41.11 How termcap and terminfo Describe Terminals
The termcap and terminfo databases ( 5.2 ) describe the capabilities of terminals using a rather obscure and compact language. At this point, the ASCII terminal market has slowed down and standardized, so it is not as essential as it used to be to write new terminal entries. However, there are still times when it's useful to know how to read an entry. For example, you may want to use particular capabilities in a shell program ( 41.10 ) or in a function key map ( 41.12 ) .
We won't give you a detailed list of all of the possible capabilities - that you can get from the termcap or terminfo manual page on your system. However, we do want to give you an introduction to the language of termcap and terminfo .
Here's a simplified entry for the Wyse Technology Wyse-50 terminal. The capabilities described here are only a subset sufficient to introduce the basic syntax of the language:
# incomplete termcap entry for the Wyse WY-50
n9|wy50|WY50| Wyse Technology WY-50:\
:bs:am:co#80:li#24:\
:up=^K:cl=^Z:ho=^^:nd=^L:cm=\E=%+ %+ :
And here is the corresponding terminfo source file:
# incomplete terminfo entry for Wyse WY-50
wy50|WY50|Wyse Technology WY-50,
am, cols#80, lines#24, cuu1=^K, clear=^Z,
home=^^, cuf1=^L, cup=\E=%p1%'\s'%+%c%p2%'\s'%+%c,
The backslash (
\
) character is used to suppress the newline in
termcap
.
termcap
entries must be defined on a
single logical line, with colons (
:
) separating each field.
terminfo
does not require the entry to be on a single line, so
backslashes are not necessary.
In
terminfo
, commas are used as
the field separator.
The language certainly is not verbose! However, if we work through it methodically, it might begin to make sense.
There are three types of lines in a termcap or terminfo file: comment lines, lines that list alias names for the terminal, and lines that specify terminal capabilities.
-
Comment lines: The first line in both the termcap and terminfo entries shown above is a comment line.
# incomplete termcap entry for the Wyse WY-50 # incomplete terminfo entry for the Wyse WY-50
All comment lines begin with a hash mark (
#). Embedded comments are not allowed: a line is either a comment or part of an entry. In termcap and terminfo , the convention is that comments precede the terminal they describe. -
Name lines: The second line is a list of alias names for the terminal, separated by the vertical bar character.
n9|wy50|WY50| Wyse Technology WY-50:\ ...termcap wy50|WY50|Wyse Technology WY-50, ...terminfo
Multiple aliases are provided as a convenience to the user. The environment variable TERM ( 5.10 ) can be set to any one of the aliases. By convention, the last alias is the full name of the terminal.
The alias list is the first field of the terminal description, with a colon ( termcap ) or comma ( terminfo ) marking the end of the alias list and the start of the capabilities list. You could begin listing the capabilities immediately after this field, but it makes reading much easier if all the aliases are on one line and the capabilities start on the next.
When a terminfo source file is compiled with tic , the compiled data is placed in a file corresponding to the first alias (in this case, /usr/lib/terminfo/w/wy50 ), and a link is created for all other aliases but the last. In this example, TERM could be set to either wy50 or WY50 to access the compiled terminal description.
-
Capability lines: The remaining lines are the list of the actual terminal capabilities. These lines are indented (using a tab or blank spaces) to distinguish them from the line of terminal aliases. Note that the indentation of continued capability lines is not just cosmetic but is a required part of the syntax.
In termcap , capabilities are identified by a two-character name; in terminfo , the capability names may have anywhere between two and five characters. The capability name is the first thing in each capability field and describes a feature of the terminal.
There are three types of capability:
-
Boolean capabilities consist of a capability name with no arguments. For example, am (both termcap and terminfo ) specifies that the terminal performs automatic right margins, wrapping the cursor to the start of the next line when the cursor reaches the last position on the current line. If am is not specified, programs will assume that your terminal does not have this feature.
am is an example of a Boolean feature that is advantageous, but Booleans are also used to specify negative features of your terminal - for example, if your terminal does not perform newlines in the expected way, you might have what is called the "newline glitch," and the entry may need to specify xn ( termcap ) or
xenl( terminfo ) to tell programs to adjust for the terminal's peculiarity. -
Numeric capabilities consist of a capability name, a sharp sign, and a number. For example,
co#80( termcap ) andcols#80( terminfo ) says that the terminal has 80 columns. All numeric values are non-negative. -
String capabilities tell how to issue a command to the terminal. The format of a string capability is the capability name, followed by an equal sign, followed by the command sequence. For example,
up=^K( termcap ) orcuu1=^K( terminfo ) specifies that the sequence CTRL-k will move the cursor up one line.
