23.2. XSLT Elements
XSLT defines 37 elements, which break down into
3 overlapping categories:
-
Two root elements:
xsl:stylesheet
xsl:transform
-
12 top-level elements. These elements may appear as immediate
children of the root and are the following:
xsl:attribute-set xsl:decimal-format
xsl:import xsl:include
xsl:key xsl:namespace-alias
xsl:output xsl:param
xsl:preserve-space xsl:strip-space
xsl:template xsl:variable
-
23 instruction elements. These elements appear in the content of
elements that contain templates. Here we don't mean
the xsl:template element. We mean the content of
that and several other elements, such as
xsl:for-each and xsl:message,
which are composed of literal result elements, character data, and
XSLT instructions that are processed to produce part of the result
tree. These elements are as follows:
xsl:apply-imports xsl:apply-templates
xsl:attribute xsl:call-template
xsl:choose xsl:comment
xsl:copy xsl:copy-of
xsl:element xsl:fallback
xsl:for-each xsl:if
xsl:message xsl:number
xsl:otherwise xsl:param
xsl:processing-instruction xsl:sort
xsl:text xsl:value-of
xsl:variable xsl:with-param
xsl:when
Most XSLT processors also provide various nonstandard extension
elements and allow you to write your own extension elements in
languages such as Java and JavaScript.
Elements in this section are arranged alphabetically from
xsl:apply-imports to
xsl:with-param. Each element begins with a
synopsis in the following form:
<xsl:elementName
attribute1 = "allowed attribute values"
attribute2 = "allowed attribute values"
>
<!-- Content model -->
</xsl:elementName>
Most attribute values are one of the following types:
- expression
-
An XPath expression. In cases where the expression is expected to
return a value of a particular type, such as node-set or number, it
is prefixed with the type and a hyphen, for example,
node-set-expression or
number-expression. However, XPath is weakly typed,
and in most cases, any supplied type will be converted to the
requested type. For instance, an attribute that should contain a
string might in fact contain a number or a node-set. The processor
automatically converts this number or set to a string, according to
the rules given in the last chapter for XPath's
string( ) function. The only exception to this
rule is node-set-expression. XSLT does not convert
other types to node-sets automatically. If an attribute requires a
node-set-expression, then it is an error to set
its value to another type of expression such as a boolean or string.
- QualifiedName
-
An XML name, such as set or
mathml:set. If the name is in a nondefault
namespace, then it has a prefix.
- PrefixedName
-
An XML name that must have a prefix such as
mathml:set but not set.
- pattern
-
An XSLT pattern; that is, a group of one or more XPath location-path
expressions separated by |. in which each location
step uses only the child or attribute axis. The initial step may be
an id( ) or key( ) function
call with a literal argument.
- langcode
-
An RFC 1766 language code, such as en or
fr-CA.
- string
-
A literal string of text.
- char
-
A single Unicode character.
- enumerated type
-
One value in a finite list of values. The values shown here are
separated by vertical bars, as in an enumerated content model in an
ATTLIST declaration.
- URI
-
A relative or absolute URI reference. In practice, these are normally
URLs. Relative URIs are relative to the location of the stylesheet
itself.
Some attributes that contain strings--whether those strings are
literals, expressions, names, or something else--can be given as
attribute value templates. This is an XPath expression enclosed in
curly braces, which is evaluated to provide the final value of the
attribute. When this is the case, it is indicated in the description
of each attribute.
Potentially nonempty elements have content models given in a comment
in the form they might appear in an ELEMENT
declaration. If an element can contain a template, we use the word
"template" to stand in for all the
possible elements that may appear.
The xsl:apply-imports instruction processes the
current node using only templates that were imported into the
stylesheet with xsl:import. A template rule that
overrides a template rule in an imported stylesheet can invoke the
overridden template rule with xsl:apply-imports.
<xsl:apply-templates
select = "node-set-expression"
mode = "QualifiedName">
<! -- (xsl:sort | xsl:with-param)* -- >
</xsl:apply-templates>
| |
The xsl:apply-templates instruction tells the
processor to search for and apply the highest-priority template in
the stylesheet that matches each node identified by the
select attribute.
Attributes
- select, optional
-
This is an XPath expression that returns a node-set. Each node in
this set will be processed further. If the select
attribute is omitted, then all child nodes of the context node should
be processed.
- mode, optional
-
If the mode attribute is present, then only
templates that have a matching mode attribute will
be applied. If the mode attribute is absent, then
only templates without a mode attribute will be
applied.
