|
|

This chapter describes the analog Microcom modem modules and cards used in the Cisco AS5300 universal access servers. This chapter includes the following sections:
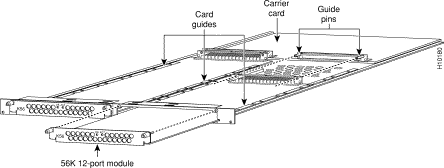
You can install up to two Microcom cards (see Figure 4-1) in any two slots of the access server chassis. Each Microcom card includes two slots in which you can install any combination of 12-port modem modules, as described below.
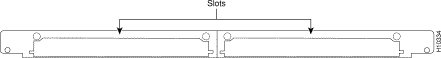
The modules connect through the Microcom card and the system backplane to a Quad or Octal T1/PRI or E1/PRI card installed in the access server chassis. Data is transmitted or received on T1 or E1 lines connected to the Quad or Octal T1/PRI or E1/PRI card and then routed to the modules installed in the Microcom card.
The access server supports any combination of the following 12-port modules:
You must install the 12-port modules in the Microcom carrier card. The 12-port modules cannot be used as standalone cards and they cannot be installed in MICA carrier cards.
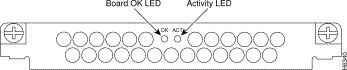
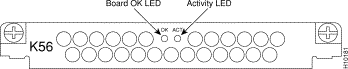
The 56K modem module uses Rockwell's K56flex technology. The modem can send data at up to 56 kbps and receive data at up to 33.6 kbps. However, the actual speed that you can achieve with the modem depends on the condition of your local telephone network.
The following requirements apply to using the 56K 12-port modem module:
The modem modules require Cisco IOS Release 11.2 (9)XA, 11.2 (10)P, or higher.
 | Caution If you skipped the chapter, "Safety Warnings, Recommendations, and Tools Required," (in the beginning of this guide), go back to that chapter and read it now. This chapter provides important safety information and a list of tools you need to successfully remove and install cards without damaging your access server. |
To install the modem module, refer to Figure 4-5 and take these steps:
 | Warning
Do not work on the system or connect or disconnect cables during periods of lightning activity. |
 | Caution The modem modules are not hot-swappable (that is, you cannot remove or install them when the power to the access server is ON). Be sure to turn OFF the power to the access server before installing or removing modem modules. Failure to do so can damage the access server. |
Step 2 Power OFF the access server. If using a DC-powered unit, refer to Figure 4-4 and complete steps a to d.
 | Warning Before performing any of the following procedures, ensure that power is removed from the DC circuit. To ensure that all power is OFF, locate the circuit breaker on the panel board that services the DC circuit, switch the circuit breaker to the OFF position, and tape the switch handle of the circuit breaker in the OFF position. |
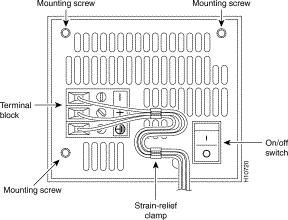
(a) Loosen the three locking screws for the negative, positive, and ground connectors on the DC power supply terminal block
(b) Remove the -48 VDC wire from the terminal block negative connector (-) .
(c) Remove the +48 VDC wire from the terminal block positive connector (+) .
(d) Remove the safety ground (green wire) from the terminal block ground connector.
Step 3 Remove all interface cables from the back panel of the access server.
Step 4 Remove the blank cover or modem module installed in the carrier card.
Step 5 Remove the modem module from the ESD-preventive shipping material.
Step 6 Slide the modem module into the card slot until it is seated completely.
Step 7 Tighten the two captive screws on the modem module to secure it to the card.
Step 8 Reconnect the AC power cord. Or, if using DC power, refer to Figure 4-6, and then complete steps a to d.

 | Caution Do not overtorque the terminal block contact screws. The recommended torque is 8.2 ± 0.4 inch-lb. |
(a) Insert the safety ground (green wire) into the terminal block ground connector and tighten the locking screw. Ensure that no bare wire is exposed.
(b) Insert the +48 VDC wire into the terminal block positive connector (+) and tighten the locking screw. Ensure that no bare wire is exposed.
