Chapter 20. The java.security.interfaces Package
As its name implies, the java.security.interfaces package contains only interfaces. These interfaces define methods that provide algorithm-specific information (such as key values and initialization parameter values) about DSA and RSA public and private keys. If you are using the RSA algorithm, for example, and working with a java.security.PublicKey object, you can cast that PublicKey to an RSAPublicKey object and use the RSA-specific methods defined by RSAPublicKey to query the key value directly. Figure 20-1 shows the class hierarchy of this package.
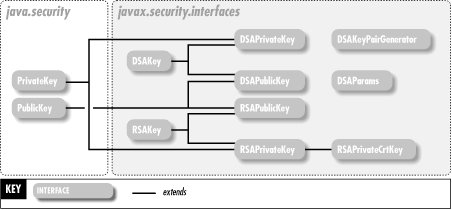
Figure 20-1. The java.security.interfaces package
The java.security.interfaces package was introduced in Java 1.1. In Java 1.2, the java.security.spec package is the preferred way for obtaining algorithm-specific information about keys and algorithm parameters. This package remains useful in Java 1.2, however, for identifying the type of a given PublicKey or PrivateKey object.
The interfaces in this package are typically of interest only to programmers who are implementing a security provider or who want to implement cryptographic algorithms themselves. Use of this package typically requires some familiarity with the mathematics underlying DSA and RSA public-key cryptography.
| DSAKey | Java 1.1 | |
|
|
||
| java.security.interfaces | PJ1.1(opt) | |
This interface defines a method that must be implemented by both public and private DSA keys.
| public interface DSAKey { | ||
| // | Public Instance Methods | |
| public abstract DSAParams getParams (); | ||
| } | ||
Implementations: DSAPrivateKey, DSAPublicKey
| DSAKeyPairGenerator | Java 1.1 | |
|
|
||
| java.security.interfaces | PJ1.1(opt) | |
This interface defines algorithm-specific KeyPairGenerator initialization methods for DSA keys. To generate a pair of DSA keys, use the static getInstance() factory method of java.security.KeyPairGenerator and specify "DSA" as the desired algorithm name. If you wish to perform DSA-specific initialization, cast the returned KeyPairGenerator to a DSAKeyPairGenerator and call one of the initialize() methods defined by this interface. Finally, generate the keys by calling generateKeyPair() on the KeyPairGenerator.
| public interface DSAKeyPairGenerator { | ||
| // | Public Instance Methods | |
| public abstract void initialize (DSAParams params, java.security.SecureRandom random) throws java.security.InvalidParameterException; | ||
| public abstract void initialize (int modlen, boolean genParams, java.security.SecureRandom random) throws java.security.InvalidParameterException; | ||
| } | ||
| DSAParams | Java 1.1 | |
|
|
||
| java.security.interfaces | PJ1.1(opt) | |
This interface defines methods for obtaining the DSA parameters g, p, and q. These methods are useful only if you wish to perform cryptographic computation yourself. Using these methods requires a detailed understanding of the mathematics underlying DSA public-key cryptography.
| public interface DSAParams { | ||
| // | Public Instance Methods | |
| public abstract java.math.BigInteger getG (); | ||
| public abstract java.math.BigInteger getP (); | ||
| public abstract java.math.BigInteger getQ (); | ||
| } | ||
Implementations: java.security.spec.DSAParameterSpec
Passed To: DSAKeyPairGenerator.initialize()
Returned By: DSAKey.getParams()
| DSAPrivateKey | Java 1.1 | |
|
|
||
| java.security.interfaces | serializable PJ1.1(opt) | |
This interface represents a DSA private key and provides direct access to the underlying key value. If you are working with a private key you know is a DSA key, you can cast the PrivateKey to a DSAPrivateKey.