Contents
The xsl:apply-templates element may have
xsl:sort child elements to specify the order in
which the selected nodes will be processed. Without any
xsl:sort children, the default is to process nodes
in document order.
The xsl:apply-templates element may have
xsl:with-param child elements to pass parameter
values to the matched templates.
<xsl:attribute
name = "QualifiedName"
namespace = "URI">
<! -- template for the attribute value -- >
</xsl:attribute>
| |
The
xsl:attribute instruction adds an attribute to an
element in the result tree. This element can be a child of an
xsl:attribute-set element, an
xsl:element instruction, or a literal result
element. In each case, all xsl:attribute elements
must precede all literal result elements and other instructions that
insert content into the output element.
Attributes
- name, required, attribute value template
-
The name of the attribute this instruction creates.
- namespace, optional, attribute value template
-
The namespace URI of the attribute. If a nonempty namespace URI is
specified, then the processor will pick an appropriate prefix for the
attribute, probably but not necessarily the one used in the
name attribute.
Contents
The contents of this element are a template whose instantiation only
produces text nodes. The value of the attribute added to the result
tree is determined by instantiating the template.
<xsl:attribute-set
name = "QualifiedName"
use-attribute-sets = "QualifiedNames">
<! -- xsl:attribute* -- >
</xsl:attribute-set>
| |
The xsl:attribute-set
top-level element defines a collection of attributes that can be
applied to elements elsewhere in the stylesheet. For instance, you
could define an attribute set that includes the necessary attributes
to create a simple XLink, and then you could attach the set to each
simple XLink element.
Attributes
- name, required
-
The name attribute gives a name for the set, by
which xsl:element and other
xsl:attribute-set elements can load this attribute
set.
- use-attribute-sets, optional
-
The use-attribute-sets attribute adds attributes
from a different attribute set into this attribute set. More than one
attribute set can be loaded by separating multiple names with
whitespace. The attributes defined in all loaded sets and all
attributes defined by child xsl:attribute elements
are merged so that no attribute appears in the set more than once. It
is an error if an attribute set uses itself directly or indirectly.
Contents
This element contains zero or more xsl:attribute
elements. Each such element adds one attribute to the set.
<xsl:call-template
name = "QualifiedName">
<! -- xsl:with-param* -- >
</xsl:call-template>
| |
The xsl:call-template
instruction invokes a template by name. The current node and context
node list are the same for the called template as for the calling
template. Templates may be called recursively; an
xsl:template element may contain an
xsl:call-template element that calls that very
xsl:template element. This technique is useful for
doing things you'd accomplish with loops in a
traditional procedural programming language.
Attributes
- name, required
-
The name of the xsl:template element to call.
Contents
This element contains zero or more xsl:with-param
elements that pass parameters to the named template.
<xsl:choose>
<! -- (xsl:when+, xsl:otherwise?) -- >
</xsl:choose>
| |
The xsl:choose element selects zero or one of a
sequence of alternatives.
Contents
This element contains one or more xsl:when
elements, each of which has a test condition. The contents are output
for the first xsl:when child whose test condition
is true.
The xsl:choose element may have an optional
xsl:otherwise element whose contents are output
only if none of the test conditions in any of the
xsl:when elements is true.
If no xsl:otherwise element exists and none of the
test conditions in any of the xsl:when child
elements is true, then this element will not produce output.
<xsl:comment>
<! -- template -- >
</xsl:comment>
| |
The xsl:comment instruction inserts a comment into
the result tree.
Contents
The content of xsl:comment is a template that will
be instantiated to form the text of the comment inserted into the
result tree. The result of instantiating this template must only be
text nodes that do not contain the double hyphen
(--) (since comments cannot contain the double
hyphen).
<xsl:copy
use-attribute-sets = "QualifiedName1 QualifiedName2...">
<! -- template -- >
</xsl:copy>
| |
The xsl:copy element copies the current node from
the source document into the output document. It copies the node
itself and any namespace nodes the node possesses. However, it does
not copy the node's children or attributes.
Attributes
- use-attribute-sets, optional
-
A whitespace-separated list of xsl:attribute-set
names. These attribute sets are merged, and all attributes in the
merged set are added to the copied element. The
use-attribute-sets attribute can be used only when
the copied node is an element node.
Contents
If the current node is an element node, attributes can be added via
xsl:attribute children. If the current node is the
root node or an element node (a node that can have children), then
xsl:copy may contain a template that specifies the
content of the element inserted into the result tree. All
xsl:attribute elements must precede the output
template.