(c) Insert the -48 VDC wire into the terminal block negative connector (-) and tighten the locking screw. Ensure that no bare wire is exposed.
(d) Make sure the power supply cord is secured to the cable strain-relief clamps on the DC power supply with cable ties.
 | Warning After wiring the DC power supply, remove the tape from the circuit breaker switch handle and reinstate power by moving the handle of the circuit breaker to the ON position. |
Step 9 Power ON the access server.
The internal power supply fan should power on.
Step 10 Proceed to the following section, "Upgrading Modem Code."
The 12-port modem module uses the following modem code images in a single-file format:
Modem code also resides on the access server: one version is bundled with Cisco IOS software, and another version can exist in system Flash memory. This modem code residing in the access server is a single file comprised of the modem firmware image combined with the DSP software image.
After power on, Cisco IOS software uses its bundled modem code file or the existing modem code file in system Flash memory to automatically update the DSP software and modem firmware on a specific modem.
When you install a new 12-port module, Cisco IOS software examines the following versions of modem code:
Then, Cisco IOS software ensures that the system uses matching DSP software and modem firmware—which may include overriding the current firmware on the modem. In some circumstances you may decide to manually update the modem code after the automatic download process completes.
Because of the possibility of multiple versions of modem code and the way Cisco IOS software process these versions, Cisco suggests that you decide between the following two strategies:
To help with the decision, Figure 4-7 shows a hypothetical release process. We recommend that you use the modem code bundled with Cisco IOS software because it is the easier strategy and enables you to take advantage of new modem code whenever you upgrade your Cisco IOS software. You can also control the modem code by reverting to previous versions by using the copy command as discussed later.
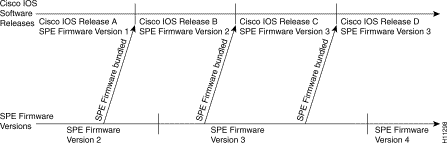
Table 4-1 provides some typical scenarios that occur when you add or replace a 12-port module. Table 4-2 provides scenarios that occur when you upgrade Cisco IOS software or modem code.
| Scenario | Update Process |
|---|---|
You replace an existing 56K 12-port module with a module that contains newer modem code.1 Option 1—Accept the version of modem code selected by Cisco IOS software. Option 2—Upgrade modem code to a different version. | Option 1—No action needed. Option 2—Copy the desired version of the modem code file to system Flash memory, then copy that file to the integrated modems on the 12-port module. See "Using the Modem Code from an External File" later in this section for details. |
You replace a V.34 12-port module with a 56K 12-port module.2 Option 1—Accept the version of modem code selected by Cisco IOS software (this is the bundled version). Option 2—Upgrade the modem code to a different version. | Option 1—No action needed. Option 2—Copy the desired version of modem code file to system Flash memory, then copy that file to the integrated modems on the 12-port module. See "Using the Modem Code from an External File" later in this section for details. |
| 1Because Cisco IOS software maps modem code (either the bundled Cisco IOS version or a system Flash memory version) to a given slot/port and not the physical modem, Cisco IOS software will automatically load the modem code mapped to the previous module. For more information, see the description of mapping in Table 4-4. 2Cisco IOS software recognizes that the modem code (which is mapped to the previous module) is invalid, so it uses the bundled version. |
| No. | Scenario | Update Process |
|---|---|---|
1 | You update Cisco IOS software, and you decide to use the version of modem code selected by Cisco IOS software. |
|
2 | You update Cisco IOS software, and you decide not to use the modem code selected by Cisco IOS software. |
|
3 | The modems are running a version of modem code from system Flash memory that is different than the version bundled with Cisco IOS software. You decide to revert to the bundled version. |
|
4 | Cisco releases new modem code, which is a later version than the version currently running on the modems. You decide to use Cisco's newest modem code.2 |
|
| 1In part, Cisco IOS software bases this decision on the last copy command issued. For more details about mapping, see Table 4-4. 2Cisco ships new modem code on a disk packed with the 12-port module. |
Figure 4-8 shows a location on the release timeline where updates might take place, and Table 4-3 explains the resulting versions of Cisco IOS software and modem code.
