following command in line configuration mode [the prompt is displayed as 5200(config-line)#]:
Use this command if you are experiencing extreme modem behavior (for example, the modem is uncontrollably dialing into the network). This command prevents the modem from establishing software relationships such as those created by the test back-to-back modem and modem startup-test commands. The modem is unusable while the this ommand is configured.
This command is also used to reset a modem that is frozen in a suspended state. Disable the suspended modem with the modem hold-reset command, and then restart hardware initialization with the no modem hold-reset command. A modem decommissioned by the modem hold-reset command does not accept modem firmware upgrades using the copy modem command.
To disable modems from dialing or answering calls, enter one of the following commands in line configuration mode [the prompt is displayed as 5200(config-line)#]:
The modem busyout command is not executed until the active modem is idle. No active connections are interrupted when you use this command. In contrast, the modem shutdown command immediately terminates all active connections on the specified modem. The resulting modem status for both these commands is the same. Enable the no form of these commands to restore a modem for dial-up services.
You can still configure the following commands on a disabled modem:
To debug a modem or group of modems, enter the following commands in enable mode (the prompt is displayed as 5200#):
Modem code is a generic term applied to a modem code file, which is also called portware for MICA modems and firmware for Microcom modems.
With new systems, Cisco loads a Cisco IOS software-compatible version of modem code and copies the version to the installed modem modules. A map of the version(s) of modem code copied to the modem RAM for each modem module is stored in nonvolatile random-access memory (NVRAM) so that it is retained over power cycles.
Note You do not have to take any action to use the pre-installed version of modem code with new systems.
You can acquire new modem code in several ways:
This section describes how to upgrade modem code on your access server modems by:
1. Understanding the modem code scenarios possible for your access server.
2. Choosing an upgrade strategy.
3. Finding out the modem code version installed on your access server.
You can obtain modem code in one of two ways:
There are several commands you use to upgrade modem code. For examples on using the commands, see "Upgrading Modem Code from the Cisco CCO TFTP Server," "Upgrading Modem Code from Diskettes," and "Using the Modem Code Bundled with Cisco IOS Software," later in this appendix, for details.
Because of multiple versions of modem code and the way Cisco IOS software processes these versions, Cisco suggests that you choose one of the following two strategies:
To help with the decision, Figure B-1 shows a hypothetical release process. Using the modem code bundled with Cisco IOS software is the easier strategy and enables you to take advantage of new modem code whenever you upgrade your Cisco IOS software. Note that you can also control the modem code by reverting to previous versions using the copy command as discussed later.
Table B-3 provides scenarios that can occur when you upgrade Cisco IOS software or modem code.
| No. | Scenario | Update Process |
|---|---|---|
You update Cisco IOS software, and decide to use the version of modem code selected by Cisco IOS software. |
||
You update Cisco IOS software, and decide not to use the modem code selected by Cisco IOS software. |
|
|
The modems are running a version of modem code from boot Flash memory that is different than the version bundled with Cisco IOS software. You decide to revert to the bundled version. |
|
|
Cisco releases new modem code, which is a later version than the version currently running on the modems. You decide to use the new Cisco modem code.3 |
|
| 1To find out the version of modem in your system, use the show modem mapping command. This command displays the versions bundled with Cisco IOS (copied into Flash memory) and running on the modems.
2 In part, Cisco IOS software bases this decision on the last copy command issued. For more details about mapping, see Table B-5. 3 Cisco might ship this modem code on a diskette packed with the 6-port module. |
Figure B-2 shows a release timeline and Table B-4 explains the resulting versions of Cisco IOS software and modem code.
| 1This example assumes the last copy command was copy bootflash modem, and Modem Code Version 1 was specified. |
Table B-5 provides a list of modem code terminology and a description of how the terms are used in the modem code update process.
| 1This command is supported in Cisco IOS Releases 11.2(11)P and 11.3(2)T. |
Use the show modem mapping command to list all modem code files in the boot Flash memory, system Flash memory, and the modem code files bundled with Cisco IOS software. This will help you decide if you need to update your modem code files.
This is an example for Microcom modems.
This is an example for MICA modems.
Upgrading modem code from the Cisco CCO TFTP server is a two-step process:
Note Cisco IOS software contains bundled modem code, which might differ from the version of modem code you download. For more information about how Cisco IOS software processes multiple modem code versions, refer to the earlier sections "Choosing an Update Strategy" and "Modem Code Scenarios" for details.