<xsl:copy-of
select = "expression" />
| |
The xsl:copy-of instruction inserts whatever is
identified by the select attribute into the output
document. This instruction copies the specific nodes identified by
the expression, as well as all those nodes'
children, attributes, namespaces, and descendants. This is how it
differs from xsl:copy: if the expression selects
something other than a node-set or a result-tree fragment, such as a
number, then the expression is converted to its string value and the
string is output.
Attributes
- select, required
-
An XPath expression identifying the object to copy into the result
tree.
<xsl:decimal-format
name = "QualifiedName">
decimal-separator = "char"
grouping-separator = "char"
infinity = "string"
minus-sign = "char"
NaN = "string"
percent = "char"
per-mille = "char"
zero-digit = "char"
digit = "char"
pattern-separator = "char" />
| |
The xsl:decimal-format top-level element defines a
pattern by which the format-number(
) function can convert floating point
numbers into text strings. The defaults work well for English, but
details may change for other languages and locales, such as French or
Chinese.
Attributes
- name, optional
-
The string by which the format-number( ) function
identifies the xsl:decimal-format element to use.
If this attribute is omitted, then this element establishes the
default decimal format used by the format-number(
) function.
- decimal-separator, optional
-
The character that separates the integer part from the fractional
point in a floating point number. This character is a period (decimal
point) in English and a comma in French. It may be something else in
other languages.
- grouping-separator, optional
-
The character that separates groups of digits (e.g., the comma that
separates every three digits in English).
- infinity, optional
-
The string that represents IEEE 754 infinity;
Infinity by default.
- minus-sign, optional
-
The character prefixed to negative numbers; a hyphen by default.
- NaN, optional
-
The string that represents IEEE 754 Not a Number;
NaN by default.
- percent, optional
-
The character that represents a percent; % by
default.
- per-mille, optional
-
The character that represents a per mille;
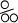 by default. by default.
- zero-digit, optional
-
The character that represents zero; 0 by default.
Digits 1 through 9 will be represented by the nine subsequent Unicode
values after this one. For instance, setting
zero-digit to A would set 1 to
B, 2 to C, 3 to
D, and so on. This is also the character used to
represent 0 in format patterns.
- digit, optional
-
The character that represents a digit in a format pattern;
# by default.
- pattern-separator, optional
-
The character that separates positive and negative subpatterns in a
format pattern; ; by default.
<xsl:element
name = "QualifiedName"
namespace = "URI"
use-attribute-sets = "QualifiedName1 QualifiedName2...">
<! -- template -- >
</xsl:element>
| |
The xsl:element instruction inserts an element
into the result tree. The element's name is given by
the name attribute. The element's
namespace URI, if any, is given by the optional
namespace attribute. Attributes can be added via
xsl:attribute children or by referencing an
xsl:attribute-set declared elsewhere in the
stylesheet from the use-attribute-sets attribute.
Finally, the element's contents are determined by
instantiating the template contained in the
xsl:element element's content.
Attributes
- name, required, attribute value template
-
The name of the element this instruction creates.
- namespace, optional, attribute value template
-
The namespace URI of the element this instruction creates. If this
attribute is omitted, then the namespace is determined by matching
the name's prefix (or lack thereof) to the namespace
declarations in scope at this point in the stylesheet.
- use-attribute-sets, optional
-
A whitespace-separated list of names of
xsl:attribute-set elements declared as top-level
elements elsewhere in the stylesheet. These attribute sets are
merged, and all attributes in the merged set are added to the
element.
Contents
The contents of this element are a template. Once instantiated, this
template forms the content of the element inserted into the result
tree.
<xsl:fallback>
<! -- template -- >
</xsl:fallback>
| |
The xsl:fallback instruction normally appears as a
child of an extension element. If the processor does not recognize
the extension element, then it instantiates the contents of all the
element's xsl:fallback children
in order. If the processor does recognize the element in which the
xsl:fallback element appears, then the contents of
the xsl:fallback element will not be output.
Contents
The contents of this element are a template that is instantiated and
output if and only if the XSLT processor does not recognize the
xsl:fallback element's parent
element.
<xsl:for-each
select = "node-set-expression">
<! -- (xsl:sort*, template) -- >
</xsl:for-each>
| |
The xsl:for-each instruction iterates over the
nodes identified by its select attribute and
applies templates to each one.
Attributes
- select, required
-
An XPath node-set expression identifying which nodes to iterate over.
Contents
Normally, the selected nodes are processed in the order in which they
appear in the document. However, nodes can be sorted using
xsl:sort child elements. The first such element is
the primary sort key; the second is the secondary sort key; and so
on.
The xsl:for-each element must also contain a
template that is instantiated once for each member of the node-set
returned by the node-set expression in the select
attribute.