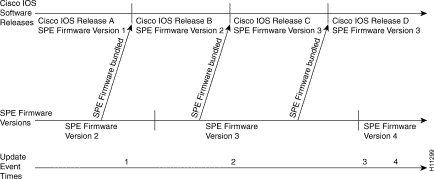
| Update Event Time | Update Event | Resulting Version of Cisco IOS Software and Modem Code |
|---|---|---|
1 | You upgrade Cisco IOS software to Release B.
|
|
2 | You upgrade Cisco IOS software to Release C. (Cisco IOS software uses mapping from last copy command at Time 1).1 | Cisco IOS Release C |
You enter copy system:/ucode/filename modem command | Cisco IOS Release C | |
3 | New Modem Code Version 4 is released, you copy the file to system Flash memory, enter copy flash modem, and specify Modem Code Version 4. | Cisco IOS Release C |
4 | You upgrade Cisco IOS software to Release D. | Cisco IOS Release D |
You enter copy system:/ucode/filename modem command | Cisco IOS Release D |
| 1This example assumes the last copy command was copy flash modem, and Modem Code Version 1 was specified. |
Table 4-4 provides a list of terms and commands and a description of how they are used in the modem code update process.
| Term | Description |
|---|---|
Modem firmware | Modem controller firmware that resides in modem Flash memory. |
DSP software | DSP controller software that resides in modem RAM. Cisco IOS software transfers a version of DSP software to modem RAM on each reboot. |
Modem code | Two images:
These images reside separately in the modems and as a single-file version in the access server's system Flash memory. System Flash memory can contain several versions of modem code: a version bundled with Cisco IOS software and multiple versions that resulted from previous copy tftp flash commands. |
copy tftp flash mcom-modem-code-x.x.x.bin | Places a copy of the modem code in system Flash memory. |
copy flash modem command | Transfers the copy tftp flash version of modem code to the modems. This command transfers the modem firmware file to modem Flash memory and the DSP software file to modem RAM. Maps the system Flash memory version to the modems. |
copy system:/ucode/filename modem command | Instructs the modems to use the version of modem code bundled with Cisco IOS software. This command does not affect any existing versions of modem code that reside in system Flash memory. After one such command, future Cisco IOS upgrades will potentially result in the downloading of new Cisco IOS bundled firmware to the modems. (If the new Cisco IOS image contains the same modem code as the old one, no new code will be downloaded to the modems.) Maps the bundled Cisco IOS software version to the modems. |
Mapping | The copy commands map a specific version of modem code to a group of modem slots/ports. The copy system:/ucode/filename modem (or copy ios-bundled modem)copy ios-bundled modem) command maps the slots/ports to the bundled version, and the copy flash modem command maps the slots/ports to a specific modem code file located in system Flash memory. Cisco IOS software uses the mapping to determine which version of modem code should be downloaded to the modems. If Cisco IOS software finds no mapping or invalid mapping, it downloads the bundled version. |
Use the procedures in this section to transfer modem code from Cisco Connection Online (CCO) to the integrated modems on the 12-port module. The procedure consists of the following tasks:
You can download the single file (mcom-modem-code-x.x.x.bin) to a TFTP server on your LAN two ways:
Log in to Cisco's Software Center at the following URL to download the modem code file:
http://www.cisco.com/kobayashi/sw-center/
You must log in as a Cisco registered user. (If you are not a registered user, note that Cisco provides modem code on a disk when are updates are necessary. This disk is shipped with the 12-port module.)
After downloading to your desktop computer, you must transfer it to a TFTP server on your network using an FTP application.
http://www.cisco.com/cgi-bin/tablebuild.pl/56K
Alternatively, you can access Cisco at http://www.cisco.com, login, and take the following path to the file:
Take the following steps to download the modem code file from Cisco's FTP server using an FTP client application. These steps assume that you want to download both the modem firmware and the DSP software.
terminal> ftp cco.cisco.com
Connected to cio-sys.cisco.com.
220-
220- Cisco Connection Online | | Cisco Systems, Inc.
