2.5. A Closer Look at MIB-II
MIB-II is a very important management group, because every device that supports SNMP must also support MIB-II. Therefore, we will use objects from MIB-II in our examples throughout this book. We won't go into detail about every object in the MIB; we'll simply define the subtrees. The section of RFC1213-MIB that defines the base OIDs for the mib-2 subtree looks like this:mib-2 OBJECT IDENTIFIER ::= { mgmt 1 }
system OBJECT IDENTIFIER ::= { mib-2 1 }
interfaces OBJECT IDENTIFIER ::= { mib-2 2 }
at OBJECT IDENTIFIER ::= { mib-2 3 }
ip OBJECT IDENTIFIER ::= { mib-2 4 }
icmp OBJECT IDENTIFIER ::= { mib-2 5 }
tcp OBJECT IDENTIFIER ::= { mib-2 6 }
udp OBJECT IDENTIFIER ::= { mib-2 7 }
egp OBJECT IDENTIFIER ::= { mib-2 8 }
transmission OBJECT IDENTIFIER ::= { mib-2 10 }
snmp OBJECT IDENTIFIER ::= { mib-2 11 }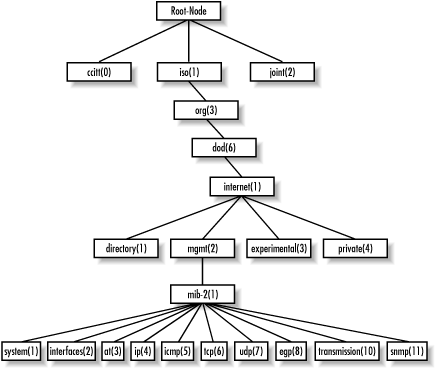
Figure 2-4. MIB-II subtree
Table 2-5 briefly describes each of the management groups defined in MIB-II. We don't go into great detail about each group, since you can pull down RFC 1213 and read the MIB yourself.Table 2-5. Brief Description of the MIB-II Groups

Copyright © 2002 O'Reilly & Associates. All rights reserved.