<xsl:if
test = "boolean-expression">
<! -- template -- >
</xsl:if>
| |
The xsl:if instruction contains a template that is
instantiated if and only if the XPath expression contained in its
test attribute is true. There
is no xsl:else or xsl:else-if
element. For these purposes, use xsl:choose
instead.
Attributes
- test, required
-
An XPath expression returning a Boolean. If this expression is
true, the contents of the
xsl:if element are instantiated. If
it's false,
they're not.
Contents
A template is instantiated if the test attribute
evaluates to true.
<xsl:import
href = "URI" />
| |
The xsl:import top-level element imports the XSLT
stylesheet found at the URI given by the href
attribute. Source documents are processed using the combination of
templates in the imported and importing stylesheets. In the event of
a conflict between templates in the two stylesheets, the ones in the
importing stylesheet take precedence. In the event of a conflict
between imported stylesheets, the last one imported takes precedence.
All xsl:import elements must be immediate children
of the root xsl:stylesheet element. Furthermore,
they must appear before all other top-level elements.
An imported stylesheet may itself import another stylesheet. A
stylesheet may not import a stylesheet that was already imported,
directly or indirectly. That is, it's an error if A
imports B, which imports A, thus creating a circular reference.
Attributes
- href, required
-
The relative or absolute URI of the stylesheet to import. Relative
URIs are resolved relative to the base URI of the importing
stylesheet.
<xsl:include
href = "URI" />
| |
The xsl:include top-level element copies the
contents of the xsl:stylesheet or
xsl:transform element found at the URI given by
the href attribute. Unlike
xsl:import, whether a template or other rule comes
from the including or the included stylesheet has absolutely no
effect on the precedence of the various rules.
An included stylesheet may include another stylesheet. A stylesheet
may not include a stylesheet that was already included, directly or
indirectly; it is an error if A includes B, which includes A.
Attributes
- href, required
-
The relative or absolute URI of the stylesheet to include. Relative
URIs are resolved relative to the including
stylesheet's base URI.
<xsl:key
name = "QualifiedName"
match = "pattern"
use = "expression" />
| |
The xsl:key top-level element defines one or more
keys that can be referenced from elsewhere in the stylesheet using
the key( ) function. Each key has a name, a string
value, and a node.
Attributes
- name, required
-
The key's name.
- match, required
-
An XSLT match pattern, like that used by
xsl:template, specifying which nodes have this
key. If this pattern matches more than one node in the source
document, then a single xsl:key element may define
many keys, all with the same name and possibly the same value, but
with different nodes.
- use, required
-
An XPath expression that is converted to a string to give the value
of keys defined by this element. The expression is evaluated with
respect to each key's node. If
match identifies multiple nodes, then
use may produce different values for each key.
<xsl:message
terminate = "yes" | "no">
<! -- template -- >
</xsl:message>
| |
The xsl:message instruction sends a message to the
XSLT processor. Which messages the processor understands and what it
does with messages it does understand is processor dependent.
Printing debugging information on stderr or
stdout is one common use of
xsl:message.
Attributes
- terminate, optional
-
If the attribute is present and has the value yes,
then the XSLT processor should halt after the message is delivered
and acted on.
Contents
An xsl:message element's content
is a template instantiated to create an XML
fragment. The result is then delivered to the XSLT
processor as the message.
WARNING:
The XSLT specification does not define XML
fragment, and various XSLT processors interpret it
differently. It may be a result tree fragment or an XML fragment, as
defined by the now moribund XML Fragment Interchange working draft.
It may be something else. Clarification from the W3C is necessary.
<xsl:namespace-alias
stylesheet-prefix = "prefix"
result-prefix = "prefix" />
| |
The top-level xsl:namespace-alias element declares
that one namespace URI in the stylesheet should be replaced by a
different namespace URI in the result tree. Aliasing is particularly
useful when you're transforming XSLT into XSLT using
XSLT; consequently, which names belong to the input, which belong to
the output, and which belong to the stylesheet is not obvious.
Attributes
- stylesheet-prefix, required
-
The prefix used inside the stylesheet itself. May be set to
#default to indicate that the nonprefixed default
namespace should be used.
- result-prefix, required
-
The prefix used in the result tree. May be set to
#default to indicate that the nonprefixed default
namespace should be used.
<xsl:number
value = "number-expression"
count = "pattern"
from = "pattern"
level = "single" | "multiple" | "any"
format = "letter or digit"
lang = "langcode"
letter-value = "alphabetic" | "traditional"
grouping-separator = "char"
grouping-size = "number" />
| |
The xsl:number instruction inserts a formatted
integer into the result tree.