Now the Wyse-50 example should make more sense. First termcap :
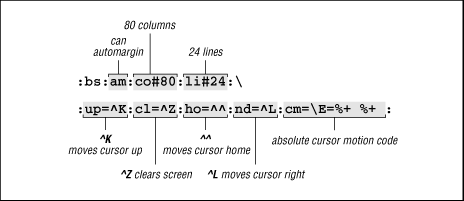
Figure 41.1: A Simplified termcap Entry
Now terminfo :
Figure 41.2: A Simplified terminfo Entry
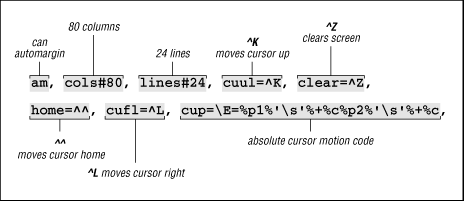
The examples demonstrate all three kinds of capabilities: Boolean, numeric, and string.
The first two capabilities in the termcap entry, and the first capability in the terminfo entry, are Boolean.
- bs
-
is the termcap backspace capability, which means that the terminal will backspace when sent the CTRL-h (
^H) character. There is no terminfo capability directly equivalent to bs , so it is considered obsolete by terminfo and by BSD 4.3 termcap . In place of the bs capability, terminfo would explicitly define CTRL-h as the string to send the cursor leftcul1=^H). - am
-
am is the automargin capability, also known as wraparound. It means that when a line reaches the right edge of the screen, the terminal automatically continues on the next line.
The next two capabilities are numeric.
- co#80
- cols#80
-
says that the terminal has 80 columns.
- li#24
- lines#24
-
says that the terminal has 24 lines.
You will find that 80 characters and 24 lines is the most common screen size but that there are exceptions. Eighty characters was originally chosen because it is the width of a punch card, and 24 lines was chosen to take advantage of cheap television screen technology.
The remainder of the fields in the Wyse-50 entry contain string capabilities. The first four of these are fairly simple:
- up=^K
- cuu1=^K
-
is the up capability; it says that to move the cursor up one line, send the
^Kcharacter to the terminal. - cl=^Z
- clear=^Z
-
is the clear capability; it says that to clear the screen, send the
^Zcharacter to the terminal. - ho=^^
- home=^^
-
is the home capability; it says that to move the cursor Home (upper-left corner), send the
^^character (CTRL-^) to the terminal. - nd=^L
- cuf1=^L
-
is the non-destructive space capability; it says that to move the cursor one space to the right without changing the text, send the
^Lcharacter to the terminal.
41.11.1 Special Character Codes
No doubt the symbols
^K
,
^Z
,
^^
, and
^L
shown above are familiar to you.
A caret (
^
) followed by a letter is a convention for representing
an unprintable control character generated by holding down the CONTROL
(CTRL) key on the keyboard while typing another.
Note that control characters
are entered into a terminal description as two characters by typing
the caret character (
^
) followed by a letter,
rather than by inserting the actual control character.
Both termcap and terminfo use other codes to write other unprintable characters, as well as characters that have special meaning in termcap or terminfo syntax. The other codes, most of which should be familiar to C programmers, are listed in Table 41.1 .
| Code | Description | Comment |
|---|---|---|
| \E | escape | termcap and terminfo |
| \e | escape | terminfo only |
^
x
|
control-
x
|
where
x
is any letter |
| \n | newline | |
| \r | return | |
| \t | tab | |
| \b | backspace | |
| \f | formfeed | |
| \s | space | terminfo only |
| \l | linefeed | terminfo only |
\
xxx
|
octal value of
xxx
|
must be three characters |
| \041 |
exclamation point
!
|
C shell history uses
!
|
| \072 |
the character
:
|
termcap uses ordinary : as separator |
| \200 | null | \\000 for null does not work |
| \0 | null | terminfo only |
| \^ | caret | terminfo only |
| \\ | backslash | terminfo only |
| \, | comma | terminfo only |
| \: | colon | terminfo only |
41.11.2 Encoding Arguments
The last capability in the Wyse-50 example is the most complicated. cm= ( termcap ) and cup= ( terminfo ) specify the cursor motion capability, which describes how to move the cursor directly to a specific location. Since the desired location is specified by the program at run-time, the capability must provide some mechanism for encoding arguments. The program uses this description to figure out what string it needs to send to move the cursor to the desired location.
Because we aren't telling you how to write
termcap
or
terminfo
entries, but just to read them, all you need to know
is that the percent sign (
%
) is used for
encoding, and when it appears in a terminal entry, the capability is
using run-time parameters.
If you need to write an entry, see O'Reilly & Associates' termcap & terminfo .
- ,