220- Email: cco-team@cisco.com ||| ||| 170 West Tasman Drive
220- Phone: +1.800.553.2447 .:|||||:..:|||||:. San Jose, CA 95134
220-
220- NOTE: As of February 1, 1997 ftp.cisco.com will now point to this
220- service. Please be advised. To use the former ftp.cisco.com after
220- February 1, connect to ftpeng.cisco.com
220-
220- You may login with:
220- + Your CCO username and password, or
220- + A special access code followed by your e-mail address, or
220- + "anonymous" followed by your e-mail address for guest access.
220-
220-
220 cio-sys FTP server (CIOESD #103 Sun Dec 15 14:43:43 PST 1996) ready.
Step 2 Enter your CCO registered username and password (for example, harry and letmein):
Name (cco.cisco.com:harry): harry
331 Password required for harry.
Password: letmein
230-##########################################################################
230-# Welcome to the Cisco Systems CCO FTP server.
230-# This server has a number of restrictions. If you are not familiar with
230-# these, please first get and read the /README or /README.TXT file.
230-# http://www.cisco.com/acs/info/cioesd.html for more info.
230-##########################################################################
230-
230- ***** NOTE: As of February 1, 1997, "cco.cisco.com", *****
230- ***** "www.cisco.com" and "ftp.cisco.com" are now all *****
230- ***** logical names for the same machine. *****
230- ***** *****
230- ***** The old "ftp.cisco.com" is an entirely *****
230- ***** different machine, which is now known as *****
230- ***** "ftpeng.cisco.com" or "ftp-eng.cisco.com". *****
230- ***** *****
230- ***** In general, "ftpeng.cisco.com" is used only for *****
230- ***** distribution of Cisco Engineering-controlled *****
230- ***** projects, such as beta programs, early field *****
230- ***** trials, developing standards documents, etc. *****
230- ***** *****
230- ***** Be sure to confirm you have connected to *****
230- ***** the machine you need to interact with. *****
230-
230- If you have any odd problems, try logging in with a minus sign (-)
230- as the first character of your password. This will turn off a feature
230- that may be confusing your ftp client program.
230- Please send any questions, comments, or problem reports about this
230- server to cco-team@cisco.com.
230-
230- NOTE:
230- o To download files from CCO, you must be running a *passive-mode*
230- capable FTP client.
230- o To drop files on this system, you must cd to the /drop directory.
230- o Mirrors of this server can be found at
230-
230- + ftp://www-europe.cisco.com European (Amsterdam)
230- + ftp://www-fr.cisco.com France (Paris)
230- + ftp://www-au.cisco.com Australia (Sydney)
230- + ftp://www-jp.cisco.com Japan (Tokyo)
230- + ftp://www-kr.cisco.com Korea (Seoul)
230-
230-
230-
230- Please read the file README
230- it was last modified on Sat Feb 1 12:49:31 1997 - 163 days ago
230- User harry logged in. Access restrictions apply.
Remote system type is UNIX.
Using binary mode to transfer files.
Step 3 Specify the directory that holds the Modem Code file, which is /cisco/access/5300:
ftp> cd /cisco/access/5300
250- Please read the file README
250- it was last modified on Tue May 27 10:07:38 1997 - 48 days ago
250- Please read the file README.txt
250- it was last modified on Tue May 27 10:07:38 1997 - 48 days ago
250- CWD command successful.
Step 4 View the contents of the directory with the ls command:
ftp> ls
227 Entering Passive Mode (192,31,7,130,218,128)
150 Opening ASCII mode data connection for /bin/ls.
total 2688
drwxr-s--T 2 ftpadmin ftpcio 512 Aug 23 18:11 .
drwxr-sr-t 19 ftpadmin ftpcio 512 Jul 18 10:26 ..
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root 3 10 Aug 9 1996 README -> README.txt
-rw-rw-r-- 1 root ftpcio 2304 Nov 8:07 README.txt
-r--r--r-- 1 ftpadmin ftpint 377112 Jul 10 18:08 mcom-modem-code.3.1.30.bin
-r--r--r-- 1 ftpadmin ftpint 635 Jul 10 18:08 mcom-modem-code.3.1.30.readme
226 Transfer complete.
Step 5 Specify a binary image transfer:
ftp> binary
200 Type set to I.
Step 6 Copy the modem code file from the server to your local environment with the get command. The filename is mcom-modem-code-3.1.30.bin.
The following example downloads the modem code file:
ftp> get mcom-modem-code-3.1.30.bin
PORT command successful.