Attributes
- value, optional
-
This XPath expression returns the number to be formatted. If
necessary, the result of the expression is rounded to the nearest
integer. The value attribute is often omitted, in
which case the number is calculated from the position of the current
node in the source document. The position is calculated as specified
by the level, count, and
from attributes.
- level, optional
-
This attribute specifies which levels of the source tree should be
considered in determining the position of the current node. It can be
set to single to count the preceding siblings of
the current node's ancestor that match the
count pattern. It can be set to
any to count all nodes in the document that match
the count pattern and precede the current node. It
can be set to multiple to produce hierarchical
sequences of numbers such as 2.7.3, where each number in the sequence
is calculated from the preceding sibling's ancestor
node that matches the count pattern. The default
is single.
- count, optional
-
This attribute contains a pattern that specifies which nodes should
be counted at those levels. The default is to count all nodes with
the same node type (element, text, attribute, etc.) and name as the
current node.
- from, optional
-
This attribute contains a pattern identifying the node from which
counting starts; that is, it identifies a node that serves as a
cutoff point. Any nodes that precede this node are not counted, even
if they match the count pattern.
- format, optional, attribute value template
-
This attribute determines how the list is numbered. Format tokens and
sequences they produce include the following:
- 1
-
1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, . . .
- 01
-
01, 02, 03, 04, 05, 06, 07, 08, 09, 10, 11, 12, . . .
- A
-
A, B, C, D, . . . ,Z, AA, AB, AC, . . .
- a
-
a, b, c, d, . . . ,z, aa, ab, ac, . . .
- i
-
i, ii, iii, iv, v, vi, vii, viii, ix, x, xi, . . .
- I
-
I, II, III, IV, V, VI, VII, VIII, IX, X, XI, XII, . . .
You can also change the starting point; for instance, setting the
format token to 5 would create the sequence 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, . . .
- lang, optional, attribute value template
-
This is the RFC 1766 language code describing the language in which
the number should be formatted (e.g., en or
fr).
- letter-value, optional, attribute value template
-
The default is traditional. However, you can set
this attribute to alphabetic to indicate that a
format of I should start the
sequence I, J, K, L, M, N, . . . rather than I, II, III, IV, V, VI, .
. .
- grouping-separator, optional, attribute value template
-
This is the character that separates groups of digits. For instance,
in English the comma customarily separates every three digits, as in
2,987,667,342. In French a space is used instead, so this number
would be formatted as 2 987 667 342.
- grouping-size, optional, attribute value template
-
This is the number of digits in each group. In most languages,
including English, digits are divided into groups of three. However,
a few languages use groups of four.
<xsl:otherwise>
<! -- template -- >
</xsl:otherwise>
| |
The xsl:otherwise element only appears as the last
child element of an xsl:choose element. It serves
as the default result if no xsl:when element in
the same xsl:choose element is instantiated.
Contents
The contents are a template that is instantiated if and only if none
of the xsl:choose element's
xsl:when sibling elements is
true.
<xsl:output
method = "xml" | "html" | "text" | "PrefixedName"
version = "NMTOKEN"
encoding = "encoding_name"
omit-xml-declaration = "yes" | "no"
standalone = "yes" | "no"
doctype-public = "PUBLIC_ID"
doctype-system = "SYSTEM_ID" cdata-section-elements = "element_name_1 element_name_2..."
indent = "yes" | "no"
media-type = "string" />
| |
The top-level xsl:output element helps determine
the exact formatting of the XML document produced when the result
tree is stored in a file, written onto a stream, or otherwise
serialized into a sequence of bytes. It has no effect on the
production of the result tree itself.
Attributes
- method, optional
-
The default method is xml, which simply means that
the serialized output document will be a well-formed external parsed
entity or XML document. If method is set to
html or if the method attribute
is not present and the root element of the output tree is
html, in any combination of case, then the
processor attempts to generate HTML that is more compatible with
existing browsers. For example, empty-element tags like
<br/> are converted to
<br>. The text method
outputs only the contents of the text nodes in the output tree. It
strips all markup. XSLT processors may also recognize and support
other values that are indicated by prefixed names such as
saxon:xhtml and
jd:canonical-xml.
- version , optional
-
This is a name token that identifies the output
method's version. In practice, this has no effect on
the output.
- encoding, optional
-
This is the name of the encoding the outputter should use, such as
ISO-8859-1 or UTF-16.
- omit-xml-declaration, optional
-
If this attribute has the value yes, then no XML
declaration is included. If it has the value no or
is not present, then an XML declaration is included.