You can download software from the CCO TFTP server using an Internet browser or FTP application. Both procedures are described below.
Note To download modem code from CCO to a PC and then upgrade the modem code to an access server connected to your PC via an Ethernet hub, you need to set up a TFTP application on your PC, establish a HyperTerminal session, and make sure your PC and access server are correctly connected and talking before downloading the modem code from CCO. All these procedures are described in "Upgrading Modem Code from Diskettes," later in this appendix.
Step 2 Bring up the Cisco Software Center home page at the following URL (this is subject to change without notice):
http://www.cisco.com/kobayashi/sw-center/
Step 3 Click Access Products (under Cisco Software Products) to open the Access Products window.
Step 4 Click Cisco AS5200 Series Software.
Step 5 Click the modem code you want and download it to your workstation or PC. For example, to download modem code for the Microcom modems, click Download Microcom V.34 Modem Firmware or Download Microcom 56K Modem Firmware under the respective sections.
Step 6 Click the modem code file you want to download, and then follow the remaining download instructions. If you are downloading the modem code file to a PC, make sure you download it to the c:\tftpboot directory; otherwise, the download process will not work.
Step 7 When the modem code is downloaded to your workstation, transfer the file to a TFTP server in your LAN using a terminal emulation software application.
Note The directory path leading to the modem code files on cco.cisco.com is subject to change without notice. If you cannot access the files using an FTP application, try the Cisco Software Center URL http://www.cisco.com/kobayashi/sw-center/.
Step 2 Enter your CCO registered username and password (for example, harry and letmein):
Step 3 Specify the directory path that holds the Modem Codem code you want to download. For example, the directory path for the Cisco AS5200 modem code is /cisco/access/5200:
Step 4 View the contents of the directory with the ls command:
Step 5 Specify a binary image transfer:
Step 6 Copy the modem code files from the Cisco AS5200 to your local environment with the get command.
Step 7 Quit your terminal session:
Step 8 Verify you successfully transferred the files to your local directory:
Step 9 Transfer these files to a local TFTP or RCP server that your access server or router can access.
The procedure for copying the modem code file from your local TFTP server to the modems involves two steps. First, you need to transfer the code to the access server's boot Flash memory. Then, you need to transfer the code to the modems.
These two steps are performed only once. After you copy the modem code file into boot Flash memory for the first time, you should not have to perform these steps again. Because the modem code runs from modem RAM, the Cisco IOS software automatically copies the modem code to each modem each time the access server power cycles.
Perform the following steps to download modem code to MICA modems:
Step 2 Enter the access server enable mode (the prompt is displayed as 5200#):
Step 3 Check the files in the access server boot Flash memory:
Step 4 Download the modem code file from TFTP server into the access server boot Flash memory using the copy tftp bootflash command. After you enter the command, you are prompted for the download destination and the remote host name as requested by the system software.
This is a Microcom modem example.
Step 5 Verify the file has been copied into the access server boot Flash memory:
Step 6 Copy the modem code file from the access server boot Flash memory to the modems by entering the copy bootflash modem command:
This is a Microcom modem example.
Note The modem code is downloaded to the module, not the individual slot/ports as indicated by the screen display.
This section describes how to copy modem code from diskettes to your hard disk in a PC environment, and then upload the modem code to the modems. The steps are similar if you are using a Macintosh or UNIX workstation.
Note If you loaded Cisco IOS software from a feature pack CD-ROM using Router Software Loader (RSL), note that the CD contains a TFTP server program for PCs using Microsoft Windows 95. Run the TFTP server program from the directory where you installed the RSL program. Remember to set the root directory to the directory where the Cisco AS5200 modem code is located. The RSL and the TFTP applications are also available on CCO in the software library in the Access Products section.
This section describes how to copy the modem code file to your hard disk in a PC environment. The steps are similar if you are using a Macintosh or a UNIX workstation.
Step 2 Use Microsoft Windows 95 Explorer to create a folder named tftpboot at your hard disk root c:.
Step 3 Use the Microsoft Windows 95 Explorer to copy the modem code file into the c:/tftpboot folder.
If you are using a PC running Microsoft Windows 95, installing the modem code from a hard drive onto a Cisco AS5200 involves installing a TFTP application on your PC, connecting your PC and the access server, establishing a HyperTerminal session on your PC, pinging the PC and access server to make sure they are talking to each other, copying the modem code from the PC to the access server, and then mapping the modem code to the modems. See the following sections for details.