| public interface DSAPrivateKey extends DSAKey, java.security.PrivateKey { | ||
| // | Public Constants | |
| 1.2 | public static final long serialVersionUID ; | =7776497482533790279 |
| // | Public Instance Methods | |
| public abstract java.math.BigInteger getX (); | ||
| } | ||
Hierarchy: (DSAPrivateKey(DSAKey,java.security.PrivateKey(java.security.Key(Serializable))))
| DSAPublicKey | Java 1.1 | |
|
|
||
| java.security.interfaces | serializable PJ1.1(opt) | |
This interface represents a DSA public key and provides direct access to the underlying key value. If you are working with a public key you know is a DSA key, you can cast the PublicKey to a DSAPublicKey.
| public interface DSAPublicKey extends DSAKey, java.security.PublicKey { | ||
| // | Public Constants | |
| 1.2 | public static final long serialVersionUID ; | =1234526332779022332 |
| // | Public Instance Methods | |
| public abstract java.math.BigInteger getY (); | ||
| } | ||
Hierarchy: (DSAPublicKey(DSAKey,java.security.PublicKey(java.security.Key(Serializable))))
| RSAKey | Java 1.3 Beta | |
|
|
||
| java.security.interfaces | ||
This is a superinterface for RSAPublicKey and RSAPrivateKey; it defines a method shared by both classes. Prior to Java 1.3, the getModulus() method was defined independently by RSAPublicKey and RSAPrivateKey.
| public interface RSAKey { | ||
| // | Public Instance Methods | |
| public abstract java.math.BigInteger getModulus (); | ||
| } | ||
Implementations: RSAPrivateKey, RSAPublicKey
| RSAPrivateCrtKey | Java 1.2 | |
|
|
||
| java.security.interfaces | serializable | |
This interface extends RSAPrivateKey and provides a decomposition (based on the Chinese remainder theorem) of the private-key value into the various pieces that comprise it. This interface is useful only if you plan to implement your own cryptographic algorithms. To use this interface, you must have a detailed understanding of the mathematics underlying RSA public-key cryptography. Given a java.security.PrivateKey object, you can use the instanceof operator to determine whether you can safely cast it to an RSAPrivateCrtKey.
| public interface RSAPrivateCrtKey extends RSAPrivateKey { | ||
| // | Property Accessor Methods (by property name) | |
| public abstract java.math.BigInteger getCrtCoefficient (); | ||
| public abstract java.math.BigInteger getPrimeExponentP (); | ||
| public abstract java.math.BigInteger getPrimeExponentQ (); | ||
| public abstract java.math.BigInteger getPrimeP (); | ||
| public abstract java.math.BigInteger getPrimeQ (); | ||
| public abstract java.math.BigInteger getPublicExponent (); | ||
| } | ||
Hierarchy: (RSAPrivateCrtKey(RSAPrivateKey(java.security.PrivateKey(java.security.Key(Serializable)),RSAKey)))
| RSAPrivateKey | Java 1.2 | |
|
|
||
| java.security.interfaces | serializable | |
This interface represents an RSA private key and provides direct access to the underlying key values. If you are working with a private key you know is an RSA key, you can cast the PrivateKey to an RSAPrivateKey.
| public interface RSAPrivateKey extends java.security.PrivateKey, RSAKey { | ||
| // | Public Instance Methods | |
| public abstract java.math.BigInteger getPrivateExponent (); | ||
| } | ||
Hierarchy: (RSAPrivateKey(java.security.PrivateKey(java.security.Key(Serializable)),RSAKey))
Implementations: RSAPrivateCrtKey
| RSAPublicKey | Java 1.2 | |
|
|
||
| java.security.interfaces | serializable | |
This interface represents an RSA public key and provides direct access to the underlying key values. If you are working with a public key you know is an RSA key, you can cast the PublicKey to an RSAPublicKey.
| public interface RSAPublicKey extends java.security.PublicKey, RSAKey { | ||
| // | Public Instance Methods | |
| public abstract java.math.BigInteger getPublicExponent (); | ||
| } | ||
Hierarchy: (RSAPublicKey(java.security.PublicKey(java.security.Key(Serializable)),RSAKey))

Copyright © 2001 O'Reilly & Associates. All rights reserved.