- standalone, optional
-
This attribute sets the standalone
attribute's value in the XML declaration. Like that
attribute, it must have the value yes or
no.
- doctype-public, optional
-
This attribute sets the public identifier used in the document type
declaration.
- doctype-system, optional
-
This attribute sets the system identifier used in the document type
declaration.
- cdata-section-elements, optional
-
This is a whitespace-separated list of qualified element names in the
result tree whose contents should be emitted using CDATA sections
rather than character references.
- indent, optional
-
If this attribute has the value yes, then the
processor is allowed (but not required) to insert extra whitespace to
attempt to "pretty-print" the
output tree. The default is no.
- media-type, optional
-
This is the output's MIME media type, such as
text/html or text/xml.
<xsl:param
name = "QualifiedName"
select = "expression">
<! -- template -- >
</xsl:param>
| |
Inside an xsl:template element, an
xsl:param element receives a named argument passed
to the template by xsl:with-param. It also
provides a default value that's used when the caller
does not provide a value for the parameter. A top-level
xsl:param element provides a default value for
multiple templates. If an xsl:apply-templates or
xsl:call-template passes in a parameter value
using xsl:with-param when the template is invoked,
then this value overrides any default value the
xsl:param element may have. The parameter can be
dereferenced using the form
$name in expressions.
Attributes
- name, required
-
The parameter's name.
- select, optional
-
An XPath expression that is evaluated to produce the
parameter's value. If xsl:param
has a select attribute, then it must be an empty
element. If a nonempty xsl:param element does not
have a select attribute, then the value is taken
from the element's contents. If an empty
xsl:param element does not have a
select attribute, then the value is the empty
string.
Contents
An xsl:param element's content is
a template that is instantiated to produce a result-tree fragment.
This result-tree fragment then becomes the
parameter's value. A nonempty
xsl:param element must not have a
select attribute.
<xsl:preserve-space
elements="QualifiedName_1 QualifiedName_2..." />
| |
The top-level xsl:preserve-space element specifies
which elements in the source document will not have whitespace
stripped from them before they are transformed. Whitespace stripping
removes text nodes that contain only whitespace (the space character,
the tab character, the carriage return, and the linefeed). By
default, whitespace is preserved in an element unless its name is
listed in the elements attribute of an
xsl:strip-space element. This element allows you
to override the list given in xsl:strip-space; if
an element is listed in both xsl:strip-space and
xsl:preserve-space, then its whitespace is
preserved.
Attributes
- elements, required
-
A whitespace-separated list of elements in which space should be
preserved. Besides element names, the elements
attribute can contain an asterisk to indicate that whitespace should
be preserved in all elements or contain a namespace prefix followed
by a colon and an asterisk to indicate that whitespace should be
preserved in all elements in the given namespace.
| xsl:processing-instruction |
|
<xsl:processing-instruction
name = "target">
<! -- template -- >
</xsl:processing-instruction>
| |
The xsl:processing-instruction element inserts a
processing instruction into the result tree.
Attributes
- name, required, attribute value template
-
The processing instruction's target.
Contents
The xsl:processing-instruction
element's contents are a template that is
instantiated to produce the processing-instruction data. This
template may include XSLT instructions, provided that the result of
instantiating this template is text that does not contain the
two-character string ?>.
<xsl:sort
select = "string-expression"
data-type = "text" | "number" | "PrefixedName"
lang = "langcode"
order = "ascending" | "descending"
case-order = "upper-first" | "lower-first" />
| |
The xsl:sort instruction appears as a child of
either xsl:apply-templates or
xsl:for-each. It changes the order in which
templates are applied to the context node list from document order to
another order, such as alphabetic. You can perform multiple key sorts
(e.g., sort first by last name, then by first name, then by middle
name) using multiple xsl:sort elements in
descending order of the keys' importance.
Attributes
- select, optional
-
This is the key to sort by. If select is omitted,
then the sort key is set to the value of the current node.
- data-type, optional, attribute value template
-
By default, sorting is purely alphabetic. However, alphabetic sorting
leads to strange results with numbers. For instance, 10, 100, and
1000 all sort before 2, 3, and 4. You can specify numeric sorting by
setting the data-type attribute to
number.
- lang, optional, attribute value template
-
Sorting is language dependent. Setting the lang
attribute to an RFC 1766 language code changes the language. The
default language is system dependent.
- order, optional, attribute value template
-
This is the order by which strings are sorted. This order can be
either descending or ascending.
The default is ascending order.