Opening BINARY mode data connection for mcom-modem-code-3.1.30.bin (377112 bytes).
Transfer complete.
local: mcom-modem-code-3.1.30.bin
remote: mcom-modem-code-3.1.30.bin
385503 bytes received in 3.6 seconds (1e+02 Kbytes/s)
Step 7 Quit your terminal session:
ftp> quit
Goodbye.
Step 8 Verify that you successfully transferred the modem code file to your local directory:
server% ls -al
total 596
-r--r--r-- 1 377112 Jul 10 18:08 mcom-modem-code-3.1.30.bin
server% pwd
/auto/tftpboot
Step 9 If you have not already done so, transfer this file to a local TFTP server that your Cisco AS5300 can access.
The procedure for copying the modem code file from your local TFTP server to the access server system Flash memory is a two-step process. First, transfer the code to the access server. Then, transfer the code to the modems.
These two steps are performed only once. After you copy the modem code file into system Flash memory for the first time and map that file to a specific modem using the copy flash modem command, you do not have to perform these steps again. Because the DSP software runs from modem RAM, the Cisco IOS software must automatically copy the DSP software to each modem each time the access server power cycles.
5300# copy tftp flash
System flash directory:
File Length Name/status
1 37712 mcom-modem-code.3.1.30.bin
[4195272 bytes used, 12581944 available, 16777216 total]
Address or name of remote host [255.255.255.255]? modem_server
Source file name? as5300/mcom-modem-code.3.1.30.bin
Destination file name [as5300/mcom-modem-code.3.1.30.bin]?
as5300/mcom-modem-code.3.1.30.bin
Accessing file 'as5300/mcom-modem-code.3.1.30.bin' on modem_server...
Loading as5300/mcom-modem-code.3.1.30.bin from 223.255.254.254 (via Ethernet0): !
[OK]
Erase flash device before writing? [confirm] no
Copy 'as5300/mcom-modem-code.3.1.30.bin' from server
as 'mcom-modem-code.3.1.30.bin' into Flash WITHOUT erase? [yes/no] yes
Loading as5300/mcom-modem-code.3.1.30.bin from 223.255.254.254 (via Ethernet0):
!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
[OK - 282106/557056 bytes]
Verifying checksum... OK (0xB163)
Flash device copy took 00:00:04 [hh:mm:ss]
Step 2 Copy the modem code file to the modems by entering the copy flash modem Privileged EXEC command.
5300# copy flash modem
Modem Numbers (<slot>/<port> | group <number> | all)? 1/0
System flash directory:
File Length Name/status
1 5424872 c5200-js-mz
2 377112 mcom-modem-code-3.1.30.bin
[5801984 bytes used, 10975232 available, 16777216 total]
Name of file to copy? mcom-modem-code-3.1.30.bin
Copy 'mcom-modem-code-3.1.30.bin' from Flash to modems? [yes/no]yes
[OK - 377112/278528 bytes]
5300#
*Mar 1 20:21:55: %MODEM-5-DL_START: Modem (1/0) started firmware download
*Mar 1 20:23:24: %MODEM-5-DL_GOOD: Modem (1/0) completed firmware download:
MNPClass10K56flexModemRev3.1.30/85
If you want to verify that the DSP software and modem firmware copied to the modems, use the show modem version command. In this example, modems 2/12 through 2/23 are loaded with the 56K modem controller firmware and DSP software:
5300# show modem version
Modem module Firmware Boot DSP
Mdm Number Rev Rev Rev
2/0 0 2.2(8) 1.0(5)
2/1 0 2.2(8) 1.0(5)
2/2 0 2.2(7) 1.0(5)
2/3 0 2.2(7) 1.0(5)
2/4 0 2.2(7) 1.0(5)
2/5 0 2.2(7) 1.0(5)
2/6 0 2.2(7) 1.0(5)
2/7 0 2.2(7) 1.0(5)
2/8 0 2.2(7) 1.0(5)
2/9 0 2.2(7) 1.0(5)
2/10 0 2.2(7) 1.0(5)
2/11 0 2.2(7) 1.0(5)
2/12 1 3.1(30) 3.0(4) 1.1(0)/1.1(0)
2/13 1 3.1(30) 3.0(4) 1.1(0)/1.1(0)
2/14 1 3.1(30) 3.0(4) 1.1(0)/1.1(0)
2/15 1 3.1(30) 3.0(4) 1.1(0)/1.1(0)
2/16 1 3.1(30) 3.0(4) 1.1(0)/1.1(0)
2/17 1 3.1(30) 3.0(4) 1.1(0)/1.1(0)
2/18 1 3.1(30) 3.0(4) 1.1(0)/1.1(0)
2/19 1 3.1(30) 3.0(4) 1.1(0)/1.1(0)
2/20 1 3.1(30) 3.0(4) 1.1(0)/1.1(0)
2/21 1 3.1(30) 3.0(4) 1.1(0)/1.1(0)
2/22 1 3.1(30) 3.0(4) 1.1(0)/1.1(0)
2/23 1 3.1(30) 3.0(4) 1.1(0)/1.1(0)