Note You can use any TFTP or RCP application available from independent software vendors. A number of TFTP programs are also available as shareware from public sources on the World Wide Web. If you are using Microsoft Windows 95, you can also download a TFTP application (as zipped files) from the Cisco Software Center at http://www.cisco.com/public/sw-center.
Step 2 Launch the TFTP application by double-clicking the application icon or its filename.
Step 3 Set your TFTP server root directory:
In this step, you connect your PC and access server.
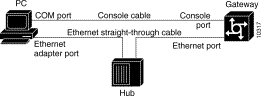
Note You can also connect your PC Ethernet port directly to the Cisco AS5200 Ethernet port using the 10BaseT crossover cable provided.
Step 2 Connect your PC COM port to the Cisco AS5200 console port, as shown in Figure B-3.
Step 3 Make sure your PC and access server are powered on.
Use the steps in this section to establish a HyperTerminal session from your local PC to the Cisco AS5200. You will use the HyperTerminal session to talk to the access server.
Step 2 Double-click Hypertrm.exe to display the Connection Description dialog box.
Step 3 Enter a name for your connection (for example, Console) and click OK. HyperTerminal displays the Phone number dialog box.
Step 4 Choose the COM port connecting the PC and the access server in the Connect using list box. You have options to connect directly to one of four COM ports.
Step 5 Click OK. HyperTerminal displays the COM Properties dialog box.
Step 6 Choose these options in the COM Properties dialog box:
Step 7 Click OK. The HyperTerminal dialog box appears.
Step 8 Press Enter to display the as5200# prompt.
Note If the access server prompt does not appear, you might have selected the wrong COM port, the cable connections could be incorrect or bad, or the access server might not be powered on.
Ping the access server and the PC to make sure they are talking to each other and there are no configuration problems on your access server.
(a). Choose Start/Run to display the Run dialog box.
(b). Enter winipcfg and click OK to display the IP Configuration dialog box.
(c). Choose the PC Ethernet adapter connector used for the connection to the access server if you have more than one Ethernet adapter connector installed on your PC.
Note Enter the show running config command at the 5200# prompt to verify the access server has an IP address assigned. If the access server does not have an IP address, assign an IP address before continuing.
Step 2 In the HyperTerminal dialog box (see the previous section "Establish a HyperTerminal Session" for details), enter the access server enable mode (the prompt is displayed as 5200#):
Step 3 Enter the ping command with your PC IP address:
The access server displays five exclamation points (!) if everything is working and it displays five dots (.) if there is a problem. In the latter case, check the cabling between the router and the PC and check the access server configuration
The procedure for copying the modem code file from your PC set up as a local TFTP server to the access server boot Flash memory is a two-step process.
These two steps are performed only once. After you copy the modem code file into boot Flash memory for the first time, you should not have to perform these steps again. Since the modem code runs from modem RAM, the Cisco IOS software automatically copies the code to each modem each time the access server power cycles.
Step 2 Download the modem code file from the TFTP server into the access server boot Flash memory using the copy tftp bootflash command. After you enter the command, you are prompted for the download destination and the remote host name as requested by the system software.
This is a Microcom modem example.
Step 3 Verify the modem code file has been copied into the access server boot Flash memory:
Step 4 Copy the modem code file from the access server boot Flash memory to the modems by entering the copy bootflash modem command:
This is a Microcom modem example.
Note The modem code is downloaded to the module, not the individual slot/ports as indicated by the screen display.
Use this procedure to update modem code on the modems in your access server if you decide to use the version of modem code bundled with Cisco IOS software instead of the version already mapped to your modems.
To set the modem code mapping to the modem code version bundled with Cisco IOS software, enter the following commands.
Step 2 Enter the copy system:/ucode/filename modem (or, for Cisco IOS releases earlier than 11.3AA or 12.0, the copy ios-bundled modem) command:
The copy system:/ucode/filename modem command does not affect any existing modem code that resides in boot Flash memory in case you later want to revert to it. If you decide to delete the code from boot Flash memory, remember that all files in boot Flash memory will be deleted, therefore save and restore any important files (for example, the Cisco IOS software image).
Note If the new Cisco IOS image contains the same modem code as the old one, no new code will be downloaded to the modems.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Posted: Sun Jan 19 10:55:40 PST 2003
All contents are Copyright © 1992--2002 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Important Notices and Privacy Statement.