- case-order, optional, attribute value template
-
The case-order attribute can be set to
upper-first or lower-first to
specify whether uppercase letters sort before lowercase letters, or
vice versa. The default depends on the language.
<xsl:strip-space
elements="QualifiedName_1 QualifiedName_2..." />
| |
The top-level xsl:strip-space element
specifies
which elements in the source document have whitespace stripped from
them before they are transformed. Whitespace stripping removes all
text nodes that contain only whitespace (the space character, the tab
character, the carriage return, and the linefeed). By default
whitespace is not stripped from an element unless its name is listed
in the elements attribute of an
xsl:strip-space element.
This element does not trim leading or trailing whitespace or
otherwise normalize whitespace in elements that contain even a single
nonwhitespace character.
Attributes
- elements, required
-
A whitespace-separated list of elements in which space should be
stripped. Besides element names, the elements
attribute can contain an asterisk to indicate that whitespace should
be stripped in all elements or contain a namespace prefix followed by
a colon and asterisk to indicate that whitespace should be stripped
in all elements in the given namespace.
<xsl:stylesheet
xmlns:xsl="http://www.w3.org/1999/XSL/Transform"
id = "ID"
extension-element-prefixes = "prefix1 prefix2..."
exclude-result-prefixes = "prefix1 prefix2..."
version = "1.0">
<! -- (xsl:import*, top-level-elements) -- >
</xsl:stylesheet>
| |
The xsl:stylesheet element is the root element for
XSLT documents.
Attributes
- xmlns:xsl, technically optional but de facto required
-
A standard namespace declaration that maps the prefix
xsl to the namespace URI
http://www.w3.org/1999/XSL/Transform. The prefix
can be changed if necessary.
- version, required
-
Currently, always the value 1.0. However, XSLT 2.0
may be released in 2003 with a concurrent updating of this number.
- id, optional
-
Any XML name that's unique within this
document's ID type attributes.
- extension-element-prefixes, optional
-
A whitespace-separated list of namespace prefixes used by this
document's extension elements.
- exclude-result-prefixes, optional
-
A whitespace-separated list of namespace prefixes whose declarations
should not be copied into the output document.
Contents
Any xsl:import elements, followed by any other
top-level elements in any order.
<xsl:template
match = "pattern"
priority = "number"
name = "QualifiedName"
mode = "QualifiedName">
<! -- (xsl:param*, template) -- >
</xsl:template>
| |
The xsl:template top-level element is the key to
all of XSLT. A little confusingly, the
xsl:template element itself is not a template.
Rather, it contains a template. The entire
xsl:template element is called a
template rule. The match
attribute contains a pattern against which nodes are compared as
they're processed. If the pattern matches a node,
then the template (i.e., the contents of the template rule) is
instantiated and inserted into the output tree.
Attributes
- match, optional
-
A pattern against which nodes can be compared. This pattern is a
location path using only the child, attribute, and descendant-or-self
axes.
- name, optional
-
A name by which this template rule can be invoked from an
xsl:call-template element, rather than by node
matching.
- priority, optional
-
A number. If more than one template rule with the same import
precedence matches a given node, the one with the highest priority is
chosen. If this attribute is not present, then the template
rule's priority is calculated in the following way:
Template rules with match patterns composed of just an element or attribute name (e.g., person or @profession) have priority 0. Template rules with match patterns composed of just a processing-instruction('target') node test have priority 0. Template rules with match patterns in the form prefix:* have priority -0.25. Template rules with match patterns that just have a wildcard node test (*, @*, comment( ), node( ), text(), and processing-instruction( )) have priority -0.5. (This means that built-in template rules have priority -0.5. However, they are also imported before all other template rules, and thus never override any explicit template rule, regardless of priority.) Template rules with any other patterns (person[name='Feynman'], people/person/@profession, person/text( ), etc.) have priority 0.5. It is an error if two or more template rules match a node and have the same priority. However, in this case most XSLT processors choose the last template rule occurring in the stylesheet rather than signaling the error.
- mode, optional
-
If the xsl:template element has a mode, then this
template rule is matched only when the calling
instruction's mode attribute
matches this mode attribute's
value.
Contents
The template that should be instantiated when this element is matched
or called by name.
<xsl:text
disable-output-escaping = "yes" | "no">
<! -- #PCDATA -- >
</xsl:text>
| |
The xsl:text instruction is used inside templates
to indicate that its contents should be output as text. Its contents
are pure text, not elements. If the contents are composed exclusively
of whitespace, then that whitespace is copied literally into the
output document, rather than being stripped as it would be by default
in most other elements.