Modem board HW version info:
Slot 2:
Carrier card:
hw version= 8, number_of_ports= 24, max_modules= 2, max_oob_ports= 2
Modem Module 0:
number_of_modems= 12, option_bits= 1,
rev_num= 03.00, vendor_model_number= 01,
vendor_banner= Microcom MNP10 V34 Modem
Modem Module 1:
number_of_modems= 12, option_bits= 1,
rev_num= 03.00, vendor_model_number= 02,
vendor_banner= Microcom MNP10 K56 Modem
Now the modems are equipped with code. The modems are configured to transmit at speeds up to 56 kbps. Each time the access server is power cycled, Cisco IOS software automatically loads the modems with the modem code in system Flash memory. If you erase the modem code file from system Flash memory, the Cisco IOS default modem code (that is, the bundled modem code) will be automatically downloaded to the modem.
If you already have a version of modem code in the Flash memory on your access server, and you upgrade to a Cisco IOS release that includes newer modem firmware, only the modems that are mapped to the bundled Cisco IOS version are updated. In order to set the modem firmware mapping to the firmware version bundled with Cisco IOS software, enter the following command:
5300# copy system:/ucode/filename modem
As a result of the copy system:/ucode/filename modem command, future Cisco IOS upgrades will potentially result in the mapping of new Cisco IOS bundled firmware to the modems. (If the new Cisco IOS image contains the same modem code as the old one, no new code will be downloaded to the modems.)
During the modem code download process, you may receive an error message if the download fails.
| Error Message | Description | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
%%ERROR: Modem <slot/port>, Modem Firmware file is not valid for modem type. | The specified modem firmware is not compatible with the target modem. For example, V.34 modems cannot be upgraded with 56K firmware. If you have a bank of non-56K modems in the access server and specify the all option in the copy tftp modem command, this error message will appear and not download 56K firmware where appropriate. | Verify that you are copying 56K modem firmware to 56K modems. Also use the show modem command to verify that you specified the correct slot/port or range. |
%%ERROR: Modem <slot/port> currently being downloaded. | The modem code is currently downloading to the 56K modems. | The first download will containue without interruption, and the second download is aborted. |
%%ERROR: Modem <slot/port>, download functions not initialized. | The modem code cannot be downloaded to the specified modem. | Use the show modem command to verify that you are downloading to a supported 56K modem. |
%%ERROR: Modem <slot/port> is held in reset. | The specified modem is held in reset mode. The DSP software will not download to this modem. | Take the modem out of reset mode, then copy the DSP software again. |
%%ERROR: NVRAM write for DSP download filename entry failed. | There is an NVRAM table problem. | Reissue the copy tftp flash command and copy the DSP file again. |
This section lists the procedures you need to complete the following configuration tasks to configure the modem modules:
1. Configure the asynchronous group interface
2. Configure the controller
3. Configure the modems
4. Configure the serial interface
See the Cisco AS5300 Universal Access Server Software Configuration Guide for details. You can find the most up-to-date version of this manual online from either CCO or the CD-ROM.
See the Cisco AS5300 Universal Access Server Software Configuration Guide publication for details.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Posted: Tue Oct 30 13:41:59 PST 2001
All contents are Copyright © 1992--2001 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Important Notices and Privacy Statement.