Attributes
- disable-output-escaping, optional
-
Setting the disable-output-escaping attribute to
yes indicates that characters such as
< and &, which are
normally replaced by character or entity references such as
< or <, should
instead be output as the literal characters themselves. Note that the
xsl:text element's content in the
stylesheet must still be well-formed, and any <
or & characters must be written as
< or & or the
equivalent character references. However, when the output document is
serialized, these references are replaced by the actual represented
characters rather than references that represent them.
<xsl:transform
xmlns:xsl="http://www.w3.org/1999/XSL/Transform"
id = "ID"
extension-element-prefixes = "prefix1 prefix2..."
exclude-result-prefixes = "prefix1 prefix2..."
version = "1.0">
<! -- (xsl:import*, top-level-elements) -- >
</xsl:transform>
| |
The xsl:transform element is a seldom-used synonym
for the xsl:stylesheet root element. It has the
same attributes and contents as xsl:stylesheet and
is used in exactly the same way as xsl:stylesheet.
See the description of the xsl:stylesheet" element
for the discussion of its attributes and content.
<xsl:value-of
select = "expression"
disable-output-escaping = "yes" | "no" />
| |
The xsl:value-of element computes the string value
of an XPath expression and inserts it into the result tree. The
values of the seven different kinds of nodes are as follows:
- element
-
The text content of the element after all entity references are
resolved and all tags, comments, and processing instructions are
stripped
- text
-
The text of the node
- attribute
-
The normalized value of the attribute
- root
-
The value of the root element
- processing instruction
-
The processing instruction data (<?,
?>, and the target are not included)
- comment
-
The text of the comment (<!-- and
--> are not included)
- namespace
-
The namespace URI
You can also take values of things that aren't
nodes. The value of a node-set is the value of the first node in the
set. The value of a string expression is the string. The value of a
number expression is the string form of the number. The value of a
Boolean expression is the string true if the
Boolean is true or the string false if the Boolean
is false.
Attributes
- select, required
-
This is the XPath expression whose value is inserted into the result
tree.
- disable-output-escaping, optional
-
If this attribute has the value yes, then when the
output document is serialized, characters such as
< and & in the value are
not replaced with entity or character references. This may result in
a malformed document.
<xsl:variable
name = "QualifiedName"
select = "expression">
<! -- template -- >
</xsl:variable>
| |
The xsl:variable element binds a name to a value
of any type (string, number, node-set, etc.). This variable can then
be dereferenced elsewhere using the form
$name in an expression.
TIP:
The word variable is a little misleading. Once
the value of an xsl:variable is set, it cannot be
changed. An xsl:variable is more like a named
constant than a traditional variable.
- name, required
-
The variable's name.
- select, optional
-
An XPath expression that sets the value of the variable. If
xsl:variable has a select
attribute, then it must be an empty element.
Contents
A template that is instantiated to produce the
variable's value as a result-tree fragment. If an
xsl:variable is not an empty element, it must not
have a select attribute. If
xsl:variable is empty and does not have a
select attribute, then its value is the empty
string.
<xsl:when
test = "boolean-expression">
<! -- template -- >
</xsl:when>
| |
The xsl:when element only appears as a child of an
xsl:choose element.
Attributes
- test, required
-
An XPath expression that evaluates to either true or false. The
xsl:when contents are inserted into the result
tree if and only if this is the first xsl:when
element in the xsl:choose element whose
test attribute evaluates to true.
Contents
The template to be instantiated and inserted into the result tree if
the test attribute is true.
<xsl:with-param
name = "QualifiedName"
select = "expression">
<! -- template -- >
</xsl:with-param>
| |
The xsl:with-param element passes a named
parameter to a template that expects it. This can either be a child
of xsl:apply-templates or
xsl:call-template. An
xsl:template element receives the parameter via an
xsl:param element with the same name. If a
template expects to receive a particular parameter and
doesn't get it, then it can take the default from
the xsl:param element instead.
Attributes
- name, required
-
The name of the parameter.
- select, optional
-
An XPath expression evaluated to form the value of the parameter. If
xsl:with-param has a select
attribute, then it must be an empty element. If
xsl:with-param does not have a
select attribute, then the value is taken from the
element's contents.
Contents
A template that is instantiated and passed as the
parameter's value. If
xsl:with-param is not an empty element, it must
not have a select attribute. If
xsl:with-param is empty and does not have a
select attribute, then its value is the empty
string.
 |  |  | | 23. XSLT Reference |  | 23.3. XSLT Functions |

Copyright © 2002 O'Reilly & Associates. All rights reserved.
|

 by default.
by default.